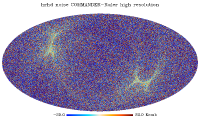
Foreground maps
Contents
[hide]Astrophysical Components[edit]
Overview[edit]
This section describes the maps of astrophysical components produced from the Planck data. These products are derived from some or all of the nine frequency channel maps described above using different techniques and, in some cases, using other constraints from external data sets. Here we give a brief description of each product and how it is obtained, followed by a description of the FITS file containing the data and associated information. All the details can be found in Planck-2020-A4[1] and Planck-2020-A8[2].
Commander-derived astrophysical foreground maps[edit]
As discussed in detail in Planck-2020-A4[1], the main Planck 2018 frequency sky maps have significantly lower systematic errors than earlier versions. At the same time, these maps are also associated with a significant limitation, in that no robust single detector or detector set maps are available. As described in Planck-2020-A3[3], such maps do not contain the full signal content of the true sky. As a result, only full frequency maps are distributed and used in the 2018 analysis.
For polarization analysis, this is not a significant issue, and the 2018 polarization foreground products therefore supersede the 2015 release in all respects. However, for temperature analysis the lack of single-detector maps strongly limits the ability to extract CO line emission from the data set, and it is also not possible to exclude known detector outliers; see Planck-2015-A10[4] for details. For these reasons, we consider the parametric foreground products from 2015 to represent a more accurate description of the true sky than the corresponding 2018 version. As a result, we do not release parametric temperature foreground products from the 2018 data set, but rather recommend continued usage of the 2015 temperature model. For polarization, we recommend usage of the 2018 model.
Two Commander-based polarization foreground products are provided for the Planck 2018 releaes, namely synchrotron and thermal dust emission. For synchrotron emission, a spatially constant spectral index of β=-3.1 is adopted. For thermal dust emission, the dust temperature is fixed to that derived from the corresponding 2018 intensity analysis, while the spectral index is fitted directly from the polarization measurements, smoothed to 3 degrees FWHM. For both synchrotron and thermal dust emission, we provide results derived from both the full-mission data set, and from the half-mission and odd-even splits.
In addition to the real observations, we also provide 300 end-to-end noise simulations processed through the algorithm with the same spectral parameters as derived from the data for each of the data splits. The filenames of these simulations have the following format:
- dx12_v3_commander_{synch,dust}_noise_{full,hm1,hm2,oe1,oe2}_00???_raw.fits
Inputs[edit]
The following data products are used for the full-mission polarization analysis (corresponding data are used for the data split products):
- Full-mission 30 GHz frequency map, LFI 30 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 44 GHz frequency map, LFI 44 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 70 GHz frequency map, LFI 70 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 100 GHz frequency map, HFI 100 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 143 GHz frequency map, HFI 143 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 217 GHz frequency map, HFI 217 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 353 GHz frequency map, HFI 353 GHz frequency maps
Outputs[edit]
Synchrotron emission[edit]
- Full-mission file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-commander_2048_R3.00_full.fits
- First half-mission split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-commander_2048_R3.00_hm1.fits
- Second half-mission split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-commander_2048_R3.00_hm2.fits
- Odd ring split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-commander_2048_R3.00_oe1.fits
- Even ring split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-commander_2048_R3.00_oe2.fits
- Nside = 2048
- Angular resolution = 40 arcmin
- Reference frequency: 30 GHz
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q_STOKES | Real*4 | μK_RJ | Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_STOKES | Real*4 | μK_RJ | Stokes U posterior maximum |
Thermal dust emission[edit]
- Full-mission file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-commander_2048_R3.00_full.fits
- First half-mission split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-commander_2048_R3.00_hm1.fits
- Second half-mission split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-commander_2048_R3.00_hm2.fits
- Odd ring split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-commander_2048_R3.00_oe1.fits
- Even ring split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-commander_2048_R3.00_oe2.fits
- Nside = 2048
- Angular resolution = 5 arcmin
- Reference frequency: 353 GHz
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q_STOKES | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Full-mission Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_STOKES | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Full-mission Stokes U posterior maximum |
SMICA-derived astrophysical foreground maps[edit]
Two SMICA-based polarization foreground products are provided, namely synchrotron and thermal dust emission. These are derived using the usual SMICA spectral matching method, tuned specifically for the reconstruction of two polarized foregrounds. Specifically, three coherent components (plus noise) are fitted at the spectral level with the first one constrained to have CMB emissivity. No assumptions are made regarding the other two components: they are not assumed to have a specific emissivity or angular spectrum, nor are they assumed to be uncorrelated. This leaves a degenerate model but that degeneracy can be entirely fixed after the spectral fit by assuming that synchrotron emission is negligible at 353 GHz and that thermal dust emission is negligible at 30 GHz. For both synchrotron and thermal dust emission, we provide results derived from both the full-mission data set, and from the half-mission and odd-even splits.
In addition to the real observations, we also provide 300 end-to-end noise simulations processed through the algorithm with the same spectral parameters as derived from the data for each of the data splits. The filenames of these simulations have the following format:
- dx12_v3_smica_{synch,dust}_noise_{full,hm1,hm2,oe1,oe2}_00???_raw.fits
Inputs[edit]
The following data products are used for the full-mission polarization analysis (corresponding data are used for the data split products):
- Full-mission 30 GHz frequency map, LFI 30 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 44 GHz frequency map, LFI 44 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 70 GHz frequency map, LFI 70 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 100 GHz frequency map, HFI 100 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 143 GHz frequency map, HFI 143 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 217 GHz frequency map, HFI 217 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 353 GHz frequency map, HFI 353 GHz frequency maps
Outputs[edit]
Synchrotron emission[edit]
- Full-mission file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-smica_2048_R3.00_full.fits
- First half-mission split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-smica_2048_R3.00_hm1.fits
- Second half-mission split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-smica_2048_R3.00_hm2.fits
- Odd ring split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-smica_2048_R3.00_oe1.fits
- Even ring split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_synchrotron-smica_2048_R3.00_oe2.fits
- Nside = 2048
- Angular resolution = 40 arcmin
- Reference frequency: Integrated 30 GHz band; no colour corrections have been applied
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q_STOKES | Real*4 | mK_RJ | Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_STOKES | Real*4 | mK_RJ | Stokes U posterior maximum |
Thermal dust emission[edit]
- Full-mission file name: COM_CompMap_QU_thermaldust-smica_2048_R3.00_full.fits
- First half-mission split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_thermaldust-smica_2048_R3.00_hm1.fits
- Second half-mission split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_thermaldust-smica_2048_R3.00_hm2.fits
- Odd ring split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_thermaldust-smica_2048_R3.00_oe1.fits
- Even ring split file name: COM_CompMap_QU_thermaldust-smica_2048_R3.00_oe2.fits
- Nside = 2048
- Angular resolution = 12 arcmin
- Reference frequency: Integrated 353 GHz band; no colour corrections have been applied
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q_STOKES | Real*4 | mK_RJ | Full-mission Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_STOKES | Real*4 | mK_RJ | Full-mission Stokes U posterior maximum |
GNILC thermal dust maps[edit]
The 2018 GNILC thermal dust products are provided as single files that include both intensity and polarization, 3x3 IQU noise covariance matrices per pixel, and as well as local smoothing scale for the variable resolution map. The structure of the data files is the following:
- Uniform resolution file name: COM_CompMap_IQU_thermaldust-gnilc-unires_2048_R3.00.fits
- Variable resolution file name: COM_CompMap_IQU_thermaldust-gnilc-varres_2048_R3.00.fits
- Nside = 2048
- Angular resolution = 80 arcmin FWHM, or variable
- Reference frequency: Integrated 353 GHz band; no colour corrections have been applied
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| I_STOKES | Real*4 | K_cmb | Stokes I estimate |
| Q_STOKES | Real*4 | K_cmb | Stokes Q estimate |
| U_STOKES | Real*4 | K_cmb | Stokes U estimate |
| II_COV | Real*4 | K_cmb^2 | Covariance matrix II element |
| IQ_COV | Real*4 | K_cmb^2 | Covariance matrix IQ element |
| IU_COV | Real*4 | K_cmb^2 | Covariance matrix IU element |
| QQ_COV | Real*4 | K_cmb^2 | Covariance matrix QQ element |
| QU_COV | Real*4 | K_cmb^2 | Covariance matrix QU element |
| UU_COV | Real*4 | K_cmb^2 | Covariance matrix UU element |
| FWHM | Real*4 | arcmin | Local FWHM smoothing scale |
2018 Lensing maps[edit]
We distribute several variations of lensing potential estimates presented in Planck-2020-A8[2] as part of the 2018 data release, together with matching simulation packages.
There are 4 lensing data packages:
- COM_Lensing_4096_R3.00
- Baseline lensing potential estimates from SMICA DX12 CMB maps. Provided are temperature-only (TT), polarization-only (PP) and minimum-variance (MV) estimates.
- COM_Lensing_Sz_4096_R3.00
- Variations obtained without galaxy cluster masking.
- COM_Lensing_Inhf_2048_R3.00
- Variations obtained using inhomogeneous noise filtering.
- COM_Lensing-Szdeproj_4096_R3.00
- Variation obtained from thermal Sunyaev-Zeldovich deprojected SMICA CMB map (TT only).
Each map represents an estimate of the CMB lensing potential on approximately 70% of the sky. The lensing estimates from COM_Lensing_4096_R3.00 also forms the basis for the Planck 2018 lensing likelihood.
These data packages have the following common file structure:
| Filename | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mask.fits.gz | HEALPix FITS format map, with | Lens reconstruction analysis mask. |
| TT/dat_klm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Estimated lensing convergence (from temperature only, after mean-field subtraction). |
| TT/mf_klm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Estimated lensing convergence mean-field subtracted from the raw temperature-only data estimate. |
| PP/dat_klm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Estimated lensing convergence (from polarization only, after mean-field subtraction). |
| PP/mf_klm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Estimated lensing convergence mean-field subtracted from the raw polarization-only data estimate. |
| MV/dat_klm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Estimated lensing convergence (minimum-variance estimate from temperature and polarization, after mean-field subtraction). |
| MV/mf_klm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Estimated lensing convergence mean-field subtracted from the raw minimum variance data estimate. |
| TT/nlkk.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, , ) | Temperature-only reconstruction approximate noise (and signal+noise, ) power spectrum of , for the fiducial cosmology used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| PP/nlkk.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, , ) | Polarization-only reconstruction approximate noise (and signal+noise, ) power spectrum of , for the fiducial cosmology used in Planck-2020-A8[2].. |
| MV/nlkk.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, , ) | Minimum-variance reconstruction approximate noise (and signal+noise, ) power spectrum of , for the fiducial cosmology used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
with slight variations:
- - in COM_Lensing_Inhf_2048_R3.00, all HEALPix FITS format alm files have .
- - COM_Lensing-Szdeproj_4096_R3.00 only provides the temperature-only reconstruction.
The matching 4 lensing simulation packages are
- COM_Lensing-SimMap_4096_R3.00
- COM_Lensing-SimMap_Sz_4096_R3.00
- COM_Lensing-SimMap_Inhf_2048_R3.00
- COM_Lensing-SimMap-Szdeproj_4096_R3.00
with the following content:
| Filenames | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| /inputs/mask.fits.gz | compressed HEALPix FITS format map, with | Lens reconstruction analysis mask. |
| /inputs/FFP10_wdipole_lenspotentialCls.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, , ,,,,,) | Input unlensed CMB spectra of the fiducial cosmology used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| TT/sim_klm_{???}.fits | 300 HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Estimated lensing convergence (from temperature only, no mean-field subtraction) of all 300 FFP10 simulations used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| PP/sim_klm_{???}.fits | 300 HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Estimated lensing convergence (from polarization only, no mean-field subtraction) of all 300 FFP10 simulations used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| MV/sim_klm_{???}.fits | 300 HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Estimated lensing convergence (minimum-variance estimate from temperature and polarization, no mean-field subtraction) of all 300 FFP10 simulations used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| TT/dat_klm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Estimated lensing convergence (from temperature only, no mean-field subtraction). |
| PP/dat_klm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Estimated lensing convergence (from polarization only, no mean-field subtraction). |
| MV/dat_klm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Estimated lensing convergence (minimum-variance estimate from temperature and polarization, no mean-field subtraction). |
| TT/nlkk.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, , , , , , ) | Temperature-only reconstruction lensing spectrum biases and quadratic estimator normalization (inverse response), as defined in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| PP/nlkk.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, , , , , , ) | Polarization-only reconstruction lensing spectrum biases and quadratic estimator normalization (inverse response), as defined in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| MV/nlkk.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, , , , , , ) | Minimum variance reconstruction lensing spectrum biases and quadratic estimator normalization (inverse response), as defined in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
with the same slight variations:
- - in COM_Lensing-SimMap_Inhf_2048_R3.00, all HEALPix FITS format alm files have .
- - COM_Lensing-SimMap-Szdeproj_4096_R3.00 only provides the temperature-only reconstructions.
We further provide the input lensing convergence realizations of all 300 FFP10 simulations in
- COM_Lensing-SimMap-inputs_4096_R3.00
with contents
| Filenames | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| /inputs/clkk.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, ) | Input lensing convergence CMB spectrum of the fiducial cosmology used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| sky_klm_{???}.fits | 300 HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Input lensing convergence realizations of all 300 FFP10 simulations used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
2018 Lensing-induced B-mode maps[edit]
We distribute maps of the lensing-induced B-modes presented in Planck-2020-A8[2], together with a matching simulation suite. The Stokes parameter maps of the lensing B-modes are produced by combining tracers of lensing potential with E-mode data from the SMICA CMB polarization maps. These lensing-induced B-mode polarization maps are provided on approximately 60% of the sky. Planck-2020-A8[2] details the construction of these maps.
These maps come in two variations. In the first we use the quadratic estimator built from the DX12 SMICA CMB maps (we discard and in order to use lensing tracers that are statistically independent of the -mode map). In the second we further add CIB information at 545 GHz (GNILC) to the lensing tracer.
These maps are filtered template of the lensing B-mode (both the lensing tracer and -mode used to build the B template are Wiener-filtered). The simulation suite may be used to assess the filter, as was done in Planck-2020-A8[2] to produce the B-mode power spectrum (Fig. 14).
The B-mode template package is
- COM_Lensing-Bmode_2048_R3.00
with contents
| Filenames | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| /inputs/mask.fits.gz | compressed HEALPix FITS format map, with | -mode analysis mask used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| /inputs/clbb.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, ) | Input lensing -mode power spectrum for the fiducial cosmology used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| dat_blm_TTTEETEE.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Lensing -mode template built from the lensing tracer and -mode map. |
| dat_blm_545_TTTEETEE.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Lensing -mode template built from the lensing tracer and -mode map. |
The B-mode template simulation package is
- COM_Lensing-SimMap-Bmode_2048_R3.00
with contents
| Filenames | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| /inputs/mask.fits.gz | compressed HEALPix FITS format map, with | -mode analysis mask used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| /inputs/clbb.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, ) | Input lensing -mode power spectrum for the fiducial cosmology used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| /TTTEETE/blm_{???}.fits | 300 HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Lensing -mode template built from the lensing tracer and -mode map of all 300 FFP10 simulations used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| /545_TTTEETE/blm_{???}.fits | 300 HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Lensing -mode template built from the lensing tracer and -mode map of all 300 FFP10 simulations used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| /TTTEETE/dat_blm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Lensing -mode template built from the lensing tracer and -mode map. |
| /545_TTTEETE/dat_blm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Lensing -mode template built from the lensing tracer and -mode map. |
2018 Lensing combined tracers maps[edit]
We distribute estimates of the CMB lensing convergence maps built combining the Planck 2018 quadratic estimators and CIB data at 545 GHz (GNILC), together with a matching simulation suite. The construction of these maps is decribed in details in Planck-2020-A8[2]. The maps are built on about 60% of the sky.
The tracer are Wiener-filtered estimates of the convergence .
These maps come in two variations. In the first we use the minimum-variance (MV) quadratic estimator together with the CIB. In the second we use the quadratic estimator together with the CIB, and is statistically independent from the CMB B-polarization.
The lensing combined tracer data package is
- COM_Lensing-CIBcomb_2000_R3.00
with contents
| Filenames | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| /inputs/mask.fits.gz | compressed HEALPix FITS format map, with | Tracer combination analysis mask used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| dat_klm_545_MV.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Lensing tracer built from the minimum-variance quadratic estimator and the CIB (GNILC 545 GHz map). |
| dat_klm_545_TTTEETEE.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Lensing tracer built from the quadratic estimator and the CIB (GNILC 545 GHz map). |
The lensing combined tracer simulation package is
- COM_Lensing-SimMap-CIBcomb_2000_R3.00
with contents
| Filenames | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| /inputs/mask.fits.gz | compressed HEALPix FITS format map, with | Tracer combination analysis mask used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| 545_MV/sim_klm_{???}.fits | 300 HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Lensing tracer built from the minimum-variance quadratic estimator and the CIB (GNILC 545 GHz map) of all 300 FFP10 simulations used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| 545_TTTEETEE/sim_klm_{???}.fits | 300 HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Lensing tracer built from the quadratic estimator and the CIB (GNILC 545 GHz map) of all 300 FFP10 simulations used in Planck-2020-A8[2]. |
| 545_MV/dat_klm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Lensing tracer built from the minimum-variance quadratic estimator and the CIB (GNILC 545 GHz map). |
| 545_TTTEETEE/dat_klm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Lensing tracer built from the quadratic estimator and the CIB (GNILC 545 GHz map). |
Also part of this package are high-resolution figures of the lensing deflection (similar to Fig. 3 and Fig. 13 of Planck-2020-A8[2]). The figures show the Wiener-filtered, gradient mode of the displacement .
Mollveide projection of the minimum variance quadratic estimator lensing map:
- Lensing_2018_MV_alphaA0_YlGnBu_300dpi_47in_moll.png
Orthographic projection of the minimum variance quadratic estimatorlensing map:
- Lensing_2018_compMV_alphaA0_YlGnBu_300dpi_47in_moll.png
Orthographic projection of the minimum variance quadratic estimator combined with the CIB (GNILC 545 GHz map) lensing tracer map:
- Lensing_2018_compMV545_alphaA0_YlGnBu_300dpi_47in_orth.png
2018 Lensing band powers and likelihood[edit]
The lensing reconstruction spectrum band powers, covariance matrix and likelihood linear corrections are provided as a zip of a series of ASCII files
- planck_lensing_2018.zip
We provide a total of four variations: temperature-only and minimum-variance reconstructions, covering the conservative || Contains the estimated lensing convergence . |- | mask.fits.gz || HEALPix FITS format map, with || Contains the lens reconstruction analysis mask. |- | nlkk.dat || ASCII text file, with columns = (, , ) || The approximate noise (and signal+noise, ) power spectrum of , for the fiducial cosmology used in Planck-2015-A13[5]. |}
2015 Compton y parameter map
We distribute here the Planck full mission Compton parameter maps (y-maps hereafter) obtained using the NILC and MILCA component-separation algorithms as described in Planck-2015-A22[6]. We also provide the ILC weights per scale and per frequency that were used to produce these y-maps. IDL routines are also provided to allow the user to apply those weights. Compton parameters produced by keeping either the first or the second half of stable pointing periods are also provided; we call these the FIRST and LAST y-maps. Additionally we construct noise estimates of full mission Planck y-maps from the half difference of the FIRST and LAST y-maps. These estimates are used to construct standard deviation maps of the noise in the full mission Planck y-maps, which are also provided. To complement this we also provide the power spectra of the noise estimate maps after correcting for inhomogeneities using the standard deviation maps. We also deliver foreground masks including point-source and Galactic masks.
Update 04 Aug 2017: The file containing the masks named COM_CompMap_Compton-SZMap-masks_2048_R2.00.fits has been updated with the file COM_CompMap_Compton-SZMap-masks_2048_R2.01.fits. The difference between the two is that in the R2.00 version a region around the Galactic pole had been masked, while only the Galactic plane should be masked. This has been fixed in version R2.01. The full updated data set is contained in a single gzipped tarball named COM_CompMap_YSZ_R2.01.fits.tgz. The R2.00 version of the mask is not available in the PLA anymore, but can be requested via the PLA Helpdesk.
The contents of the full data set are described below.
| Filename | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| nilc_ymaps.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the NILC full mission, FIRST and LAST y-maps. |
| milca_ymaps.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the MILCA full mission, FIRST and LAST y-maps. |
| nilc_weights_BAND.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the NILC ILC weights for the full mission y-map for band BAND 0 to 9. For each band we provide a weight map per frequency. |
| milca_FREQ_Csz.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the MILCA ILC weights for the full mission y-map for frequency FREQ (100, 143, 217, 353, 545, 857). For each frequency we provide a weight map per filter band. |
| nilc_stddev.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the stddev map for the NILC full mission y-map. |
| milca_stddev.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the stddev maps for the MILCA full mission y-map. |
| nilc_homnoise_spect.fits | ASCII table FITS format | Contains the angular power spectrum of the homogeneous noise in the NILC full mission y-map. |
| milca_homnoise_spect.fits | ASCII table FITS format | Contains the angular power spectrum of the homogeneous noise in the MILCA full mission y-map. |
| masks.fits | HEALPix FITS format map, with | Contains foreground masks. |
| nilc_bands.fits | ASCII table FITS format | Contains NILC wavelet bands in multipole space |
2015 lensing-induced B-mode map
We distribute the lensing-induced B-mode map presented in Planck-2015-XLI[7]. The lensing B-mode Stokes parameter maps are produced by combining the lensing potential reconstruction from the SMICA CMB temperature map with E-mode data from the SMICA CMB polarization maps. The SMICA temperature and polarization products are described in Planck-2015-A09[8]. The lensing-induced B-mode polarization maps are used in cross-correlation with the SMICA CMB polarization maps to obtain a lensing B-mode power spectrum measurement from approximately 70% of the sky, as described in Planck-2015-XLI[7].
We provide both raw products, which can be utilized to generate products adapted to one's specific needs in term of mask, filtering, etc., and "ready-to-use" products for cross-correlation study purposes.
Raw products
We deliver the non-normalized lensing-induced Stokes parameter maps, labelled and , which form the basis of the final lensing B-mode estimator defined in equation (6) of Planck-2015-XLI[7]. They are defined as
where and are the filtered pure E-mode polarization maps given in equation (5) of Planck-2015-XLI[7], and is the filtered lensing potential estimate.
We also provide the normalization transfer function defined in equation (11) of Planck-2015-XLI[7], as well as the "L70" mask that retains 69% of the sky before apodization, and its apodized version , which has an effective sky fraction .
As an example of the utilization of these products, the lensing B-mode maps that are shown in figure 4 of Planck-2015-XLI[7] are generated from
,
where is a Gaussian of 60 arcmin FWHM (introduced for highlighting large angular scales, although it can be removed or replaced by any other filter). This can be practically done by ingesting and in the HEALPix "smoothing" routine, and using the product as an input filtering function.
Specific products
We provide the lensing B-mode spherical harmonic coefficient estimate over approximately 70% of the sky.
It can also be constructed using the raw products described above from
,
where is a function for producing band-powers over the range , and is a short-hand notation for transforming a map into spin-weighted spherical harmonic coefficients , and forming . This can be done using, e.g., the HEALPix "anafast" tool.
The lensing B-mode power spectrum estimate discussed in Planck-2015-XLI[7] is obtained by forming the cross-correlation power spectrum of and the B-mode data from the SMICA polarization maps :
,
where is the 5 arcmin Gaussian beam that convolves the SMICA CMB maps.
The products are contained in a single gzipped tarball named COM_Lensing-Bmode_R2.00.tgz. Its contents are described below.
| Filename | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bar_q_lens_map.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the non-normalized lensing-induced Q Stokes parameter map . |
| bar_u_lens_map.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the non-normalized lensing-induced U Stokes parameter map . |
| mask.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | The L70 mask. |
| mask_noapo.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | The L70 mask without apodization. |
| transfer_function_b_l.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, ) | The transfer function. |
| lensing_bmode_b_lm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Contains the lensing B-mode harmonic coefficients . |
| lensing_bmode_bandpowers.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, , , , ) | The lensing B-mode bandpower estimate on approximativily 70% of the sky and over the multipole range from 10 to 2000 shown in figure 9 of Planck-2015-XLI[7] (for plotting purposes only). |
2015 Integrated Sachs-Wolfe effect map
We distribute estimates of the integrated Sachs-Wolfe (ISW) maps presented in Planck-2015-A21[9] as part of the 2015 data release. These map represents an estimate of the ISW anisotropies using different data sets:
- SEVEM DX11 CMB map, together with all the large-scale structure tracers considered in the ISW paper, namely: NVSS, SDSS, WISE, and the Planck lensing map
- Using only the large-scale structure tracers mentioned above
- SEVEM DX11 CMB map, together with NVSS and the Planck lensing maps (since these two tracers capture most of the information, as compared to SDSS and WISE)
For all the three cases, the reconstruction is provided on approximately 85% of the sky, and they are produced using the LCB filter described in the Planck ISW paper (Section 5), described in detail in Barreiro et al. 2008 and Bonavera et al. 2016.
These ISW maps, together with their corresponding uncertainties maps and masks, are given in a file named COM_CompMap_ISW_0064_R2.00.fits. Its contents are described below.
| Extension | Format | Description | Used data sets |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | HEALPix FITS format map with three components, , Ordering='Nest' | Contains three components: i) ISW map [Kelvin], ii) Error map [Kelvin], iii) Mask map | SEVEM DX11 CMB + NVSS + SDSS + WISE + Planck lensing. |
| 1 | HEALPix FITS format map with three components, , Ordering='Nest' | Contains three components: i) ISW map [Kelvin], ii) Error map [Kelvin], iii) Mask map | NVSS + SDSS + WISE + Planck lensing. |
| 2 | HEALPix FITS format map with three components, , Ordering='Nest' | Contains three components: i) ISW map [Kelvin], ii) Error map [Kelvin], iii) Mask map | SEVEM DX11 CMB + NVSS + Planck lensing. |
2015 Low-frequency foregrounds maps (Planck only & Planck+WMAP)
1) CMB/free-free/Dust Nulled ILC at 28.4 GHz (Planck only)
Linear combination of Planck 28.4, 44.1, 143 and 353 GHz maps (all at 1 degree resolution), with weights listed in column w_2 of Table 1 in Planck-2015-A25[10]. These weights exactly null the CMB, almost exactly null free-free emission, and null thermal dust emission to high accuracy except along the inner Galactic plane,where the brightness is uncertain by around 20% due to variation in the dust spectrum. The normalisation leaves a beta = -3 power law at the same amplitude as in the Planck 28.4 GHz map. (As presented in Fig. 3a of Planck 2015 Results XXV.)
2) CMB/free-free/Dust Nulled ILC at 28.4 GHz (Planck + WMAP) Linear combination of WMAP K, Ka, and Q band, and Planck 28.4, 44.1, 143 and 353 GHz maps (all at 1 degree resolution), with weights listed in column w_3 of Table 1 in Planck-2015-A25[10]. These weights exactly null the CMB, almost exactly null free-free emission, and null thermal dust emission to high accuracy except along the inner Galactic plane, where the brightness is uncertain by around 20% due to variation in the dust spectrum. The normalisation leaves a beta = -3 power law at the same amplitude as in the Planck 28.4 GHz map. (As presented in Fig. 3b of Planck-2015-A25[10].)
Astrophysical components based on the 2013 data release
References[edit]
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.01.1 Planck 2018 results. IV. Diffuse component separation, Planck Collaboration, 2020, A&A, 641, A4.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.002.012.022.032.042.052.062.072.082.092.102.112.122.132.142.152.162.172.182.192.202.212.222.232.242.252.262.272.28 Planck 2018 results. VIII. Lensing, Planck Collaboration, 2020, A&A, 641, A8.
- Jump up ↑ Planck 2018 results. III. High Frequency Instrument data processing and frequency maps, Planck Collaboration, 2020, A&A, 641, A3.
- Jump up ↑ Planck 2015 results. X. Diffuse component separation: Foreground maps, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A10.
- Jump up ↑ Planck 2015 results. XIII. Cosmological parameters, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A13.
- Jump up ↑ Planck 2015 results. XXII. A map of the thermal Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A22.
- ↑ Jump up to: 7.07.17.27.37.47.57.67.7 Planck intermediate results. XLI. A map of lensing-induced B-modes, Planck Collaboration Int. XLI A&A, 596, A102, (2016).
- Jump up ↑ Planck 2015 results. XI. Diffuse component separation: CMB maps, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A9.
- Jump up ↑ Planck 2015 results. XXI. The integrated Sachs-Wolfe effect, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A21.
- ↑ Jump up to: 10.010.110.2 Planck 2015 results. XXV. Diffuse low frequency Galactic foregrounds, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A25.
- ↑ Jump up to: 11.011.111.211.311.411.511.611.7 Planck 2013 results. XI. Component separation, Planck Collaboration, 2014, A&A, 571, A11.
- Jump up ↑ Component separation methods for the PLANCK mission, S. M. Leach, J.-F. Cardoso, C. Baccigalupi, R. B. Barreiro, M. Betoule, J. Bobin, A. Bonaldi, J. Delabrouille, G. de Zotti, C. Dickinson, H. K. Eriksen, J. González-Nuevo, F. K. Hansen, D. Herranz, M. Le Jeune, M. López-Caniego, E. Martínez-González, M. Massardi, J.-B. Melin, M.-A. Miville-Deschênes, G. Patanchon, S. Prunet, S. Ricciardi, E. Salerno, J. L. Sanz, J.-L. Starck, F. Stivoli, V. Stolyarov, R. Stompor, P. Vielva, A&A, 491, 597-615, (2008).
- Jump up ↑ Multiresolution internal template cleaning: an application to the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe 7-yr polarization data, R. Fernández-Cobos, P. Vielva, R. B. Barreiro, E. Martínez-González, MNRAS, 420, 2162-2169, (2012).
- Jump up ↑ Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe 7-yr constraints on fNL with a fast wavelet estimator, B. Casaponsa, R. B. Barreiro, A. Curto, E. Martínez-González, P. Vielva, MNRAS, 411, 2019-2025, (2011).
- ↑ Jump up to: 15.015.1 Planck 2013 results. XXIII. Isotropy and statistics of the CMB, Planck Collaboration, 2014, A&A, 571, A23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 16.016.1 Planck 2013 results. XIX. The integrated Sachs-Wolfe effect, Planck Collaboration, 2014, A&A, 571, A19.
- ↑ Jump up to: 17.017.1 Planck 2013 results. XII. All-sky model of thermal dust emission, Planck Collaboration, 2014, A&A, 571, A12.
- Jump up ↑ Calibrating Milky Way dust extinction using cosmological sources, E. Mörtsell, A&A, 550, A80, (2013).
- Jump up ↑ The Sloan Digital Sky Survey Quasar Catalog. IV. Fifth Data Release, D. P. Schneider, P. B. Hall, G. T. Richards, M. A. Strauss, D. E. Vanden Berk, S. F. Anderson, W. N. Brandt, X. Fan, S. Jester, J. Gray, J. E. Gunn, M. U. SubbaRao, A. R. Thakar, C. Stoughton, A. S. Szalay, B. Yanny, D. G. York, N. A. Bahcall, J. Barentine, M. R. Blanton, H. Brewington, J. Brinkmann, R. J. Brunner, F. J. Castander, I. Csabai, J. A. Frieman, M. Fukugita, M. Harvanek, D. W. Hogg, Z. Ivezic, S. M. Kent, S. J. Kleinman, G. R. Knapp, R. G. Kron, J. Krzesinski, D. C. Long, R. H. Lupton, A. Nitta, J. R. Pier, D. H. Saxe, Y. Shen, S. A. Snedden, D. H. Weinberg, J. Wu, ApJ, 134, 102-117, (2007).
- Jump up ↑ Planck 2013 results. XIII. Galactic CO emission, Planck Collaboration, 2014, A&A, 571, A13.
- ↑ Jump up to: 21.021.121.221.321.421.5 Planck 2013 results. XVII. Gravitational lensing by large-scale structure, Planck Collaboration, 2014, A&A, 571, A17.
Flexible Image Transfer Specification
Full-Width-at-Half-Maximum
Cosmic Microwave background
(Hierarchical Equal Area isoLatitude Pixelation of a sphere, <ref name="Template:Gorski2005">HEALPix: A Framework for High-Resolution Discretization and Fast Analysis of Data Distributed on the Sphere, K. M. Górski, E. Hivon, A. J. Banday, B. D. Wandelt, F. K. Hansen, M. Reinecke, M. Bartelmann, ApJ, 622, 759-771, (2005).
(Planck) Low Frequency Instrument
Sunyaev-Zel'dovich
(Planck) High Frequency Instrument
Planck Legacy Archive
reduced IMO