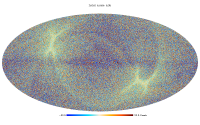
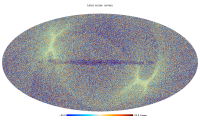
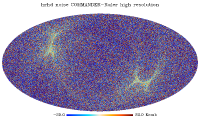
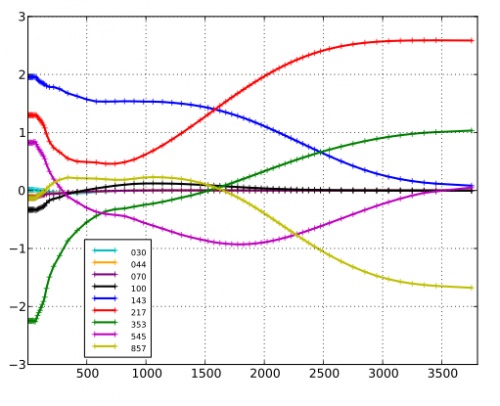
Foreground maps
Contents
[hide]- 1 Astrophysical Components
- 1.1 Overview
- 1.2 Astrophysical foregrounds from parametric component separation
- 1.3 Modelling of the thermal dust emission with the Draine and Li dust model
- 1.4 Thermal dust and CIB all-sky maps from GNILC component separation
- 2 Other maps that require special processing
- 3 Previous Releases: (2015) and (2013) CMB Maps
- 4 References
Astrophysical Components[edit]
Overview[edit]
This section describes the maps of astrophysical components produced from the Planck data. These products are derived from some or all of the nine frequency channel maps described above using different techniques and, in some cases, using other constraints from external data sets. Here we give a brief description of each product and how it is obtained, followed by a description of the FITS file containing the data and associated information. All the details can be found in Planck-2015-A10[1] and {PlanckPapers|planck20}}.
Astrophysical foregrounds from parametric component separation[edit]
We describe diffuse foreground products for the Planck 2015 release. See the Planck Foregrounds Component Separation paper Planck-2015-A10[1] for a detailed description of these products. Further scientific discussion and interpretation may be found in Planck-2015-A25[2].
Low-resolution temperature products[edit]
- The Planck 2015 astrophysical component separation analysis combines Planck observations with the 9-year WMAP temperature sky maps (Bennett et al. 2013) and the 408 MHz survey by Haslam et al. (1982). This allows a direct decomposition of the low-frequency foregrounds into separate synchrotron, free-free and spinning dust components without strong spatial priors.
Inputs[edit]
The following data products are used for the low-resolution analysis:
- Full-mission 30 GHz frequency map, LFI 30 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 44 GHz frequency map, LFI 44 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 70 GHz ds1 (18+23), ds2 (19+22), and ds3 (20+21) detector-set maps
- Full-mission 100 GHz ds1 and ds2 detector set maps
- Full-mission 143 GHz ds1 and ds2 detector set maps and detectors 5, 6, and 7 maps
- Full-mission 217 GHz detector 1, 2, 3 and 4 maps
- Full-mission 353 GHz detector set ds2 and detector 1 maps
- Full-mission 545 GHz detector 2 and 4 maps
- Full-mission 857 GHz detector 2 map
- Beam-symmetrized 9-year WMAP K-band map (Lambda)
- Beam-symmetrized 9-year WMAP Ka-band map (Lambda)
- Default 9-year WMAP Q1 and Q2 differencing assembly maps (Lambda)
- Default 9-year WMAP V1 and V2 differencing assembly maps (Lambda)
- Default 9-year WMAP W1, W2, W3, and W4 differencing assembly maps (Lambda)
- Re-processed 408 MHz survey map, Remazeilles et al. (2014) (Lambda)
All maps are smoothed to a common resolution of 1 degree FWHM by deconvolving their original instrumental beam and pixel window, and convolving with the new common Gaussian beam, and repixelizing at Nside=256.
Outputs[edit]
Synchrotron emission[edit]
- File name: COM_CompMap_Synchrotron-commander_0256_R2.00.fits
- Reference frequency: 408 MHz
- Nside = 256
- Angular resolution = 60 arcmin
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| I_ML | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_MEAN | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Amplitude posterior mean |
| I_RMS | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Amplitude posterior rms |
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nu | Real*4 | Hz | Frequency |
| intensity | Real*4 | W/Hz/m2/sr | GALPROP z10LMPD_SUNfE spectrum |
Free-free emission[edit]
- File name: COM_CompMap_freefree-commander_0256_R2.00.fits
- Reference frequency: NA
- Nside = 256
- Angular resolution = 60 arcmin
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| EM_ML | Real*4 | cm^-6 pc | Emission measure posterior maximum |
| EM_MEAN | Real*4 | cm^-6 pc | Emission measure posterior mean |
| EM_RMS | Real*4 | cm^-6 pc | Emission measure posterior rms |
| TEMP_ML | Real*4 | K | Electron temperature posterior maximum |
| TEMP_MEAN | Real*4 | K | Electron temperature posterior mean |
| TEMP_RMS | Real*4 | K | Electron temperature posterior rms |
Spinning dust emission[edit]
- File name: COM_CompMap_AME-commander_0256_R2.00.fits
- Nside = 256
- Angular resolution = 60 arcmin
Note: The spinning dust component has two independent constituents, each corresponding to one spdust2 component, but with different peak frequencies. The two components are stored in the two first FITS extensions, and the template frequency spectrum is stored in the third extension.
- Reference frequency: 22.8 GHz
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| I_ML | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Primary amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_MEAN | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Primary amplitude posterior mean |
| I_RMS | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Primary amplitude posterior rms |
| FREQ_ML | Real*4 | GHz | Primary peak frequency posterior maximum |
| FREQ_MEAN | Real*4 | GHz | Primary peak frequency posterior mean |
| FREQ_RMS | Real*4 | GHz | Primary peak frequency posterior rms |
- Reference frequency: 41.0 GHz
- Peak frequency: 33.35 GHz
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| I_ML | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Secondary amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_MEAN | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Secondary amplitude posterior mean |
| I_RMS | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Secondary amplitude posterior rms |
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nu | Real*4 | GHz | Frequency |
| j_nu/nH | Real*4 | Jy sr-1 cm2/H | spdust2 spectrum |
CO line emission[edit]
- File name: COM_CompMap_CO-commander_0256_R2.00.fits
- Nside = 256
- Angular resolution = 60 arcmin
Note: The CO line emission component has three independent objects, corresponding to the J1->0, 2->1 and 3->2 lines, stored in separate extensions.
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| I_ML | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | CO(1-0) amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_MEAN | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | CO(1-0) amplitude posterior mean |
| I_RMS | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | CO(1-0) amplitude posterior rms |
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| I_ML | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | CO(2-1) amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_MEAN | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | CO(2-1) amplitude posterior mean |
| I_RMS | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | CO(2-1) amplitude posterior rms |
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| I_ML | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | CO(3-2) amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_MEAN | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | CO(3-2) amplitude posterior mean |
| I_RMS | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | CO(3-2) amplitude posterior rms |
94/100 GHz line emission[edit]
- File name: COM_CompMap_xline-commander_0256_R2.00.fits
- Nside = 256
- Angular resolution = 60 arcmin
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| I_ML | Real*4 | uK_cmb | Amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_MEAN | Real*4 | uK_cmb | Amplitude posterior mean |
| I_RMS | Real*4 | uK_cmb | Amplitude posterior rms |
Note: The amplitude of this component is normalized according to the 100-ds1 detector set map, ie., it is the amplitude as measured by this detector combination.
Thermal dust emission[edit]
- File name: COM_CompMap_dust-commander_0256_R2.00.fits
- Nside = 256
- Angular resolution = 60 arcmin
- Reference frequency: 545 GHz
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| I_ML | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_MEAN | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Amplitude posterior mean |
| I_RMS | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Amplitude posterior rms |
| TEMP_ML | Real*4 | K | Dust temperature posterior maximum |
| TEMP_MEAN | Real*4 | K | Dust temperature posterior mean |
| TEMP_RMS | Real*4 | K | Dust temperature posterior rms |
| BETA_ML | Real*4 | NA | Emissivity index posterior maximum |
| BETA_MEAN | Real*4 | NA | Emissivity index posterior mean |
| BETA_RMS | Real*4 | NA | Emissivity index posterior rms |
Thermal Sunyaev-Zeldovich emission around the Coma and Virgo clusters[edit]
- File name: COM_CompMap_SZ-commander_0256_R2.00.fits
- Nside = 256
- Angular resolution = 60 arcmin
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y_ML | Real*4 | y_SZ | Y parameter posterior maximum |
| Y_MEAN | Real*4 | y_SZ | Y parameter posterior mean |
| Y_RMS | Real*4 | y_SZ | Y parameter posterior rms |
High-resolution temperature products[edit]
High-resolution foreground products at 7.5 arcmin FWHM are derived with the same algorithm as for the low-resolution analyses, but including frequency channels above (and including) 143 GHz.
Inputs[edit]
The following data products are used for the low-resolution analysis:
- Full-mission 143 GHz ds1 and ds2 detector set maps and detectors 5, 6, and 7 maps
- Full-mission 217 GHz detector 1, 2, 3 and 4 maps
- Full-mission 353 GHz detector set ds2 and detector 1 maps
- Full-mission 545 GHz detector 2 and 4 maps
- Full-mission 857 GHz detector 2 map
All maps are smoothed to a common resolution of 7.5 arcmin FWHM by deconvolving their original instrumental beam and pixel window, and convolving with the new common Gaussian beam, and repixelizing at Nside=2048.
Outputs[edit]
CO J2->1 emission[edit]
- File name: COM_CompMap_CO21-commander_2048_R2.00.fits
- Nside = 2048
- Angular resolution = 7.5 arcmin
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| I_ML_FULL | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | Full-mission amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_ML_HM1 | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | First half-mission amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_ML_HM2 | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | Second half-mission amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_ML_HR1 | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | First half-ring amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_ML_HR2 | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | Second half-ring amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_ML_YR1 | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | "First year" amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_ML_YR2 | Real*4 | K_RJ km/s | "Second year" amplitude posterior maximum |
Thermal dust emission[edit]
- File name: COM_CompMap_ThermalDust-commander_2048_R2.00.fits
- Nside = 2048
- Angular resolution = 7.5 arcmin
- Reference frequency: 545 GHz
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| I_ML_FULL | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Full-mission amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_ML_HM1 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | First half-mission amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_ML_HM2 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Second half-mission amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_ML_HR1 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | First half-ring amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_ML_HR2 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Second half-ring amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_ML_YR1 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | "First year" amplitude posterior maximum |
| I_ML_YR2 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | "Second year" amplitude posterior maximum |
| BETA_ML_FULL | Real*4 | NA | Full-mission emissivity index posterior maximum |
| BETA_ML_HM1 | Real*4 | NA | First half-mission emissivity index posterior maximum |
| BETA_ML_HM2 | Real*4 | NA | Second half-mission emissivity index posterior maximum |
| BETA_ML_HR1 | Real*4 | NA | First half-ring emissivity index posterior maximum |
| BETA_ML_HR2 | Real*4 | NA | Second half-ring emissivity index posterior maximum |
| BETA_ML_YR1 | Real*4 | NA | "First year" emissivity index posterior maximum |
| BETA_ML_YR2 | Real*4 | NA | "Second year" emissivity index posterior maximum |
Polarization products[edit]
Two polarization foreground products are provided, namely synchrotron and thermal dust emission. The spectral models are assumed identical to the corresponding temperature spectral models.
Inputs[edit]
The following data products are used for the polarization analysis:
- (Only low-resolution analysis) Full-mission 30 GHz frequency map, LFI 30 GHz frequency maps
- (Only low-resolution analysis) Full-mission 44 GHz frequency map, LFI 44 GHz frequency maps
- (Only low-resolution analysis) Full-mission 70 GHz frequency map, LFI 70 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 100 GHz frequency map, HFI 100 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 143 GHz frequency map, HFI 143 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 217 GHz frequency map, HFI 217 GHz frequency maps
- Full-mission 353 GHz frequency map, HFI 353 GHz frequency maps
In the low-resolution analysis, all maps are smoothed to a common resolution of 40 arcmin FWHM by deconvolving their original instrumental beam and pixel window, and convolving with the new common Gaussian beam, and repixelizing at Nside=256. In the high-resolution analysis (including only CMB and thermal dust emission), the corresponding resolution is 10 arcmin FWHM and Nside=1024.
Outputs[edit]
Synchrotron emission[edit]
- File name: COM_CompMap_SynchrotronPol-commander_0256_R2.00.fits
- Nside = 256
- Angular resolution = 40 arcmin
- Reference frequency: 30 GHz
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q_ML_FULL | Real*4 | μK_RJ | Full-mission Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_FULL | Real*4 | μK_RJ | Full-mission Stokes U posterior maximum |
| Q_ML_HM1 | Real*4 | μK_RJ | First half-mission Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_HM1 | Real*4 | μK_RJ | First half-mission Stokes U posterior maximum |
| Q_ML_HM2 | Real*4 | μK_RJ | Second half-mission Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_HM2 | Real*4 | μK_RJ | Second half-mission Stokes U posterior maximum |
| Q_ML_HR1 | Real*4 | μK_RJ | First half-ring Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_HR1 | Real*4 | μK_RJ | First half-ring Stokes U posterior maximum |
| Q_ML_HR2 | Real*4 | μK_RJ | Second half-ring Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_HR2 | Real*4 | μK_RJ | Second half-ring Stokes U posterior maximum |
| Q_ML_YR1 | Real*4 | μK_RJ | "First year" Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_YR1 | Real*4 | μK_RJ | "First year" Stokes U posterior maximum |
| Q_ML_YR2 | Real*4 | μK_RJ | "Second year" Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_YR2 | Real*4 | μK_RJ | "Second year" Stokes U posterior maximum |
Thermal dust emission[edit]
- File name: COM_CompMap_DustPol-commander_1024_R2.00.fits
- Nside = 1024
- Angular resolution = 10 arcmin
- Reference frequency: 353 GHz
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q_ML_FULL | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Full-mission Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_FULL | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Full-mission Stokes U posterior maximum |
| Q_ML_HM1 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | First half-mission Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_HM1 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | First half-mission Stokes U posterior maximum |
| Q_ML_HM2 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Second half-mission Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_HM2 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Second half-mission Stokes U posterior maximum |
| Q_ML_HR1 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | First half-ring Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_HR1 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | First half-ring Stokes U posterior maximum |
| Q_ML_HR2 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Second half-ring Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_HR2 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | Second half-ring Stokes U posterior maximum |
| Q_ML_YR1 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | "First year" Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_YR1 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | "First year" Stokes U posterior maximum |
| Q_ML_YR2 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | "Second year" Stokes Q posterior maximum |
| U_ML_YR2 | Real*4 | uK_RJ | "Second year" Stokes U posterior maximum |
Modelling of the thermal dust emission with the Draine and Li dust model[edit]
The Planck, IRAS, and WISE infrared observations were fit with the dust model presented by Draine & Li in 2007 (DL07). The input maps, the DL07 model, and the fitting procedure and results are presented in Planck-2014-XXIX[3]. Here, we describe the input maps and the output maps, which are made available on the Planck Legacy Archive.
Inputs[edit]
The following data have been fit:
- WISE 12 micron map
- IRAS 60 micron map
- IRAS 100 micron map
- Full-mission 353 GHz PR2 map
- Full-mission 545 GHz PR2 map
- Full-mission 857 GHz PR2 map
The CIB monopole, the CMB anisotropries and the zodiacal light were subtracted to obtain dust emission maps from the sky emission maps. All maps were smoothed to a common angular resolution of 5'.
Model Parameters[edit]
For each pixel of the inputs maps, we have fitted four parameters of the DL07 model:
- the dust mass surface density, Sigma_Mdust,
- the dust mass fraction in small PAH grains, q_PAH,
- the fraction of the total luminosity from dust heated by intense radiation fields, f_PDR,
- the starlight intensity heating the bulk of the dust, U_min.
The parameter maps and their uncertainties are gathered in one file. This file also includes the chi2 of the fit per degree of freedom.
- File name: COM_CompMap_Dust-DL07-Parameters_2048_R2.00.fits
- Nside = 2048
- Angular resolution = 5 arcmin
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma_Mdust | Real*4 | Solar masses/kpc^2 | Dust mass surface density |
| Sigma_Mdust_unc | Real*4 | Solar masses/kpc^2 | Uncertainty (1 sigma) on Sigma_Mdust |
| q_PAH | Real*4 | dimensionless | Dust mass fraction in small PAH grains |
| q_PAH_unc | Real*4 | dimensionless | Uncertainty (1 sigma) on q_PAH |
| f_PDR | Real*4 | dimensionless | Fraction of the total luminosity from dust heated by intense radiation fields |
| f_PDR_unc | Real*4 | dimensionless | Uncertainty (1 sigma) on f_PDR |
| U_min | Real*4 | dimensionless | Starlight intensity heating the bulk of the dust |
| U_min_unc | Real*4 | dimensionless | Uncertainty (1 sigma) on U_min |
| Chi2_DOF | Real*4 | dimensionless | Chi2 of the fit per degree of freedom |
Visible extinction maps[edit]
We provide two exinctions maps at the visible V band: the value from the model (Av_DL) and the renormalized one (Av_RQ) that matches extinction estimates for quasars (QSOs) derived from the Sloan digital sky survey (SDSS) data.
- File name: COM_CompMap_Dust-DL07-AvMaps_2048_R2.00.fits
- Nside = 2048
- Angular resolution = 5 arcmin
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Av_DL | Real*4 | magnitude | Extinction in the V band from the DL model |
| Av_DL_unc | Real*4 | magnitude | Uncertainty (1 sigma) on Av_DL |
| Av_RQ | Real*4 | magnitude | Extinction in the V band renormalized to match estimates from QSO SDSS observations |
| Av_RQ_unc | Real*4 | magnitude | Uncertainty (1 sigma) on Av_RQ |
Model Fluxes[edit]
We provide the model predicted fluxes in the following file.
- File name: COM_CompMap_Dust-DL07-ModelFluxes_2048_R2.00.fits
- Nside = 2048
- Angular resolution = 5 arcmin
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planck_857 | Real*4 | MJy/sr | Model flux in the Planck 857 GHz band |
| Planck_545 | Real*4 | MJy/sr | Model flux in the Planck 545 GHz band |
| Planck_353 | Real*4 | MJy/sr | Model flux in the Planck 353 GHz band |
| WISE_12 | Real*4 | MJy/sr | Model flux in the WISE 12 micron band |
| IRAS_60 | Real*4 | MJy/sr | Model flux in the IRAS 60 micron band |
| IRAS_100 | Real*4 | MJy/sr | Model flux in the IRAS 100 micron band |
Thermal dust and CIB all-sky maps from GNILC component separation[edit]
We describe diffuse foreground products for the Planck 2015 release produced with the GNILC component separation method. See the Planck paper Planck-2016-XLVIII[4] for a detailed discussion on these products.
Method[edit]
- The basic idea behind the Generalized Needlet Internal Linear Combination (GNILC) component-separation method (Remazeilles et al, MNRAS 2011) is to disentangle specific components of emission not on the sole basis of the spectral (frequency) information but also on the basis of their distinct spatial information (angular power spectrum). The GNILC method has been applied to Planck data in order to disentangle Galactic dust emission and Cosmic Infrared Background (CIB) anisotropies. Both components have a similar spectral signature but a distinct angular power spectrum (spatial signature). The spatial information used by GNILC is under the form of priors for the angular power spectra of the CIB, the CMB, and the instrumental noise. No assumption is made on the Galactic signal, neither spectral or spatial. In that sense, GNILC is a blind component-separation method. GNILC operates on a needlet (spherical wavelet) frame, therefore adapting the component separation to the local conditions of contamination both over the sky and over the angular scales.
Data[edit]
- The data used by GNILC for the analysis are the Planck data release 2 (PR2) frequency maps from 30 to 857 GHz, and a 100 micron hybrid map combined from the SFD map (Schlegel et al, ApJ 1998) at large angular scales (> 30') and the IRIS map (Miville-Deschênes et al, ApJS 2005) at small angular scales (< 30'). This special 100 micron map can be obtained in the External Maps section of the PLA.
Pre-processing[edit]
- The point-sources with a signal-to-noise ratio, S/N > 5, in each individual frequency map (30 to 857 GHz, and 100 micron) have been pre-processed by a minimum curvature surface inpainting technique (Remazeilles et al, MNRAS 2015) prior to performing component separation with GNILC.
GNILC thermal dust and CIB products[edit]
The result of GNILC component separation are thermal dust and CIB maps at 353, 545, and 857 GHz. In addition, by fitting a modified blackbody model to the GNILC thermal dust products at 353, 545, 857, and 100 micron, we have created all-sky maps of the dust optical depth, dust temperature, and dust emmissivity index. Note that the thermal dust maps have a variable angular resolution over the sky with an effective beam FWHM varying from 21.8' to 5'. The dust beam FWHM map is also released as a product.
Thermal dust maps[edit]
CIB maps[edit]
| File Name | Nside | Units | Reference frequency | Angular resolution | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COM_CompMap_CIB-GNILC-F353_2048_R2.00.fits | 2048 | MJy/sr | 353 GHz | 5 arcmin | CIB amplitude at 353 GHz |
| COM_CompMap_CIB-GNILC-F545_2048_R2.00.fits | 2048 | MJy/sr | 545 GHz | 5 arcmin | CIB amplitude at 545 GHz |
| COM_CompMap_CIB-GNILC-F857_2048_R2.00.fits | 2048 | MJy/sr | 857 GHz | 5 arcmin | CIB amplitude at 857 GHz |
Other maps that require special processing[edit]
2015 Lensing map[edit]
We distribute the minimum-variance (MV) lensing potential estimate presented in Planck-2015-A15[5] as part of the 2014 data release. This map represents an estimate of the CMB lensing potential on approximately 70% of the sky, and also forms the basis for the Planck 2014 lensing likelihood. It is produced using filtered temperature and polarization data from the SMICA DX11 CMB map; its construction is discussed in detail in Planck-2015-A09[6].
The estimate is contained in a single gzipped tarball named COM_CompMap_Lensing_2048_R2.00.tgz. Its contents are described below. The convergence map "dat_klm.fits" that can be found in the tarball, has been categorized as COM_Lensing-Convergence-dat-klm_2048_R2.00.fits in the Lensing Products section of the archive.
| Filename | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| dat_klm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Contains the estimated lensing convergence . |
| mask.fits.gz | HEALPix FITS format map, with | Contains the lens reconstruction analysis mask. |
| nlkk.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, , ) | The approximate noise (and signal+noise, ) power spectrum of , for the fiducial cosmology used in Planck-2015-A13[7]. |
Previous Releases: (2013) Lensing Maps[edit]
2013 Release of the lensing map
2015 Compton y parameter map[edit]
We distribute here the Planck full mission Compton parameter maps (y-maps hereafter) obtained using the NILC and MILCA component-separation algorithms as described in Planck-2015-A22[9]. We also provide the ILC weights per scale and per frequency that were used to produce these y-maps. IDL routines are also provided to allow the user to apply those weights. Compton parameters produced by keeping either the first or the second half of stable pointing periods are also provided; we call these the FIRST and LAST y-maps. Additionally we construct noise estimates of full mission Planck y-maps from the half difference of the FIRST and LAST y-maps. These estimates are used to construct standard deviation maps of the noise in the full mission Planck y-maps, which are also provided. To complement this we also provide the power spectra of the noise estimate maps after correcting for inhomogeneities using the standard deviation maps. We also deliver foreground masks including point-source and Galactic masks.
The full data set is contained in a single gzipped tarball named COM_CompMap_YSZ_R2.00.fits.tgz. Its contents are described below. Temporarily the tarball file can be found in the Supplement Data area of the PLA (go to pla.esac.esa.int/pla, go to Subsection Supplementary Data and type "YSZ" in the search form)
| Filename | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| nilc_ymaps.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the NILC full mission, FIRST and LAST y-maps. |
| milca_ymaps.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the MILCA full mission, FIRST and LAST y-maps. |
| nilc_weights_BAND.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the NILC ILC weights for the full mission y-map for band BAND 0 to 9. For each band we provide a weight map per frequency. |
| milca_FREQ_Csz.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the MILCA ILC weights for the full mission y-map for frequency FREQ (100, 143, 217, 353, 545, 857). For each frequency we provide a weight map per filter band. |
| nilc_stddev.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the stddev map for the NILC full mission y-map. |
| milca_stddev.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the stddev maps for the MILCA full mission y-map. |
| nilc_homnoise_spect.fits | ASCII table FITS format | Contains the angular power spectrum of the homogeneous noise in the NILC full mission y-map. |
| milca_homnoise_spect.fits | ASCII table FITS format | Contains the angular power spectrum of the homogeneous noise in the MILCA full mission y-map. |
| masks.fits | HEALPix FITS format map, with | Contains foreground masks. |
| nilc_bands.fits | ASCII table FITS format | Contains NILC wavelet bands in multipole space |
2015 Lensing-induced B-mode map[edit]
We distribute the Planck map of the lensing-induced B-modes presented in Planck-2015-XLI[10]. The Stokes parameter maps of the lensing B-modes are produced by combining the lensing potential map extracted from the SMICA CMB temperature map with E-mode data from the SMICA CMB polarization maps. The SMICA temperature and polarization products are described in Planck-2015-A09[6]. The lensing-induced B-mode polarization maps are used in cross-correlation with the SMICA CMB polarization maps to obtain a lensing B-mode power spectrum measurement from approximately 70% of the sky.
We provide both raw products, which can be utilized to generate products adapted to one's specific needs in term of mask, filtering, etc., and "ready-to-use" products for cross-correlation study purposes.
Raw products[edit]
We deliver the non-normalized lensing-induced Stokes parameter maps, labelled and , which form the basis of the final lensing B-mode estimator defined in equation (6) of the paper. They are defined as
where and are the filtered pure E-mode polarization maps given in equation (5), and is the filtered lensing potential estimate.
We also provide the normalization transfer function defined in equation (12), as well as the "B70" mask that retains 69% of the sky before apodization, and its apodized version , which has an effective sky fraction .
As an example of the utilization of these products, the lensing B-mode maps that are shown in figure 4 are generated from
,
where is a Gaussian filter of 60 arcmin FWHM (introduced for highlighting large angular scales, although it can be removed or replaced by any other filter). This can be practically done by ingesting and in the HEALPix "smoothing" routine, and using the product as an input filtering function.
The lensing-induced Stokes parameter maps are provided without being masked for the user's convenience (in particular, it allows for various filtering to be tested). However, whenever they are utilized in view of obtaining scientific outcomes, they should be masked using the B70 mask, which is also provided.
Specific products[edit]
We provide the lensing B-mode spherical harmonic coefficient estimate over approximately 70% of the sky.
It can also be constructed using the raw products described above from
,
where is a band-pass filter that retain the multipole range , and is a short-hand notation for transforming a map into spin-weighted spherical harmonic coefficients , and forming . This can be done using, e.g., the HEALPix "anafast" tool.
The lensing B-mode power spectrum estimate is obtained by forming the cross-correlation power spectrum of and the B-mode data from the SMICA polarization maps :
,
where is the 5 arcmin Gaussian beam that convolves the SMICA CMB maps.
The products are contained in a single gzipped tarball named COM_Lensing-Bmode_R2.01.tgz. Its contents are described below.
| Filename | Format | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bar_q_lens_map.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the non-normalized lensing-induced Q Stokes parameter map . |
| bar_u_lens_map.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | Contains the non-normalized lensing-induced U Stokes parameter map . |
| mask.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | The B70 mask (apodized version). |
| mask_noapo.fits | HEALPix FITS format map in Galactic coordinates with | The B70 mask without apodization. |
| transfer_function_b_l.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, ) | The transfer function of the lensing B-mode estimator. |
| lensing_bmode_b_lm.fits | HEALPix FITS format alm, with | Contains the lensing B-mode harmonic coefficients . |
| lensing_bmode_bandpowers.dat | ASCII text file, with columns = (, , , , ) | The lensing B-mode bandpower estimate on approximativily 70% of the sky and over the multipole range from 10 to 2000 shown in figure 10 of Planck-2015-XLI[10] (for plotting purposes only). |
2015 Integrated Sachs-Wolfe effect map[edit]
We distribute estimates of the integrated Sachs-Wolfe (ISW) maps presented in Planck-2015-A21[11] as part of the 2015 data release. These map represents an estimate of the ISW anisotropies using different data sets:
- SEVEM DX11 CMB map, together with all the large-scale structure tracers considered in the ISW paper, namely: NVSS, SDSS, WISE, and the Planck lensing map
- Using only the large-scale structure tracers mentioned above
- SEVEM DX11 CMB map, together with NVSS and the Planck lensing maps (since these two tracers capture most of the information, as compared to SDSS and WISE)
For all the three cases, the reconstruction is provided on approximately 85% of the sky, and they are produced using the LCB filter described in the Planck ISW paper (Section 5), described in detail in Barreiro et al. 2008 and Bonavera et al. 2016.
These ISW maps, together with their corresponding uncertainties maps and masks, are given in a file named COM_CompMap_ISW_0064_R2.00.fits. Its contents are described below.
| Extension | Format | Description | Used data sets |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | HEALPix FITS format map with three components, , Ordering='Nest' | Contains three components: i) ISW map [Kelvin], ii) Error map [Kelvin], iii) Mask map | SEVEM DX11 CMB + NVSS + SDSS + WISE + Planck lensing. |
| 1 | HEALPix FITS format map with three components, , Ordering='Nest' | Contains three components: i) ISW map [Kelvin], ii) Error map [Kelvin], iii) Mask map | NVSS + SDSS + WISE + Planck lensing. |
| 2 | HEALPix FITS format map with three components, , Ordering='Nest' | Contains three components: i) ISW map [Kelvin], ii) Error map [Kelvin], iii) Mask map | SEVEM DX11 CMB + NVSS + Planck lensing. |
2013 IRAM Maps of the Crab nebula[edit]
Maps of the Crab nebula at 89.189 GHz (HCO+(1-0) transition) in both temperature and polarization, prodouced from observations performed at the IRAM 30m telescope from January 9th to January 12th 2009, are delivered as a tarball of 416 KB in the file
See README in the tarball for full details. These data were used in[12]
Previous Releases: (2015) and (2013) CMB Maps[edit]
Astrophysical components based on the 2015 data release
Astrophysical components based on the 2013 data release
References[edit]
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.01.11.21.3 Planck 2015 results. X. Diffuse component separation: Foreground maps, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A10.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.02.1 Planck 2015 results. XXV. Diffuse low frequency Galactic foregrounds, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A25.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.03.1 Planck intermediate results. XXIX. All-sky dust modelling with Planck, IRAS, and WISE observations', Planck Collaboration Int. XXIX, A&A, 586, A132, (2016).
- Jump up ↑ Planck intermediate results. XLVIII. Disentangling Galactic dust emission and cosmic infrared background anisotropies, Planck Collaboration Int. XLVIII A&A, 596, A109, (2016).
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.05.1 Planck 2015 results. XV. Gravitational Lensing, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A15.
- ↑ Jump up to: 6.06.16.26.3 Planck 2015 results. XI. Diffuse component separation: CMB maps, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A9.
- ↑ Jump up to: 7.07.1 Planck 2015 results. XIII. Cosmological parameters, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A13.
- ↑ Jump up to: 8.08.18.28.38.48.5 Planck 2013 results. XVII. Gravitational lensing by large-scale structure, Planck Collaboration, 2014, A&A, 571, A17.
- ↑ Jump up to: 9.09.1 Planck 2015 results. XXII. A map of the thermal Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A22.
- ↑ Jump up to: 10.010.110.210.310.410.510.610.710.810.9 Planck intermediate results. XLI. A map of lensing-induced B-modes, Planck Collaboration Int. XLI A&A, 596, A102, (2016).
- ↑ Jump up to: 11.011.1 Planck 2015 results. XXI. The integrated Sachs-Wolfe effect, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A21.
- Jump up ↑ Measurement of the Crab nebula polarization at 90 GHz as a calibrator for CMB experiments, J. Aumont, L. Conversi, C. Thum, H. Wiesemeyer, E. Falgarone, J. F. Macías-Pérez, F. Piacentini, E. Pointecouteau, N. Ponthieu, J. L. Puget, C. Rosset, J. A. Tauber, M. Tristram, A&A, 514, A70+, (2010).
- ↑ Jump up to: 13.013.113.213.313.413.513.613.7 Planck 2013 results. XI. Component separation, Planck Collaboration, 2014, A&A, 571, A11.
- Jump up ↑ Component separation methods for the PLANCK mission, S. M. Leach, J.-F. Cardoso, C. Baccigalupi, R. B. Barreiro, M. Betoule, J. Bobin, A. Bonaldi, J. Delabrouille, G. de Zotti, C. Dickinson, H. K. Eriksen, J. González-Nuevo, F. K. Hansen, D. Herranz, M. Le Jeune, M. López-Caniego, E. Martínez-González, M. Massardi, J.-B. Melin, M.-A. Miville-Deschênes, G. Patanchon, S. Prunet, S. Ricciardi, E. Salerno, J. L. Sanz, J.-L. Starck, F. Stivoli, V. Stolyarov, R. Stompor, P. Vielva, A&A, 491, 597-615, (2008).
- Jump up ↑ Multiresolution internal template cleaning: an application to the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe 7-yr polarization data, R. Fernández-Cobos, P. Vielva, R. B. Barreiro, E. Martínez-González, MNRAS, 420, 2162-2169, (2012).
- Jump up ↑ Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe 7-yr constraints on fNL with a fast wavelet estimator, B. Casaponsa, R. B. Barreiro, A. Curto, E. Martínez-González, P. Vielva, MNRAS, 411, 2019-2025, (2011).
- ↑ Jump up to: 17.017.1 Planck 2013 results. XXIII. Isotropy and statistics of the CMB, Planck Collaboration, 2014, A&A, 571, A23.
- ↑ Jump up to: 18.018.1 Planck 2013 results. XIX. The integrated Sachs-Wolfe effect, Planck Collaboration, 2014, A&A, 571, A19.
- ↑ Jump up to: 19.019.1 Planck 2013 results. XII. All-sky model of thermal dust emission, Planck Collaboration, 2014, A&A, 571, A12.
- Jump up ↑ Calibrating Milky Way dust extinction using cosmological sources, E. Mörtsell, A&A, 550, A80, (2013).
- Jump up ↑ The Sloan Digital Sky Survey Quasar Catalog. IV. Fifth Data Release, D. P. Schneider, P. B. Hall, G. T. Richards, M. A. Strauss, D. E. Vanden Berk, S. F. Anderson, W. N. Brandt, X. Fan, S. Jester, J. Gray, J. E. Gunn, M. U. SubbaRao, A. R. Thakar, C. Stoughton, A. S. Szalay, B. Yanny, D. G. York, N. A. Bahcall, J. Barentine, M. R. Blanton, H. Brewington, J. Brinkmann, R. J. Brunner, F. J. Castander, I. Csabai, J. A. Frieman, M. Fukugita, M. Harvanek, D. W. Hogg, Z. Ivezic, S. M. Kent, S. J. Kleinman, G. R. Knapp, R. G. Kron, J. Krzesinski, D. C. Long, R. H. Lupton, A. Nitta, J. R. Pier, D. H. Saxe, Y. Shen, S. A. Snedden, D. H. Weinberg, J. Wu, ApJ, 134, 102-117, (2007).
- Jump up ↑ Planck 2013 results. XIII. Galactic CO emission, Planck Collaboration, 2014, A&A, 571, A13.
Flexible Image Transfer Specification
Full-Width-at-Half-Maximum
Sunyaev-Zel'dovich
Cosmic Microwave background
Planck Legacy Archive
(Hierarchical Equal Area isoLatitude Pixelation of a sphere, <ref name="Template:Gorski2005">HEALPix: A Framework for High-Resolution Discretization and Fast Analysis of Data Distributed on the Sphere, K. M. Górski, E. Hivon, A. J. Banday, B. D. Wandelt, F. K. Hansen, M. Reinecke, M. Bartelmann, ApJ, 622, 759-771, (2005).
(Planck) Low Frequency Instrument
(Planck) High Frequency Instrument
reduced IMO