Difference between revisions of "Appendix of HFI DPC paper"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
---- | ---- | ||
<span style="font-size:150%">'''Section 3.1.2: masks of the very bright regions where the sub-pixel effect in the foreground templates prevent them to be used for cosmology or astrophysics analysis''' </span> | <span style="font-size:150%">'''Section 3.1.2: masks of the very bright regions where the sub-pixel effect in the foreground templates prevent them to be used for cosmology or astrophysics analysis''' </span> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| + | ---- | ||
<span style="font-size:150%">'''Section 3.2: complementary figures of Fig. 11''' </span> | <span style="font-size:150%">'''Section 3.2: complementary figures of Fig. 11''' </span> | ||
| Line 122: | Line 123: | ||
| + | ---- | ||
<span style="font-size:150%">'''Section 5.3.10: for convenience, we reproduce here Figures 6, 7 and 8 of Rosset et al.''' </span> | <span style="font-size:150%">'''Section 5.3.10: for convenience, we reproduce here Figures 6, 7 and 8 of Rosset et al.''' </span> | ||
| Line 144: | Line 146: | ||
| + | ---- | ||
<span style="font-size:150%">'''Section 5.5: complementary figures of Fig. 29''' </span> | <span style="font-size:150%">'''Section 5.5: complementary figures of Fig. 29''' </span> | ||
| Line 266: | Line 269: | ||
| + | ---- | ||
<span style="font-size:150%">'''Section 5.13: complementary figures of Fig. 47''' </span> | <span style="font-size:150%">'''Section 5.13: complementary figures of Fig. 47''' </span> | ||
Revision as of 13:57, 6 October 2017
This page is intented to provide complementary figures to those of the 2017 HFI DPC paper (Planck-2020-A3[1]).
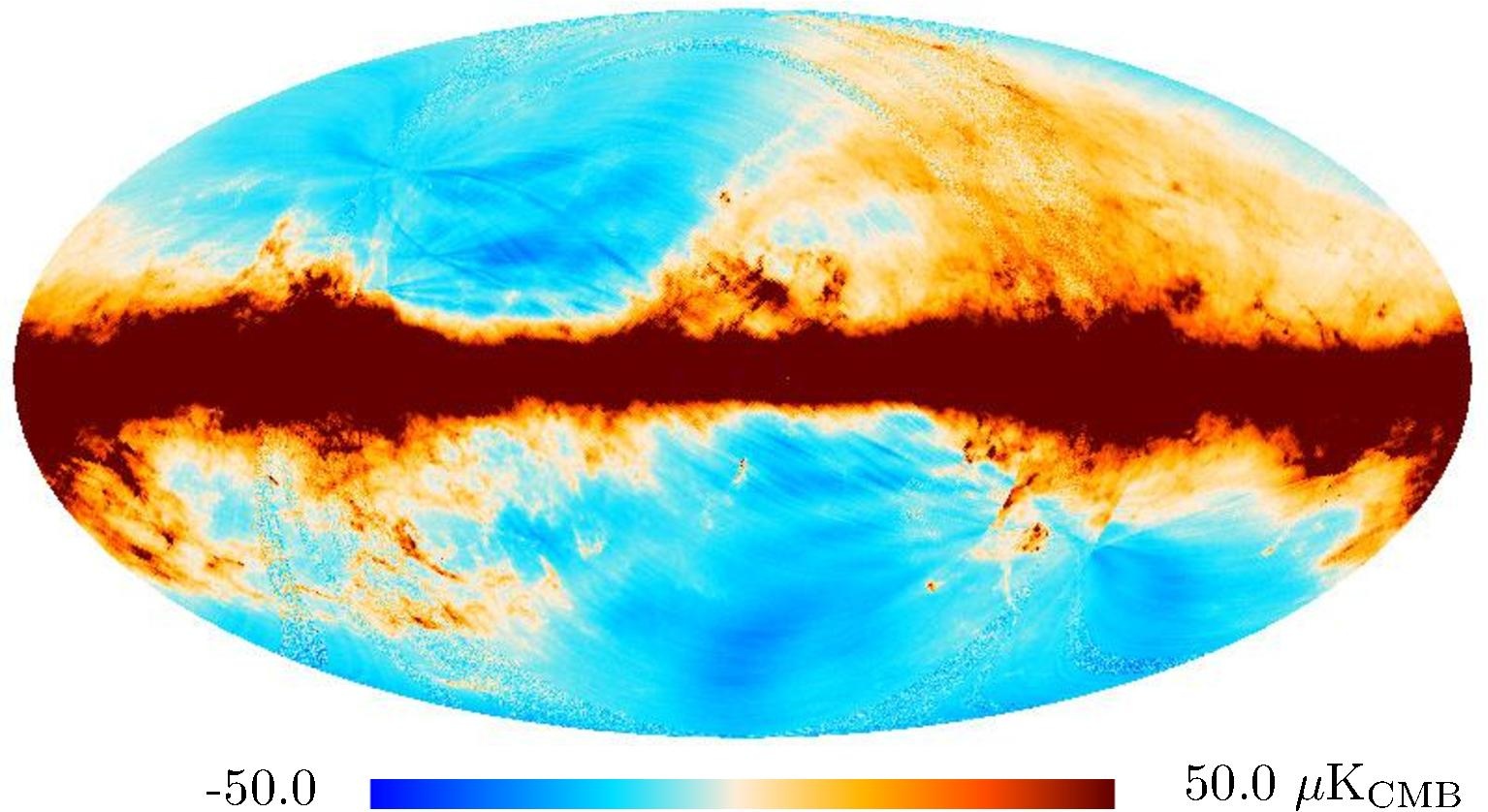
Section 3.1.2: masks of the very bright regions where the sub-pixel effect in the foreground templates prevent them to be used for cosmology or astrophysics analysis
Those masks are provided in the PLA.
| 100 GHz | 143 GHz | 217 GHz | 353 GHz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO template | 
|
. | 
|
|
| Dust template | 
|

|

|
|
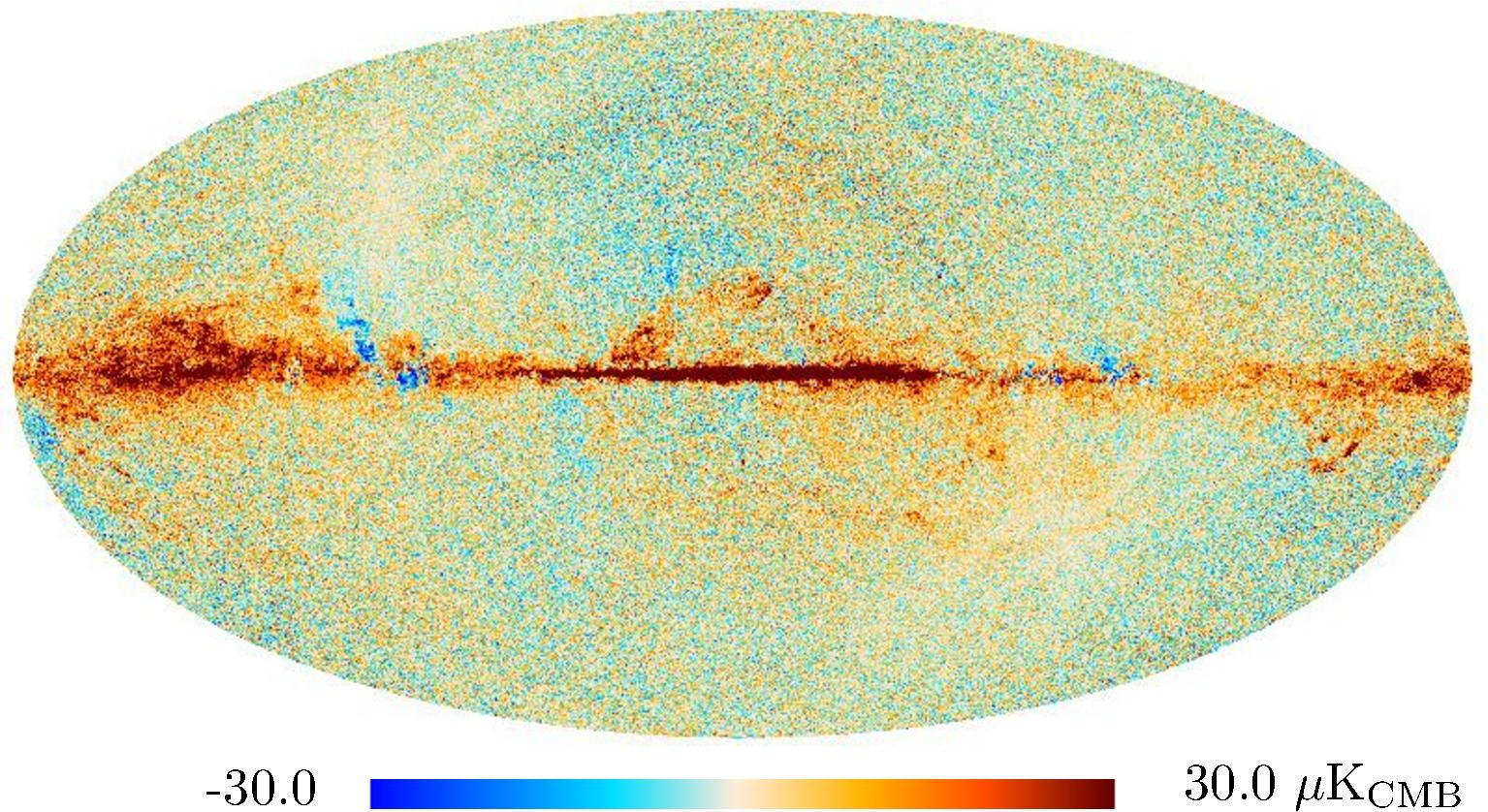
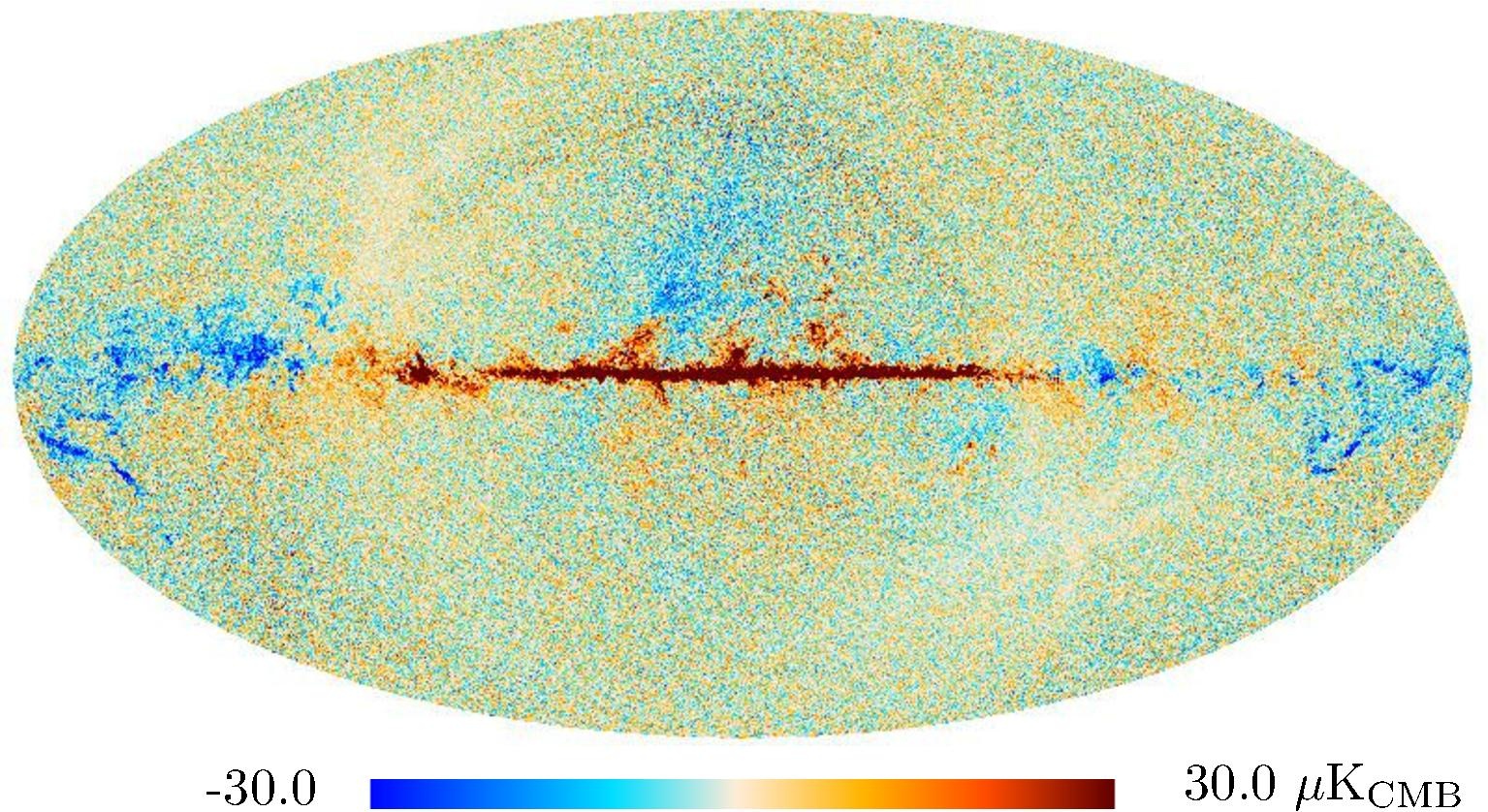
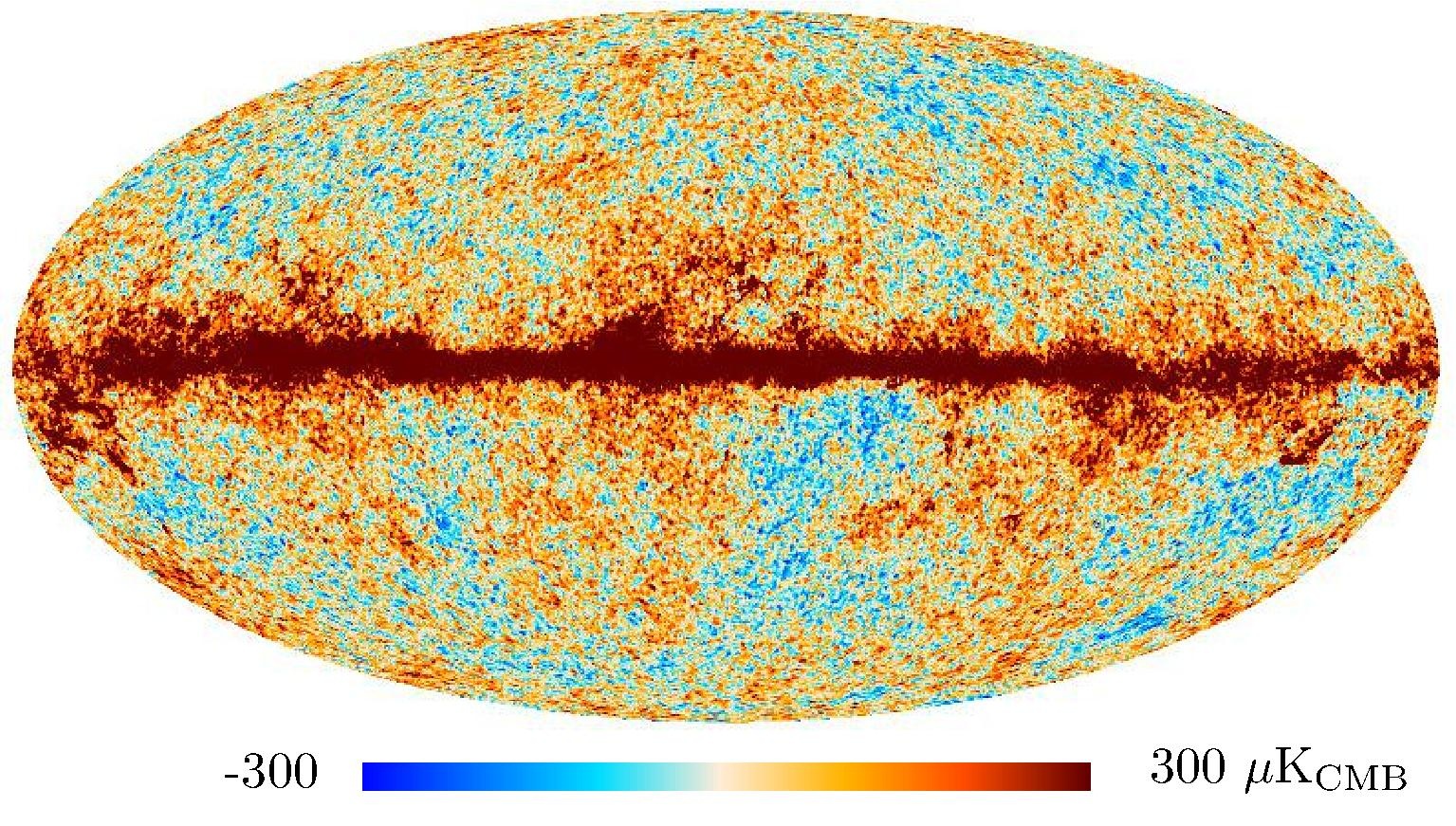
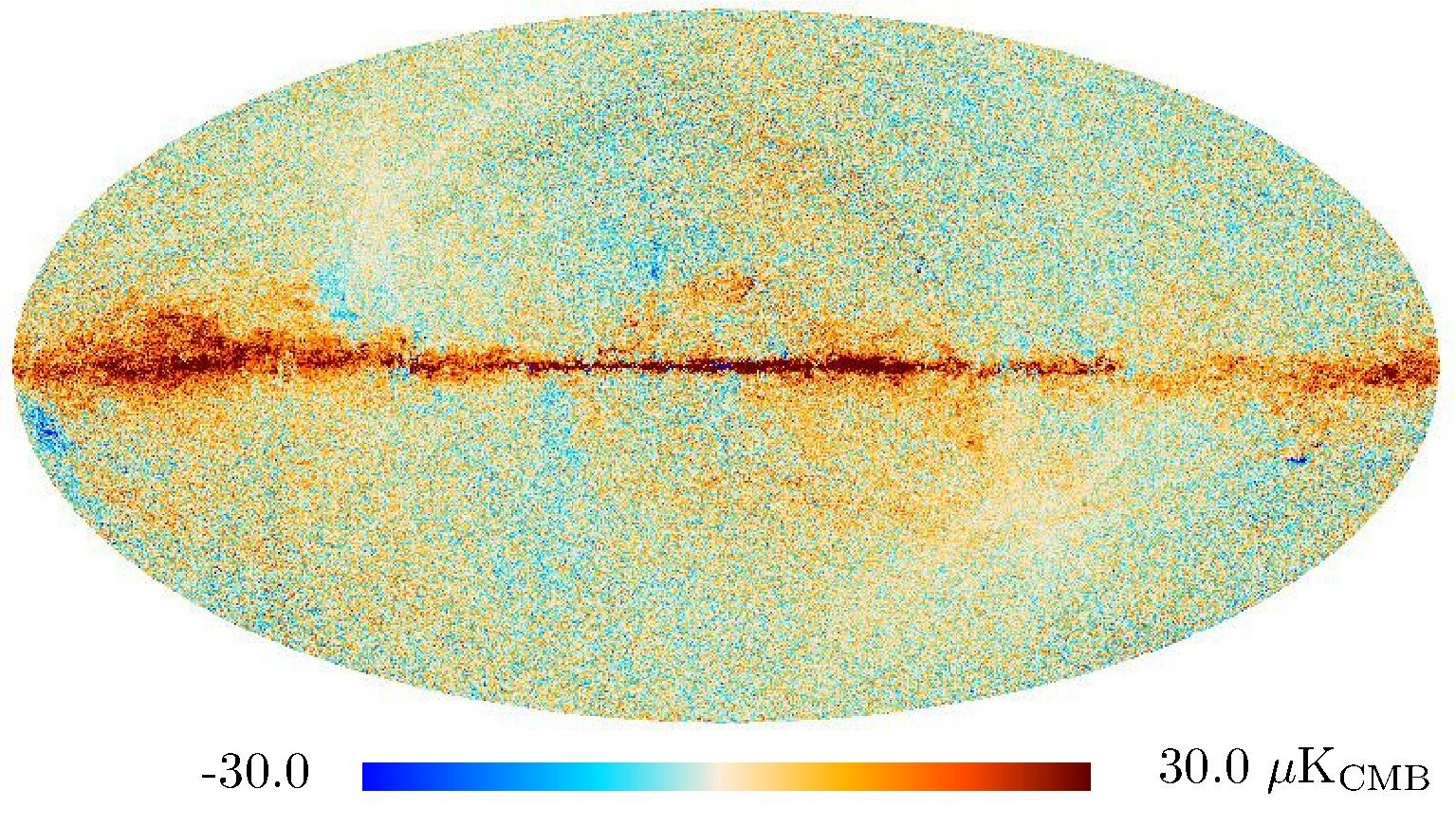
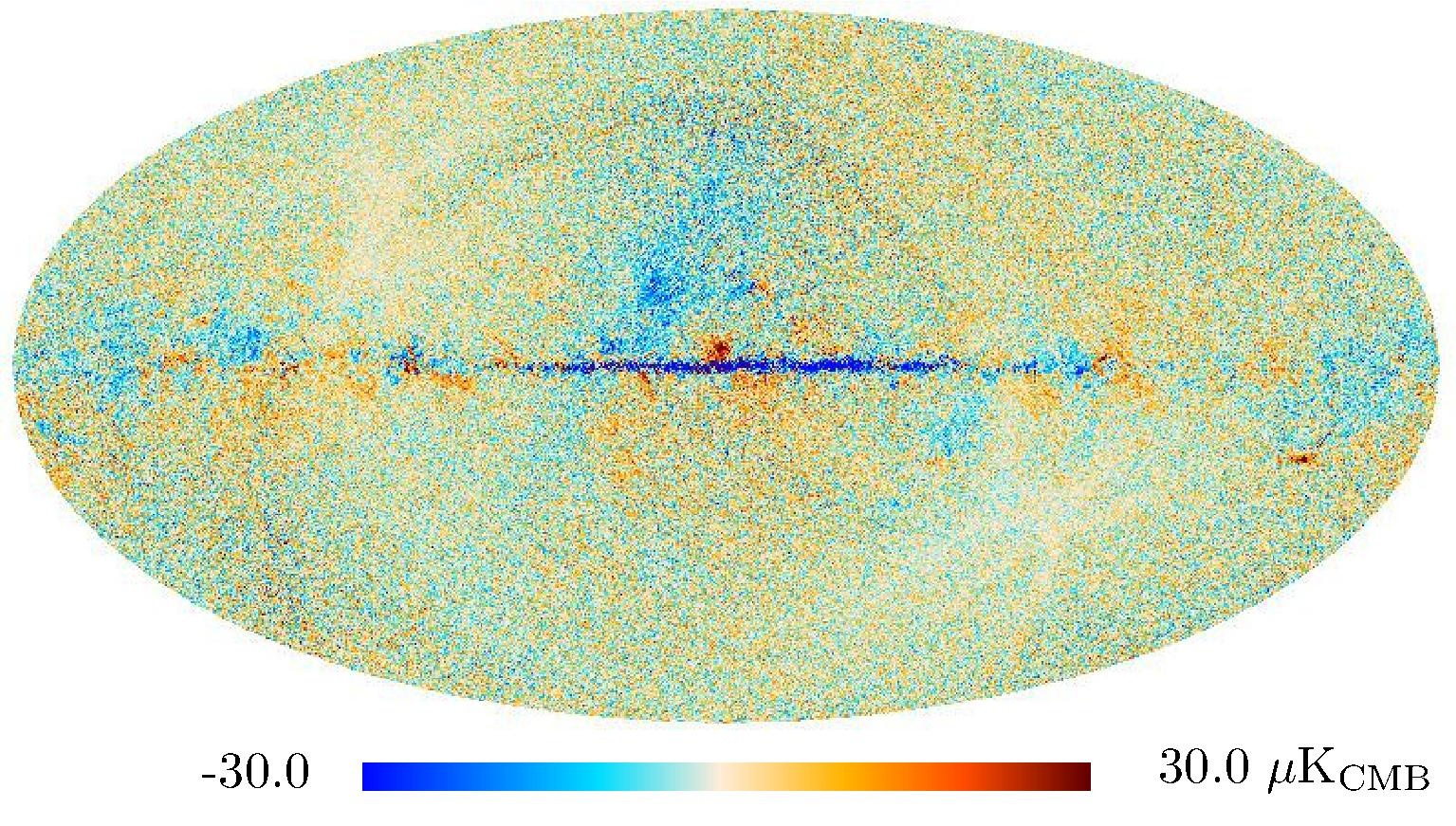
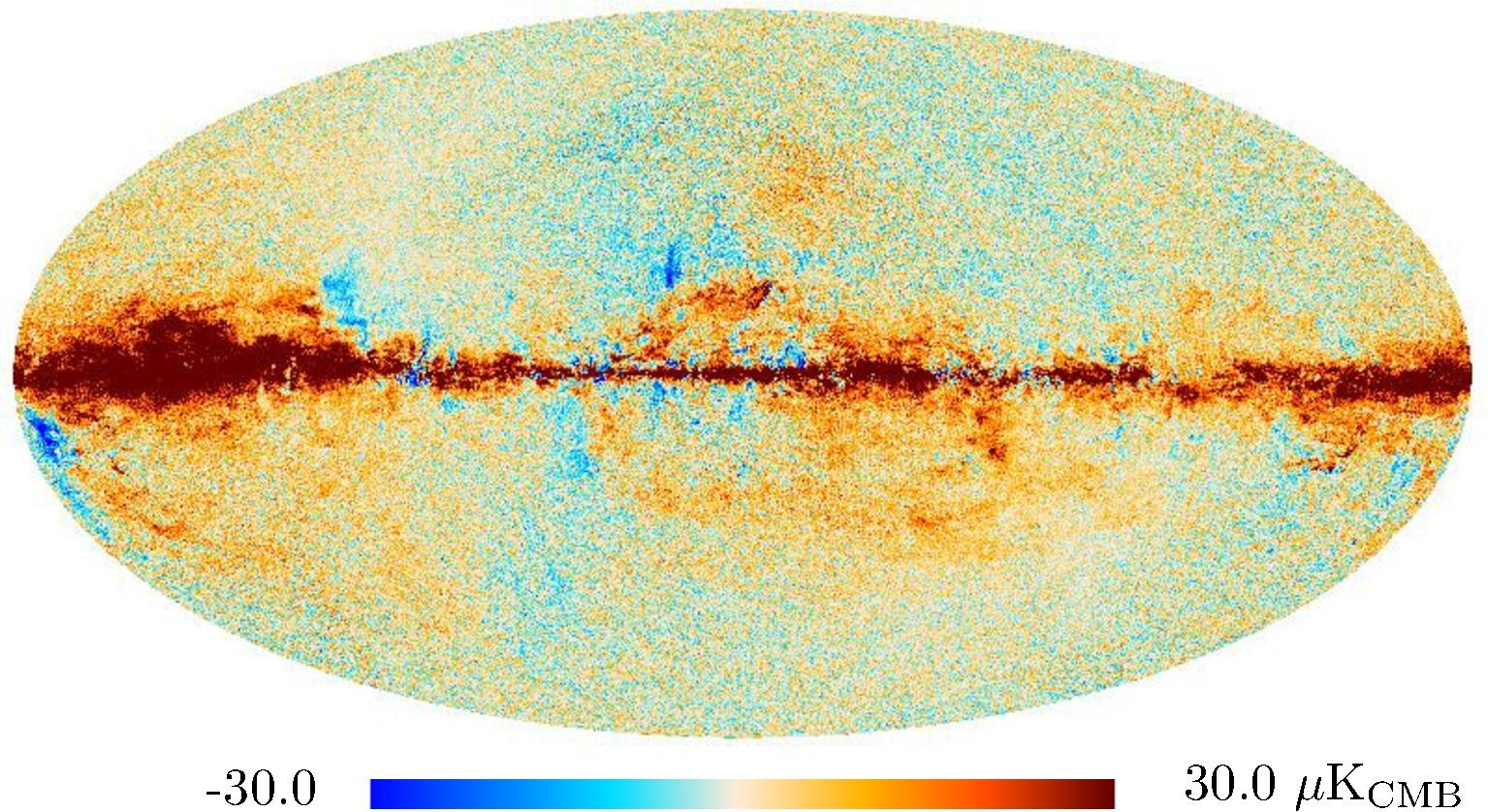
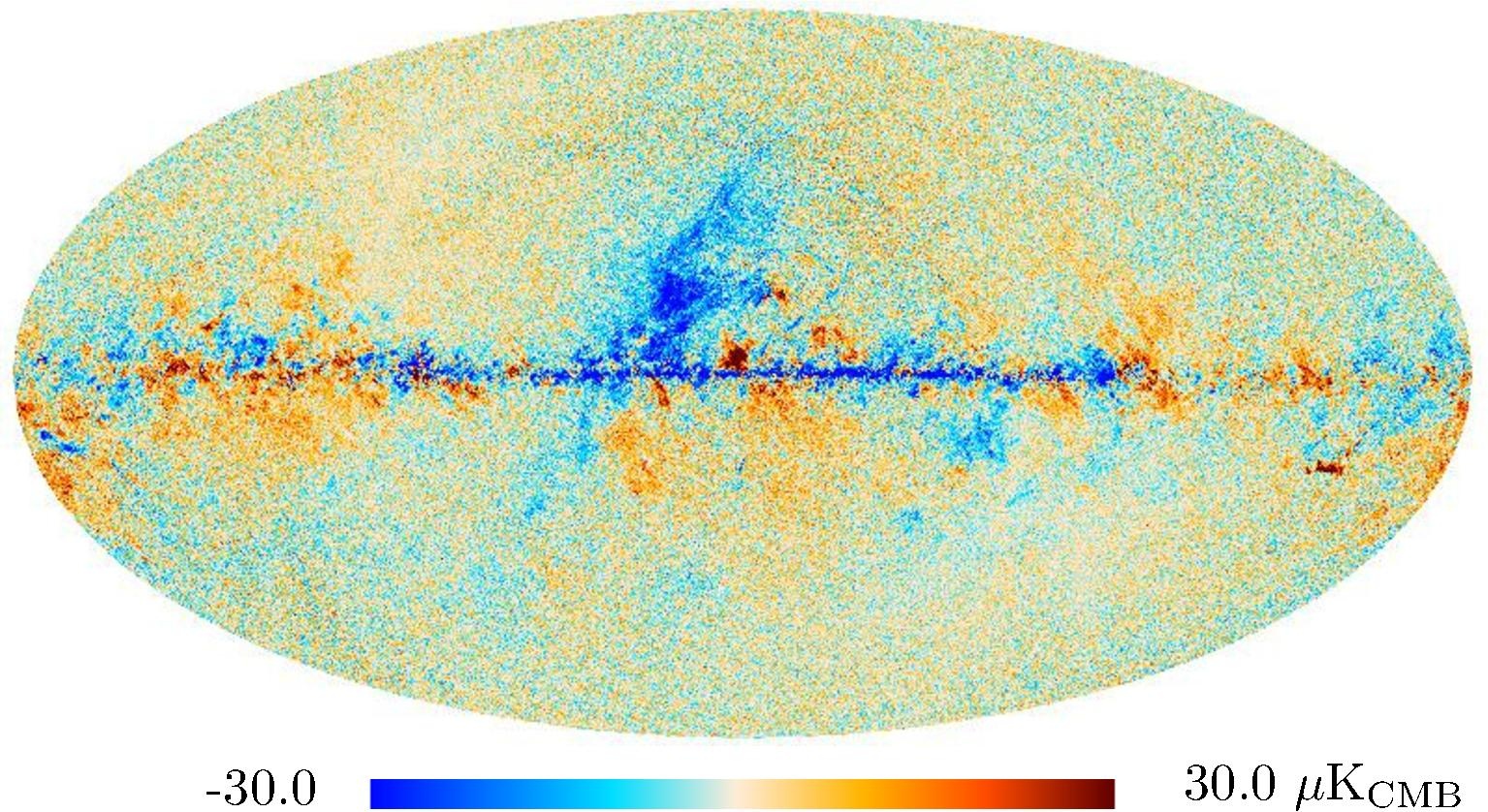
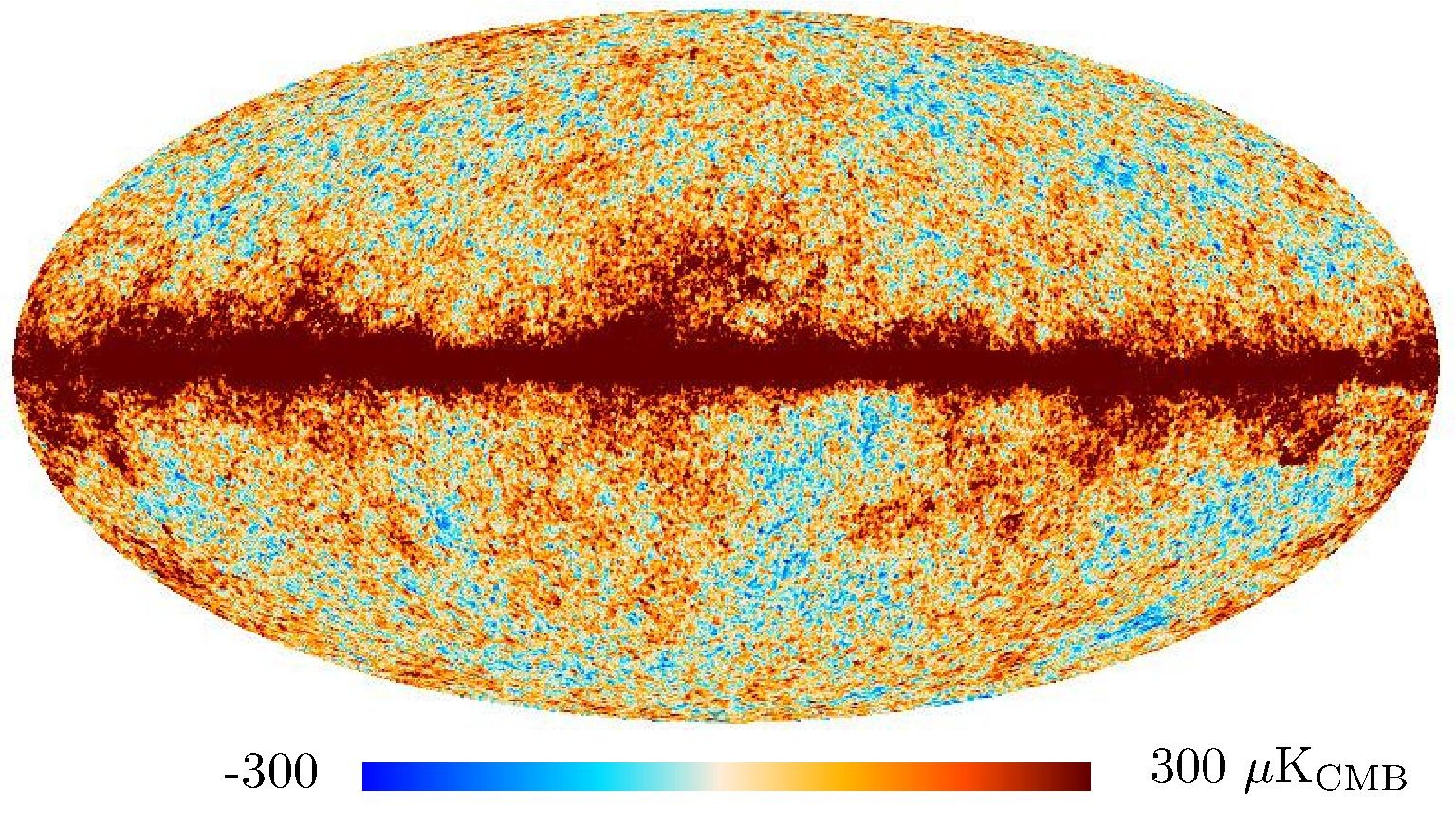
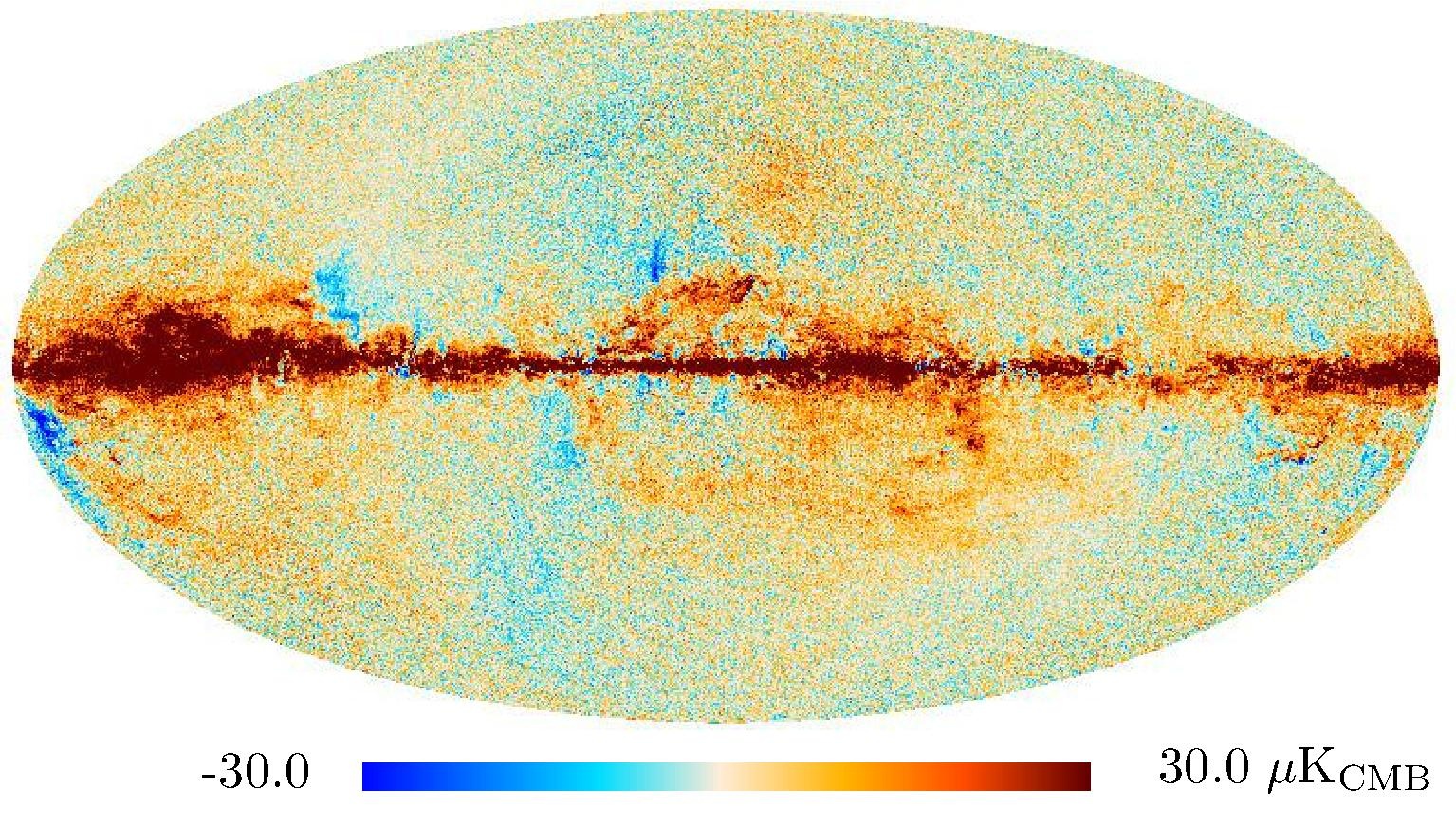
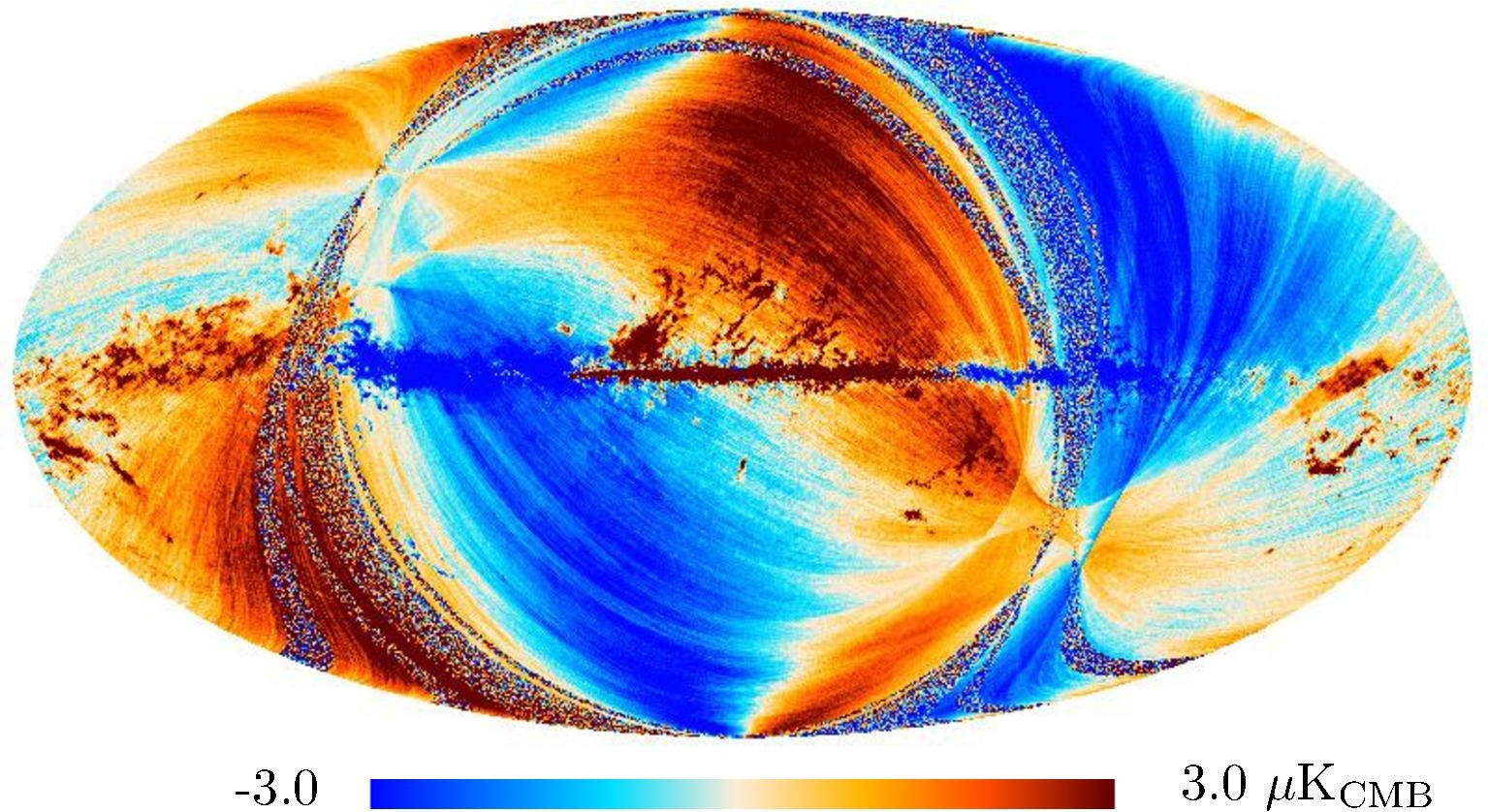
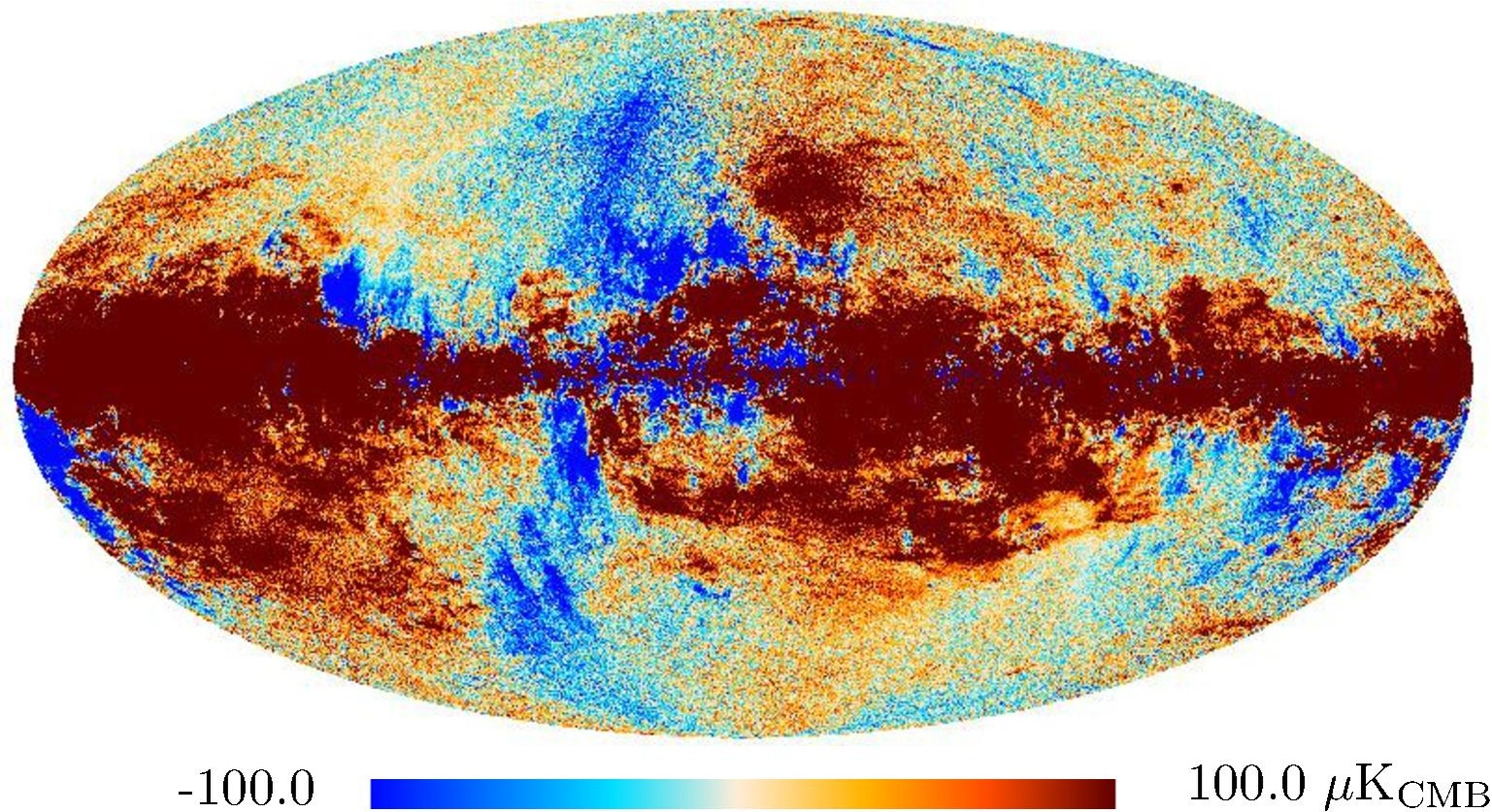
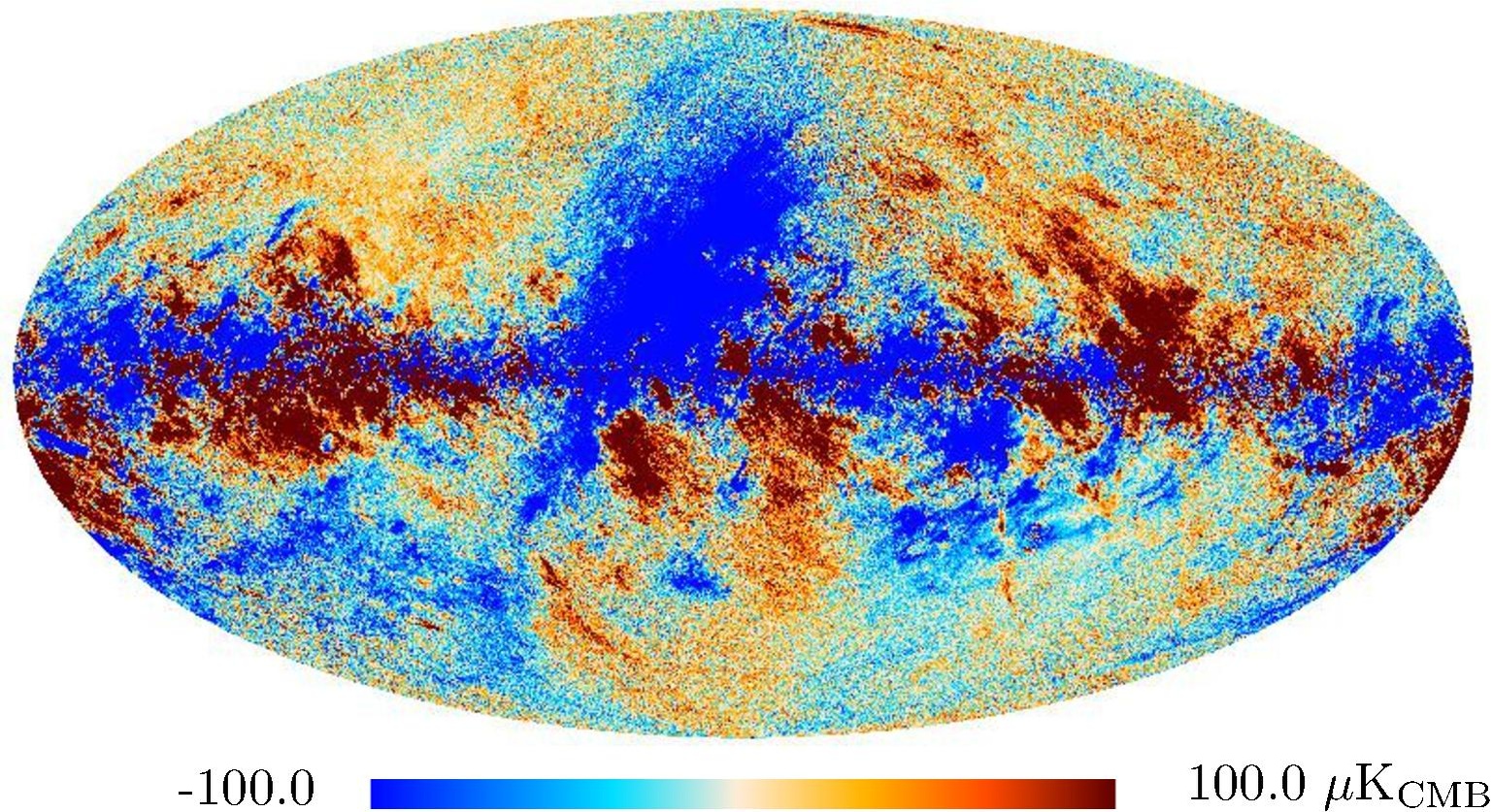
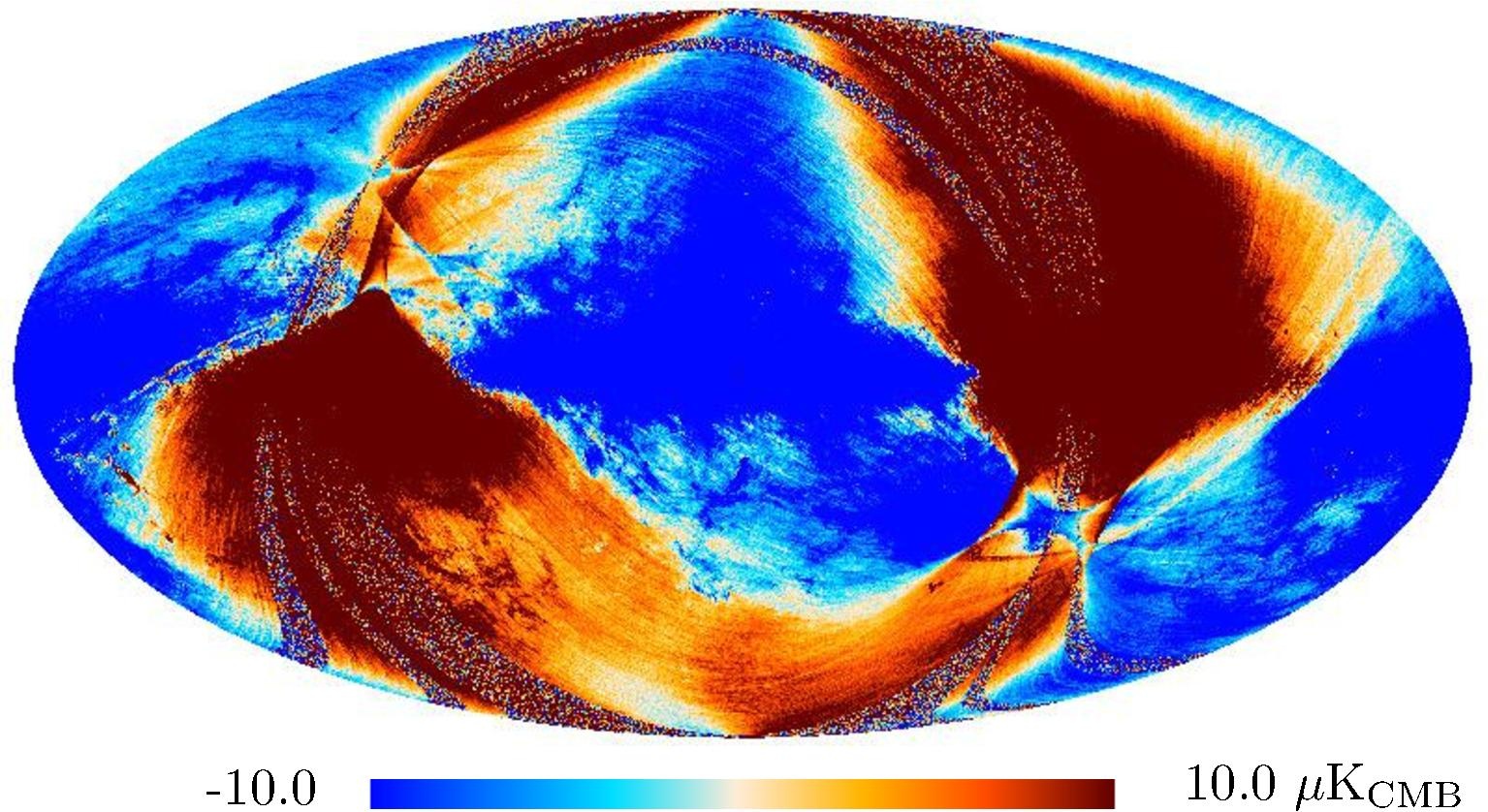
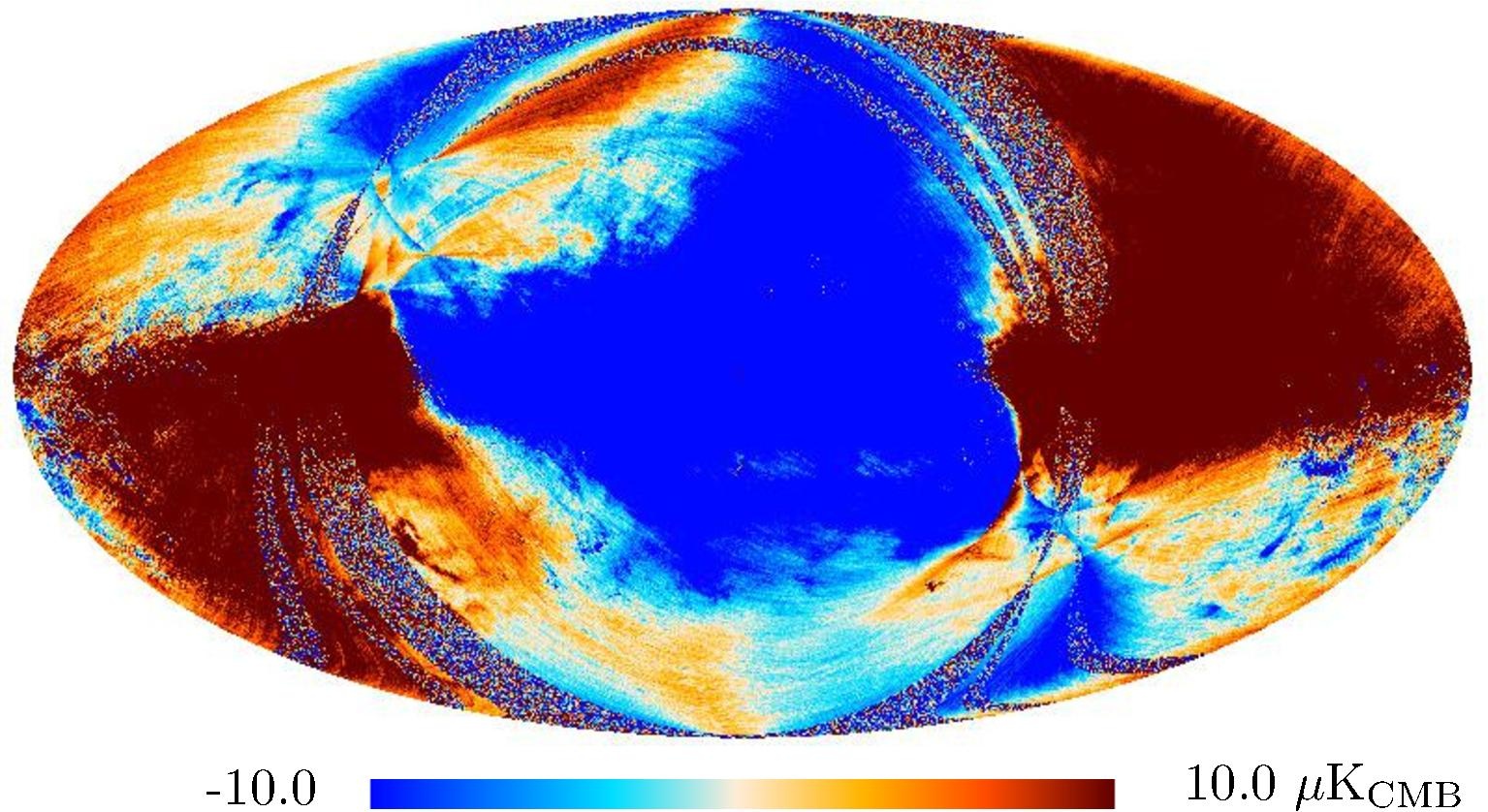
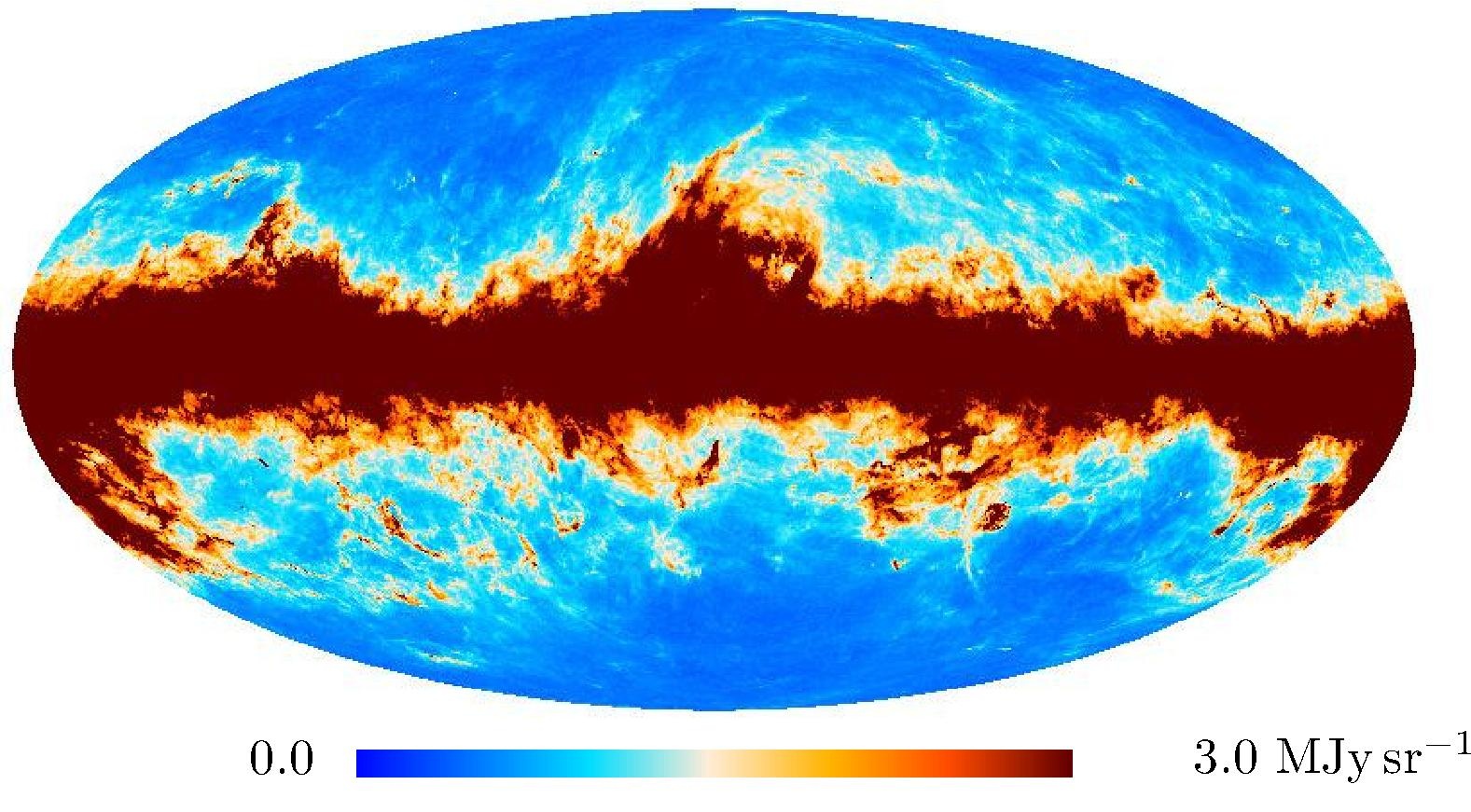
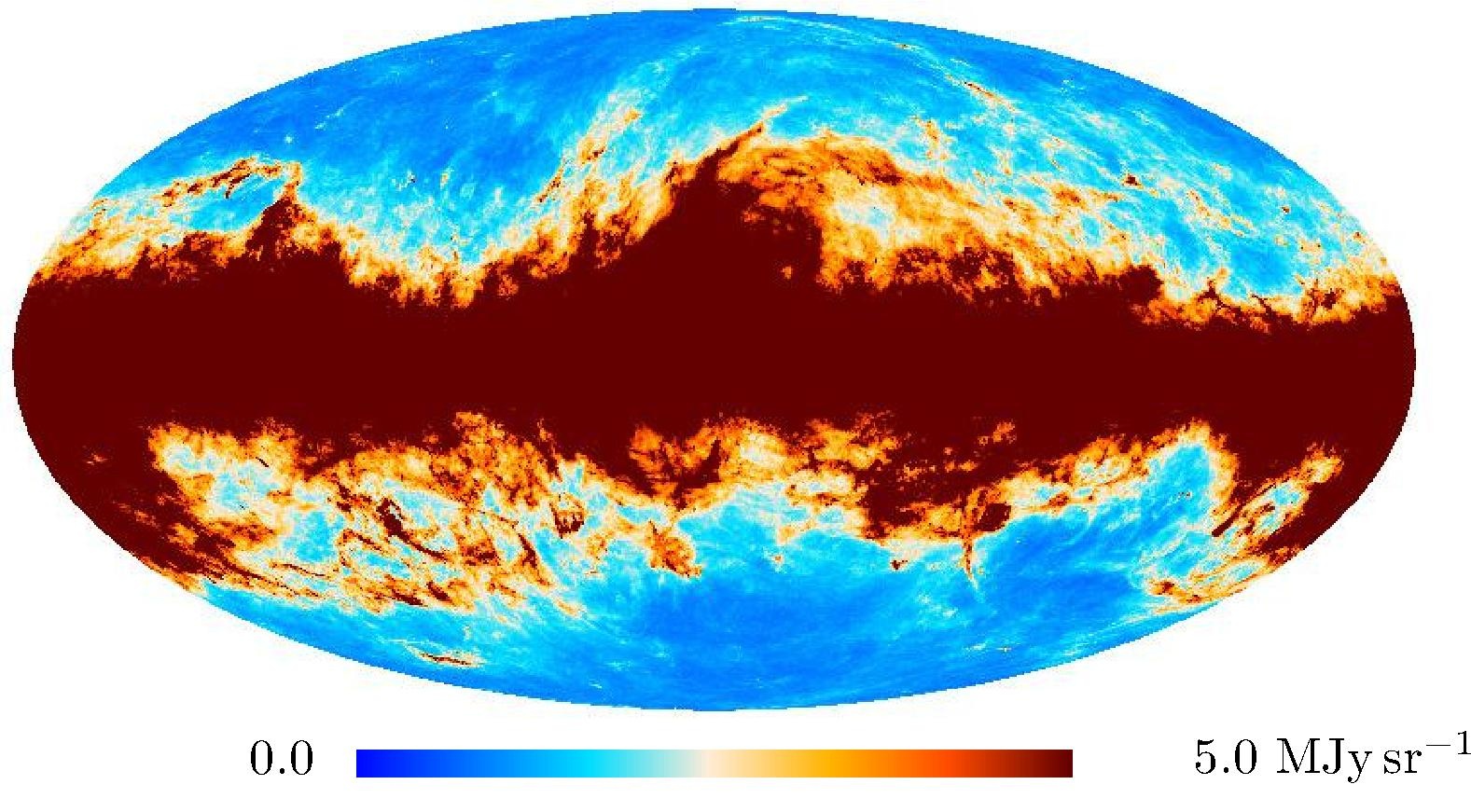
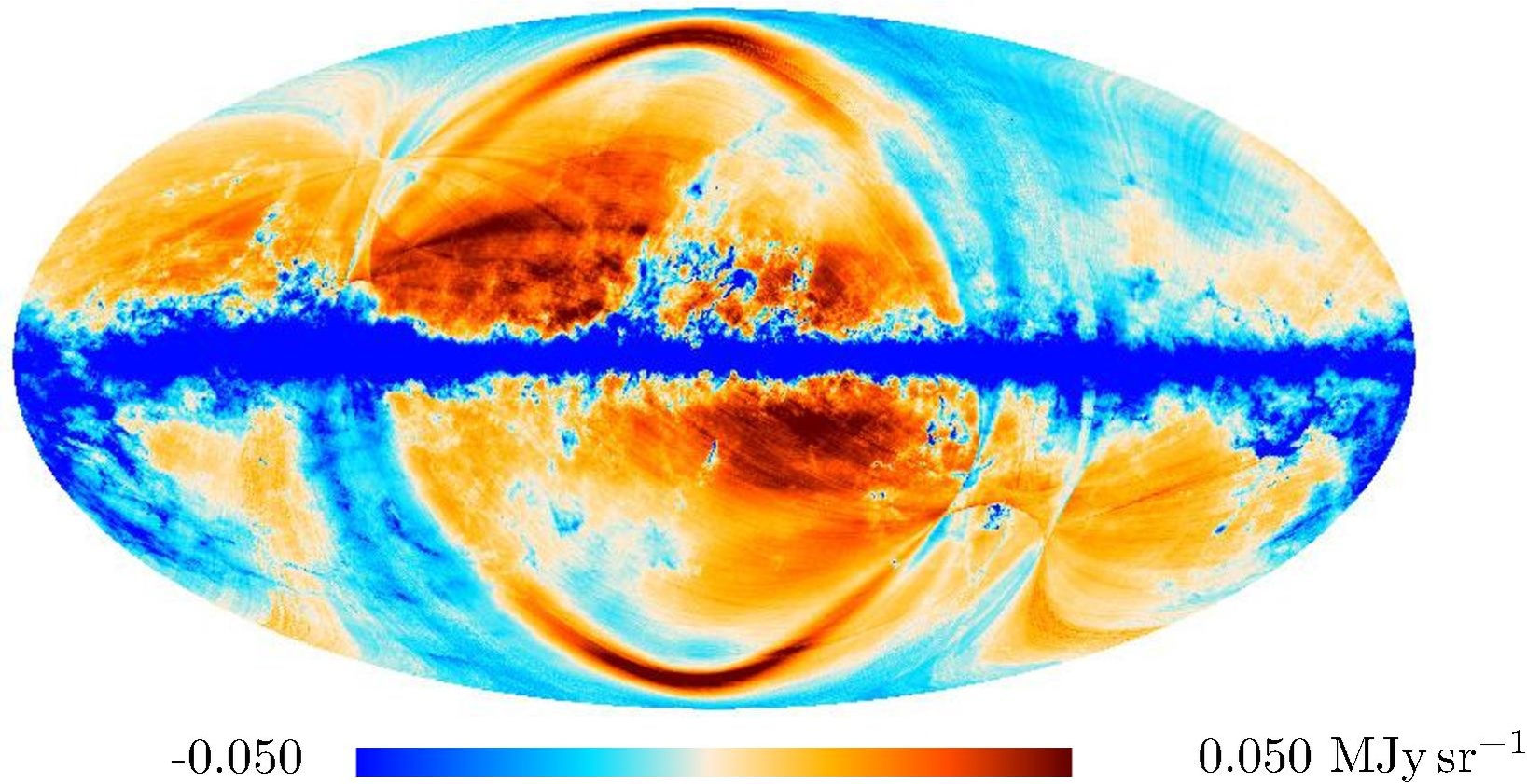
Section 3.2: complementary figures of Fig. 11
| 2015 maps | 2017 maps | difference | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Q | U | I | Q | U | I | Q | U | |
| 100 GHz | 
|
|
|
|
|
|
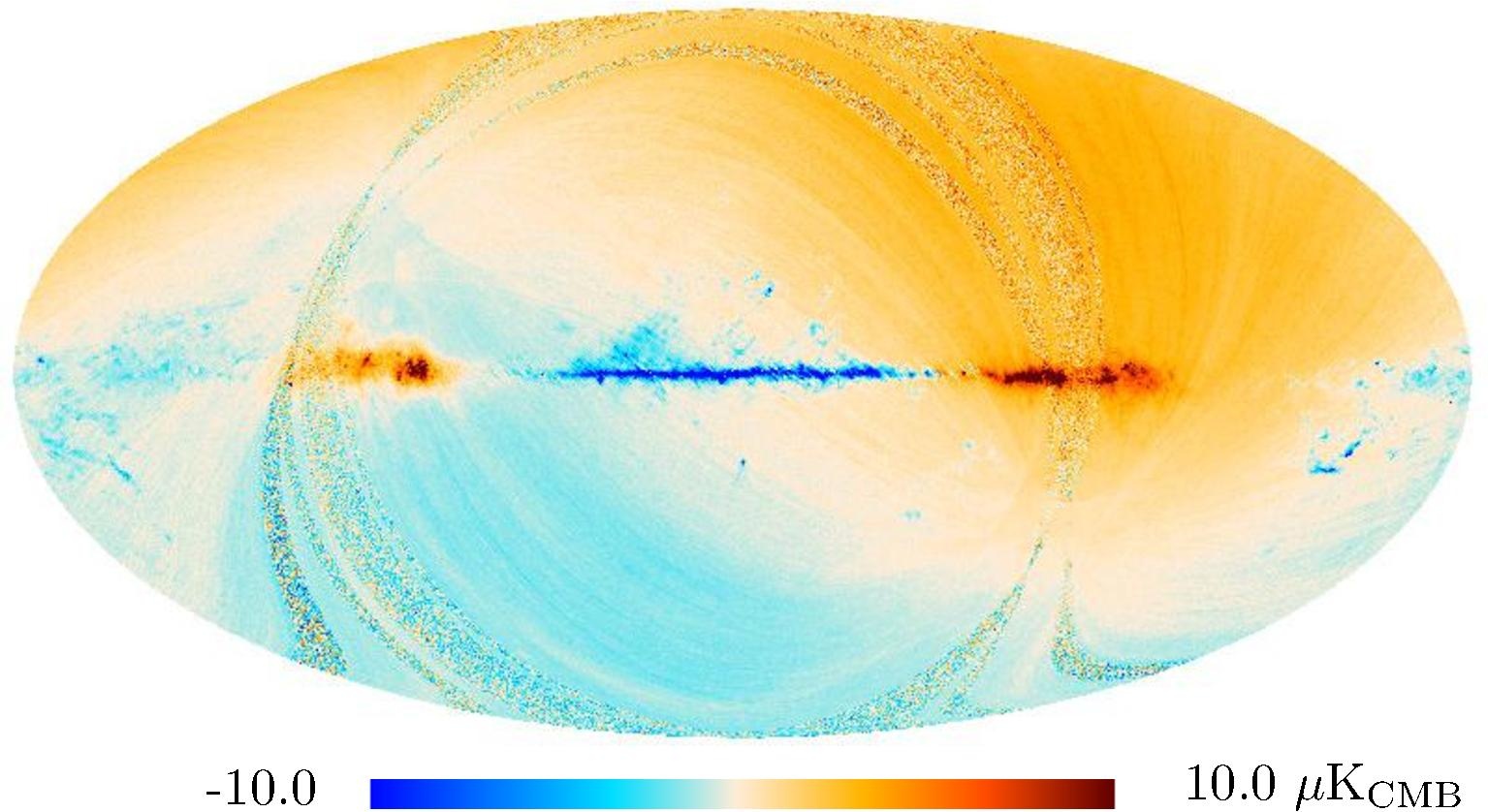
|
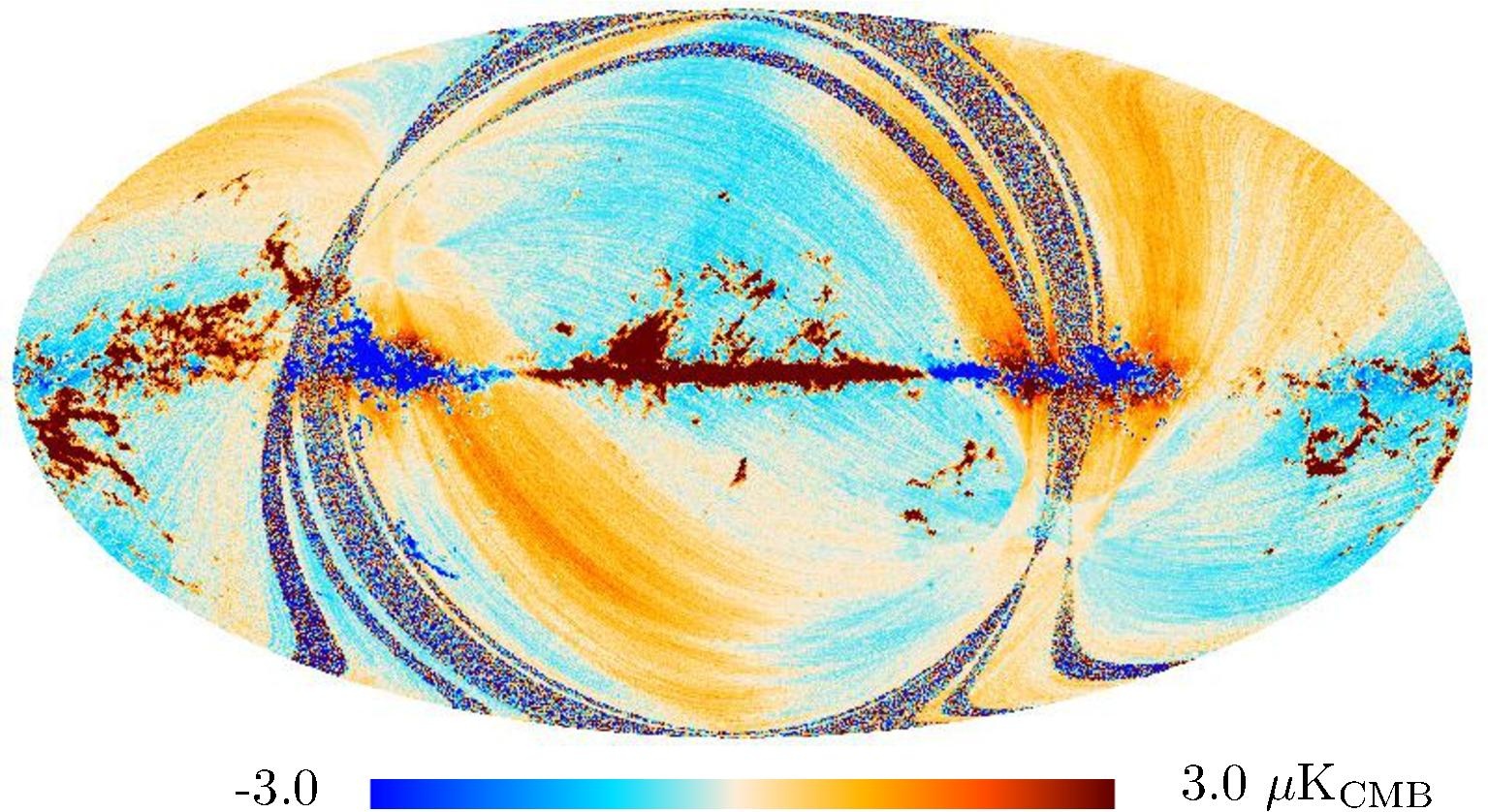
|
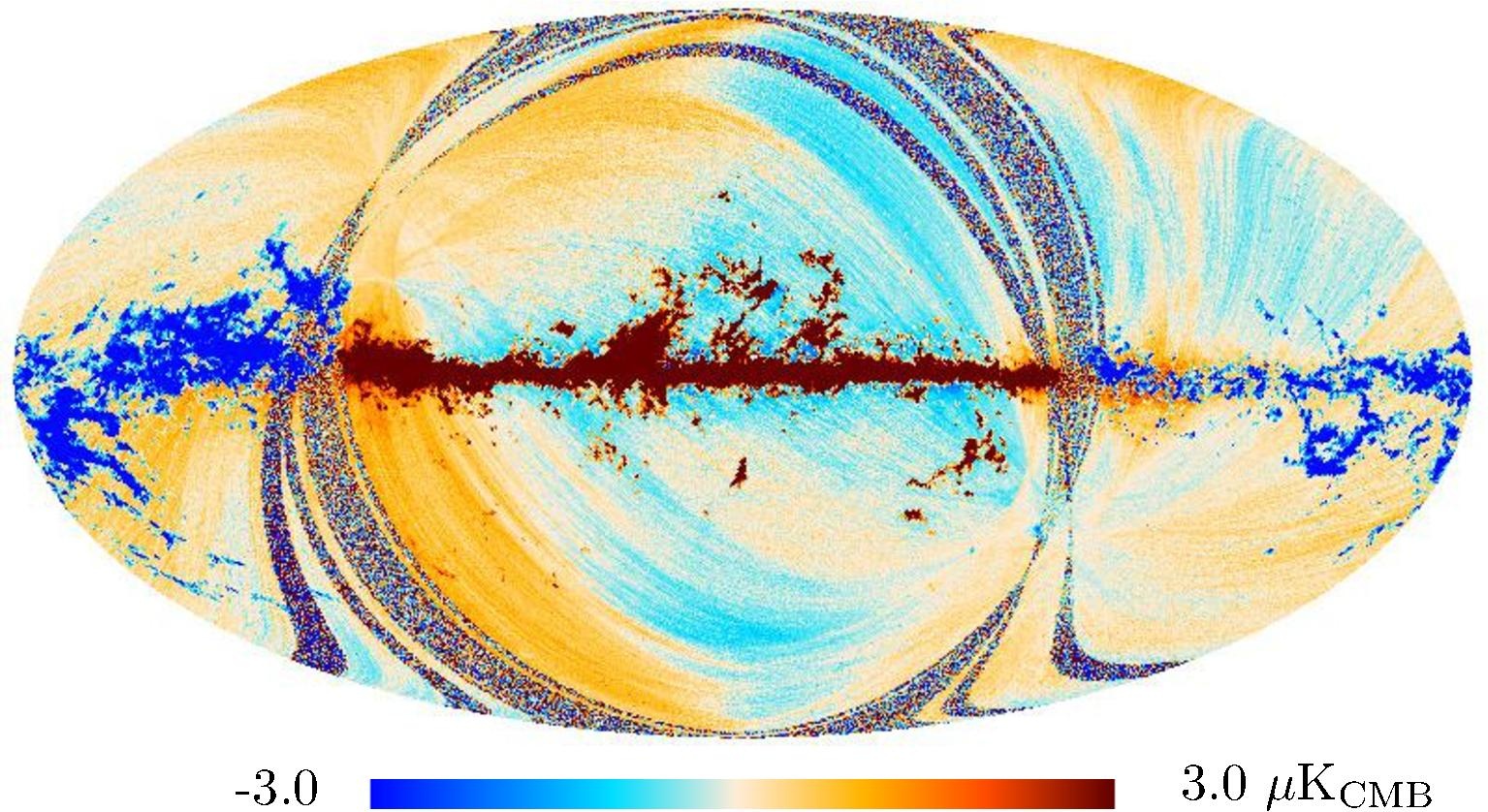
|
| 143 GHz | 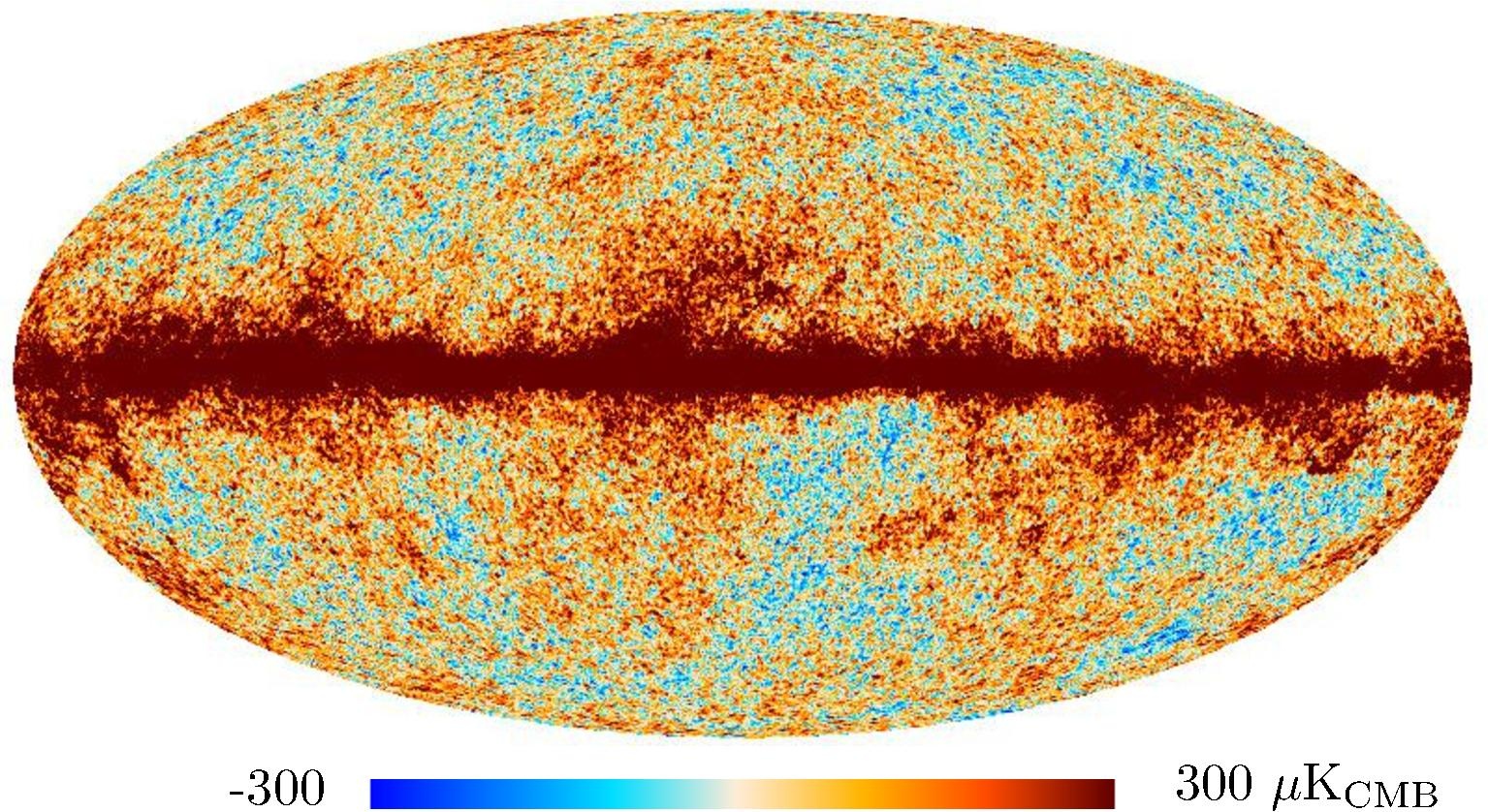
|
|
|
|
|
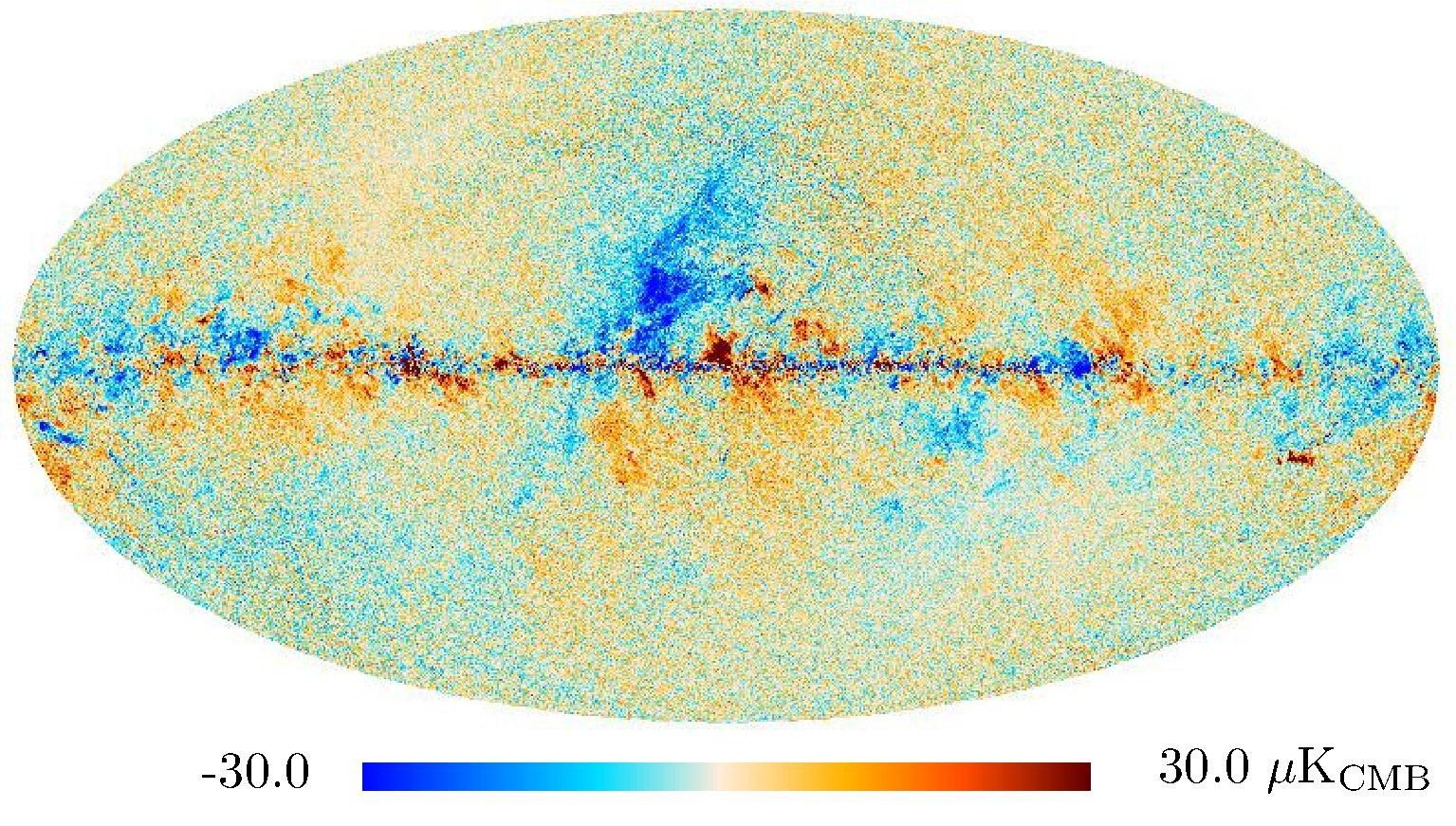
|
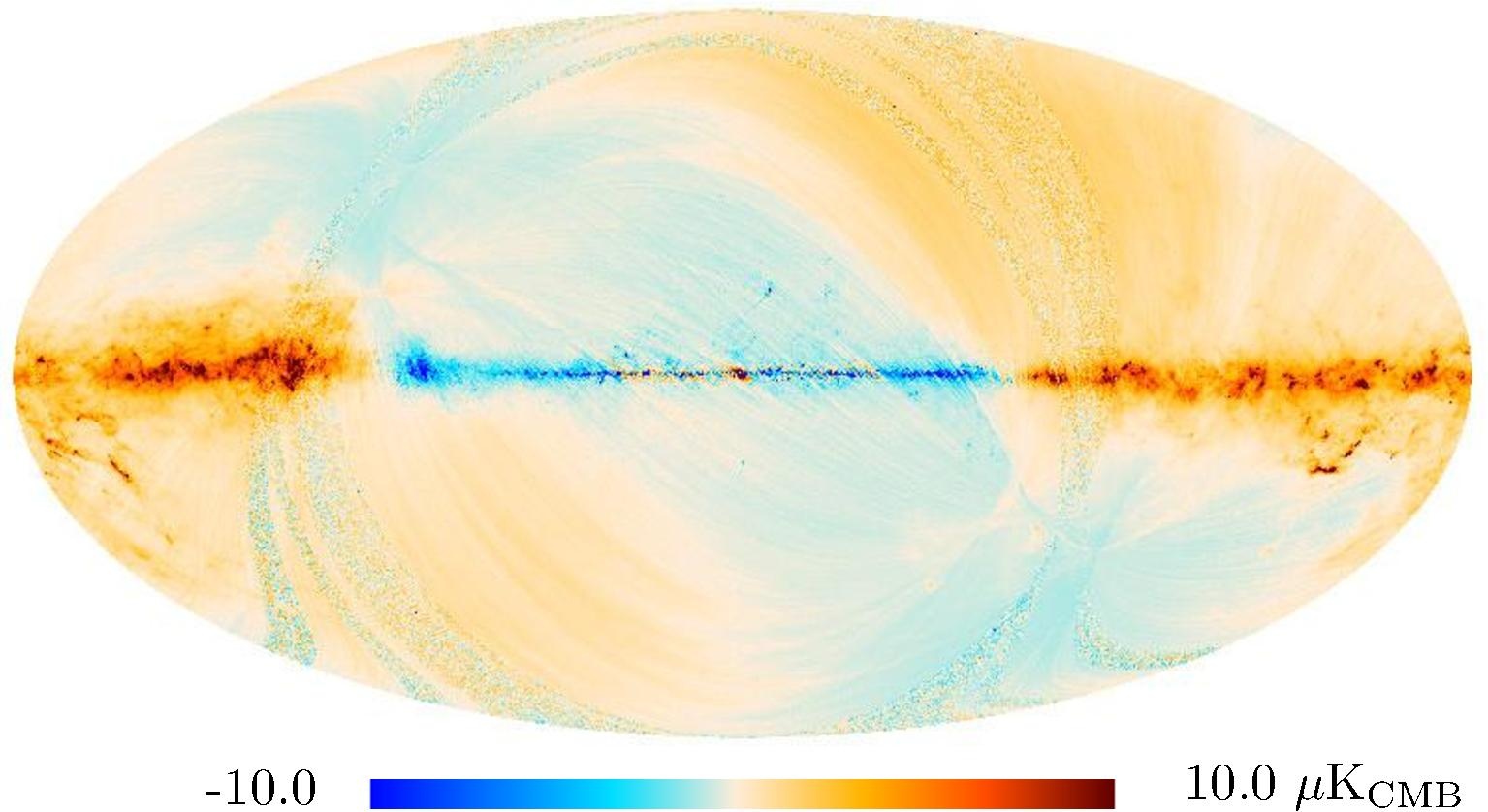
|
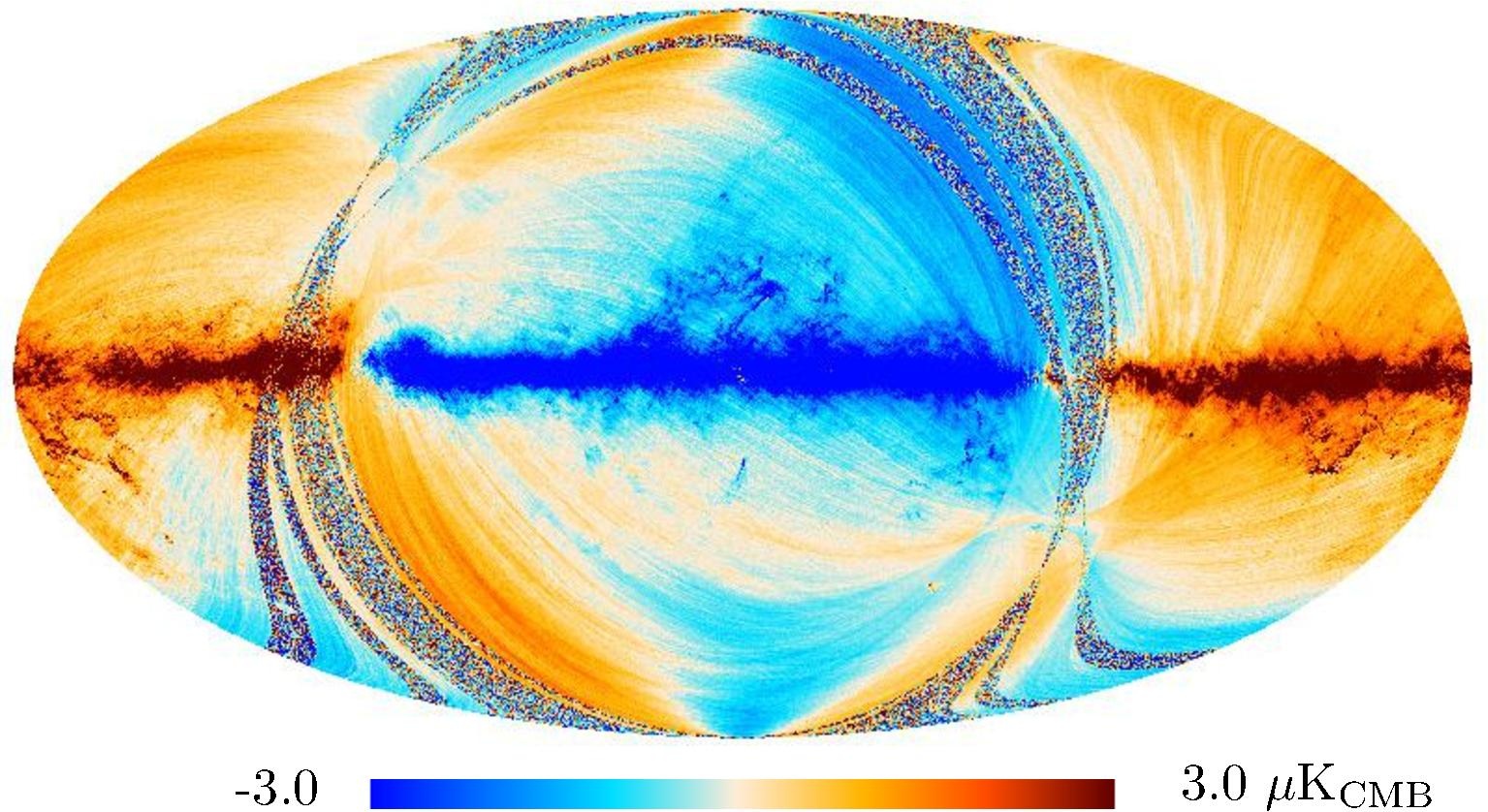
|
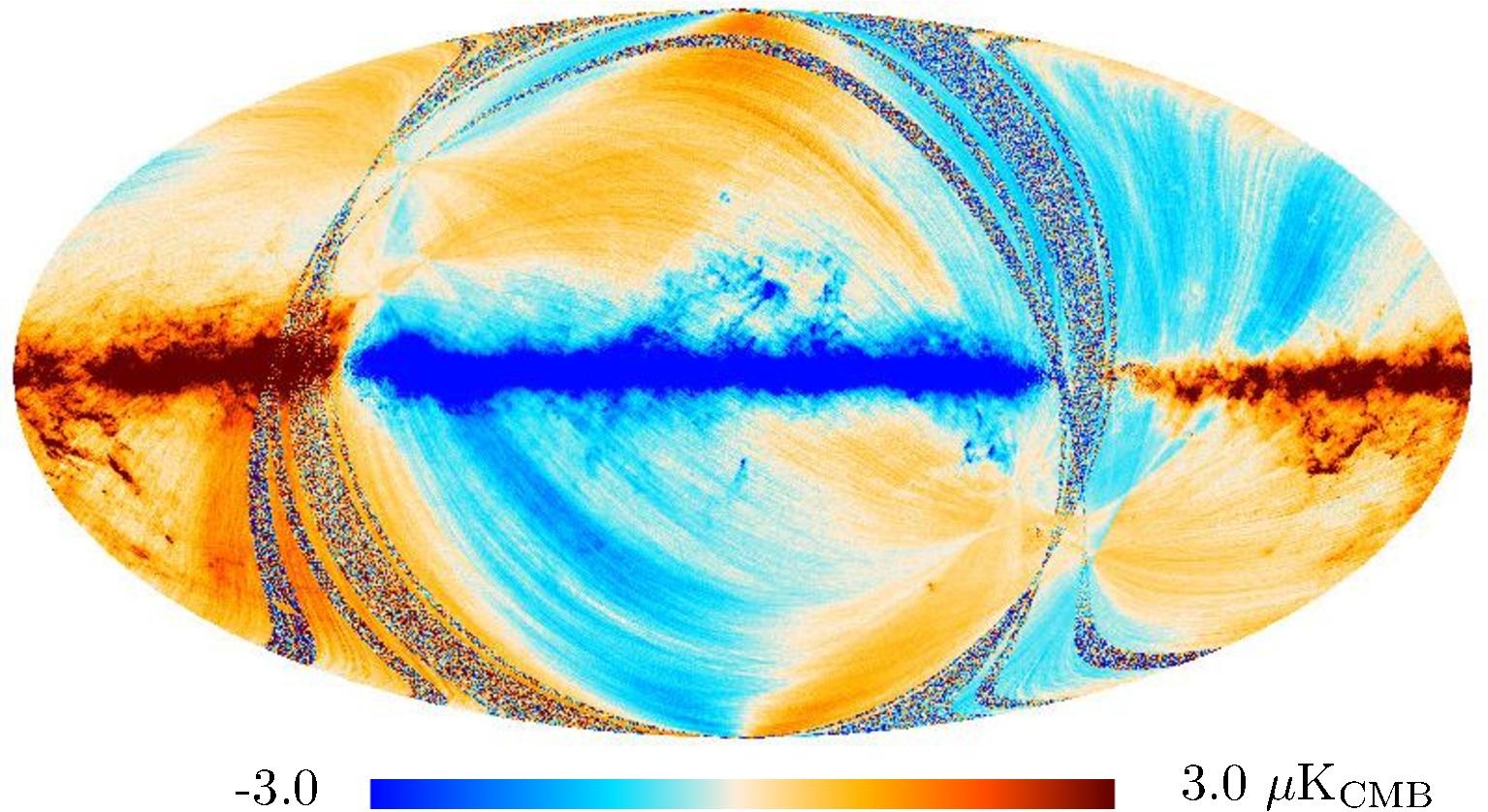
|
| 217 GHz | 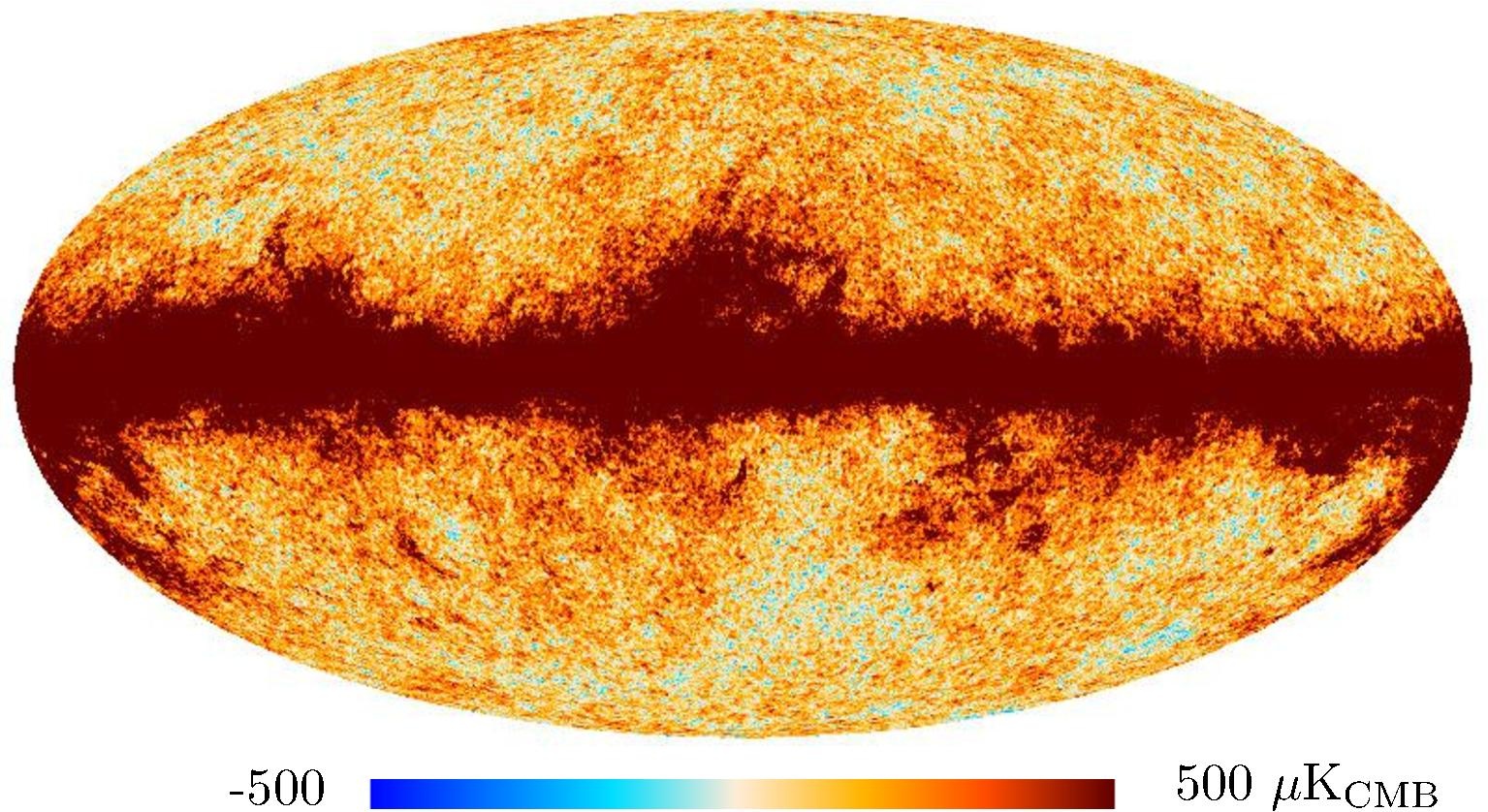
|
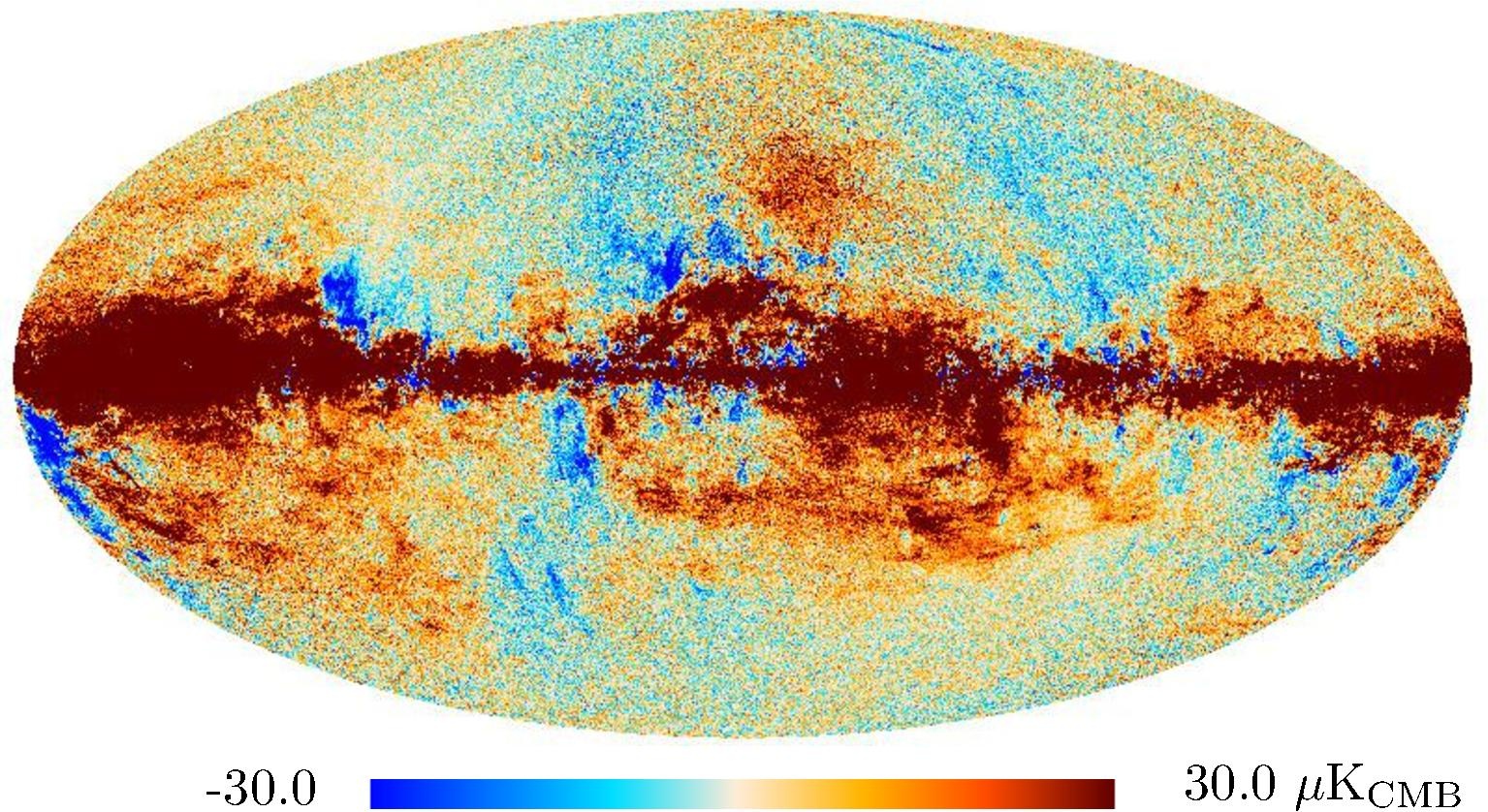
|
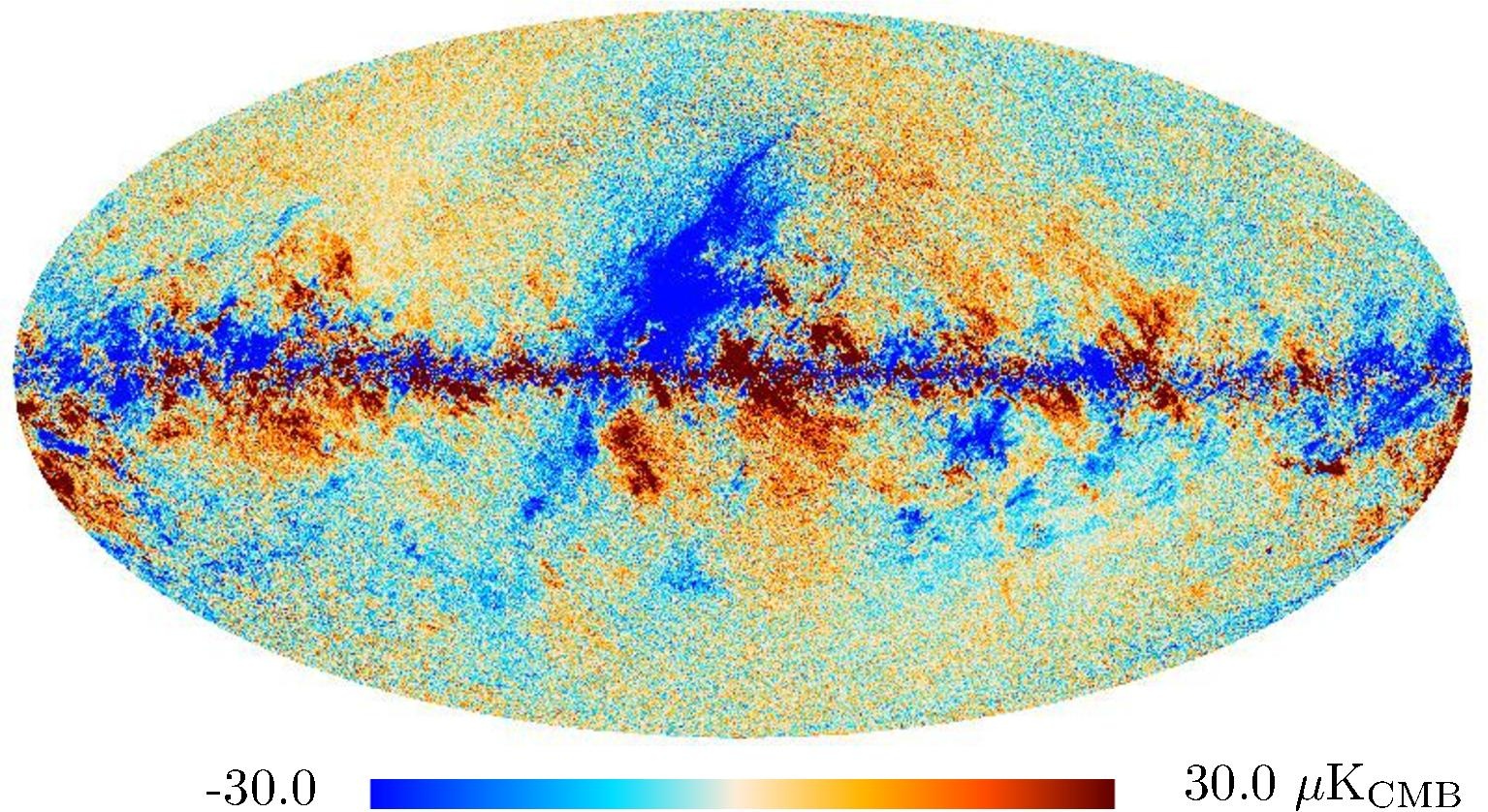
|
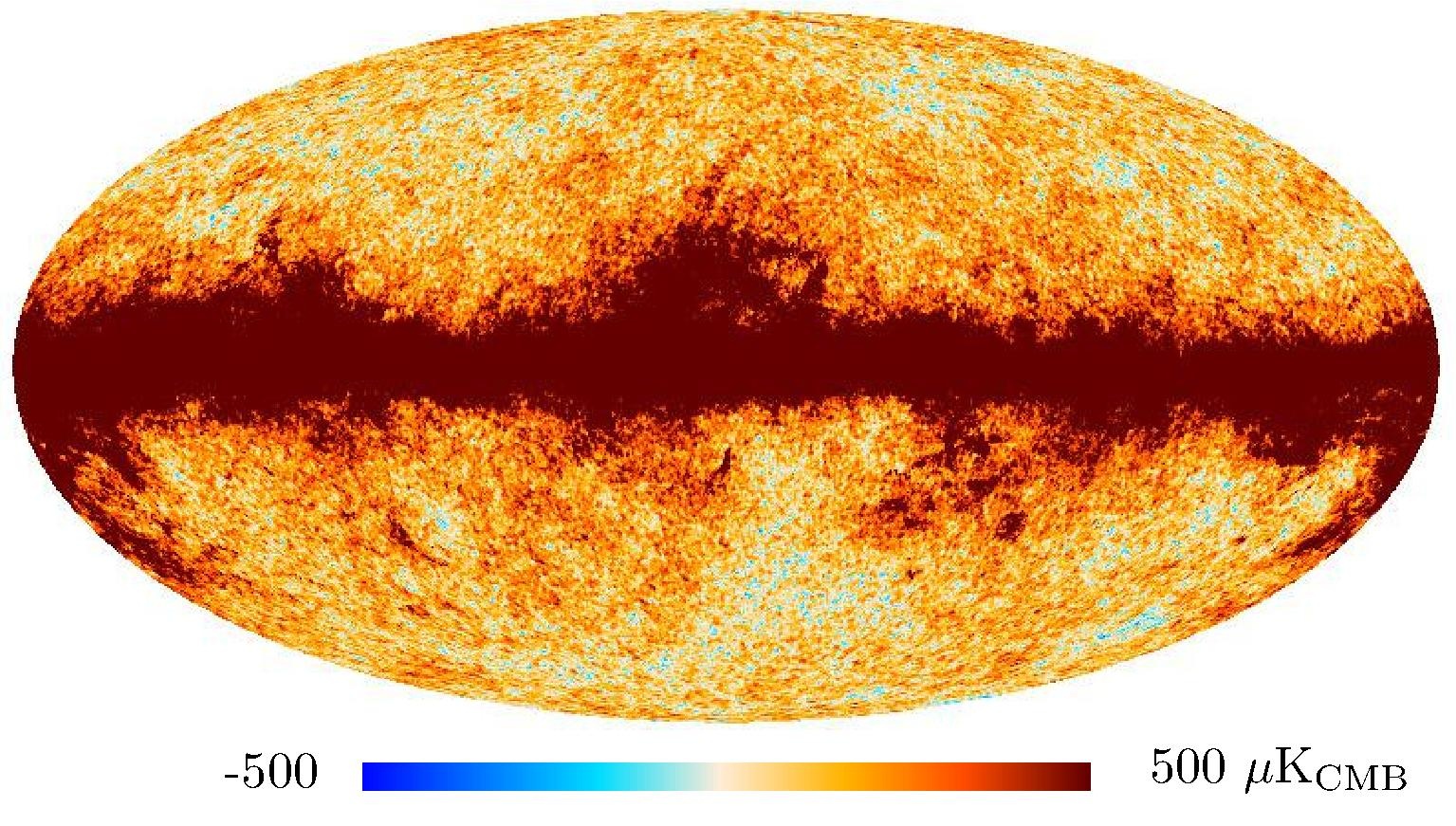
|
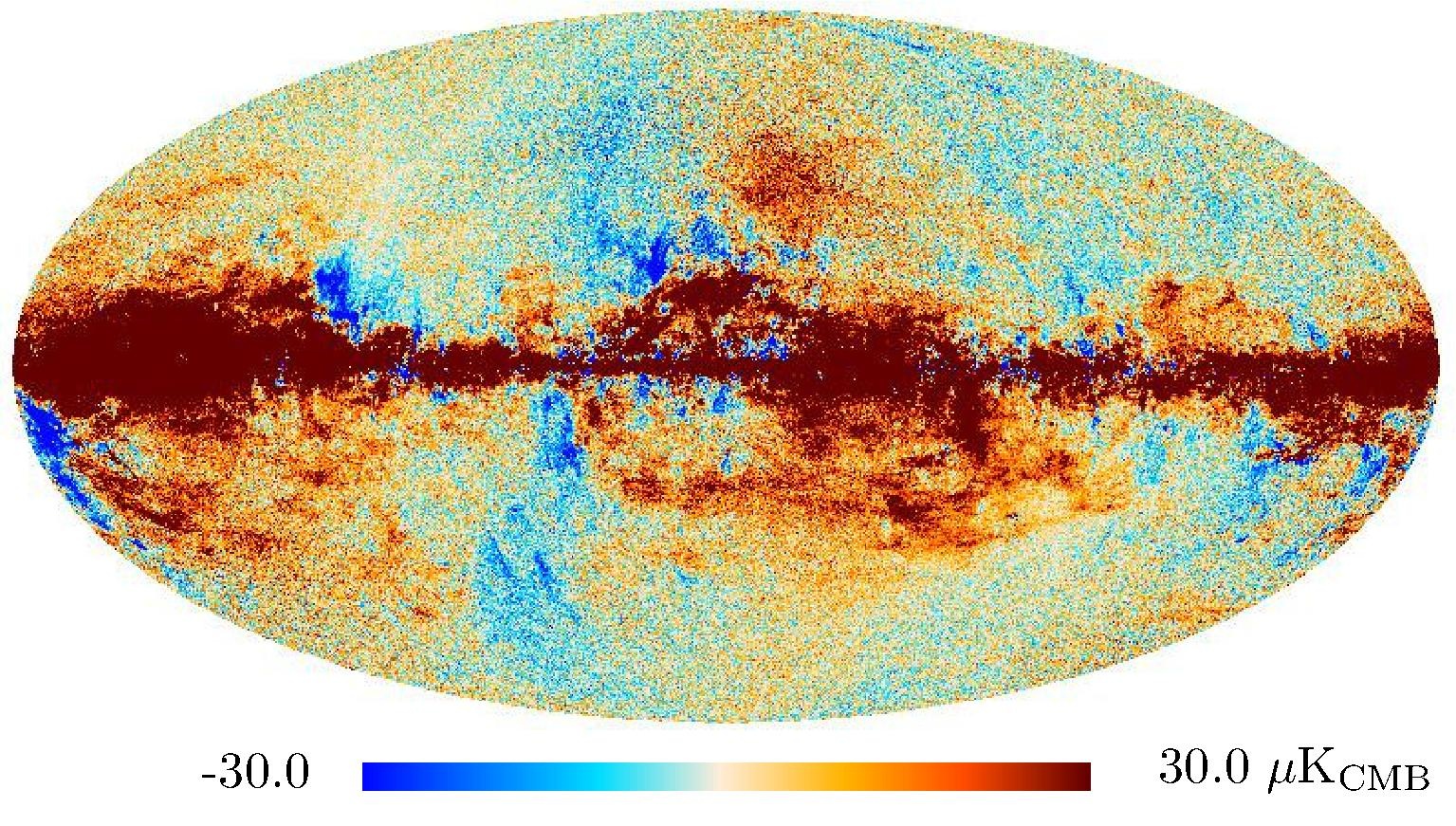
|
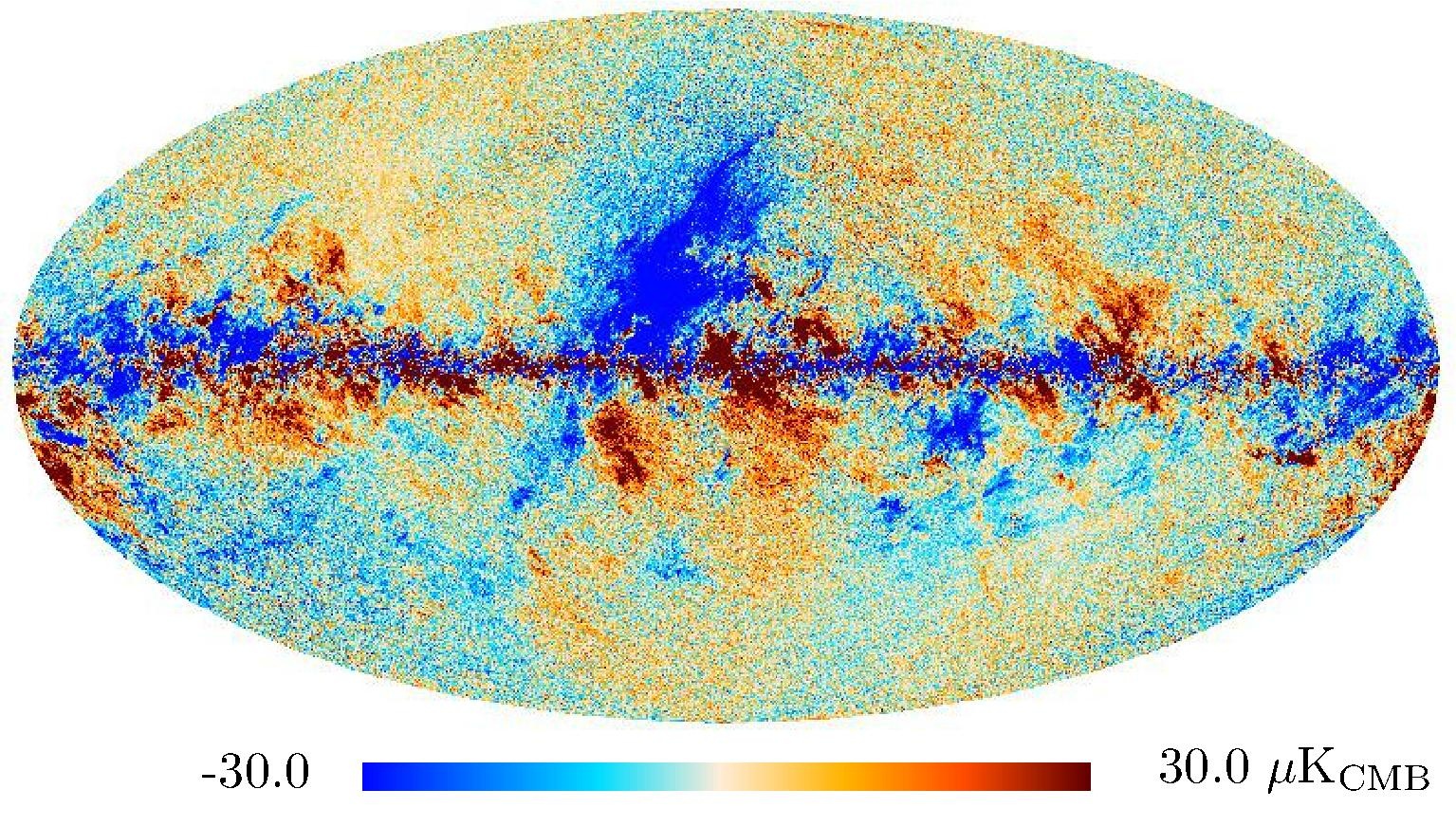
|
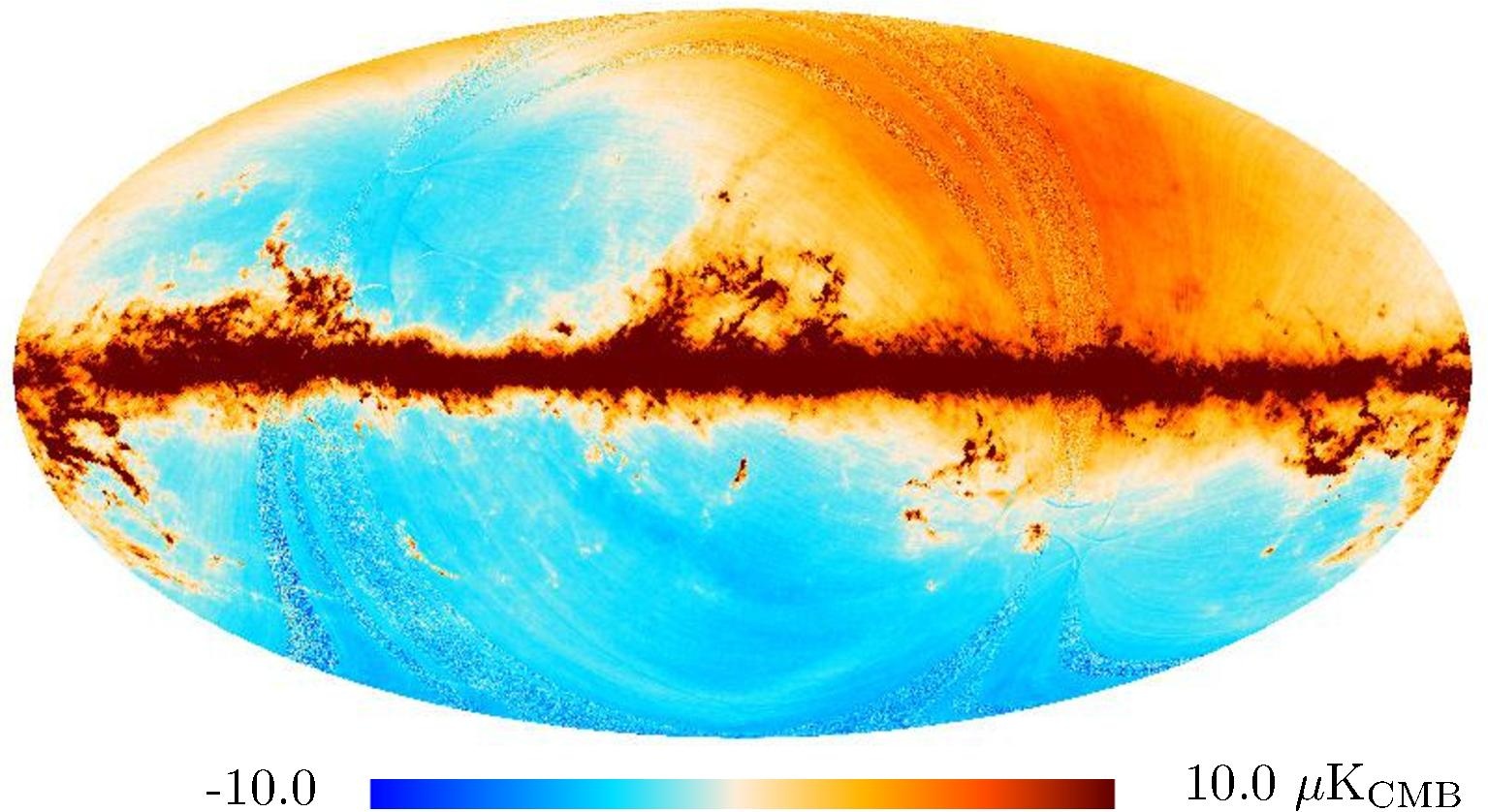
|
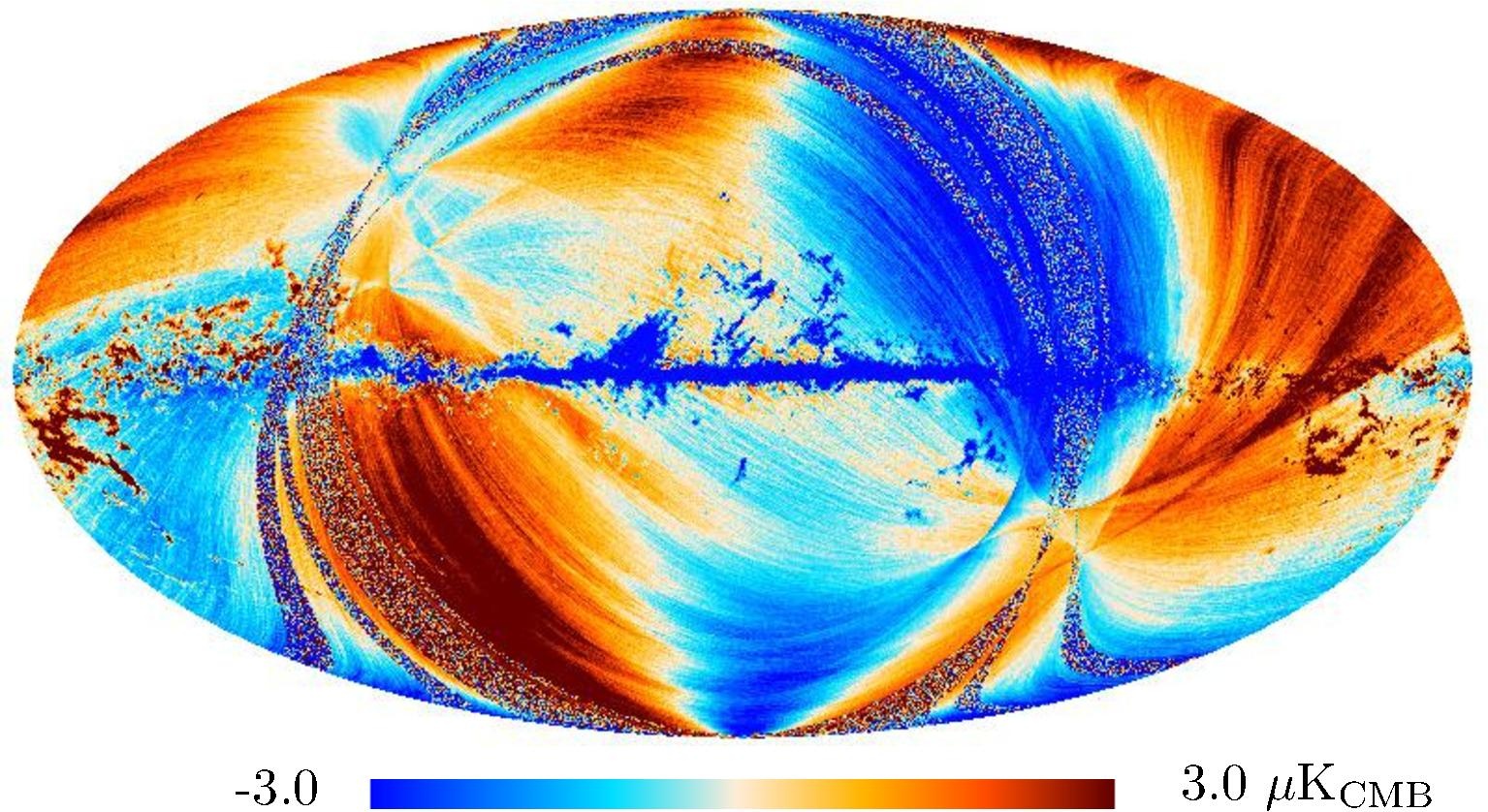
|
|
| 353 GHz | 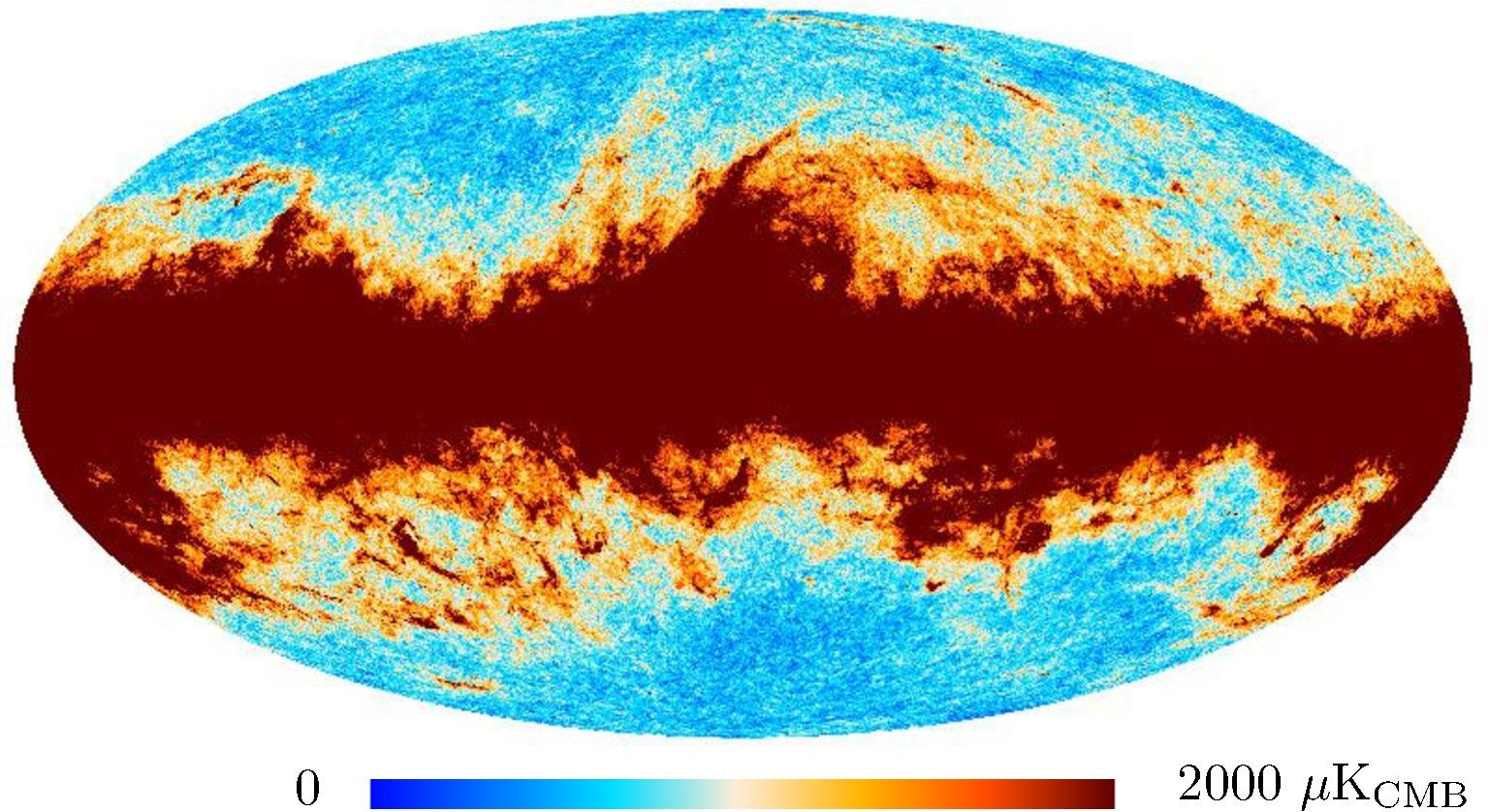
|
|
|
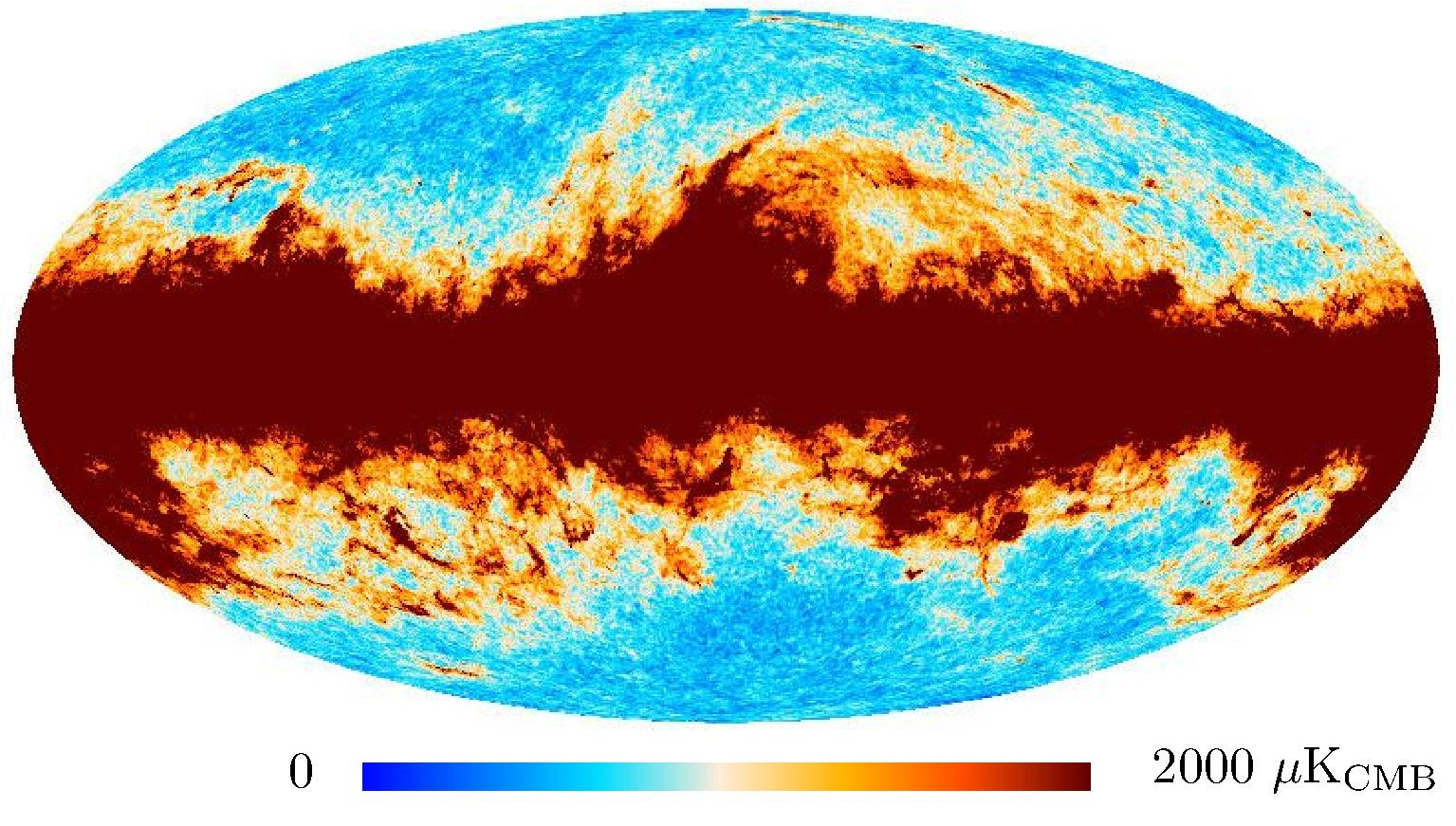
|
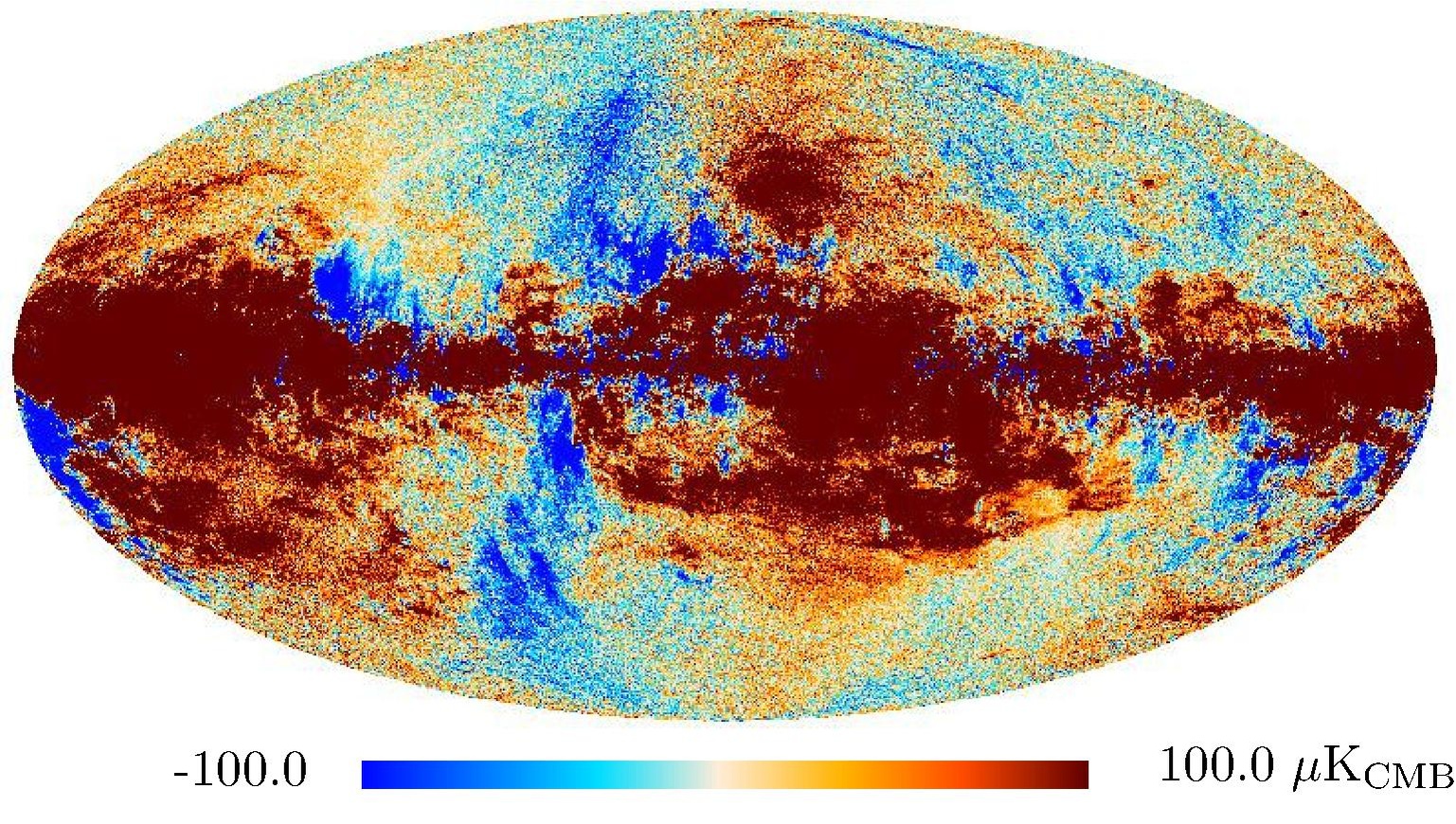
|
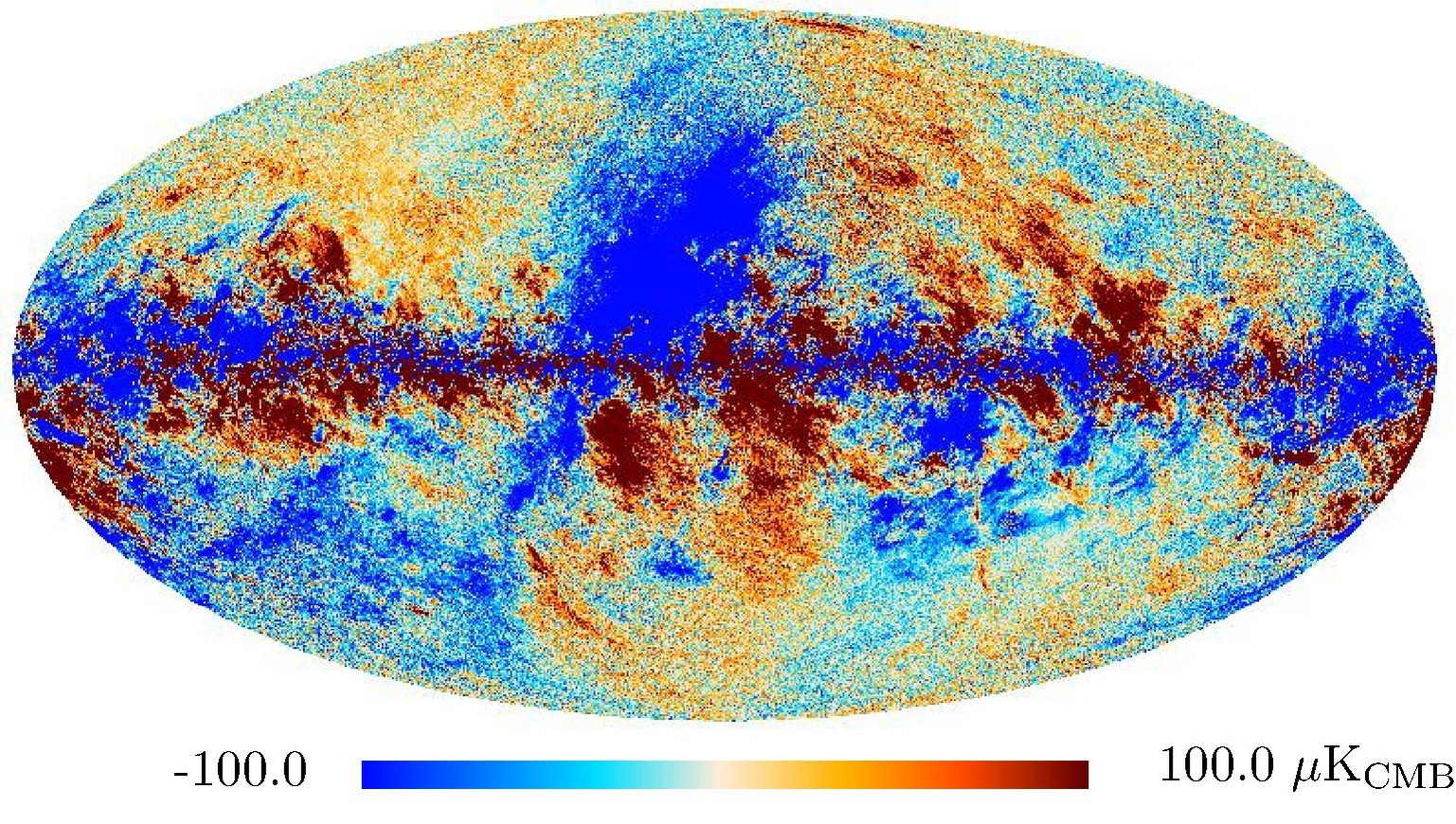
|
|
|
|
| 545 GHz | 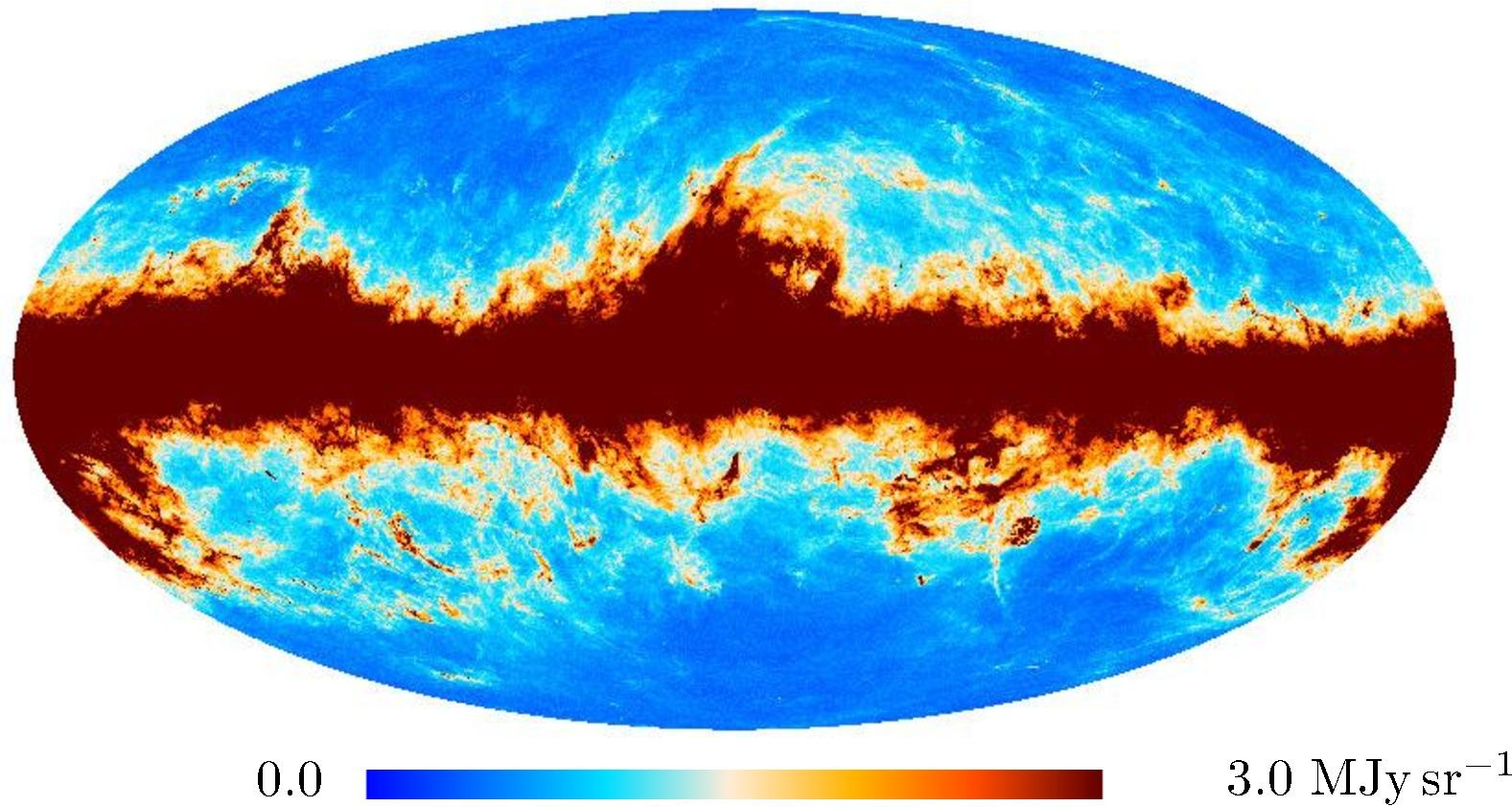
|
. | . | 
|
. | . | 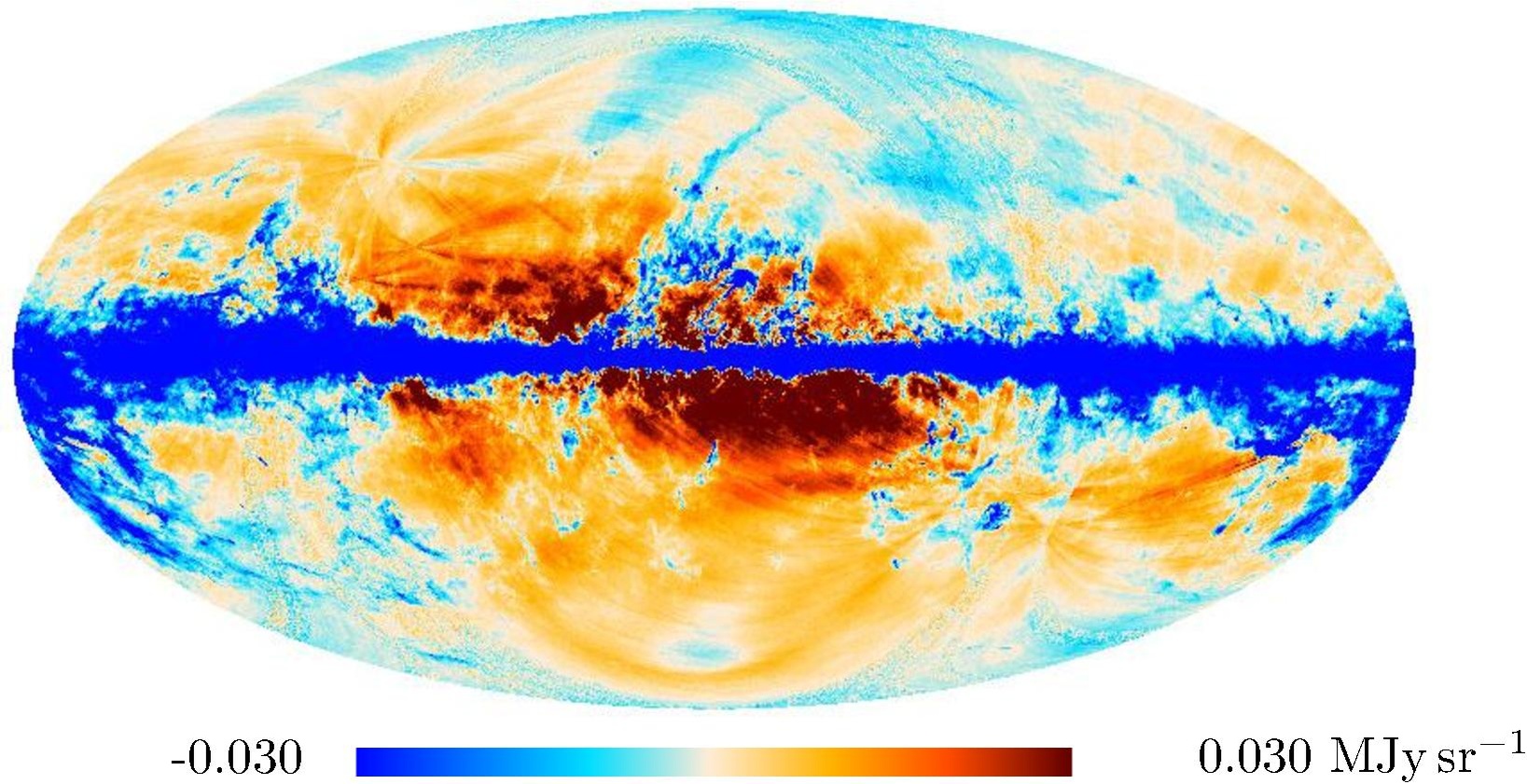
|
. | . |
| 857 GHz | 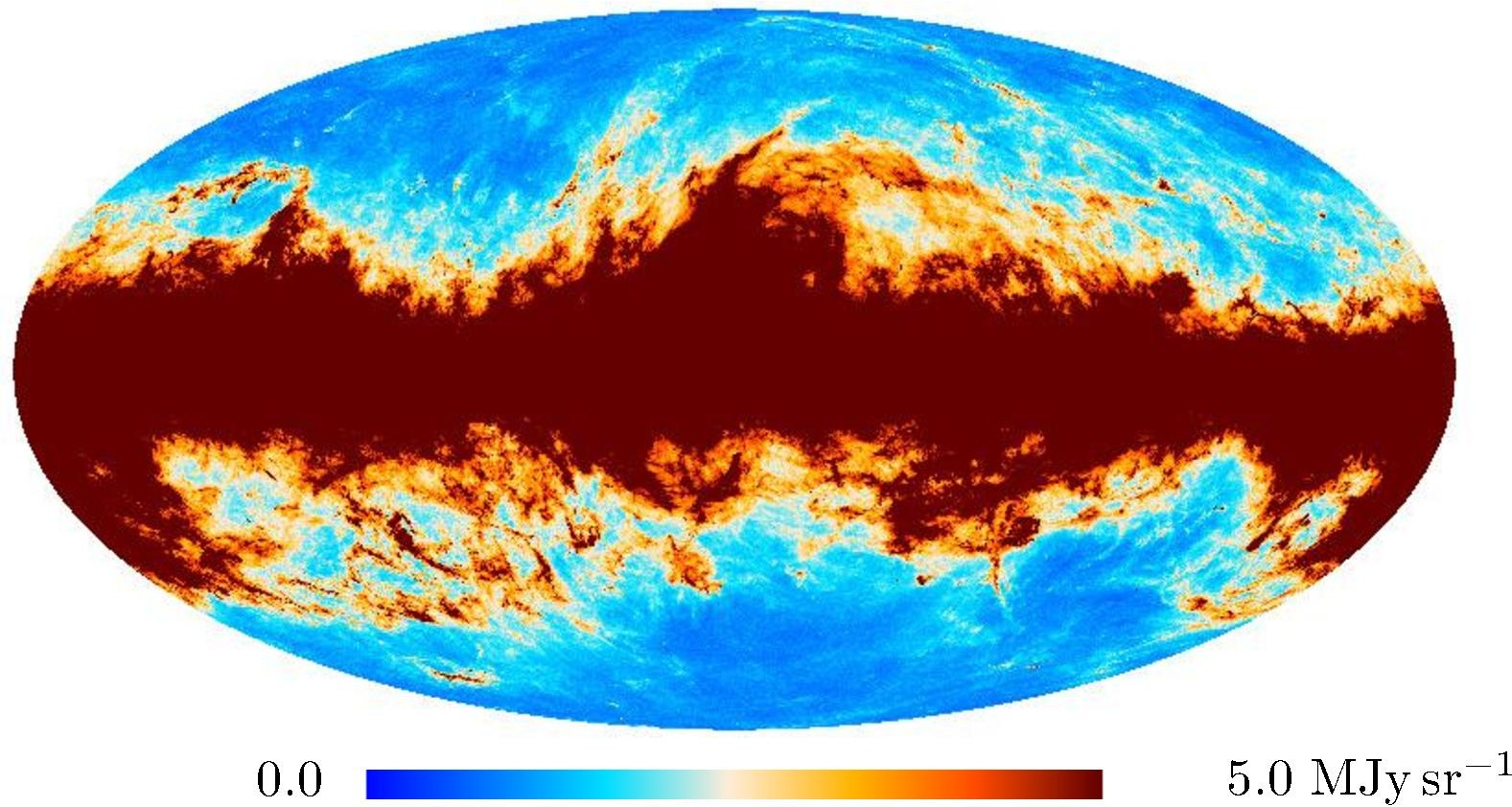
|
. | . | 
|
. | . | 
|
. | . |
Section 5.3.10: for convenience, we reproduce here Figures 6, 7 and 8 of Rosset et al.
This paper is published as Rosset et al. Planck pre-launch status: High Frequency Instrument polarization calibration. 2010b, A&A, 520, A13. ([2]) The figures 6, 7 et 8 reproduced hereunder are given in the version on ArXiv 1004.2595
| gain errors (1) | polarization efficiency errors (2) | orientation errors (3) |
|---|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: convert: unable to extend cache `/tmp/magick-12741tqk1aRr9cXW0': File too large @ error/cache.c/OpenPixelCache/4091.
|
Error creating thumbnail: convert: unable to extend cache `/tmp/magick-12748CuDeZbqIA2JM': File too large @ error/cache.c/OpenPixelCache/4091.
|
Error creating thumbnail: convert: unable to extend cache `/tmp/magick-12756ILfztajmmJZl': File too large @ error/cache.c/OpenPixelCache/4091.
|
(1) in rms due to gain errors from 0.01% to 1% for E-mode (top) and B-mode (bottom) compared to initial spectrum (solid black lines). Cosmic variance for E-mode is plotted in dashed black line.
(2) in rms due to polarization efficiency errors from 0.1% to 4% for E-mode (top) and B-mode (bottom) compared to initial spectrum (solid black lines). Cosmic variance for E-mode is plotted in dashed black line.
(3) in rms due to various orientation errors from 0.25 to 2 degrees for E-mode (top) and B-mode (bottom) compared to initial spectrum (solid black lines). Cosmic variance for E-mode is plotted in dashed black line.
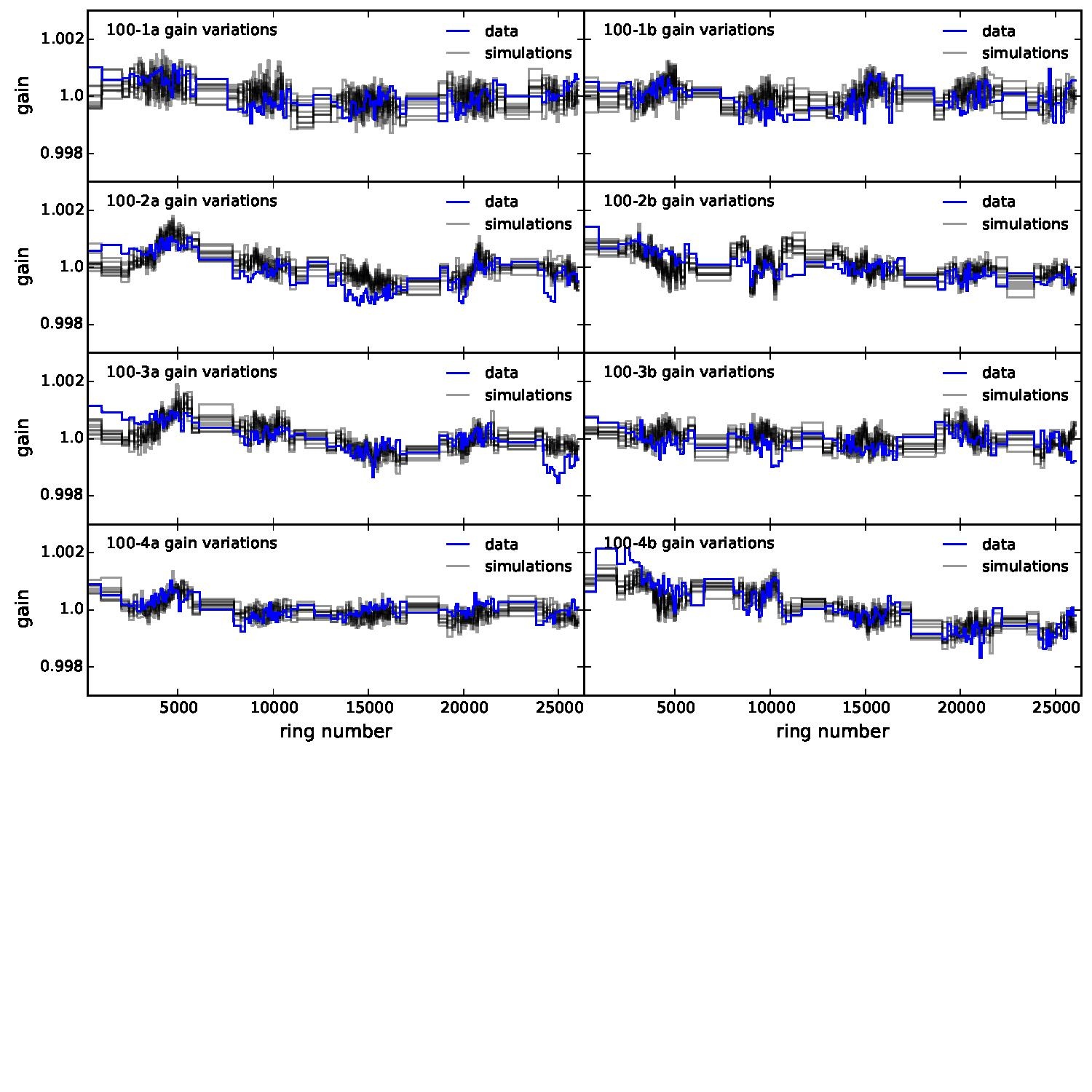
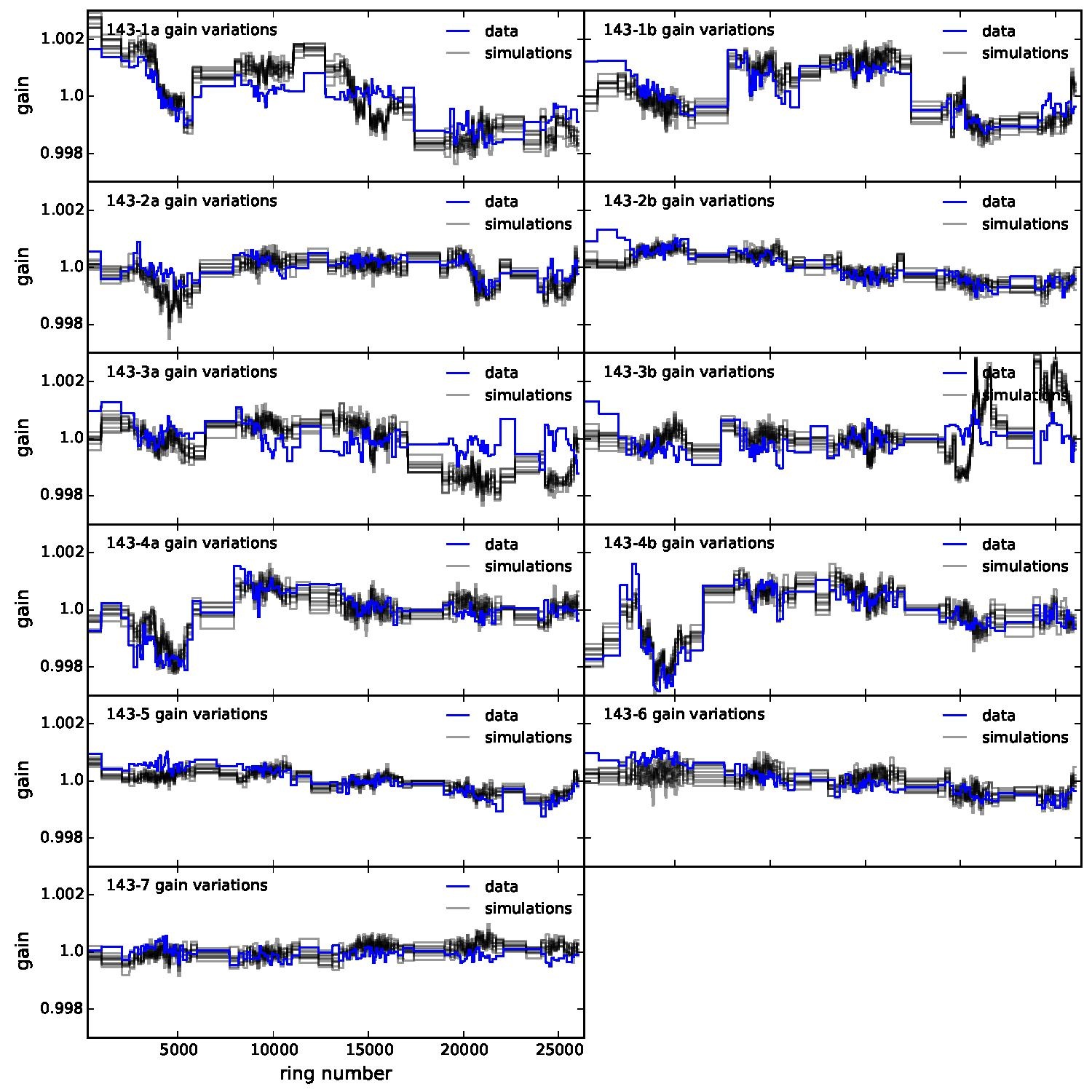
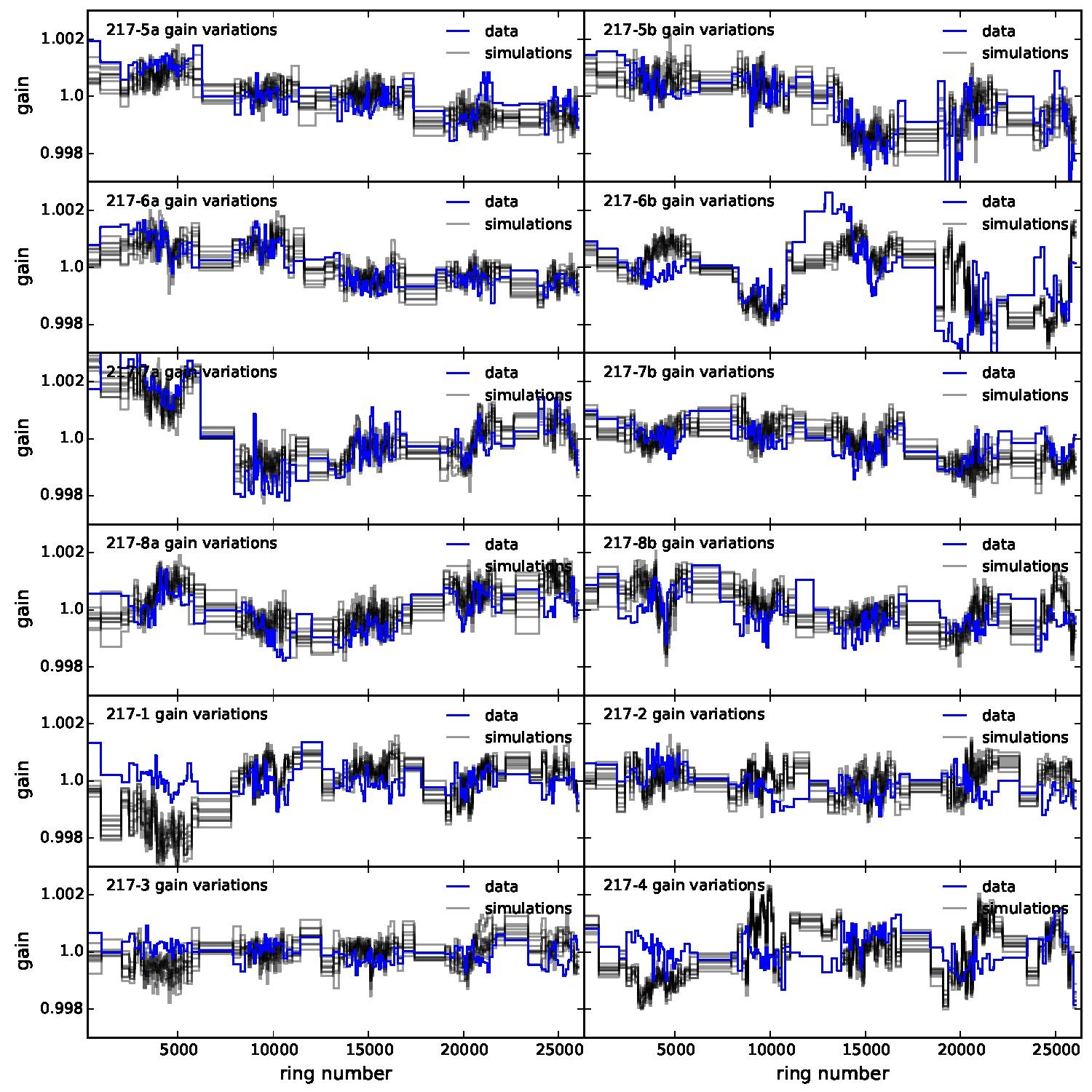
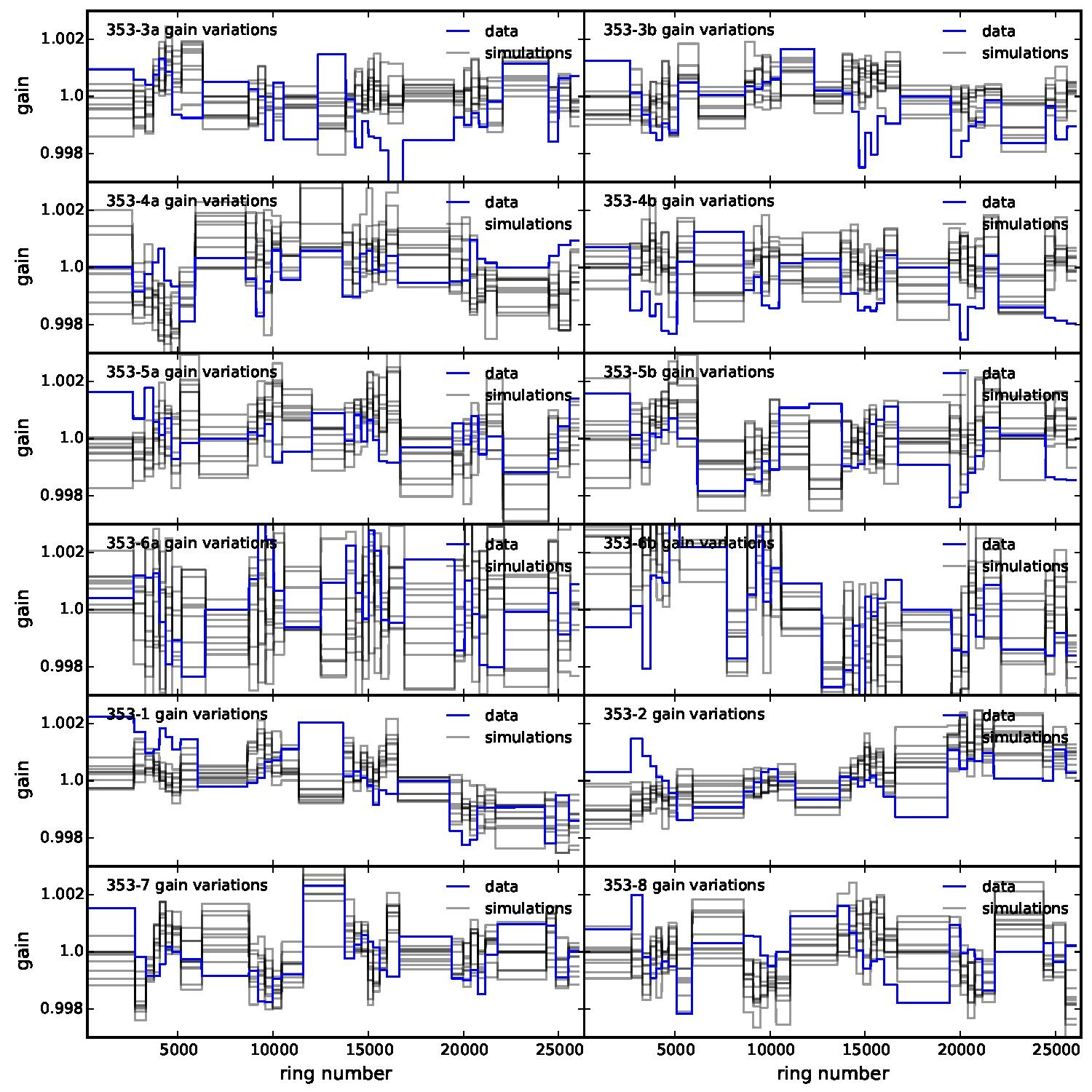
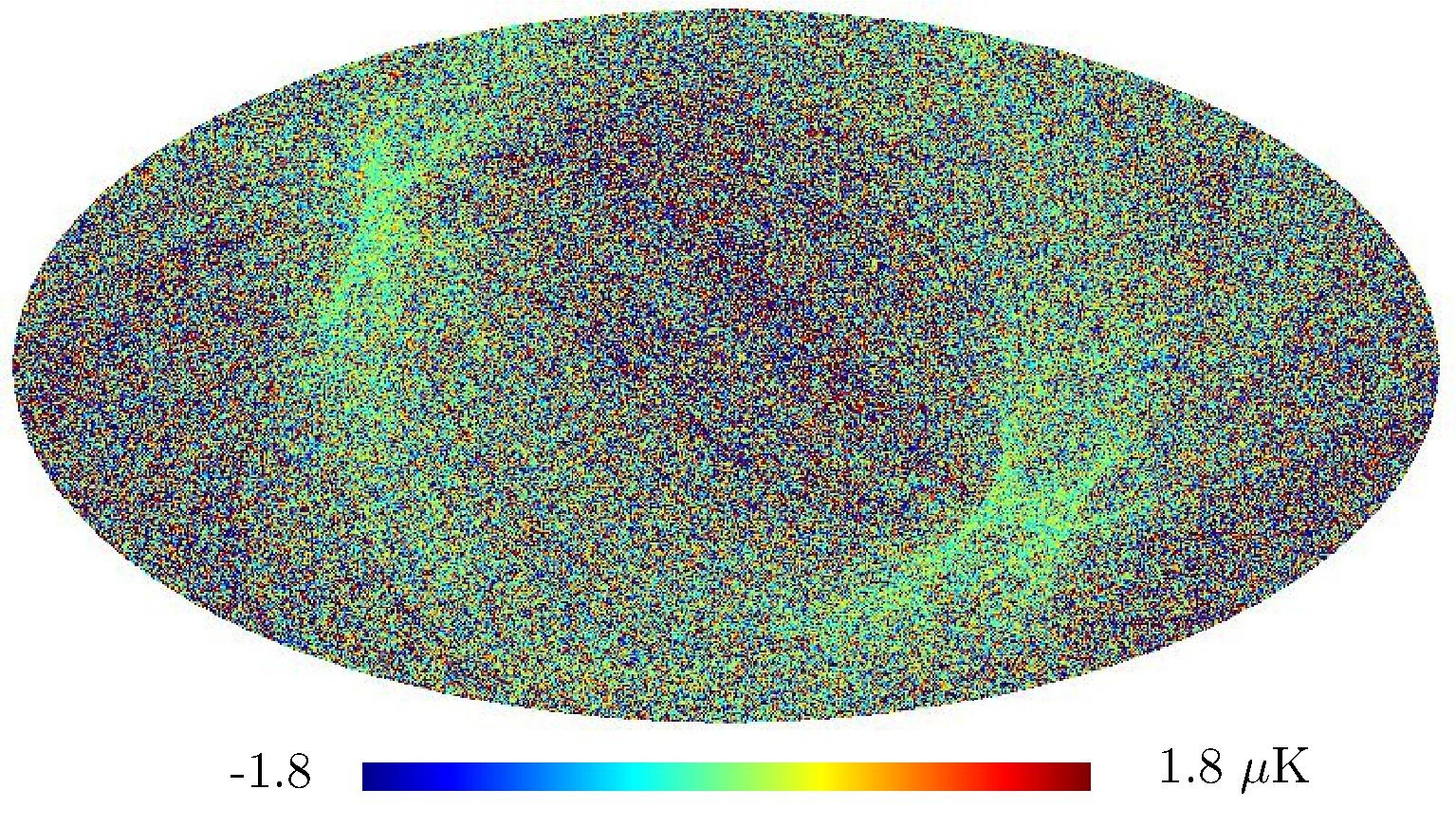
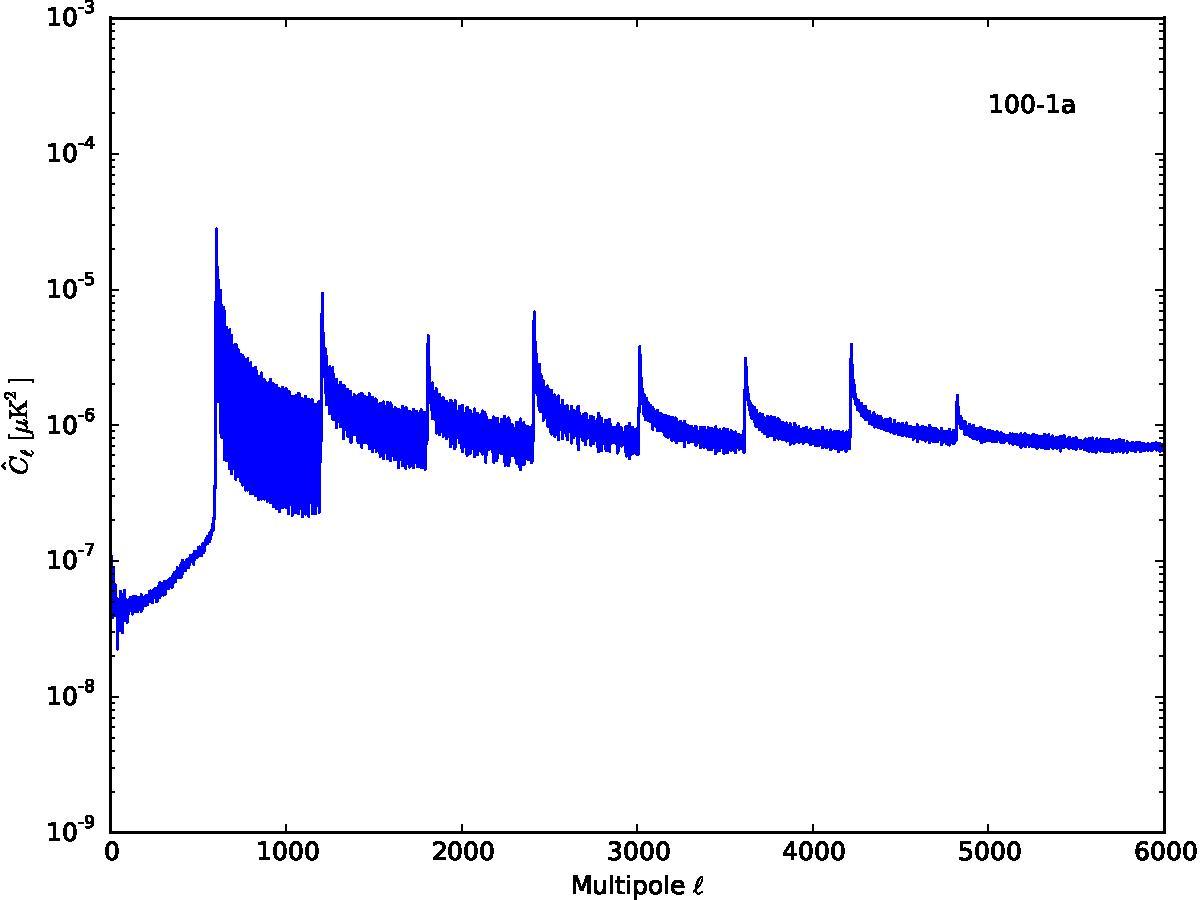
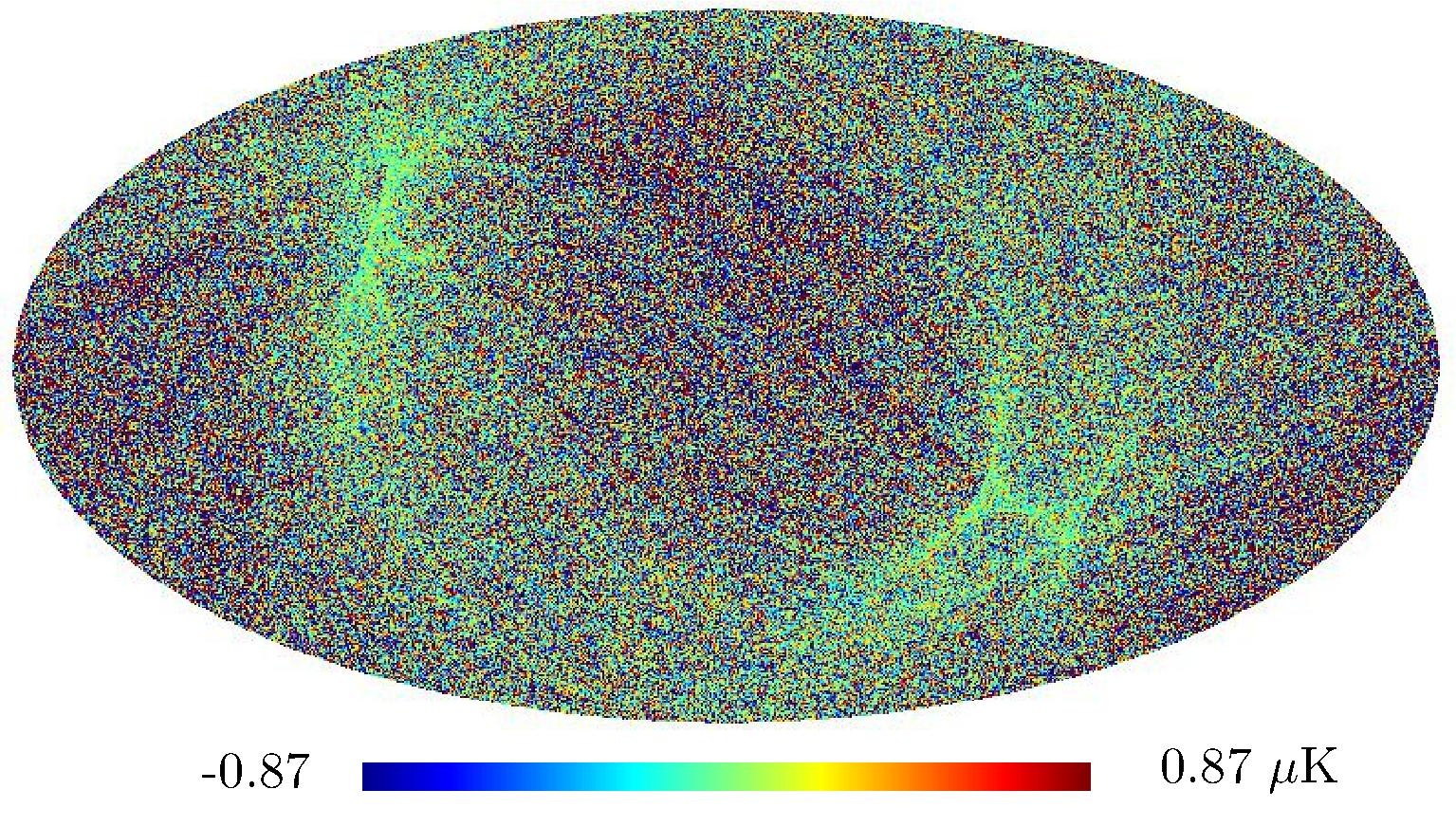
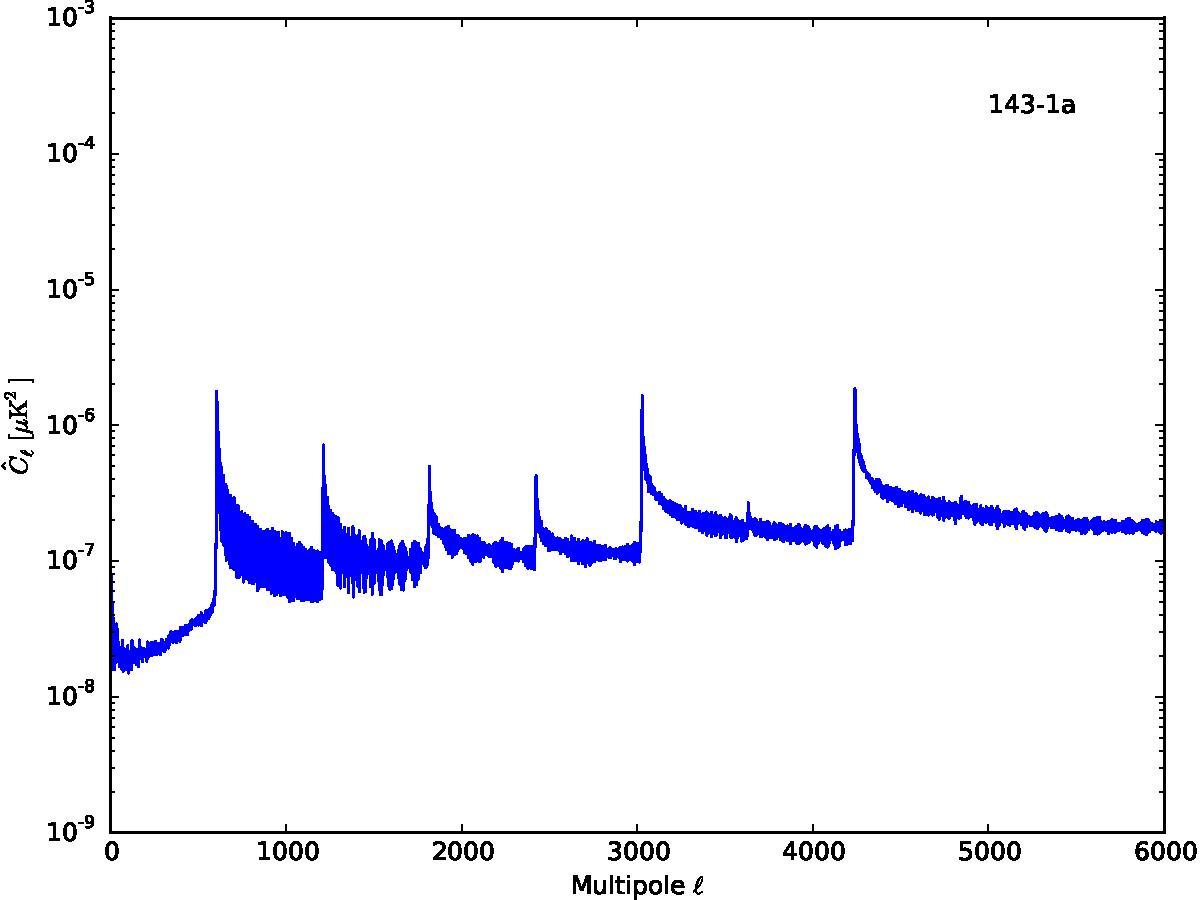
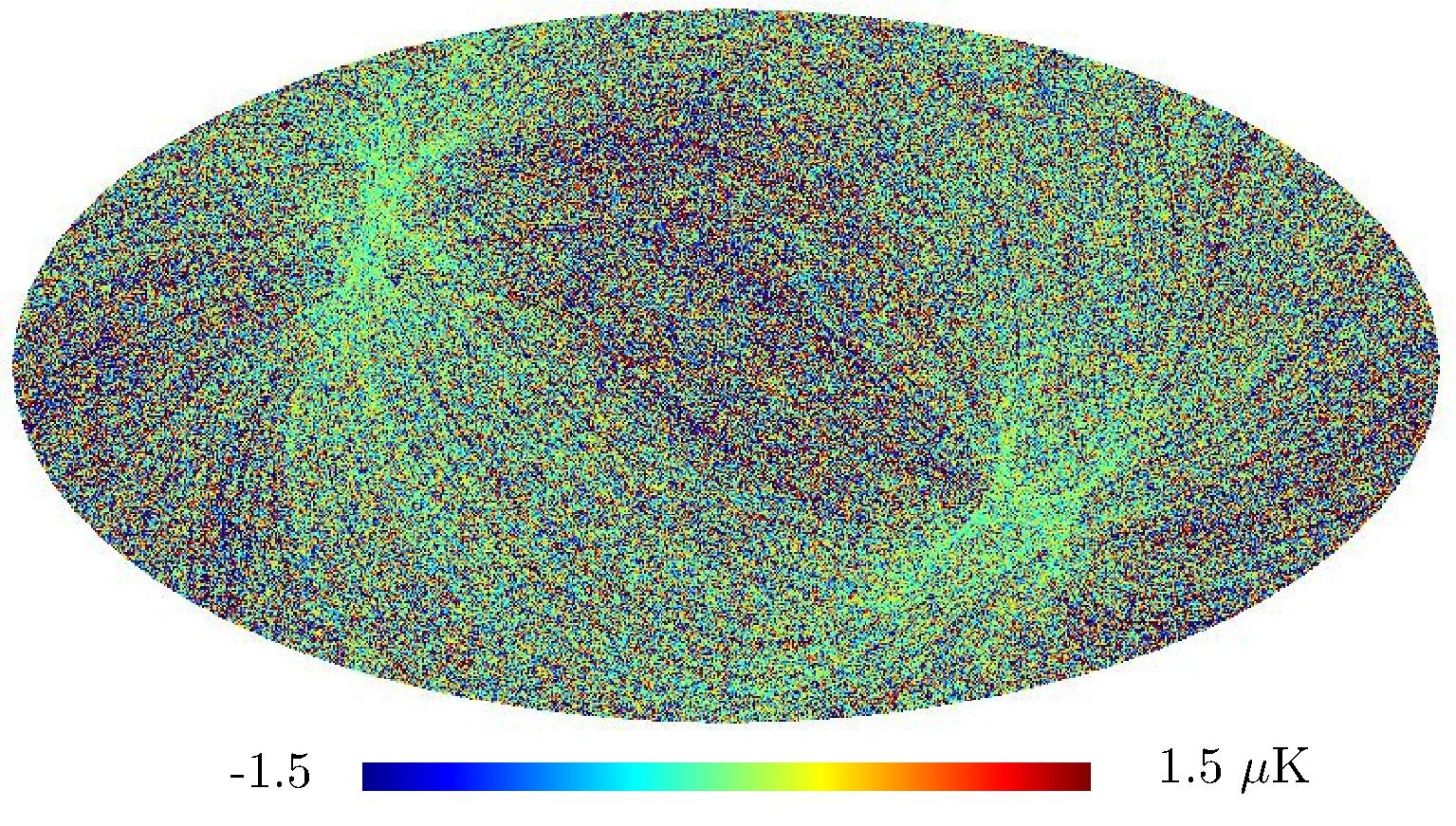
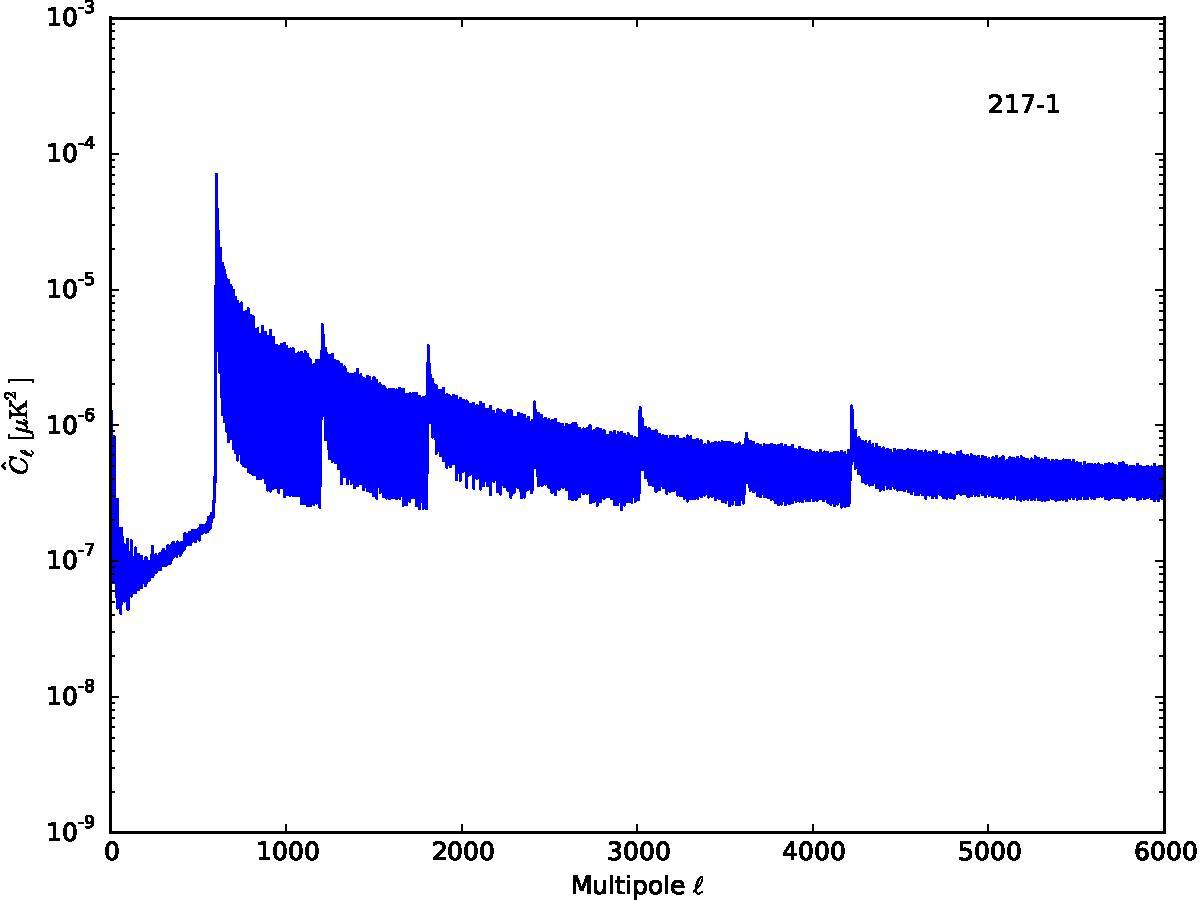
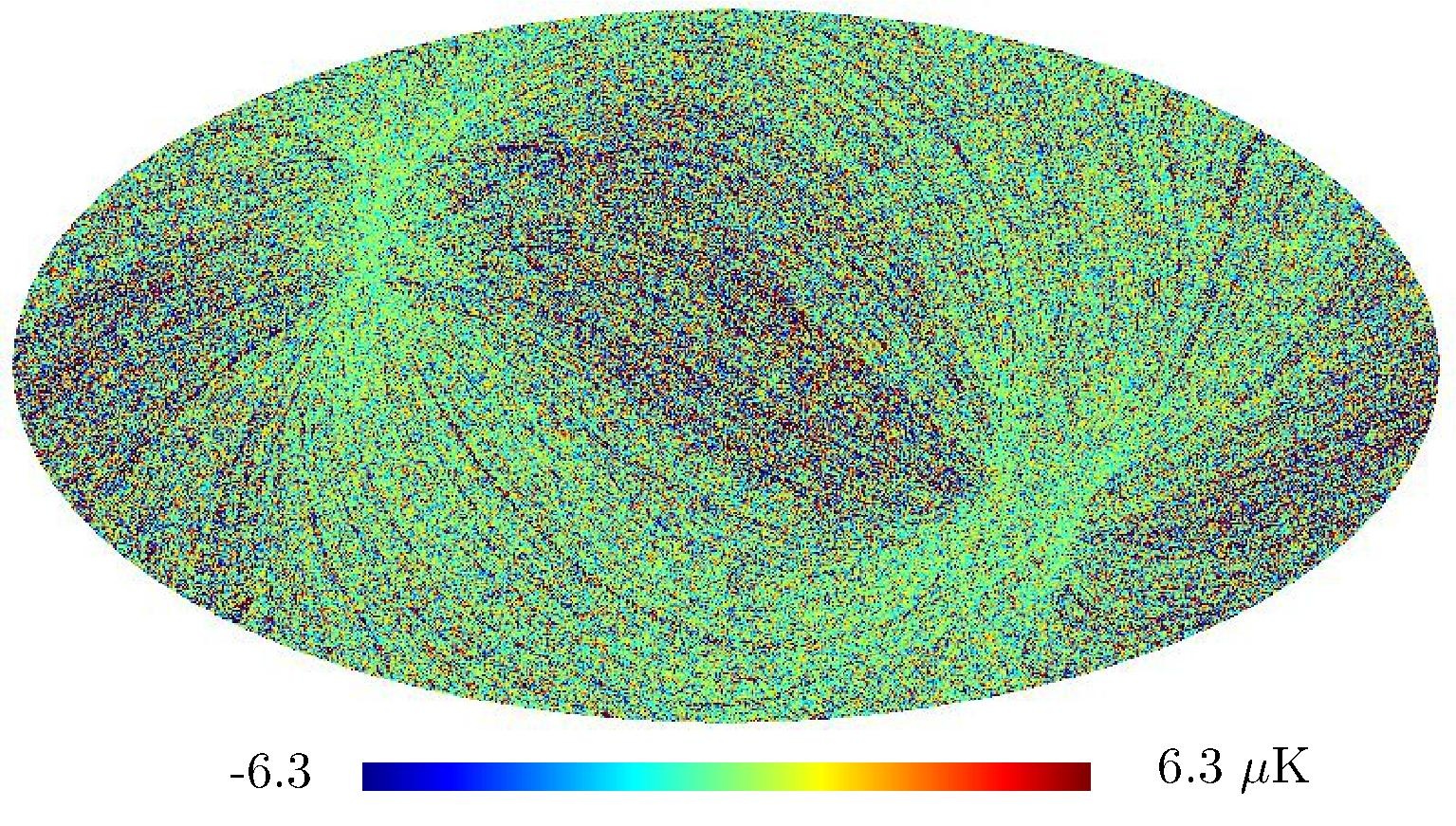
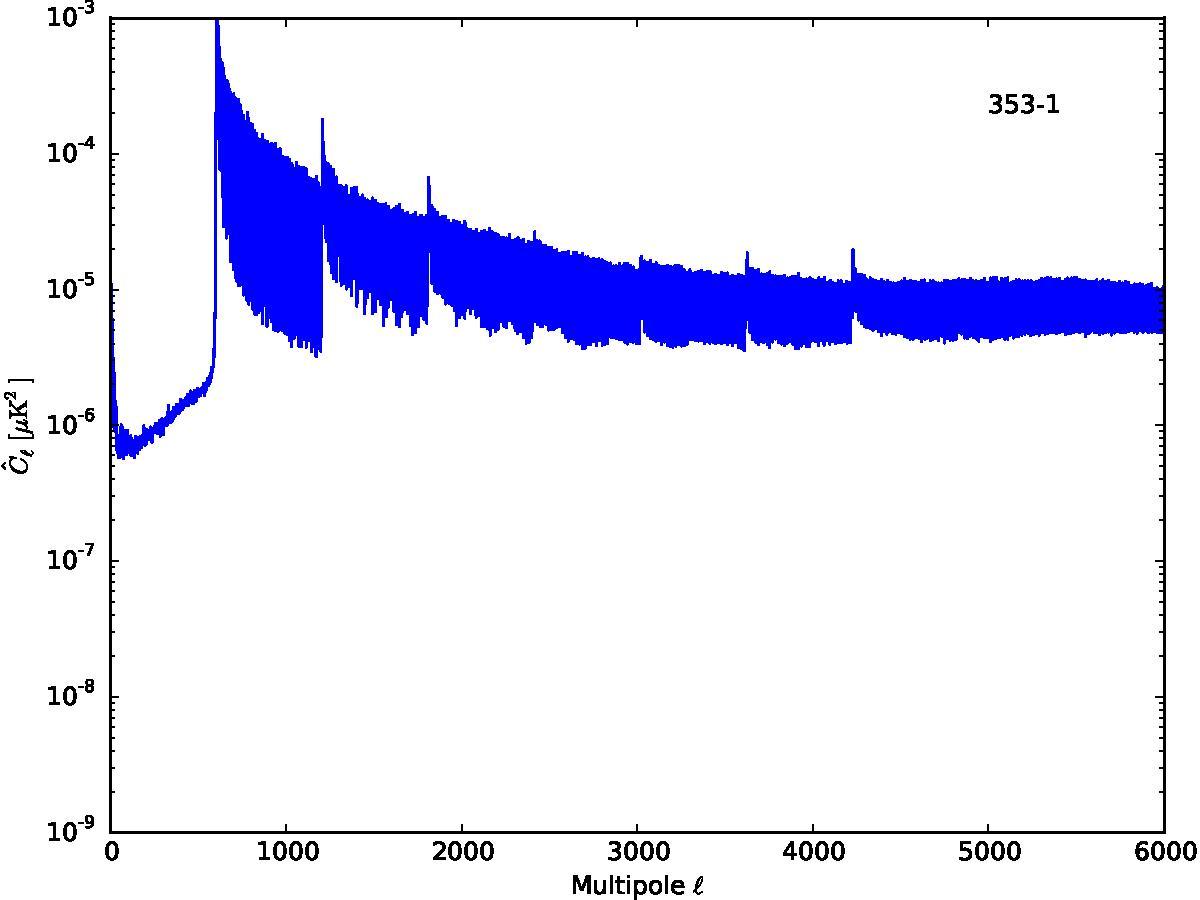
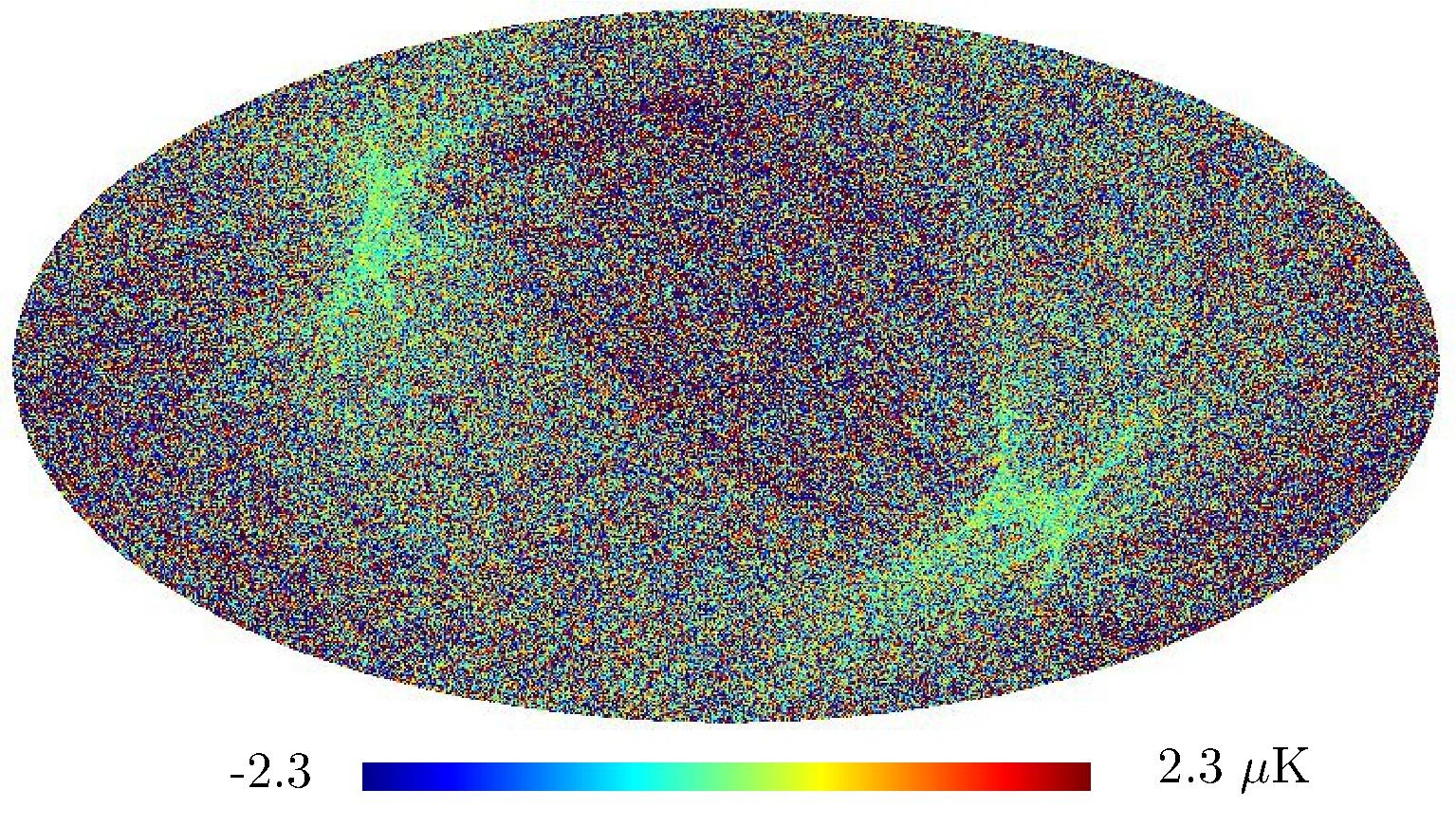
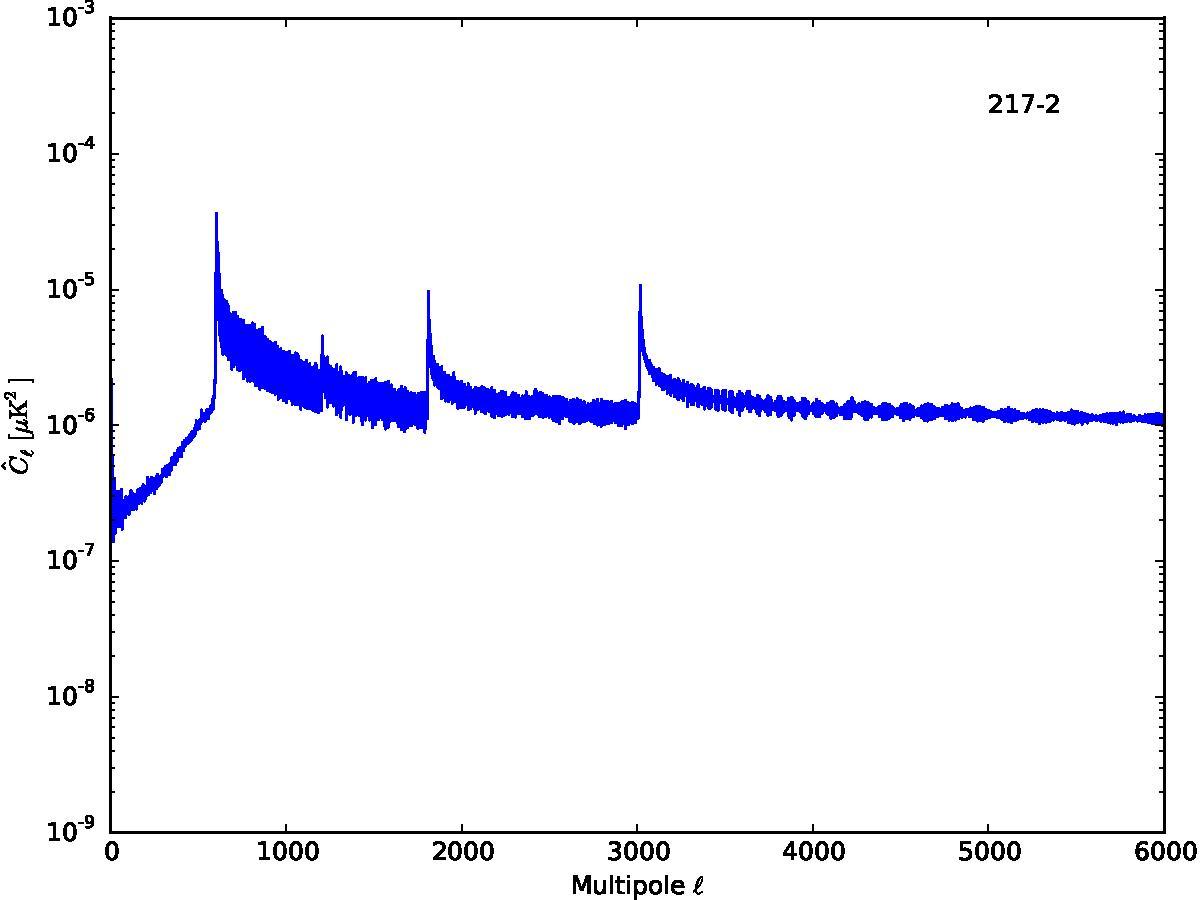
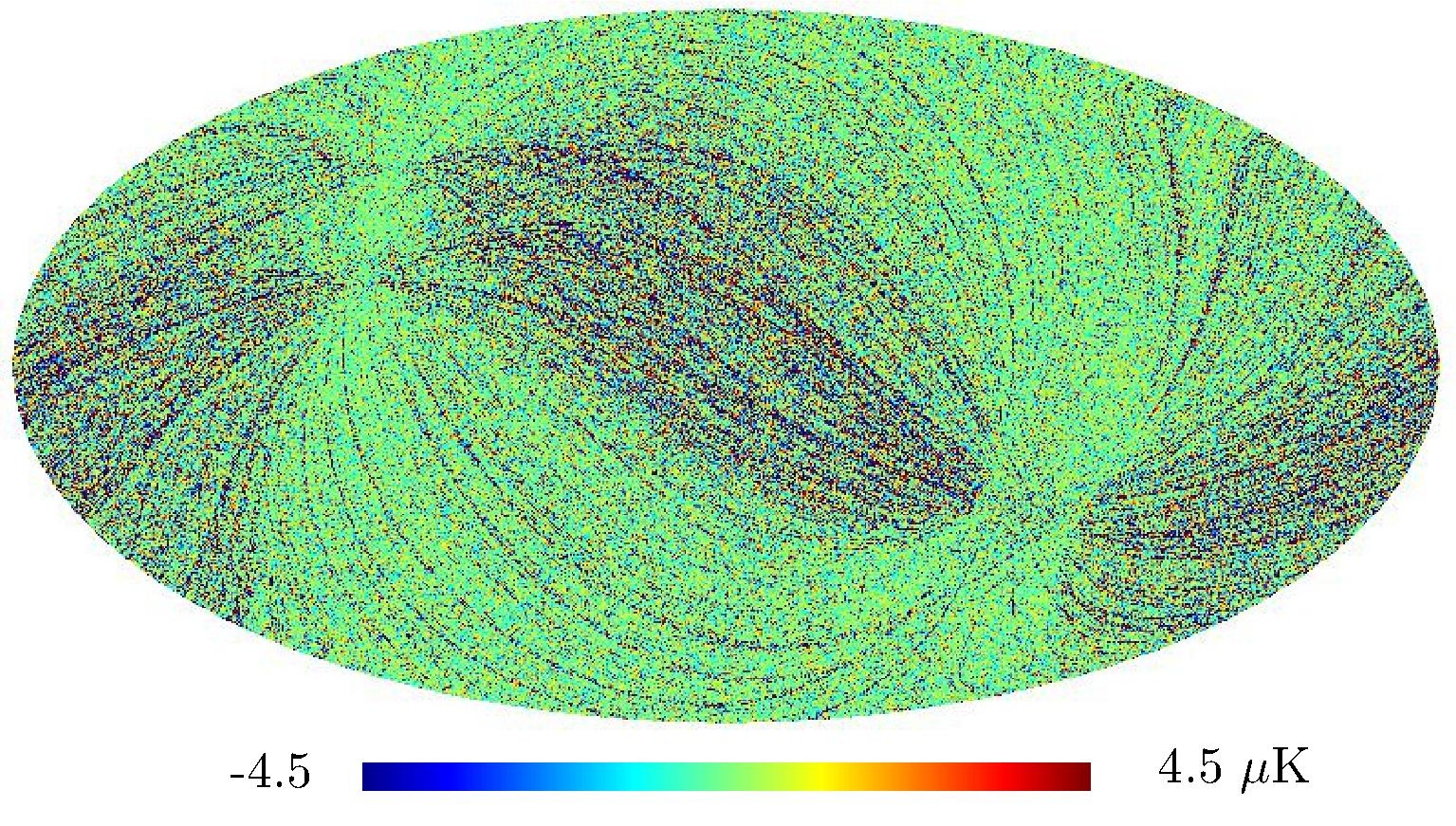
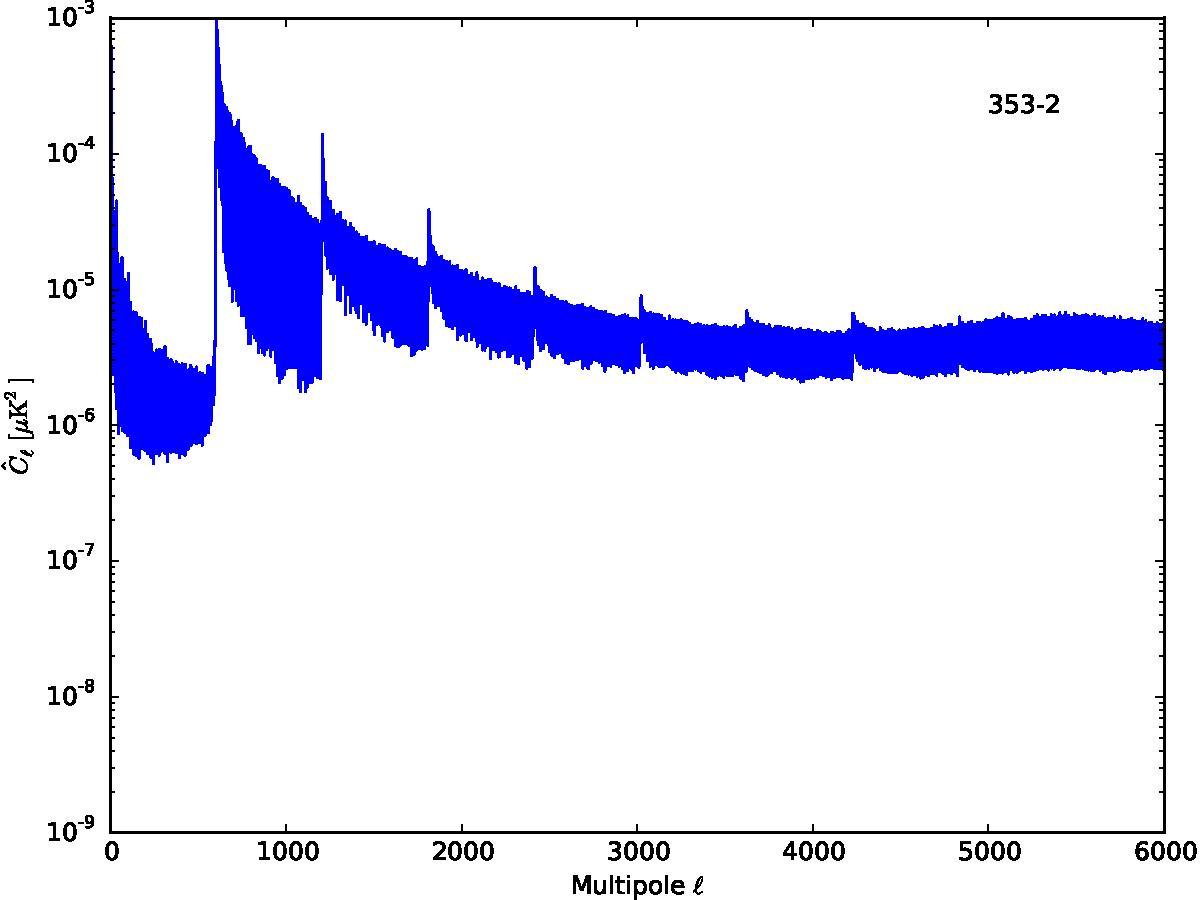
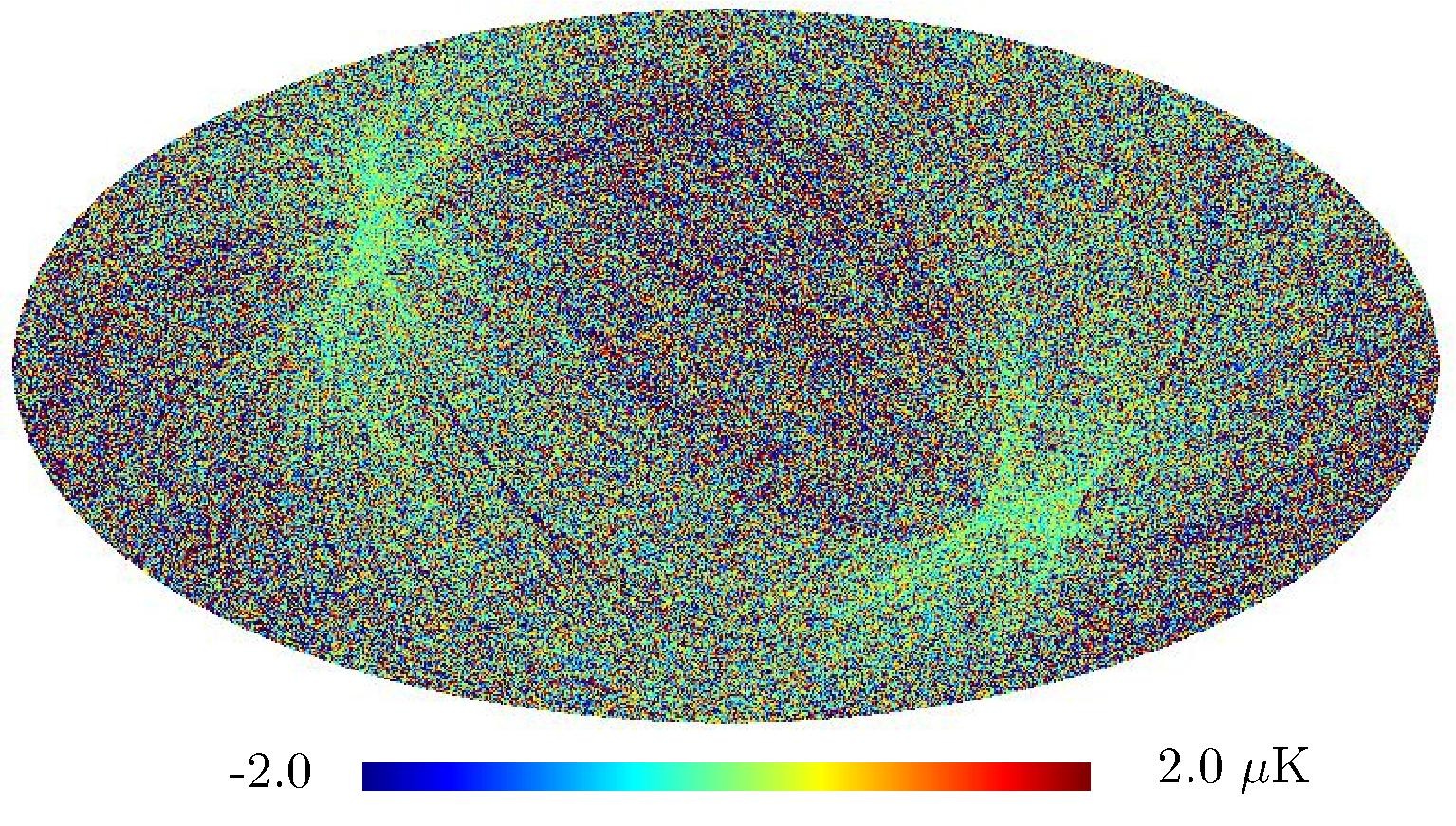
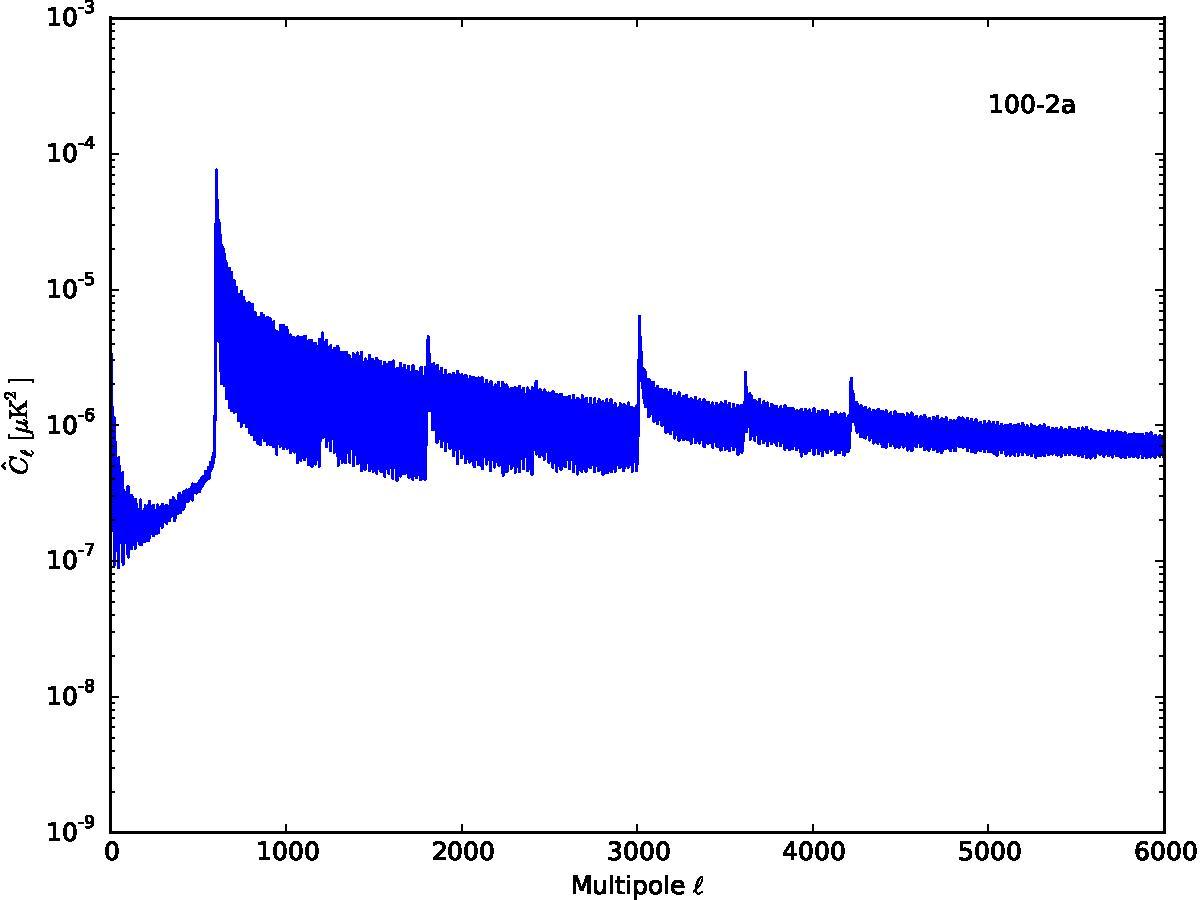
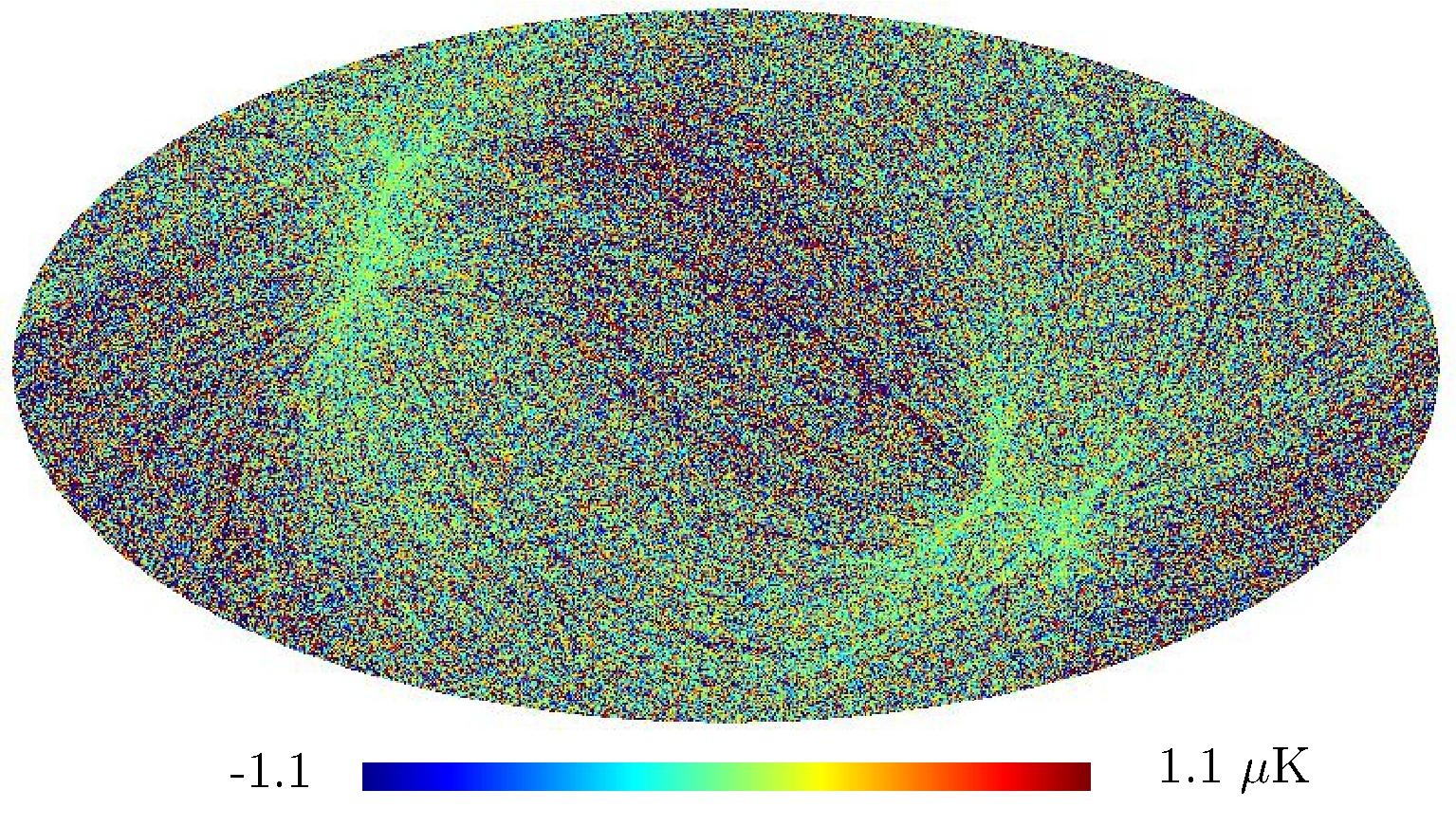
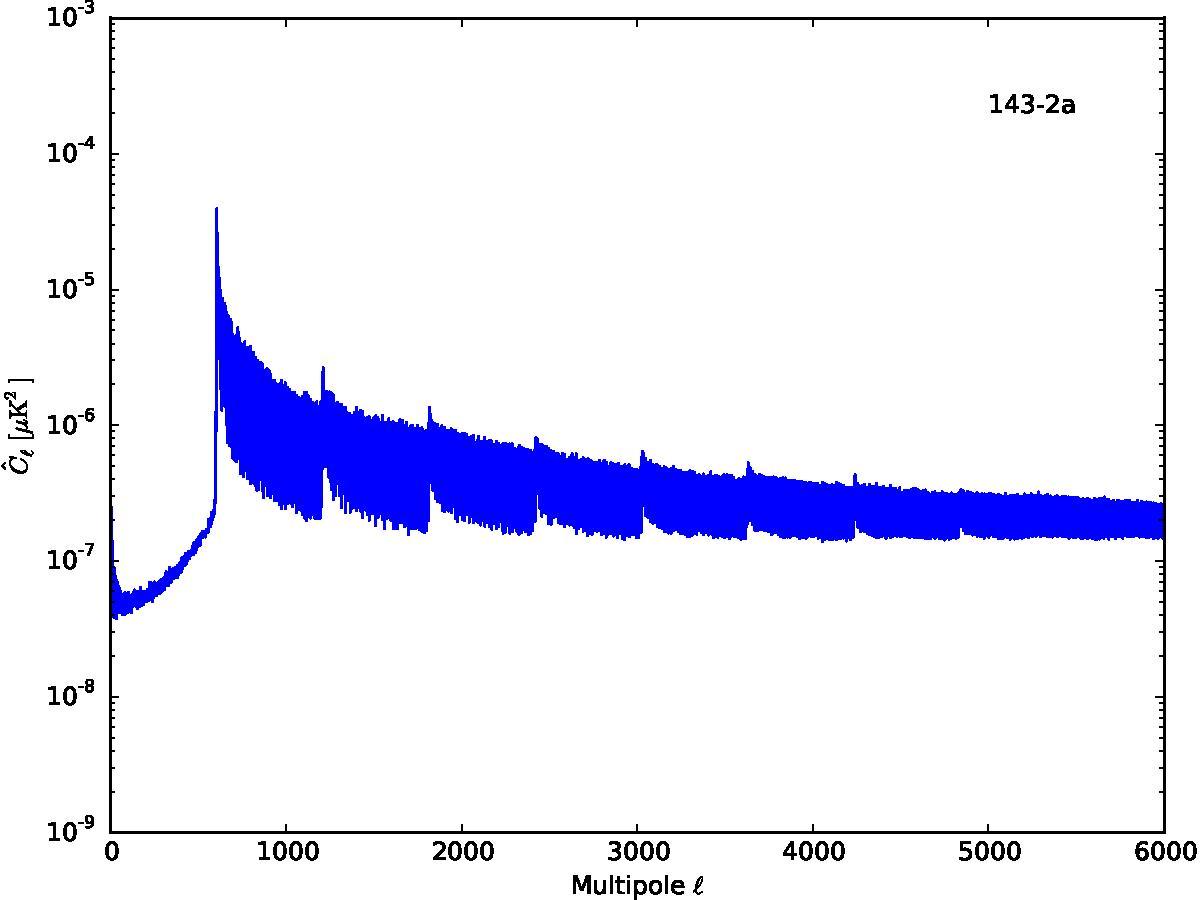
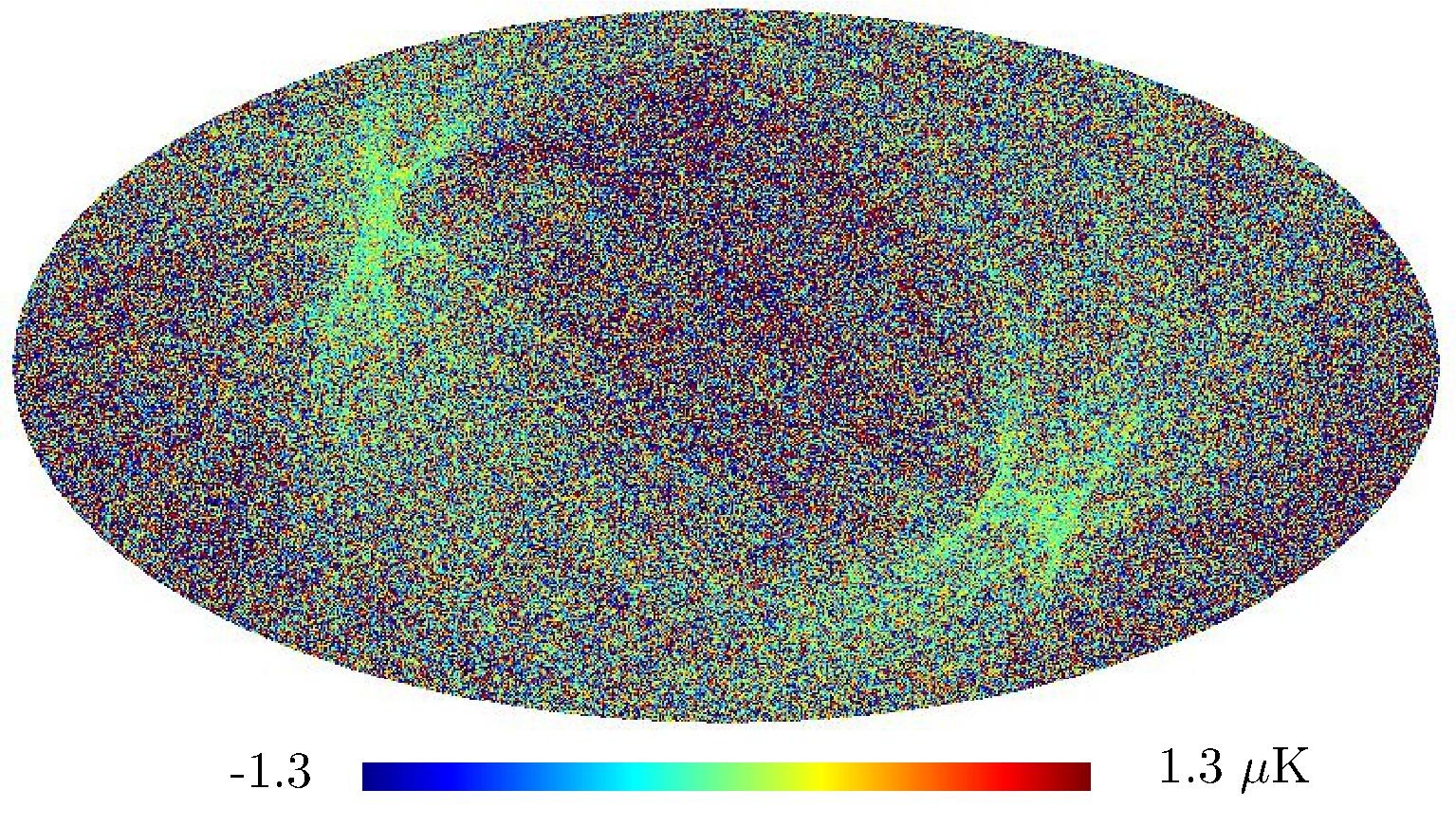
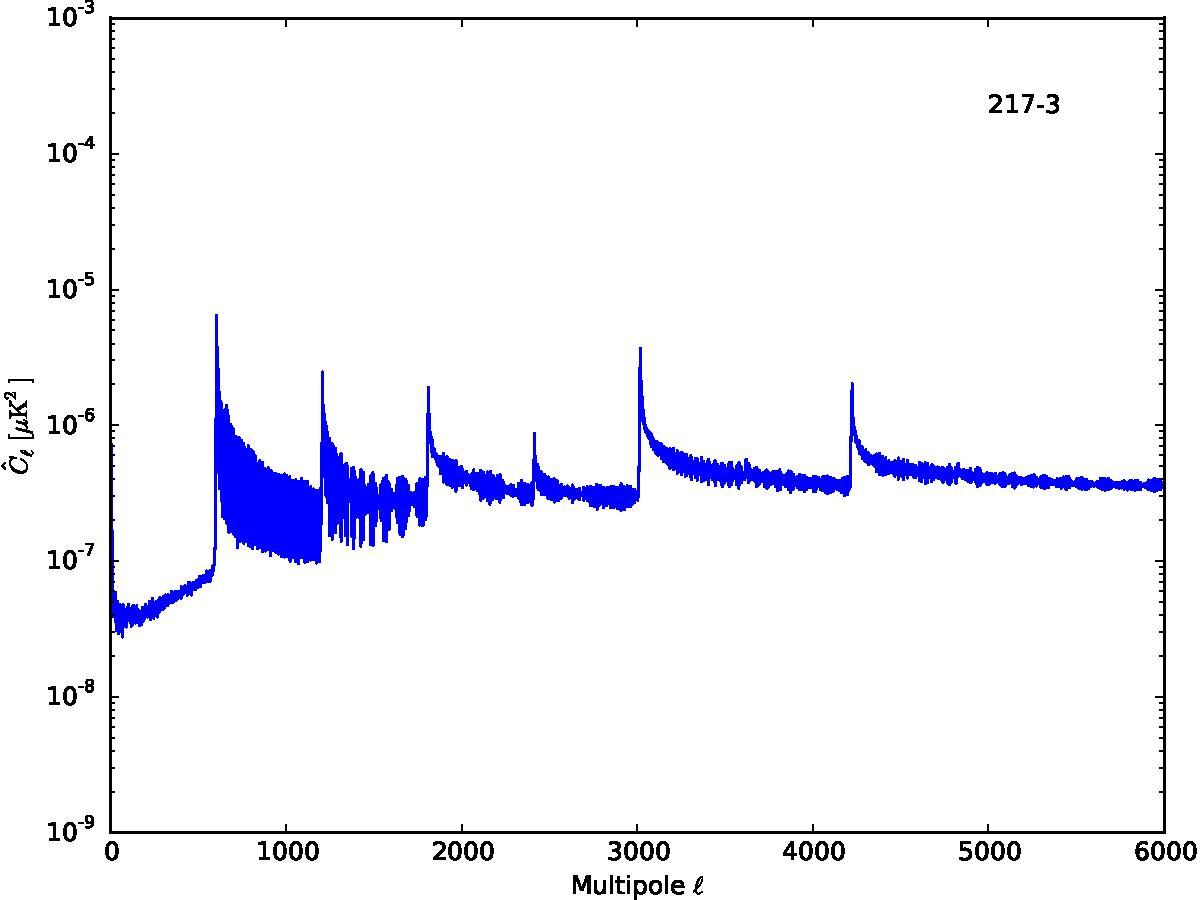
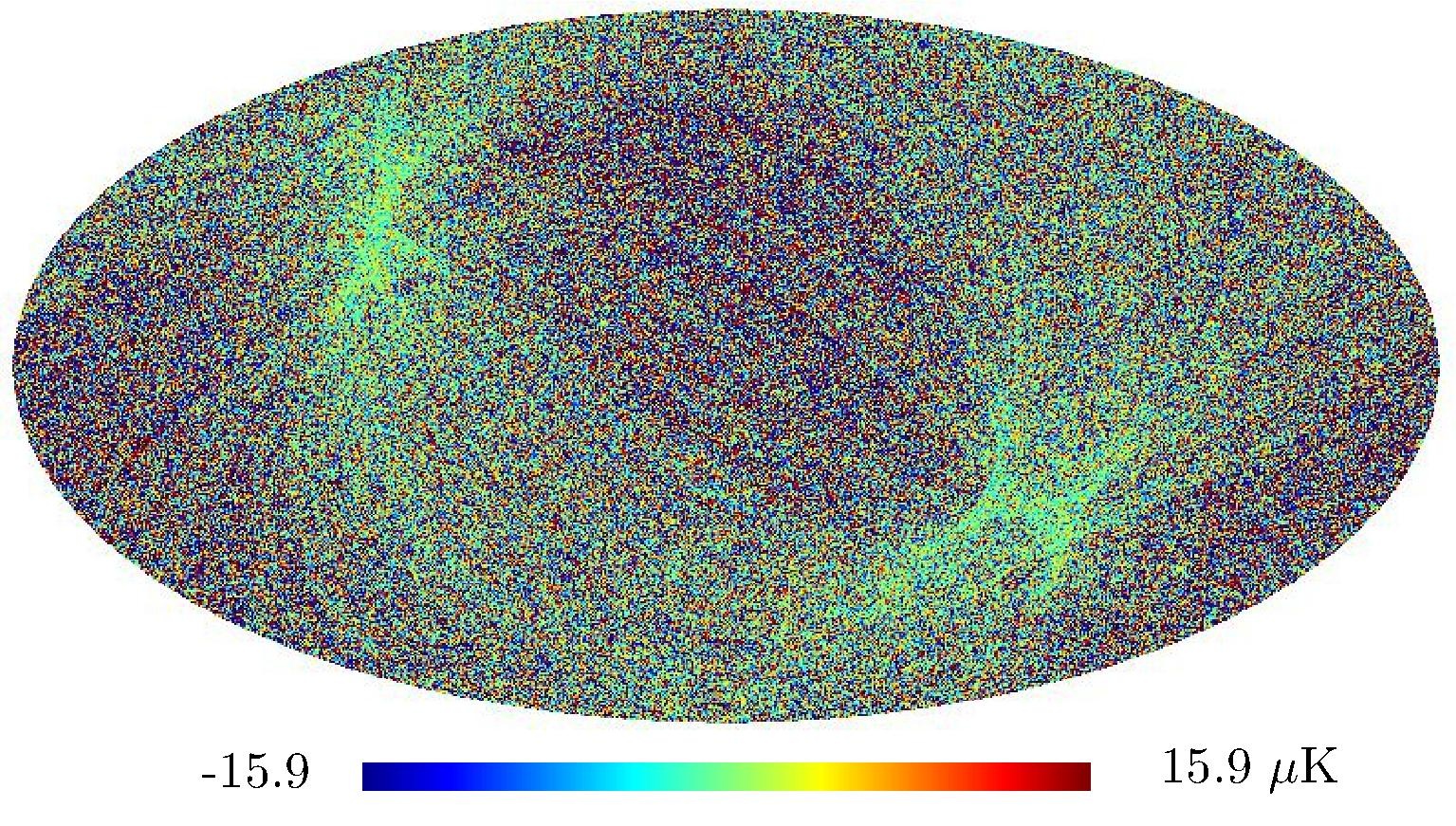
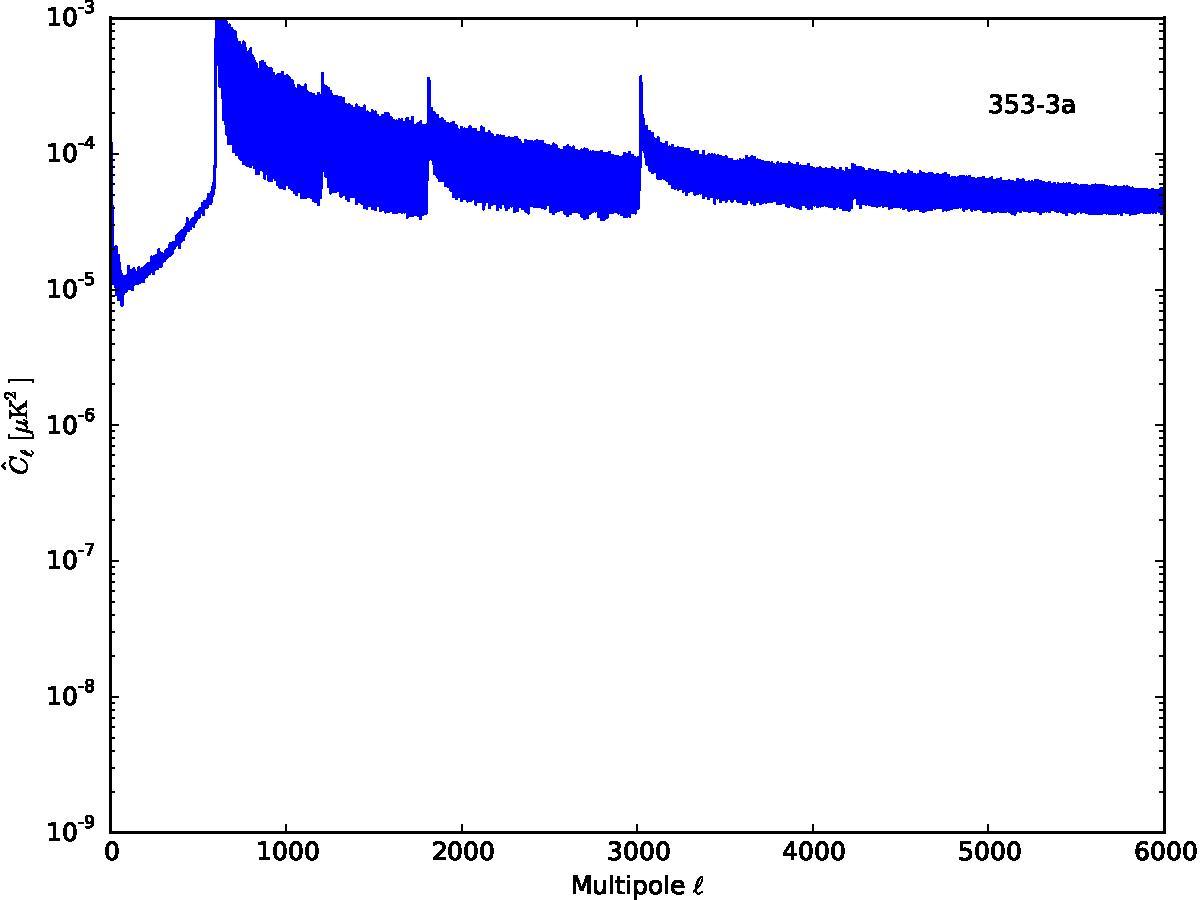
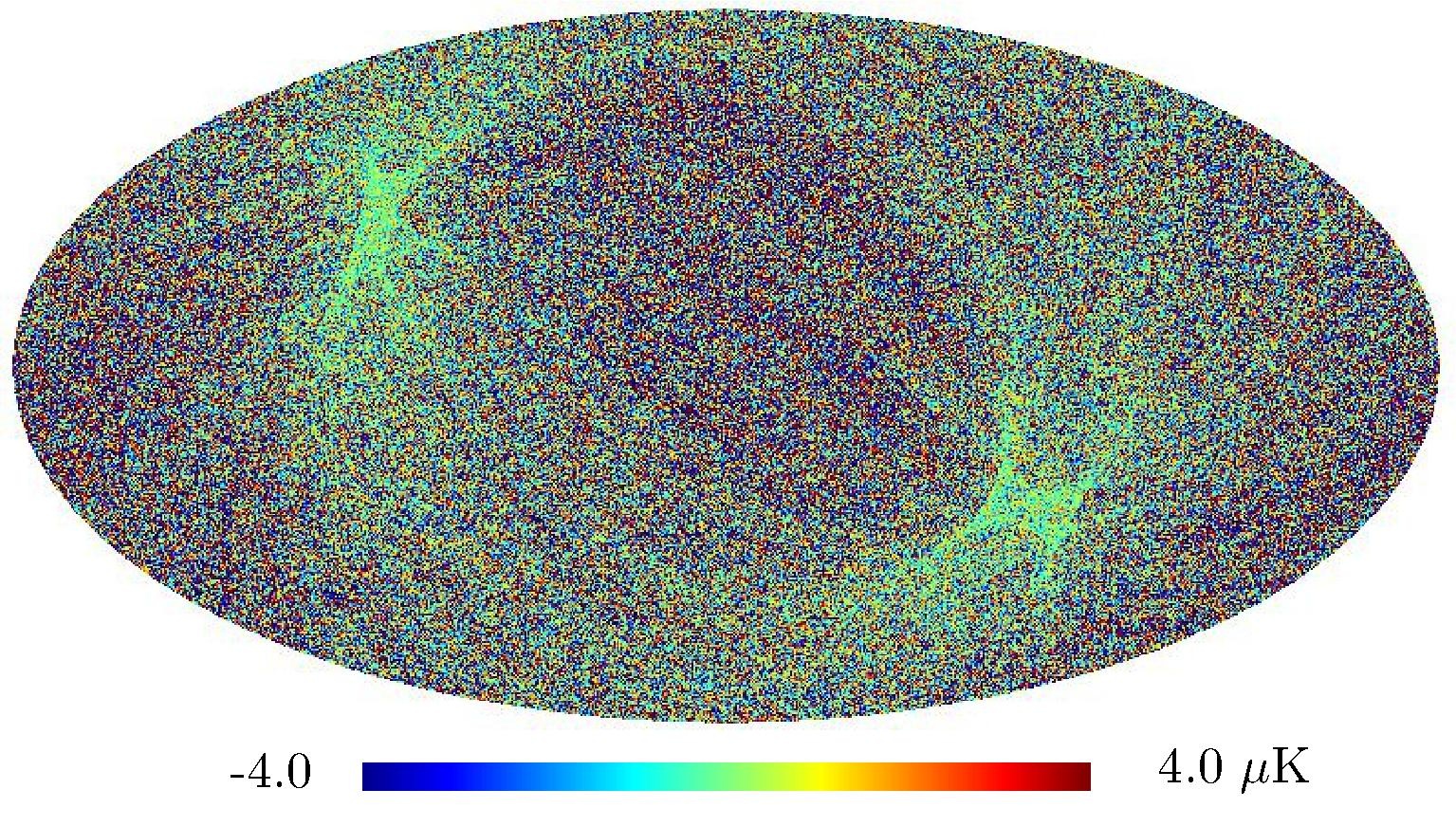
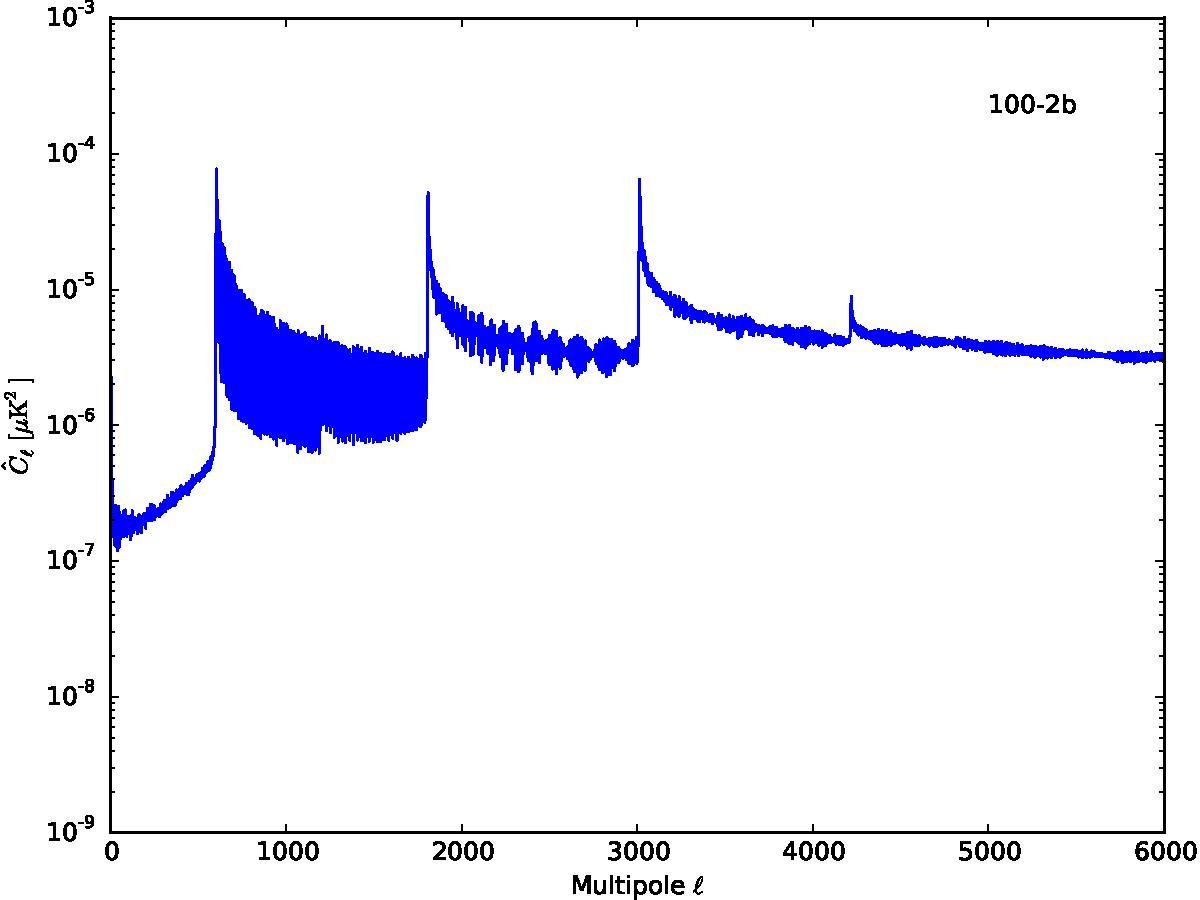
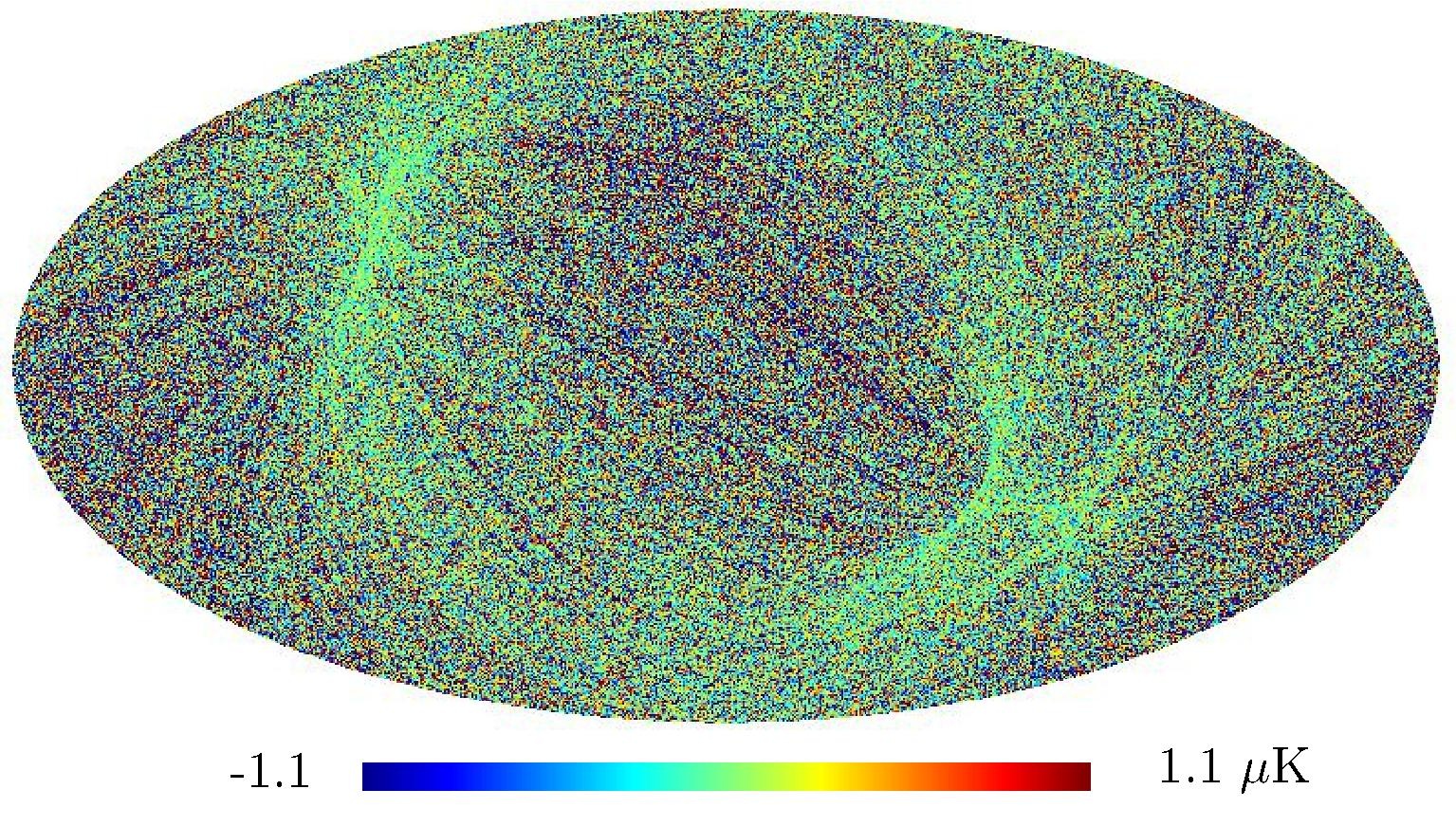
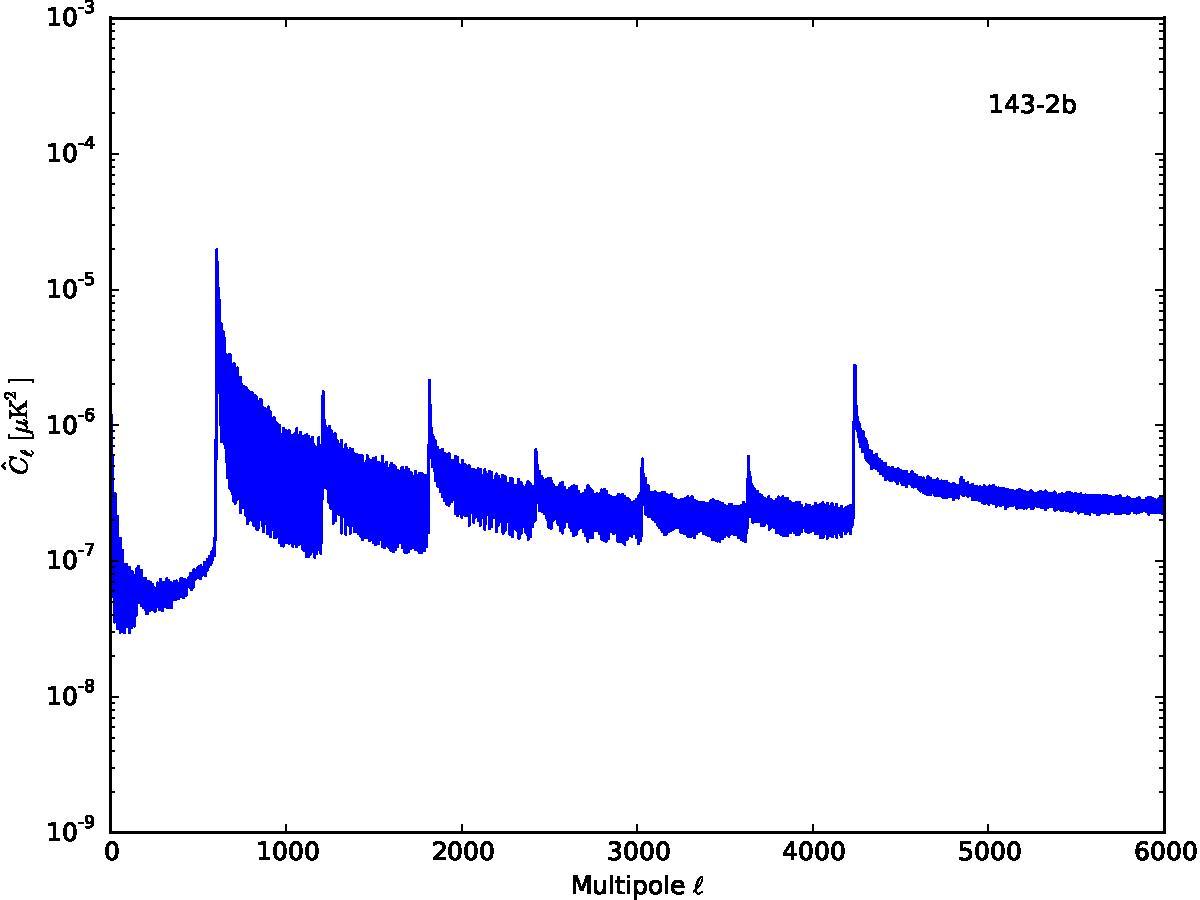
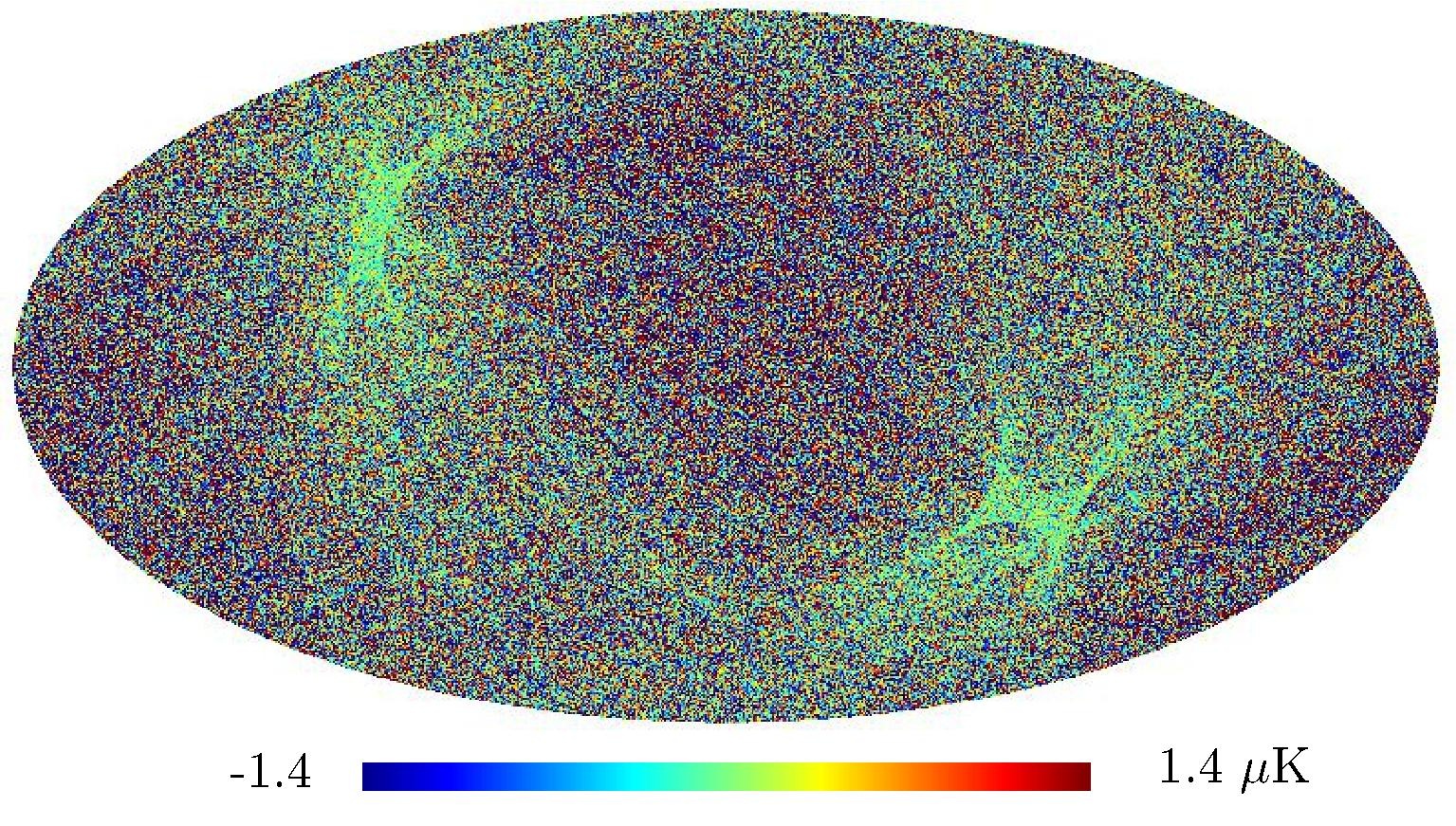
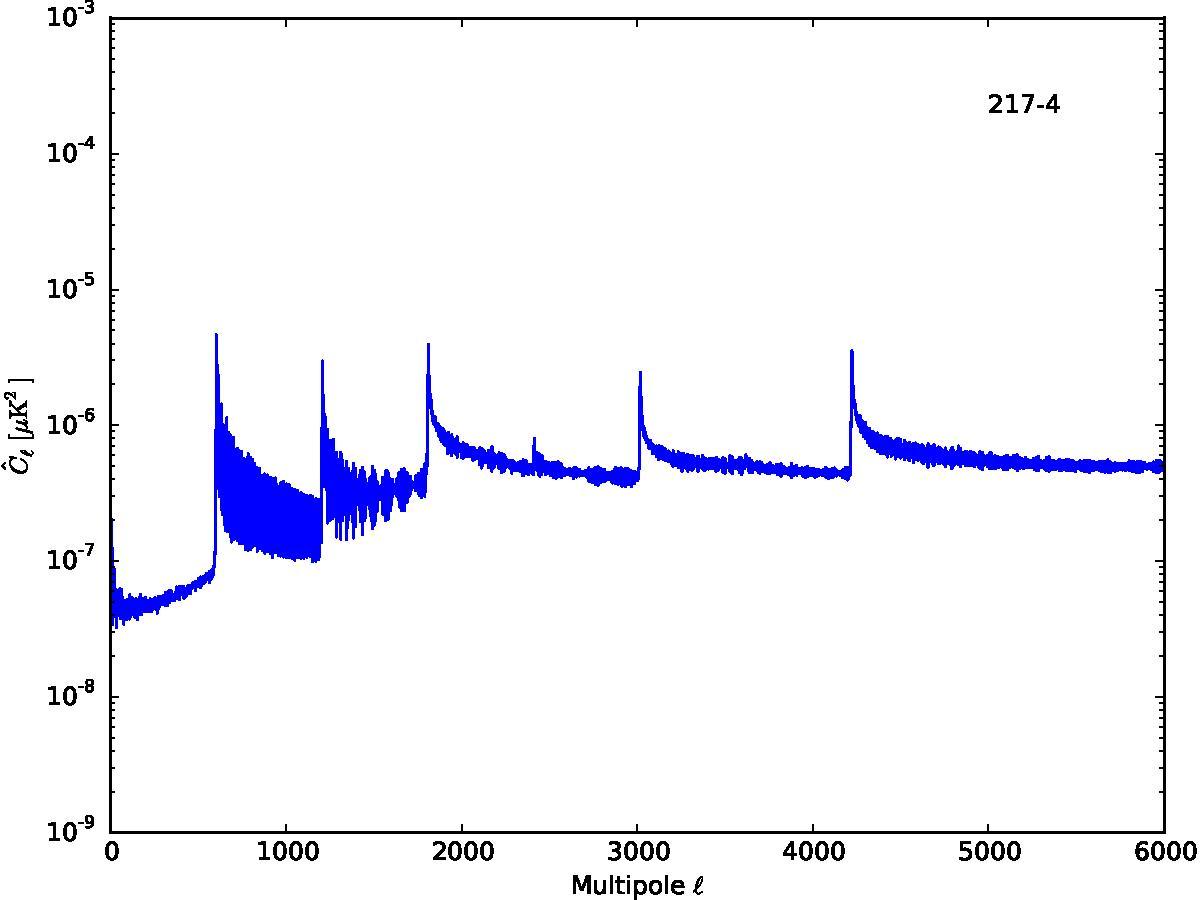
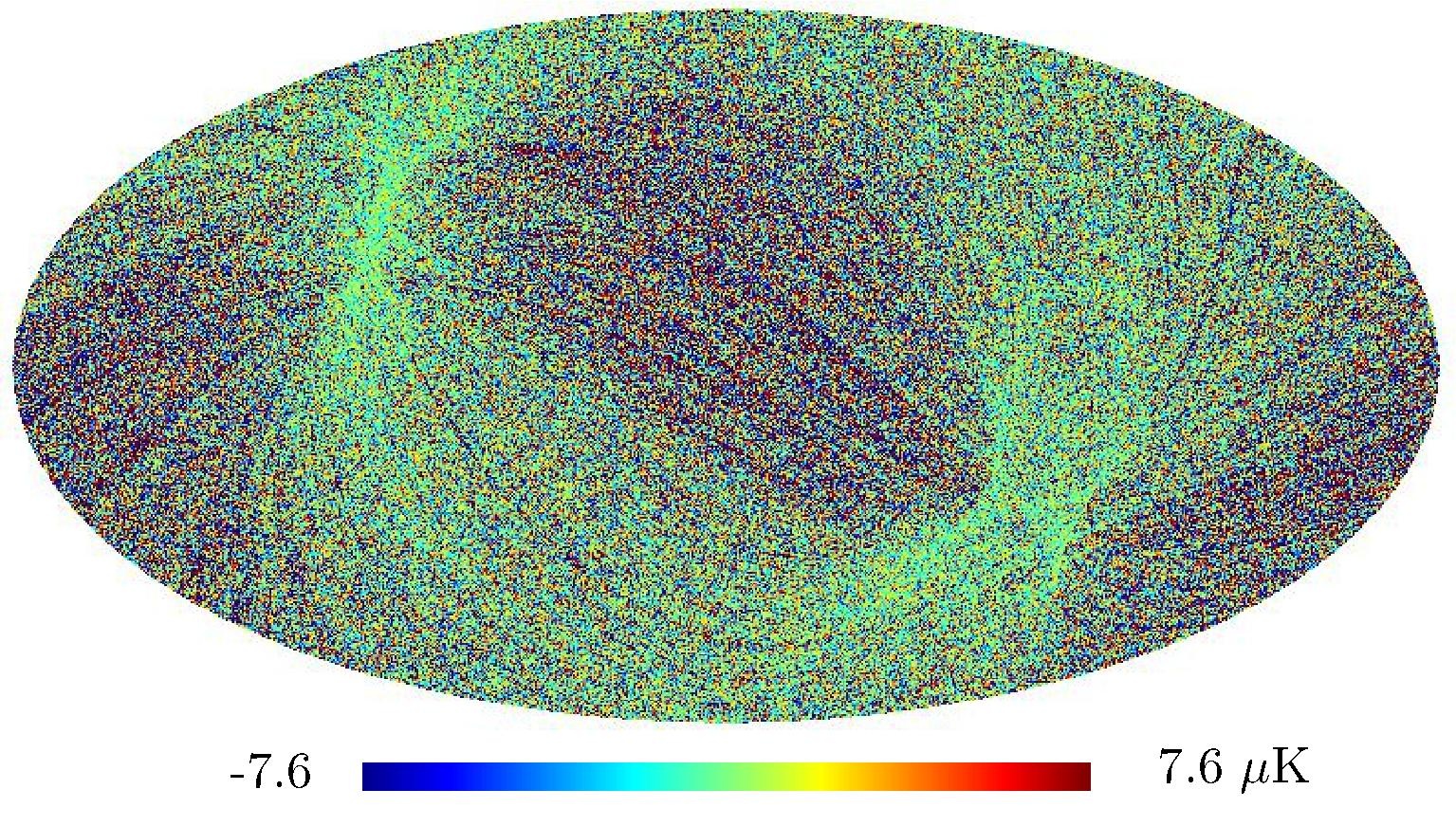
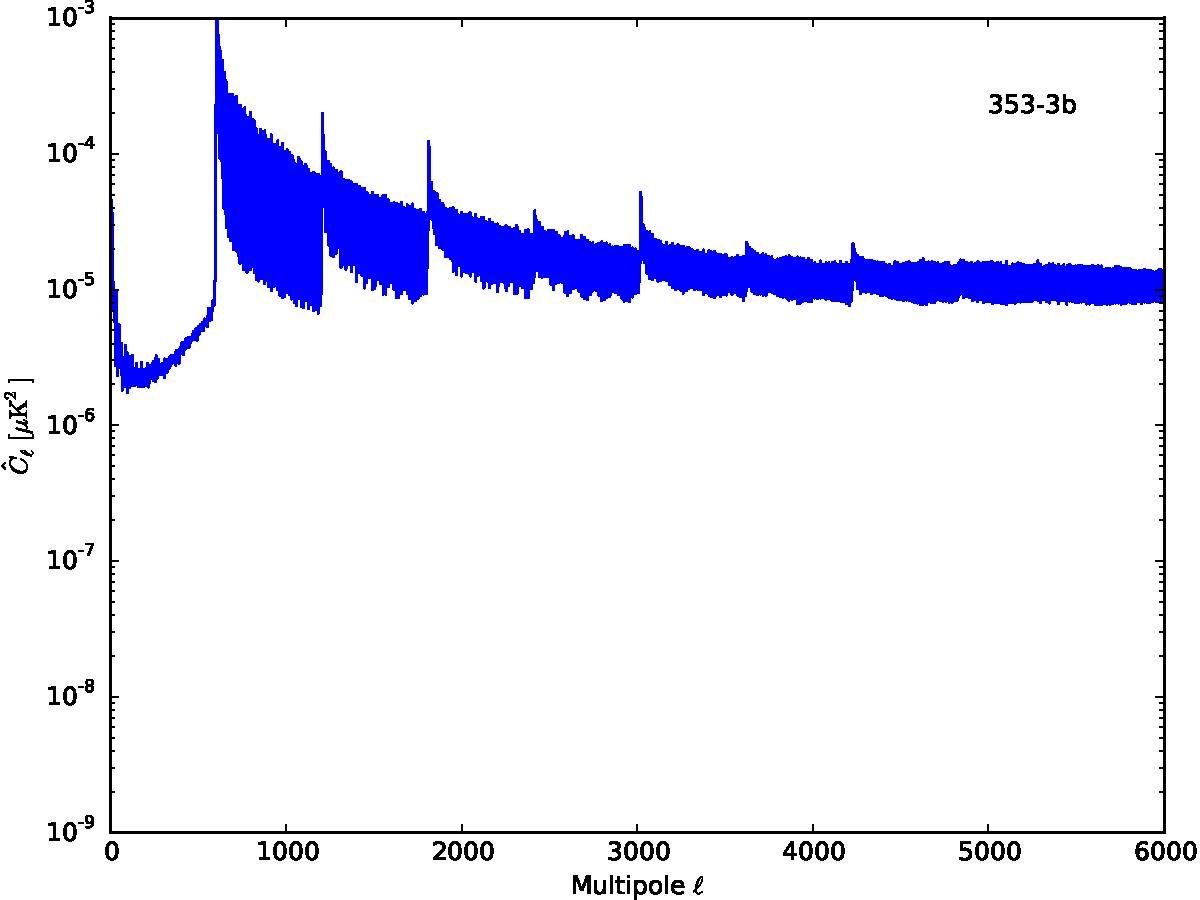
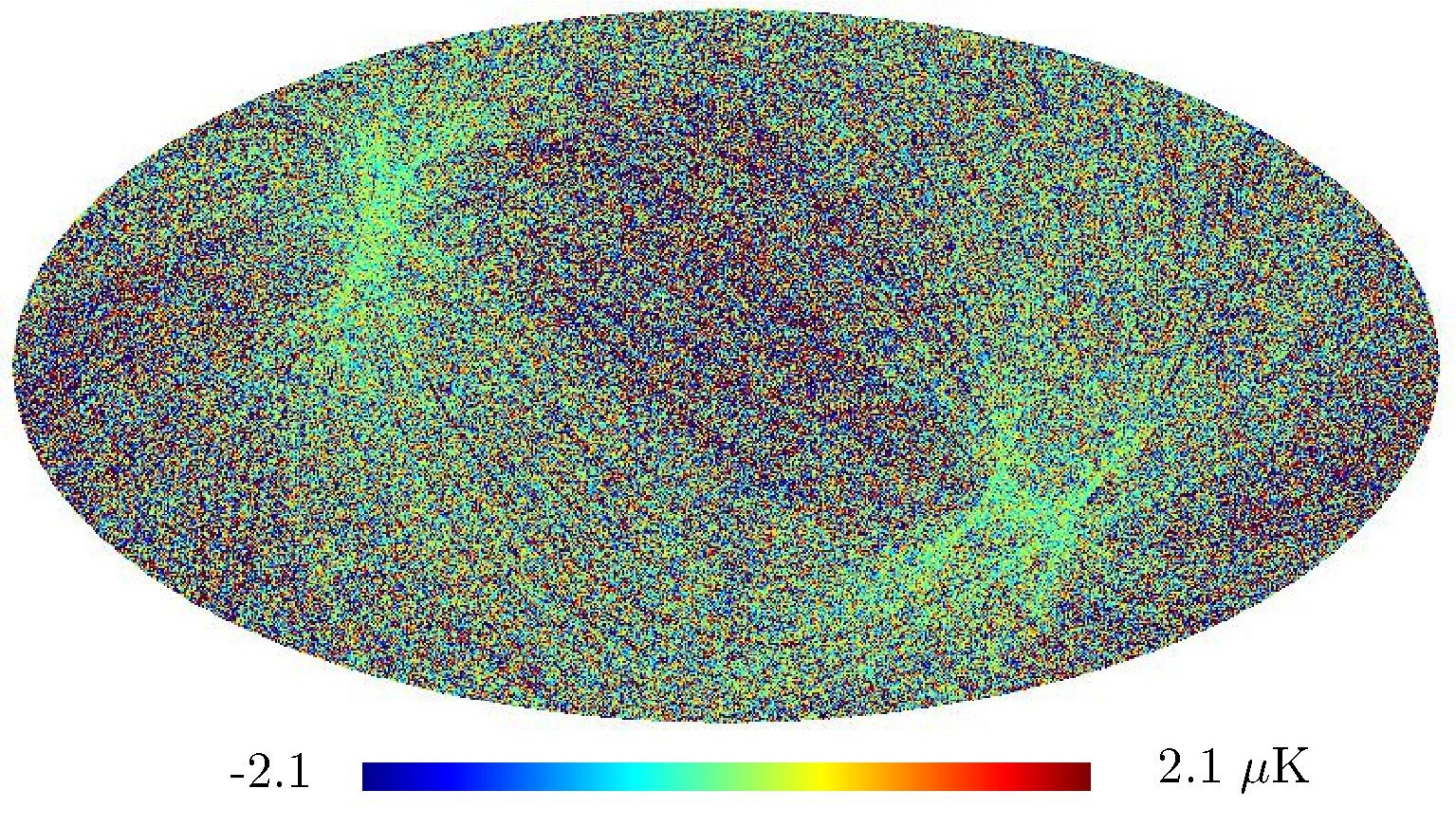
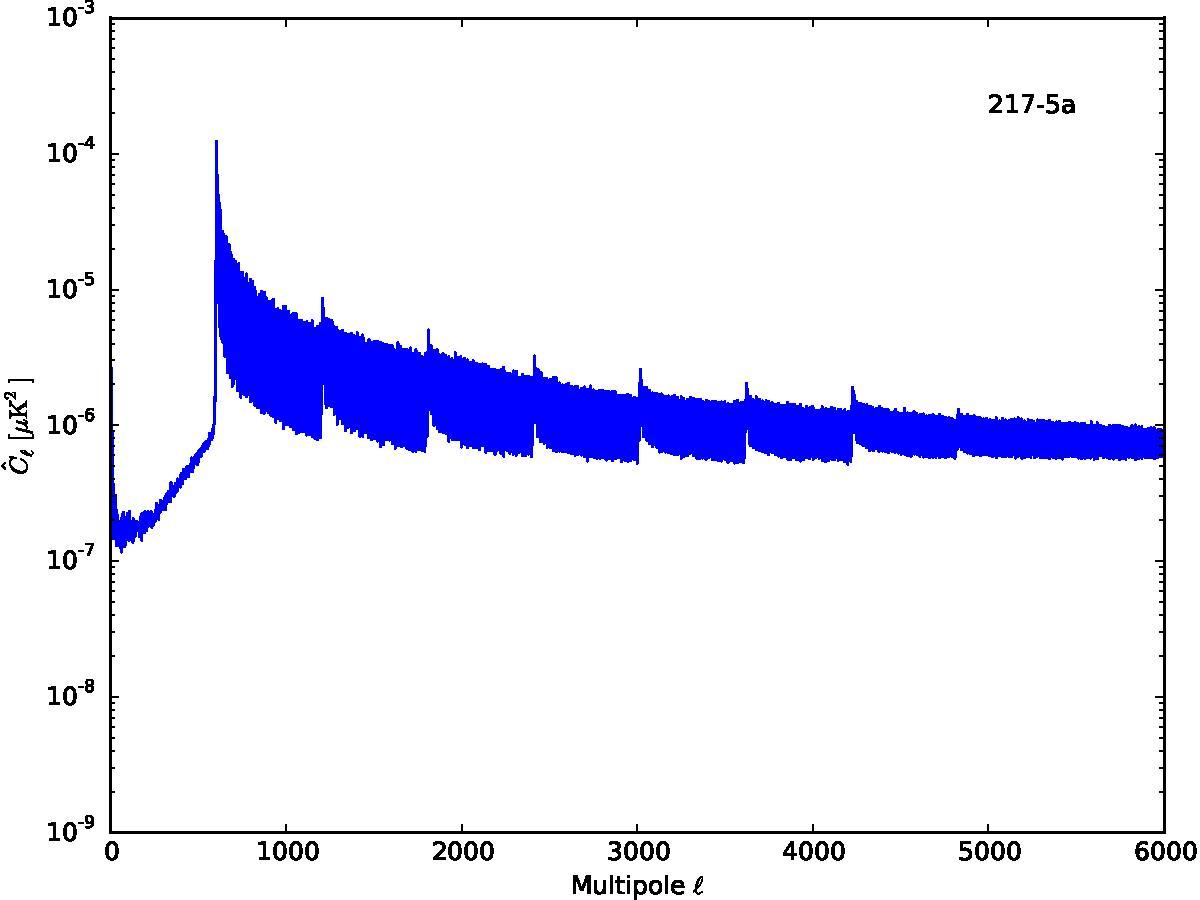
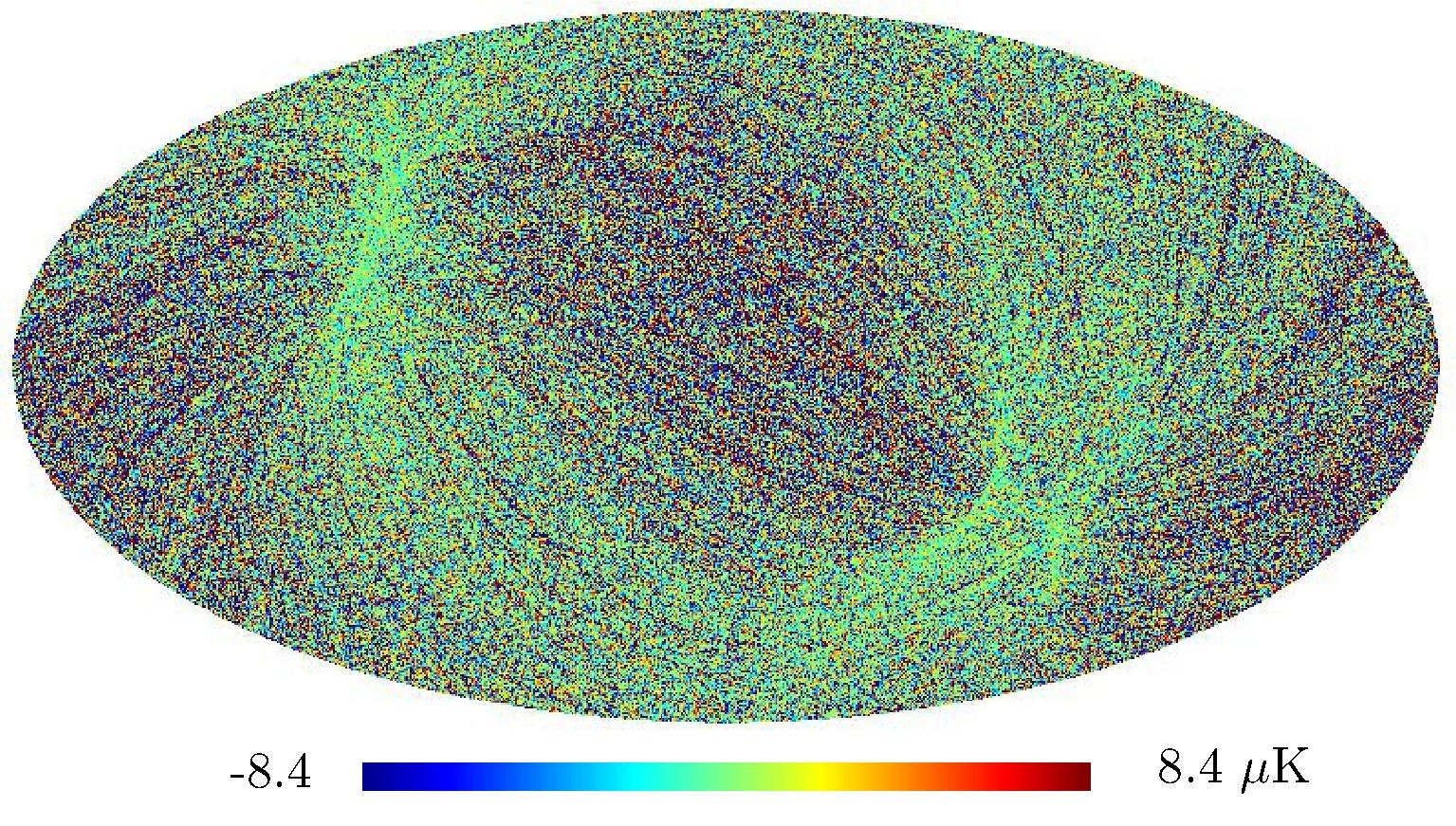
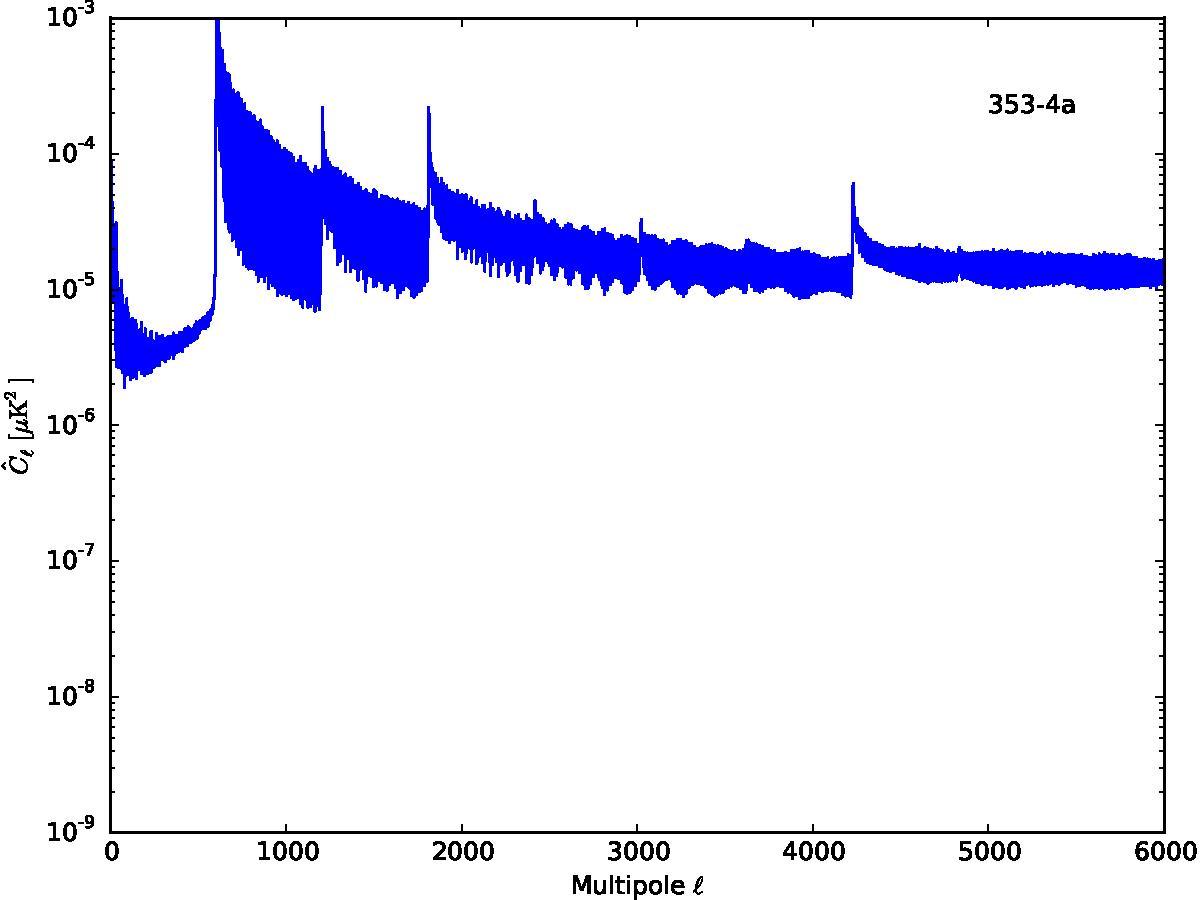
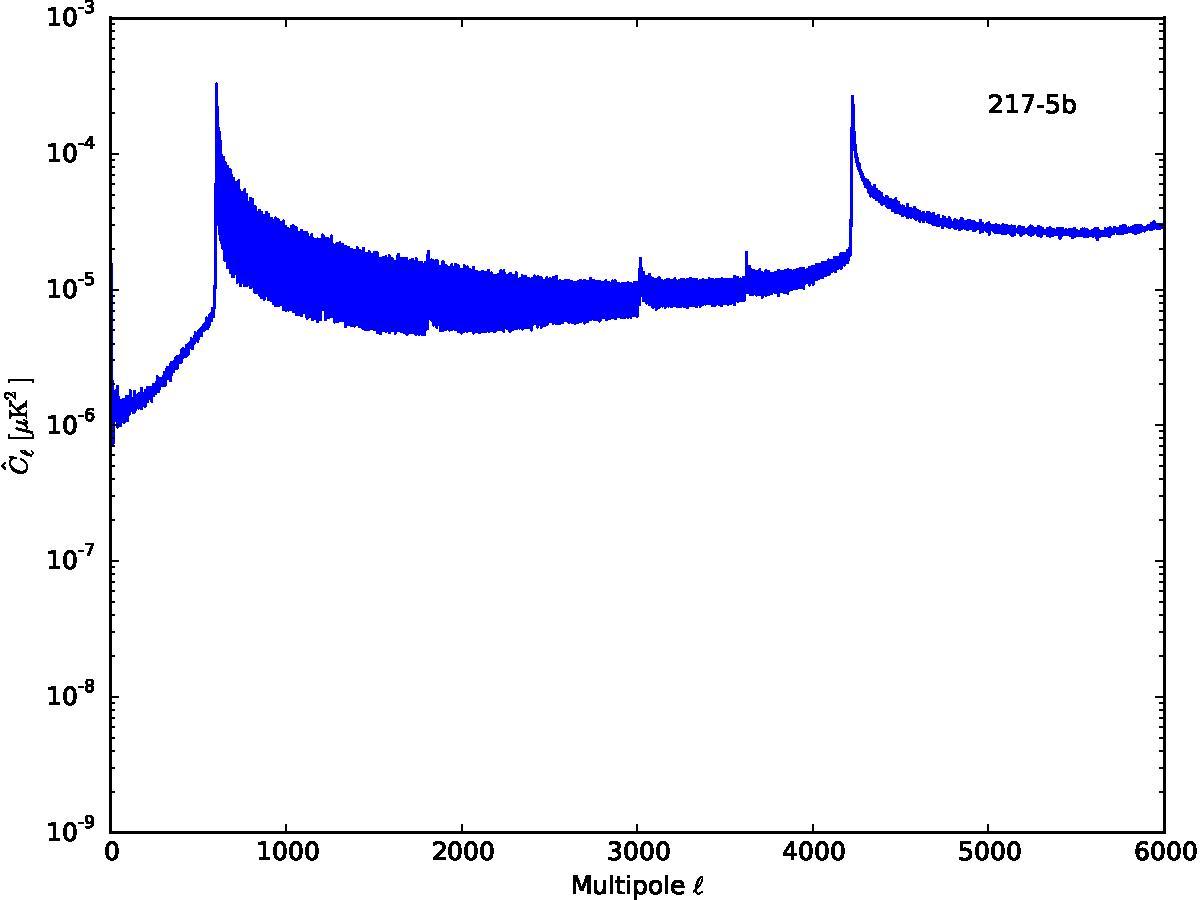
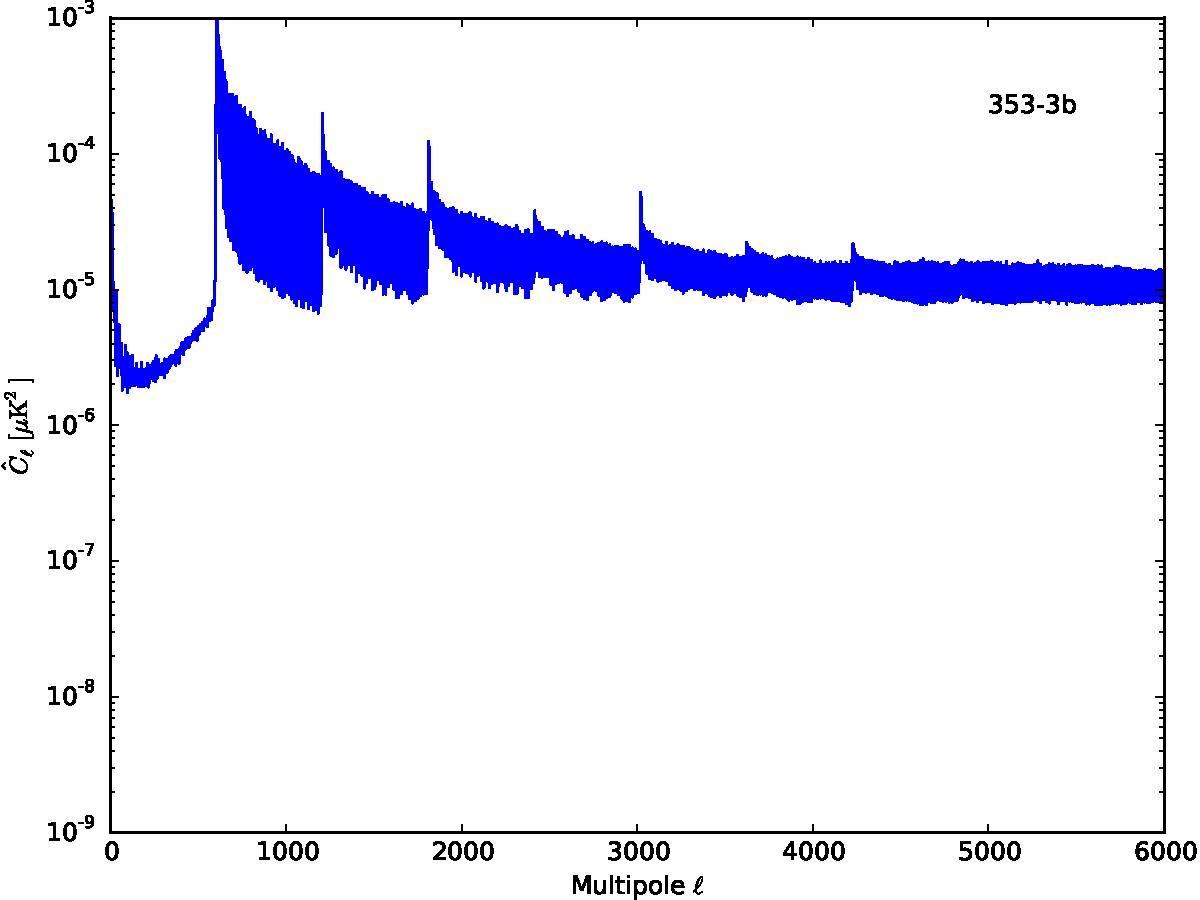
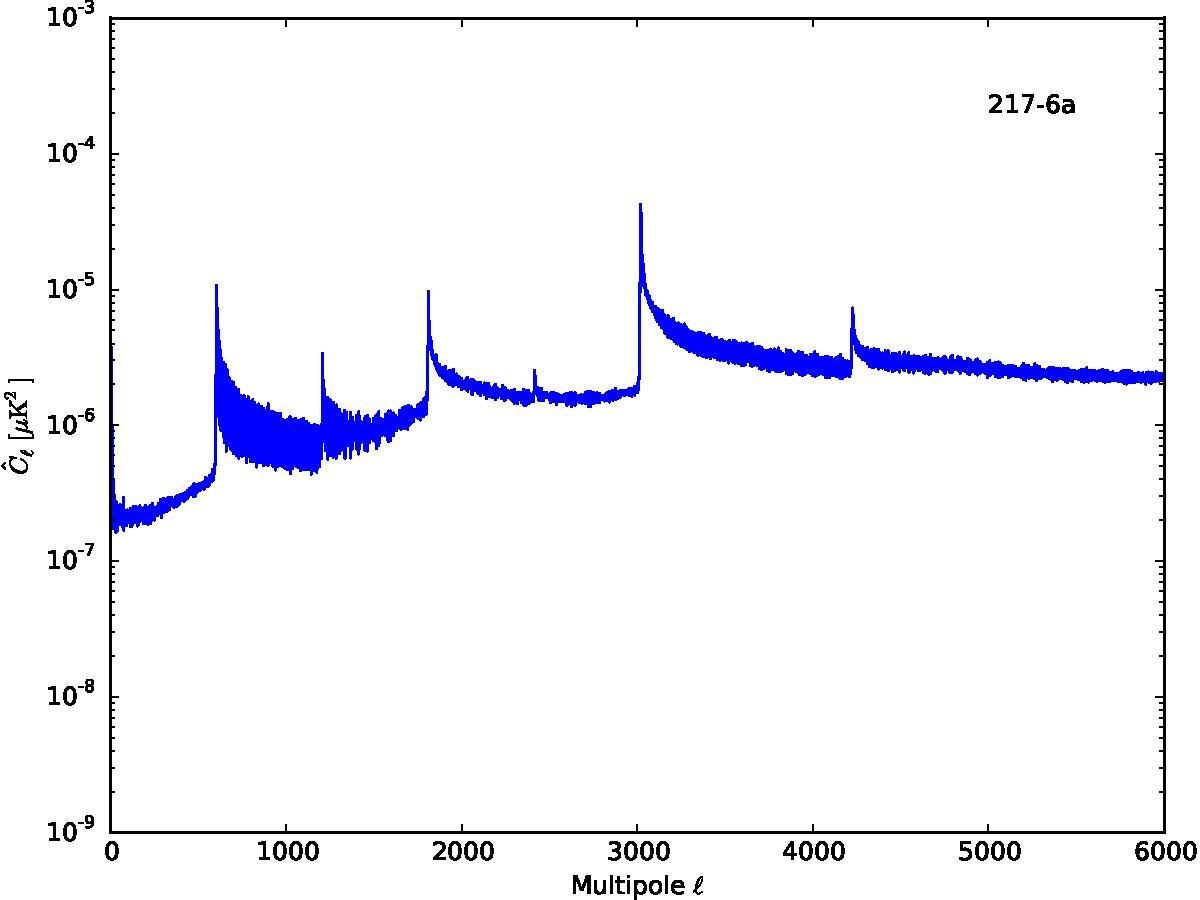
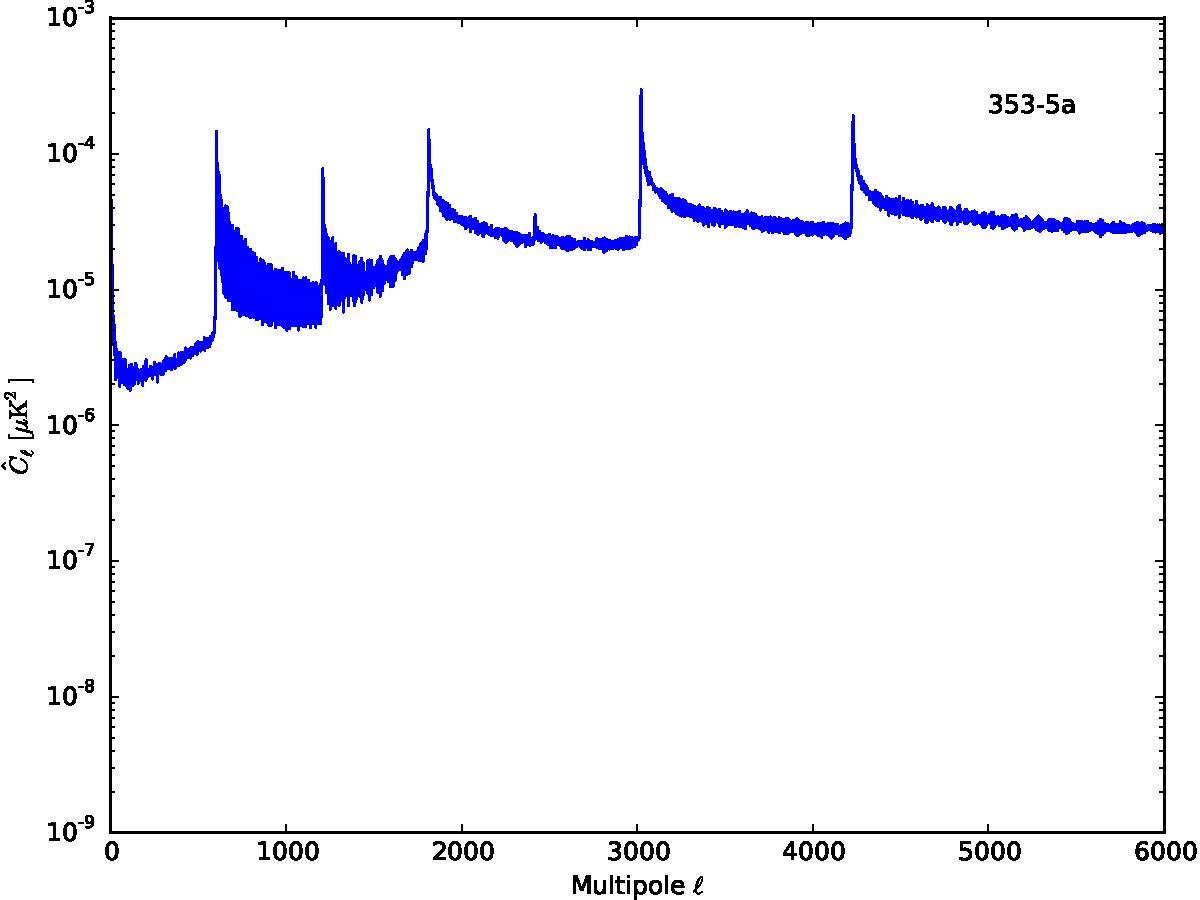
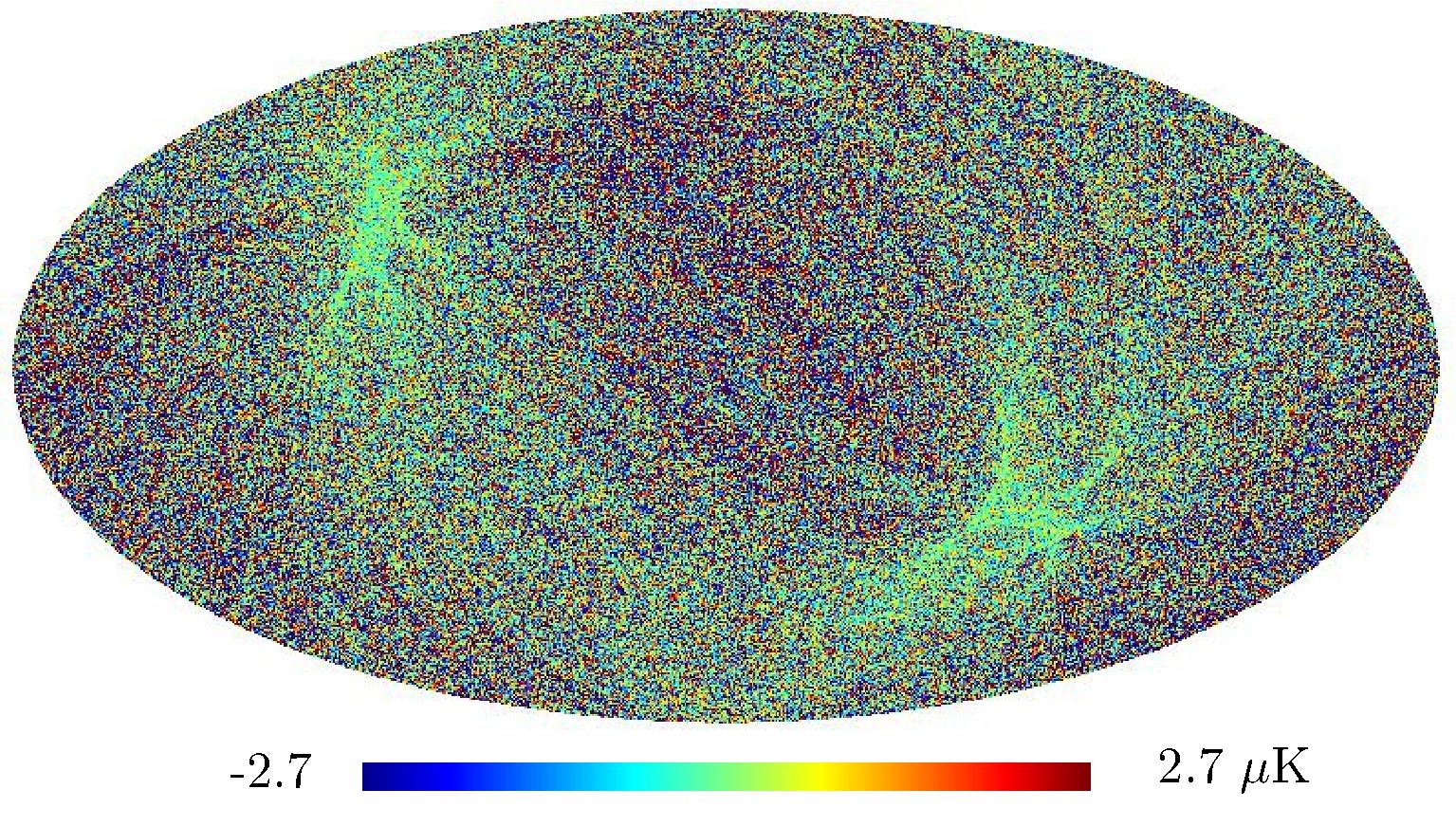
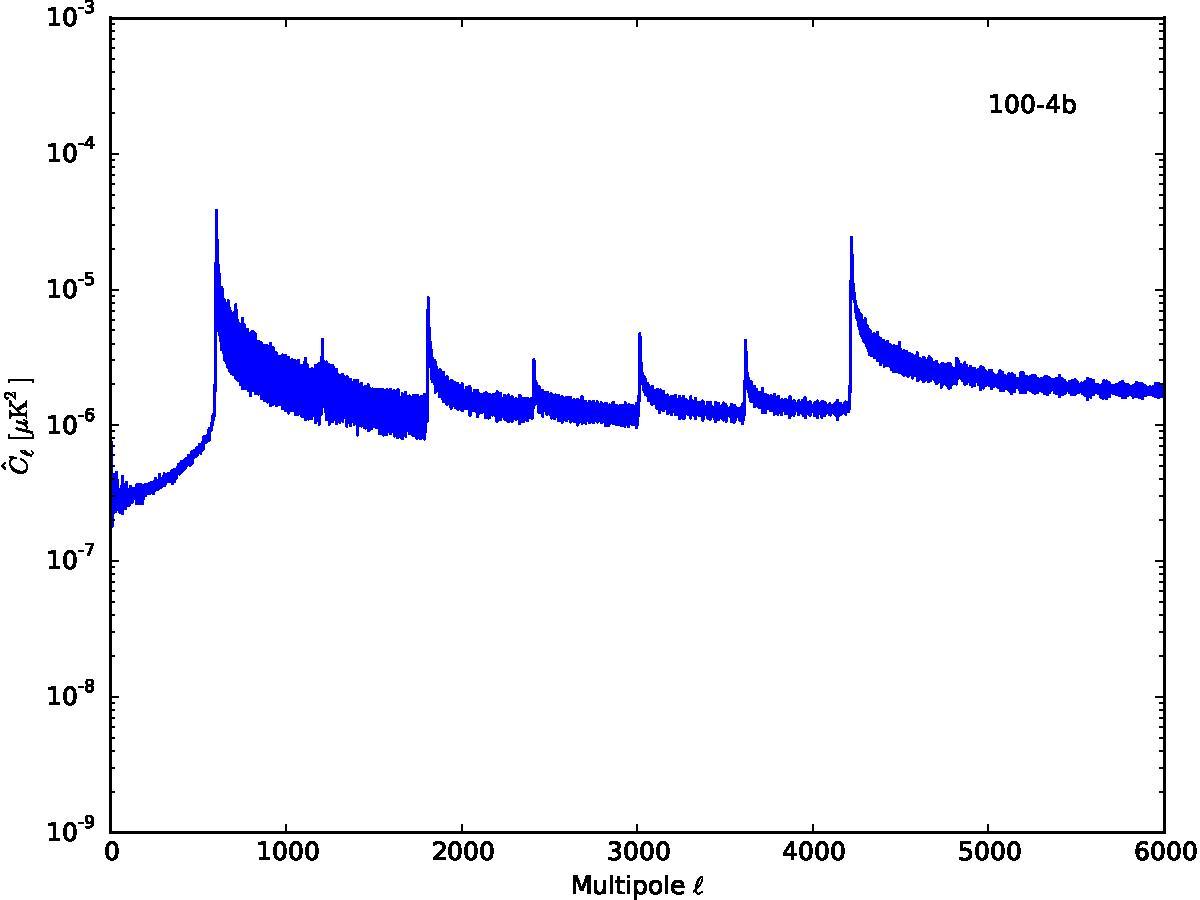
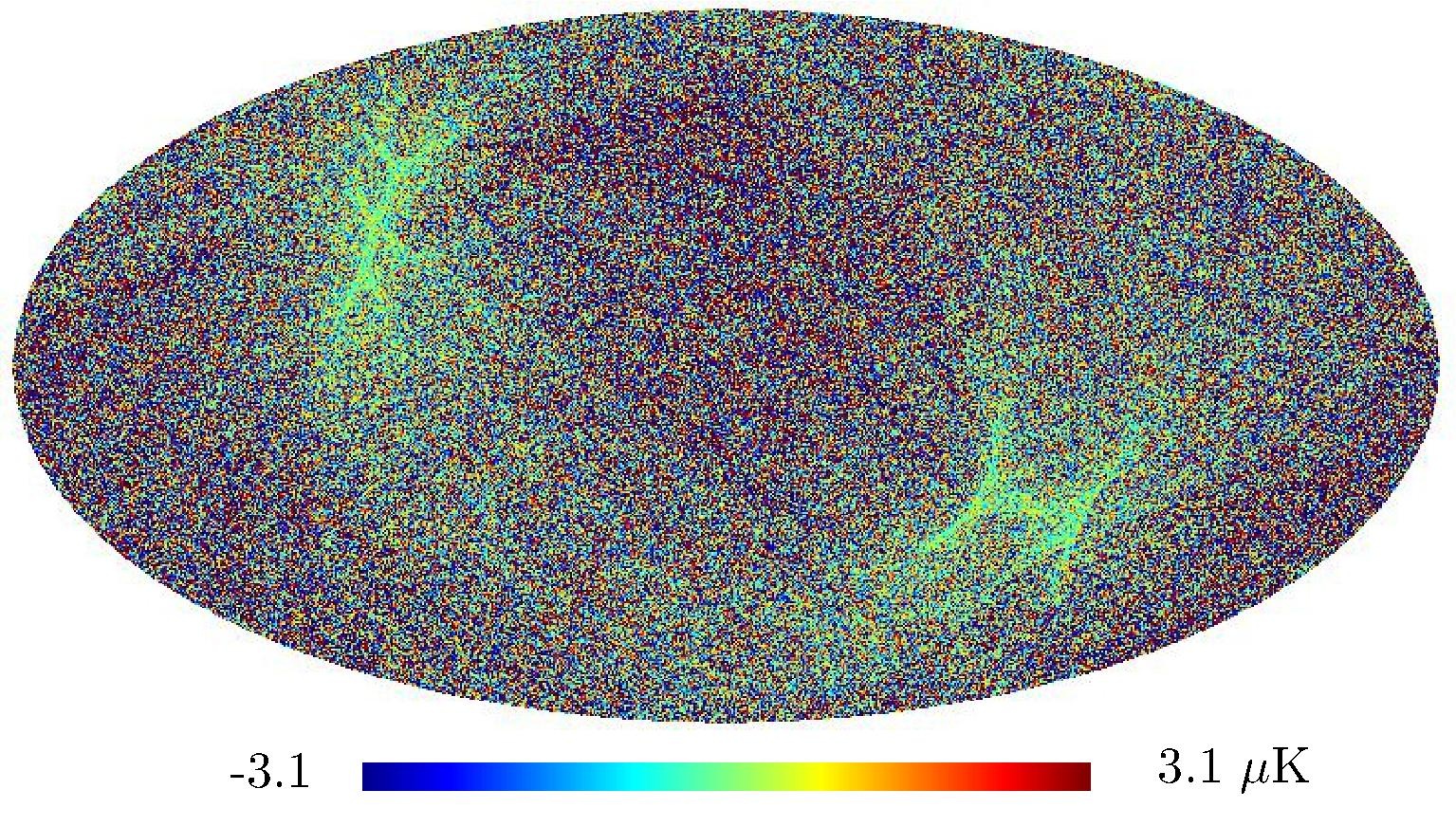
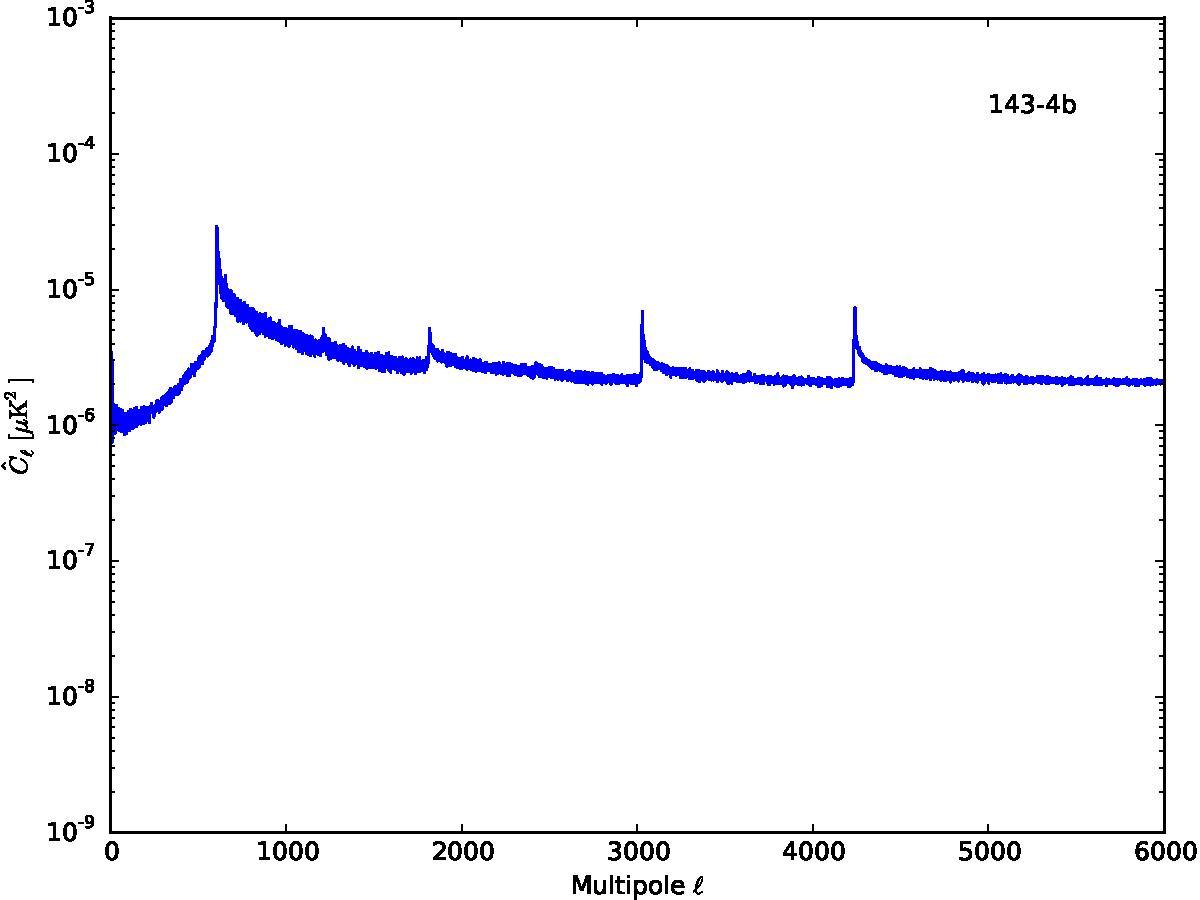
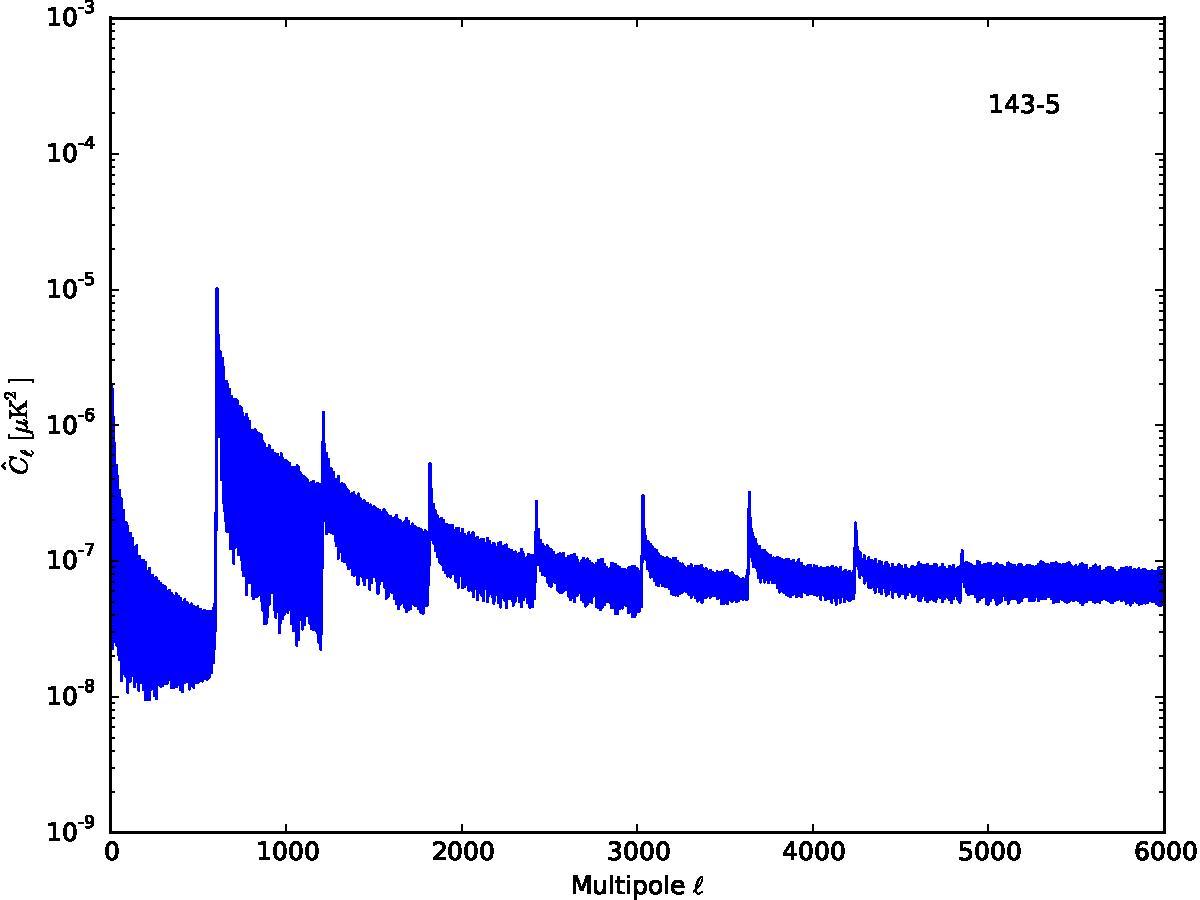
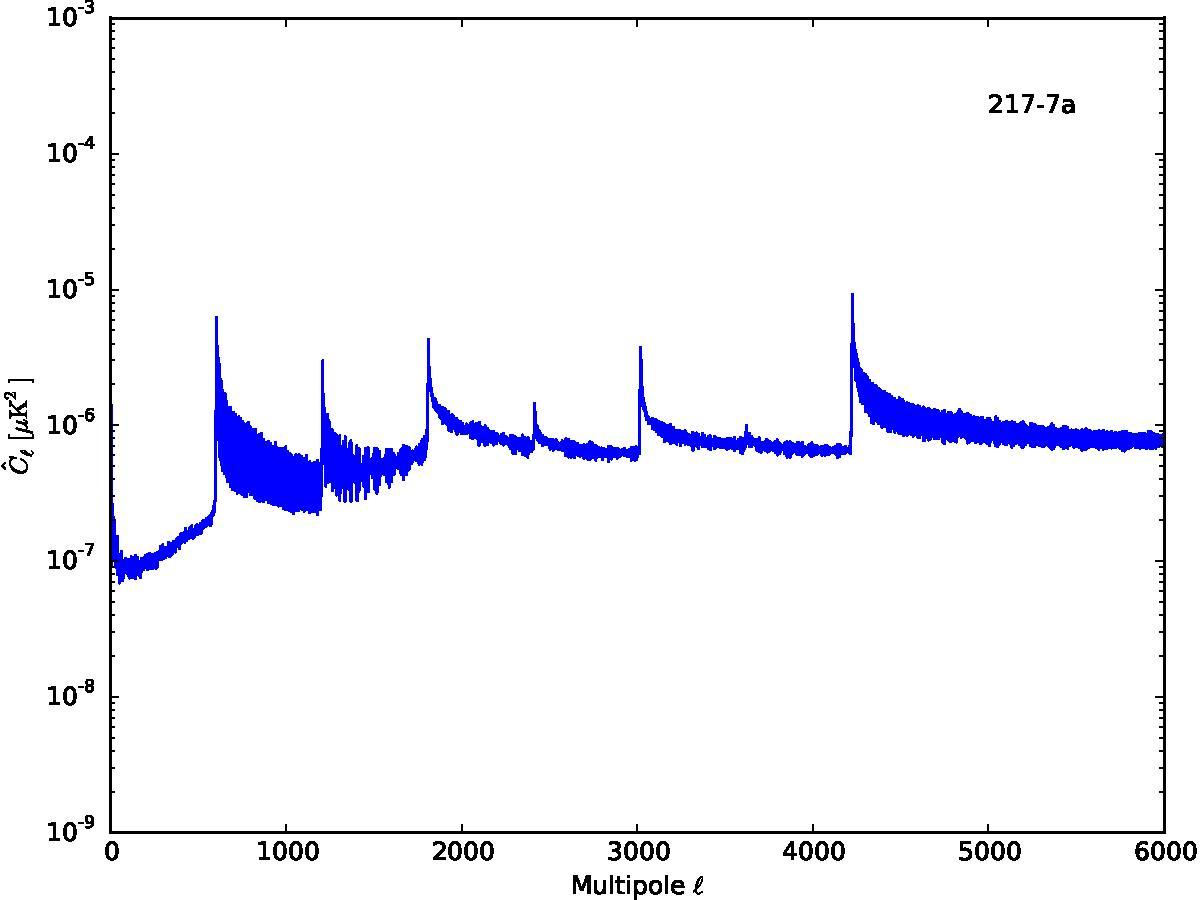
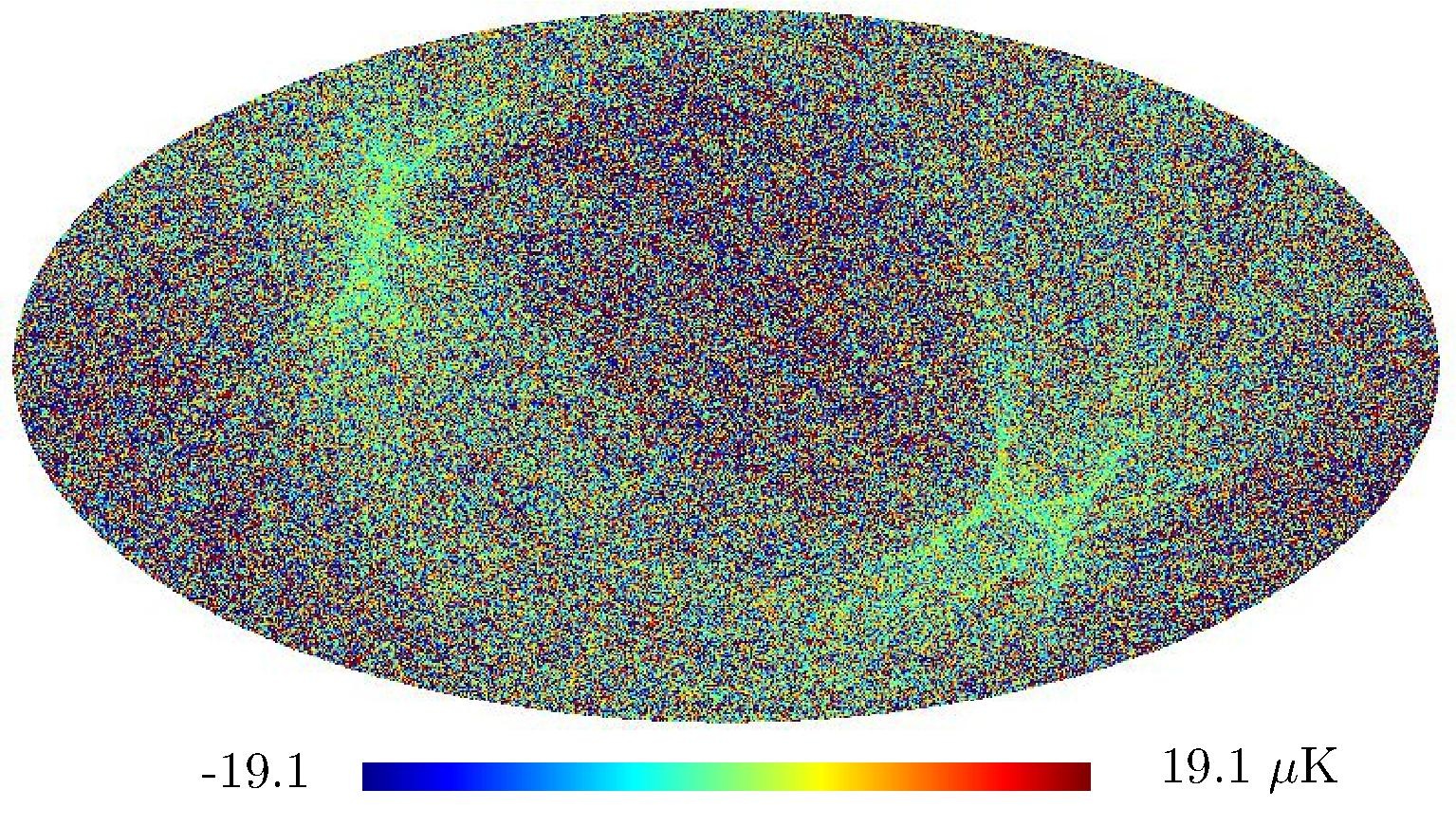
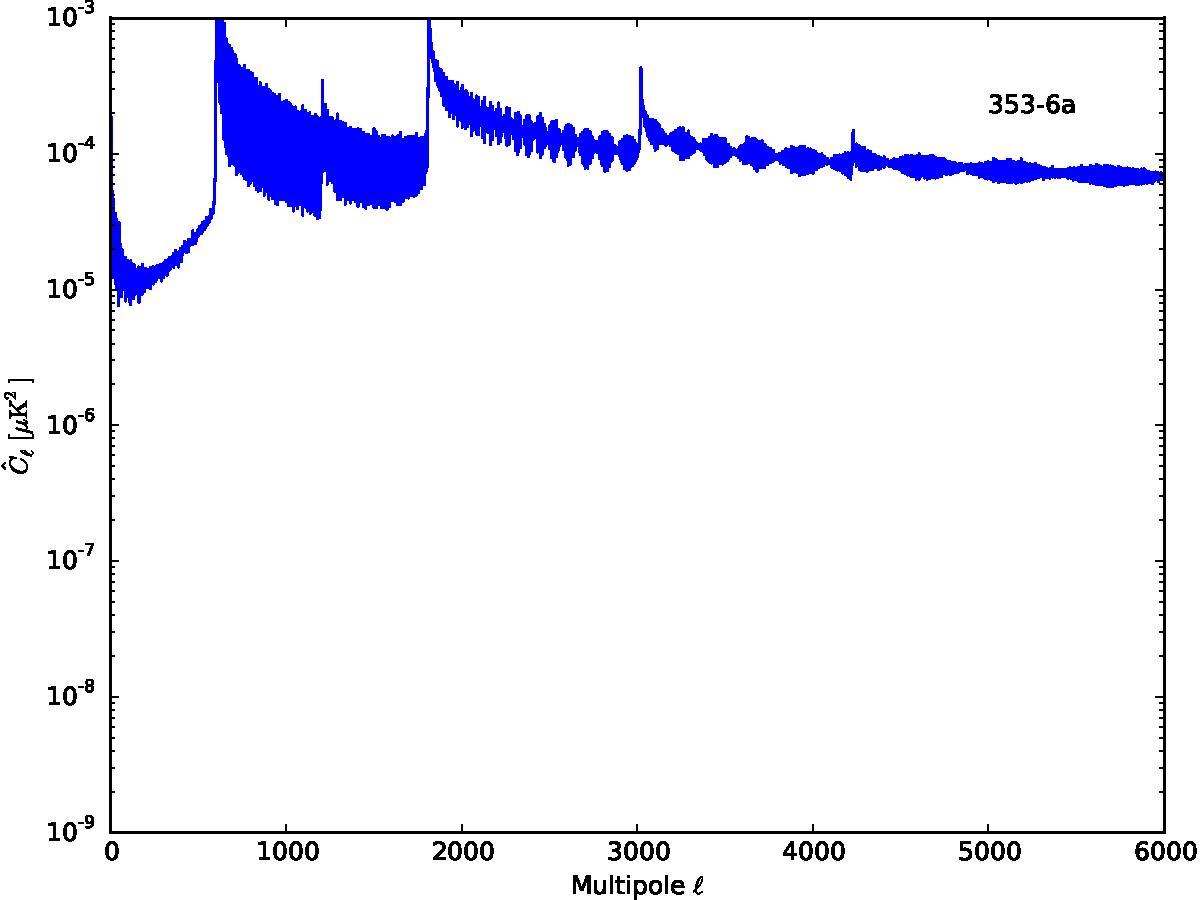
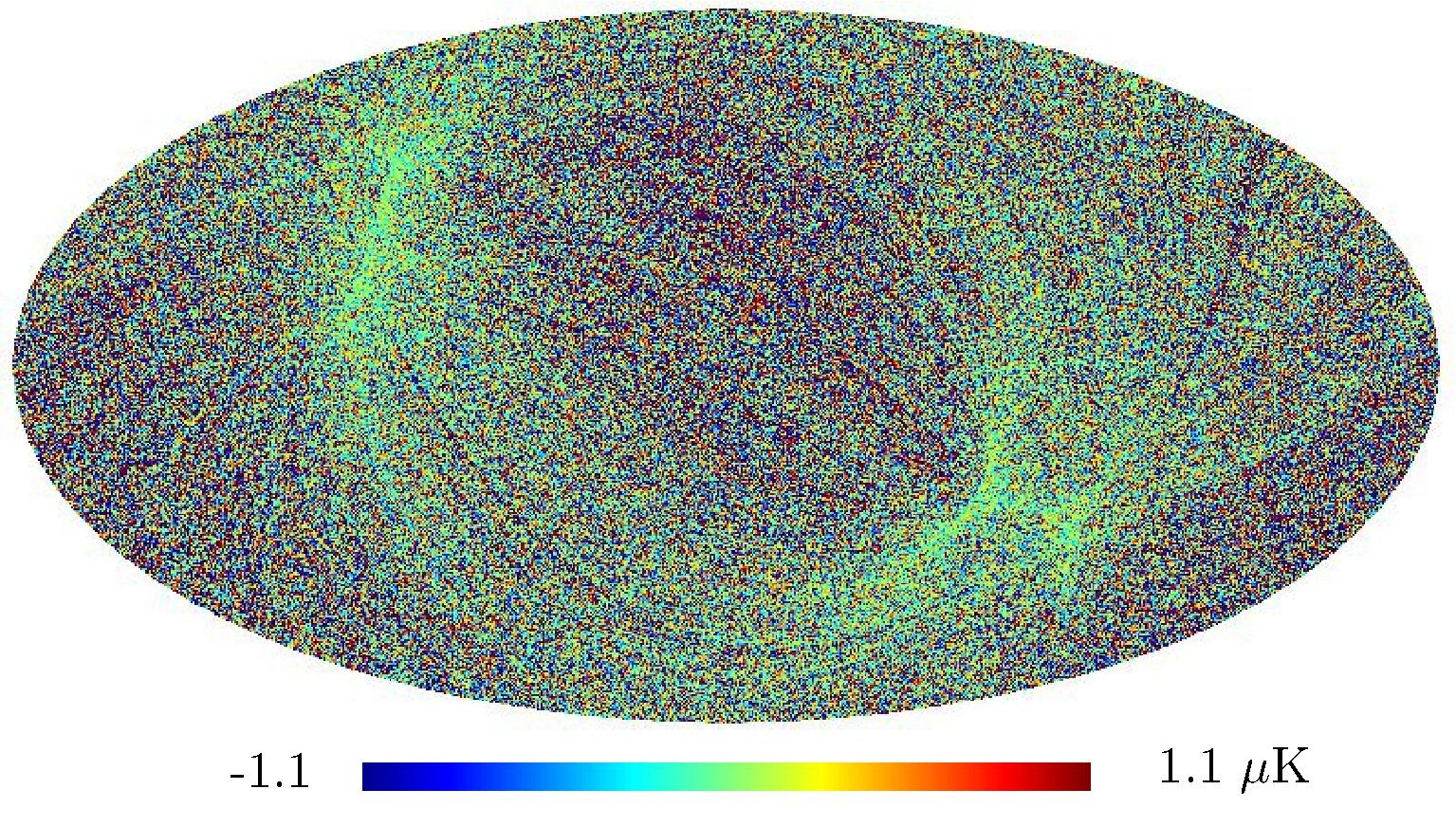
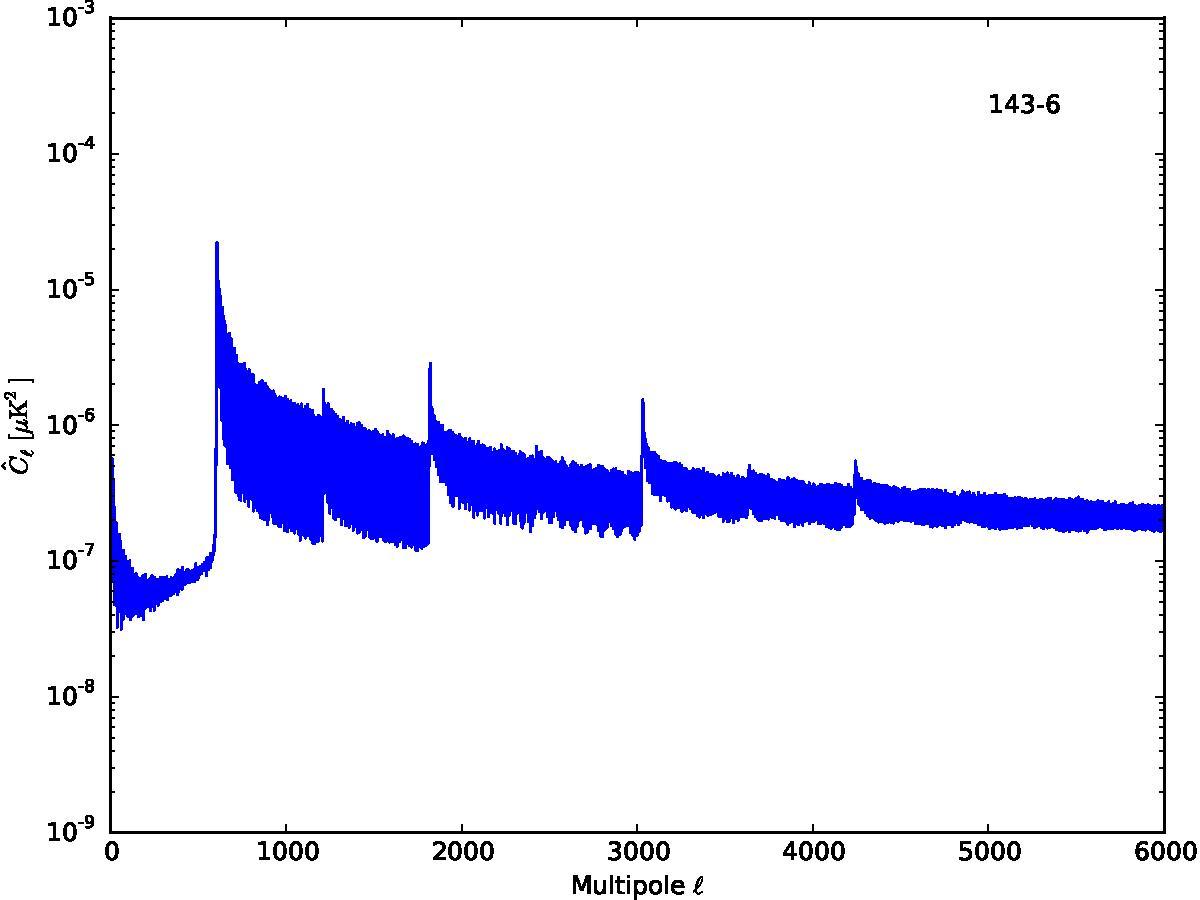
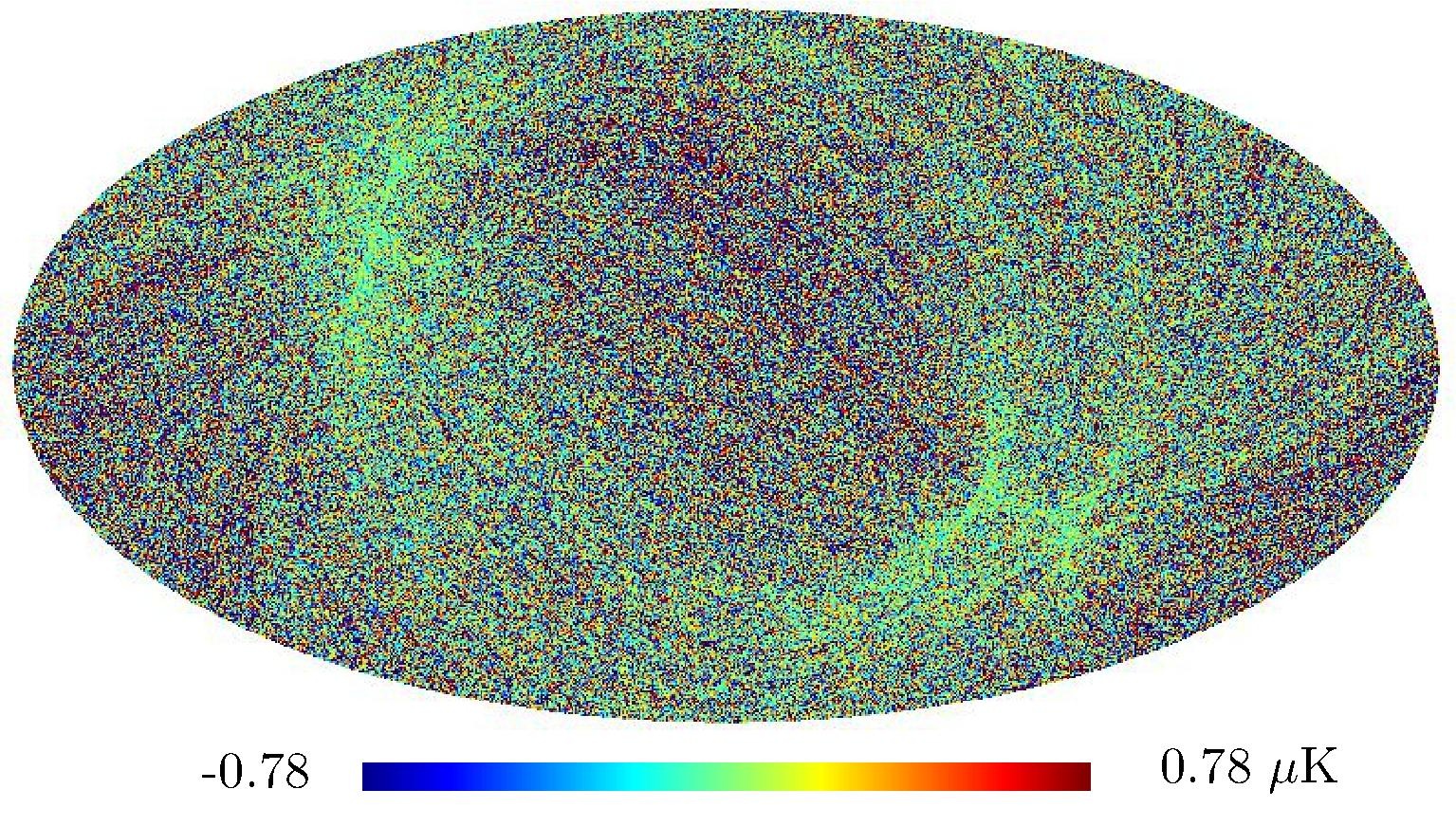
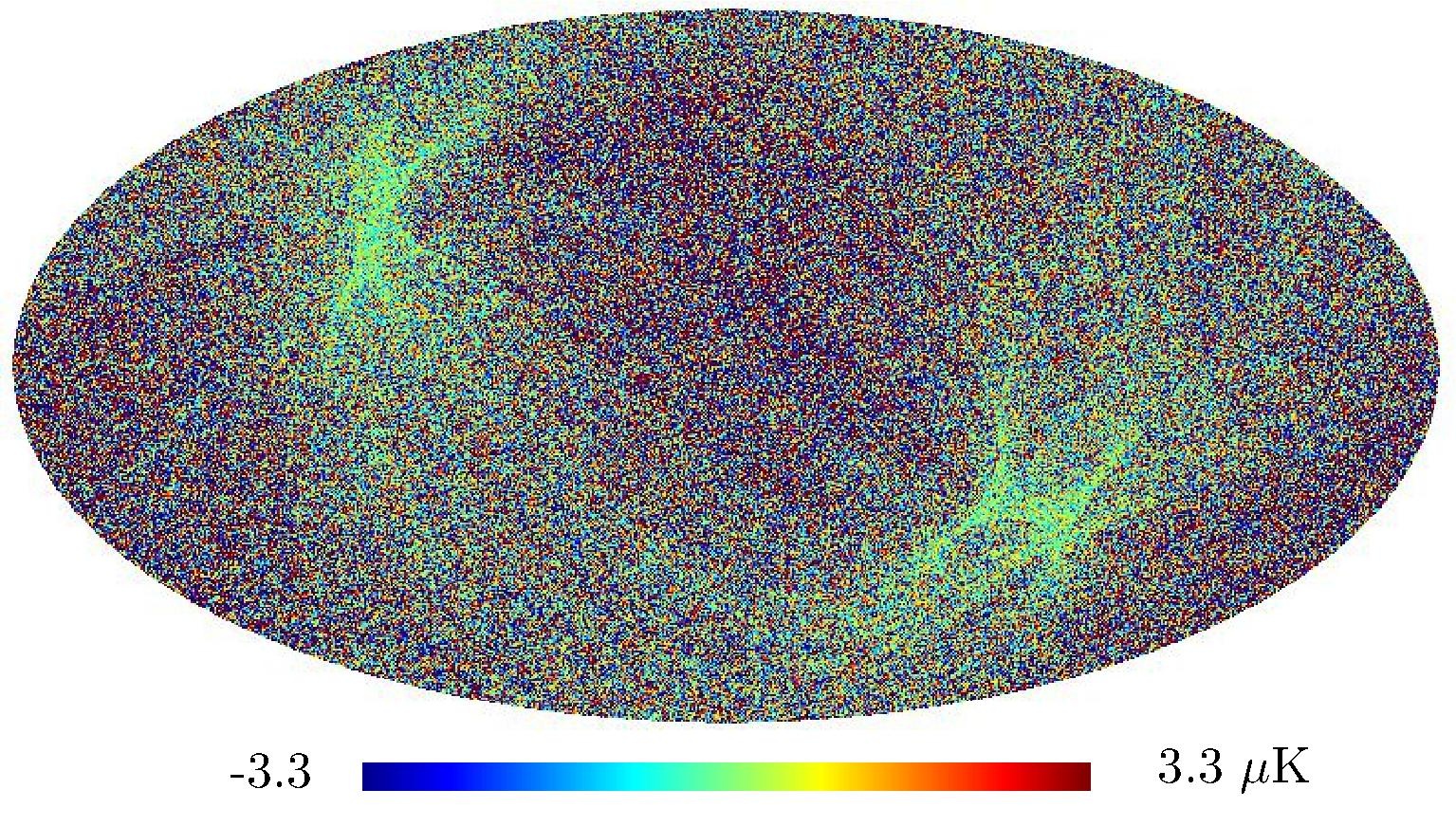
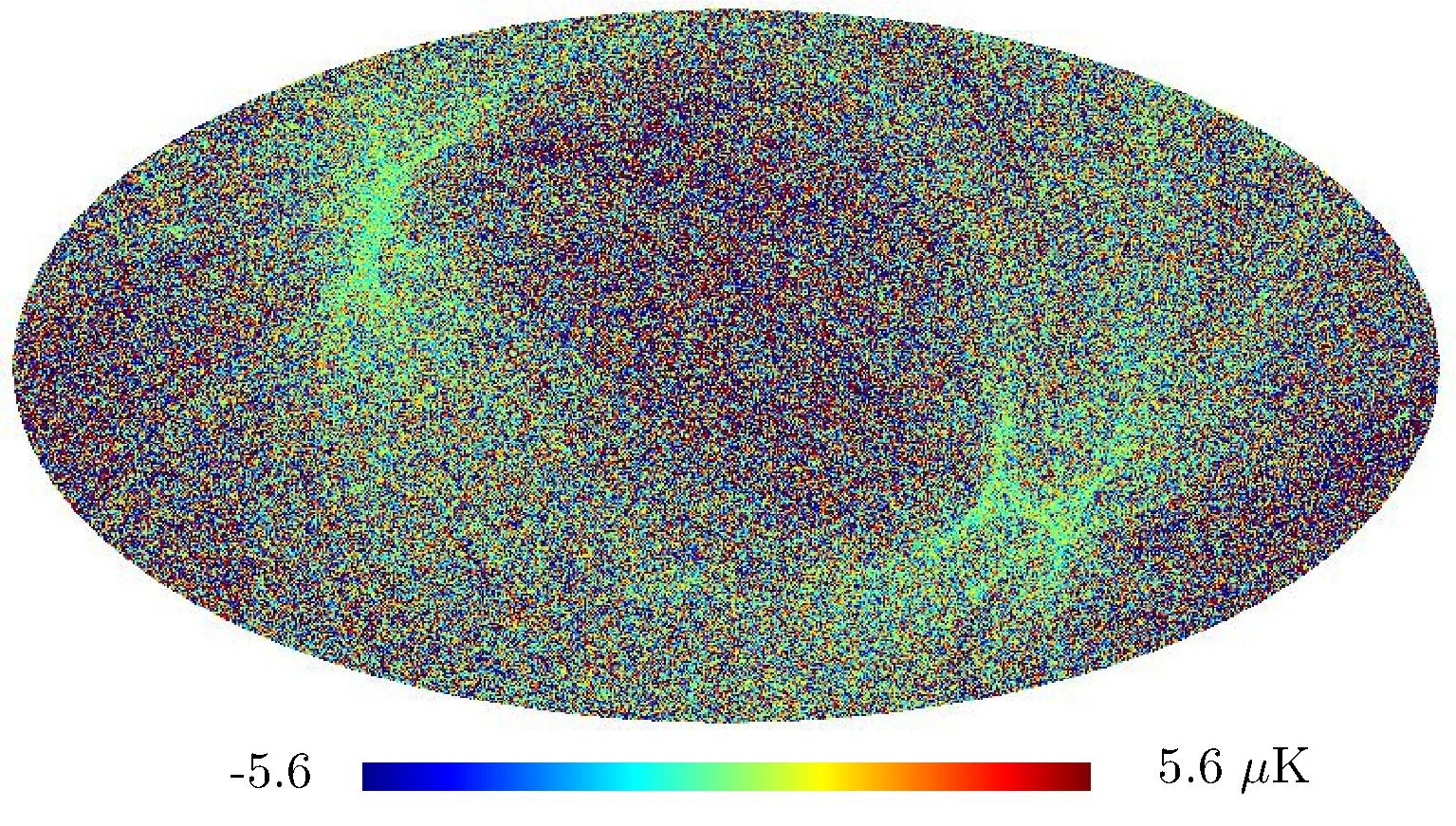
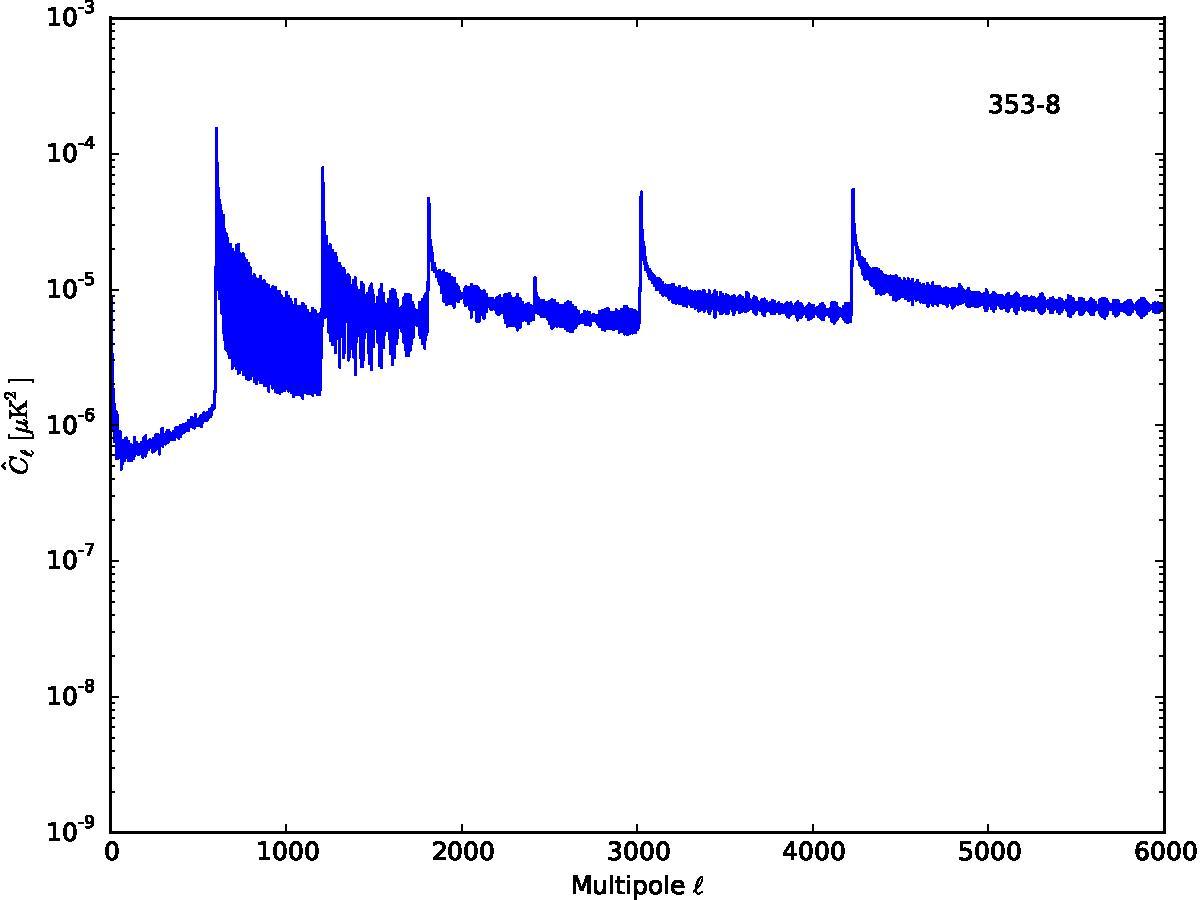
Section 5.5: complementary figures of Fig. 29
| 100 GHz bolometers | 143 GHz bolometers | 217 GHz bolometers | 353 GHz bolometers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
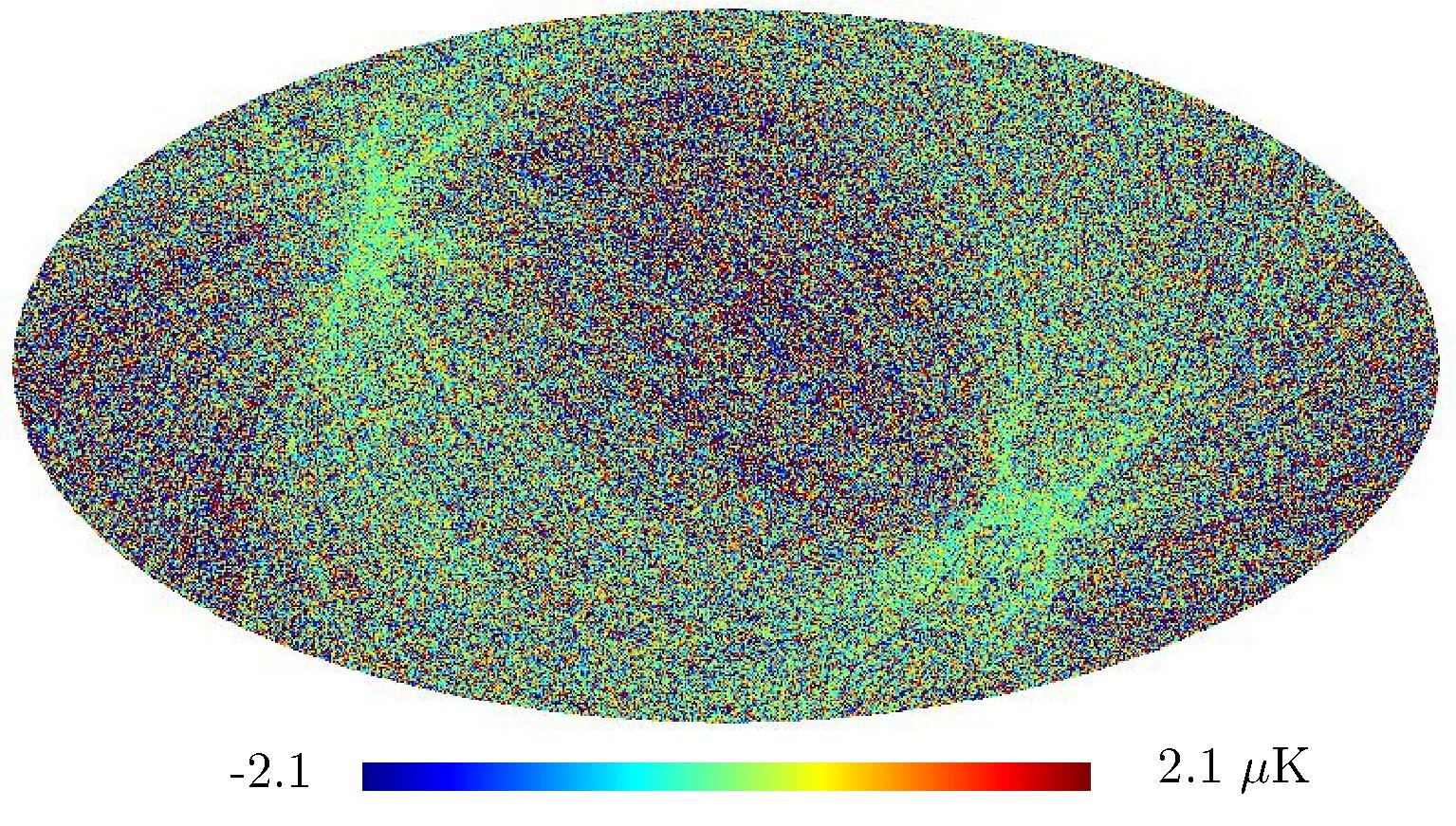
|
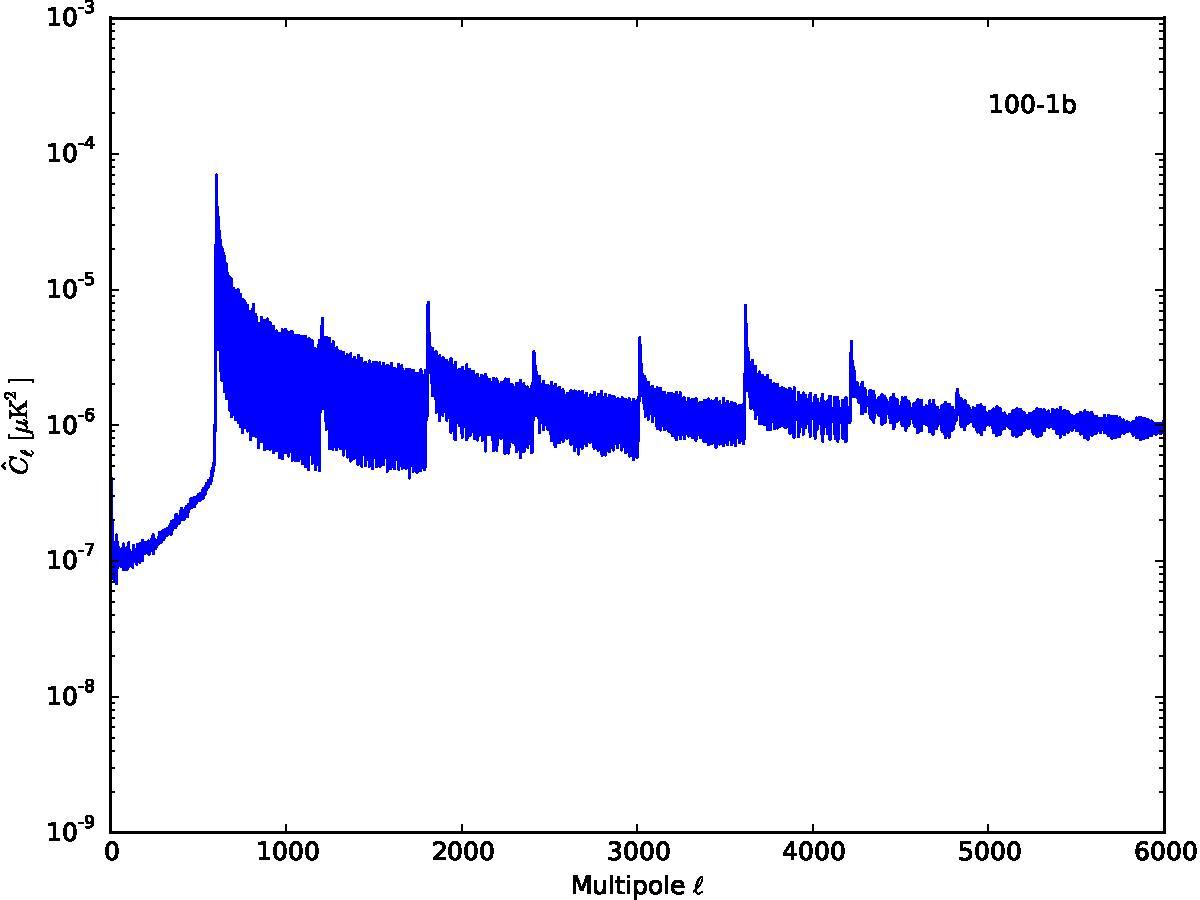
|
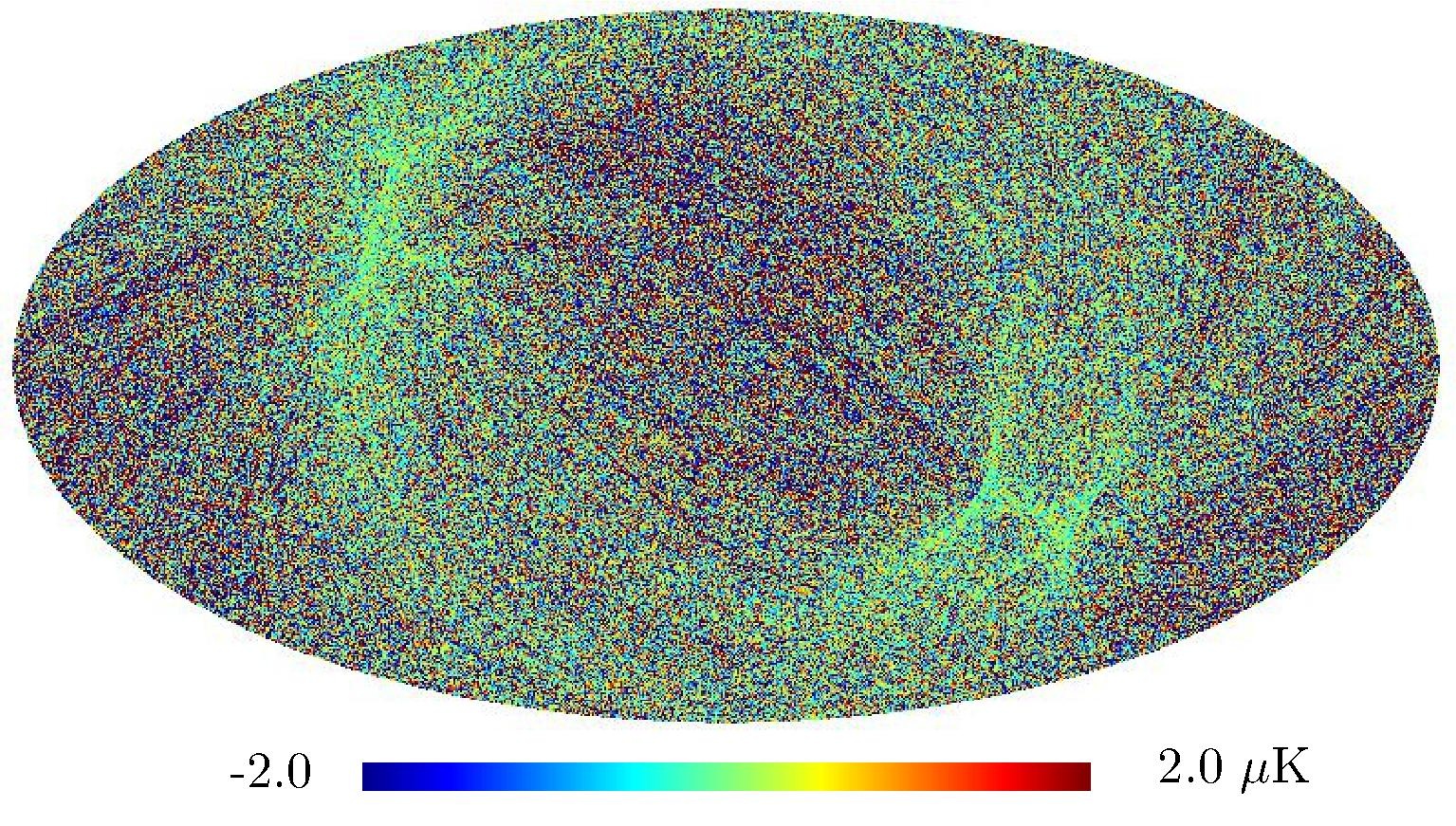
|
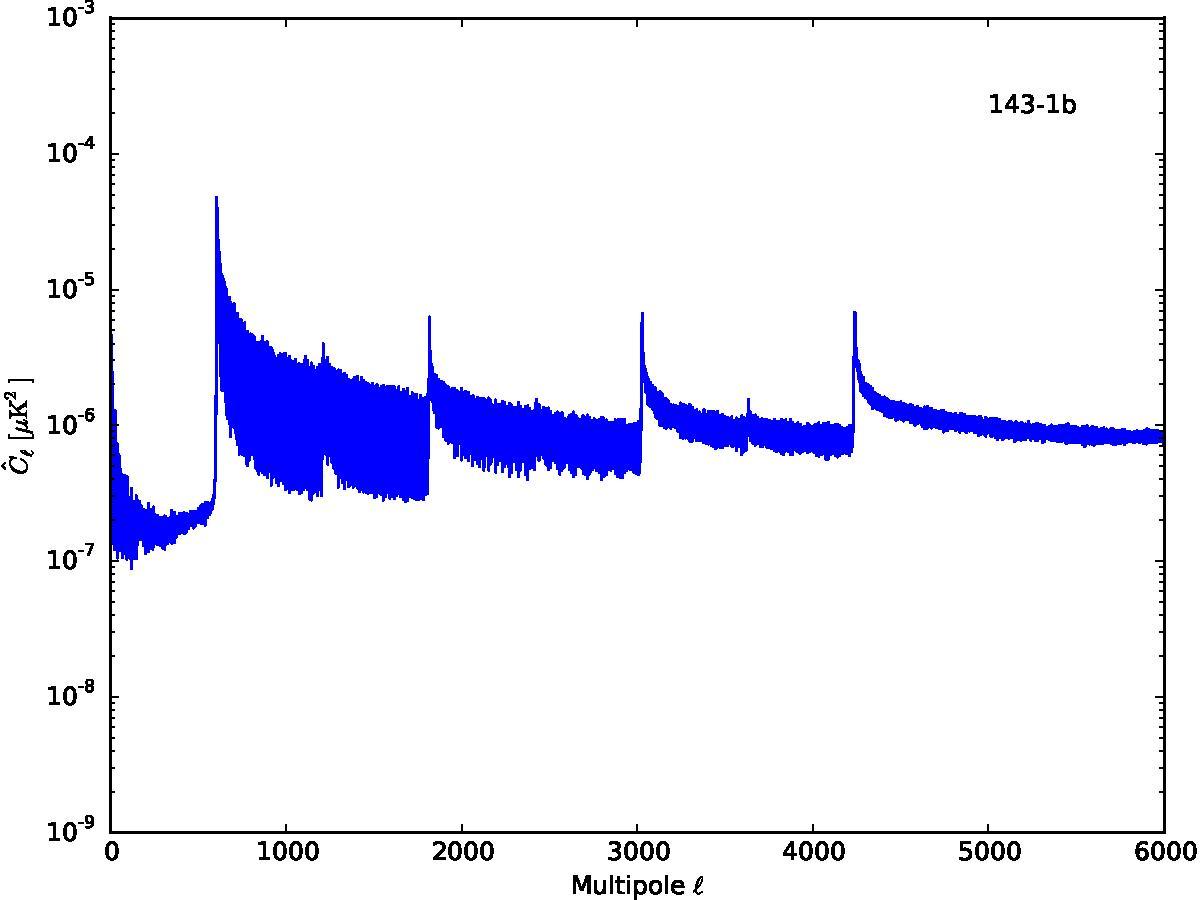
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
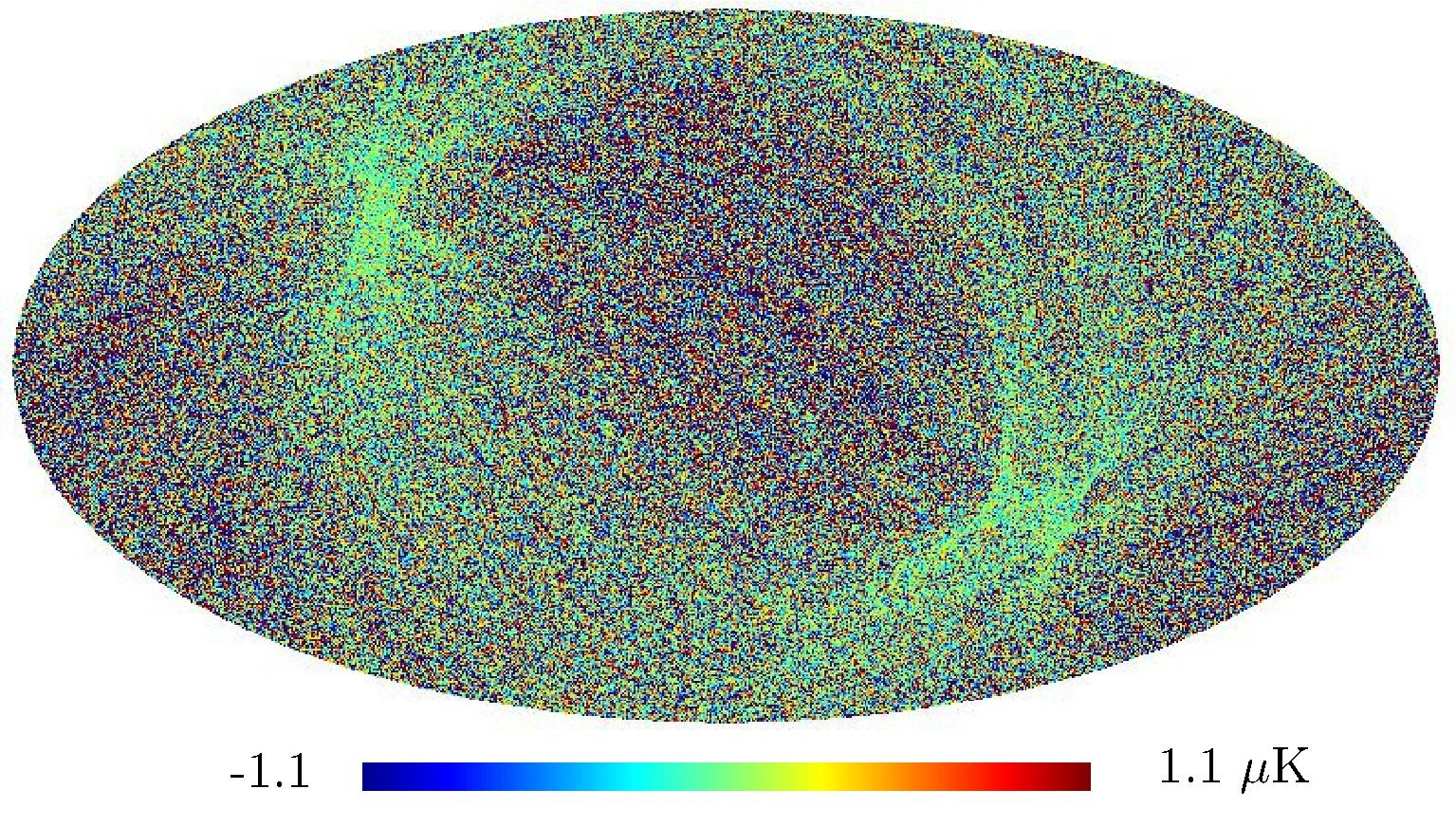
|
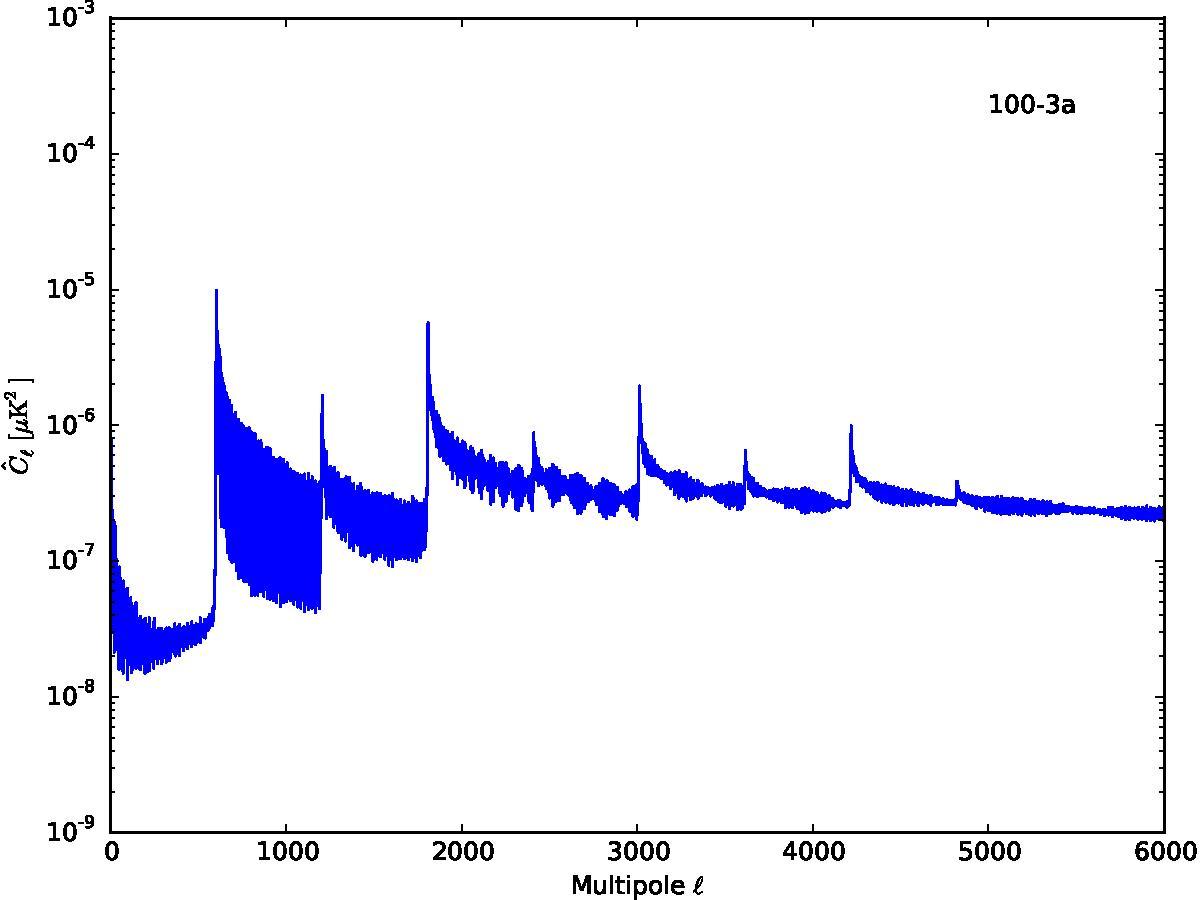
|
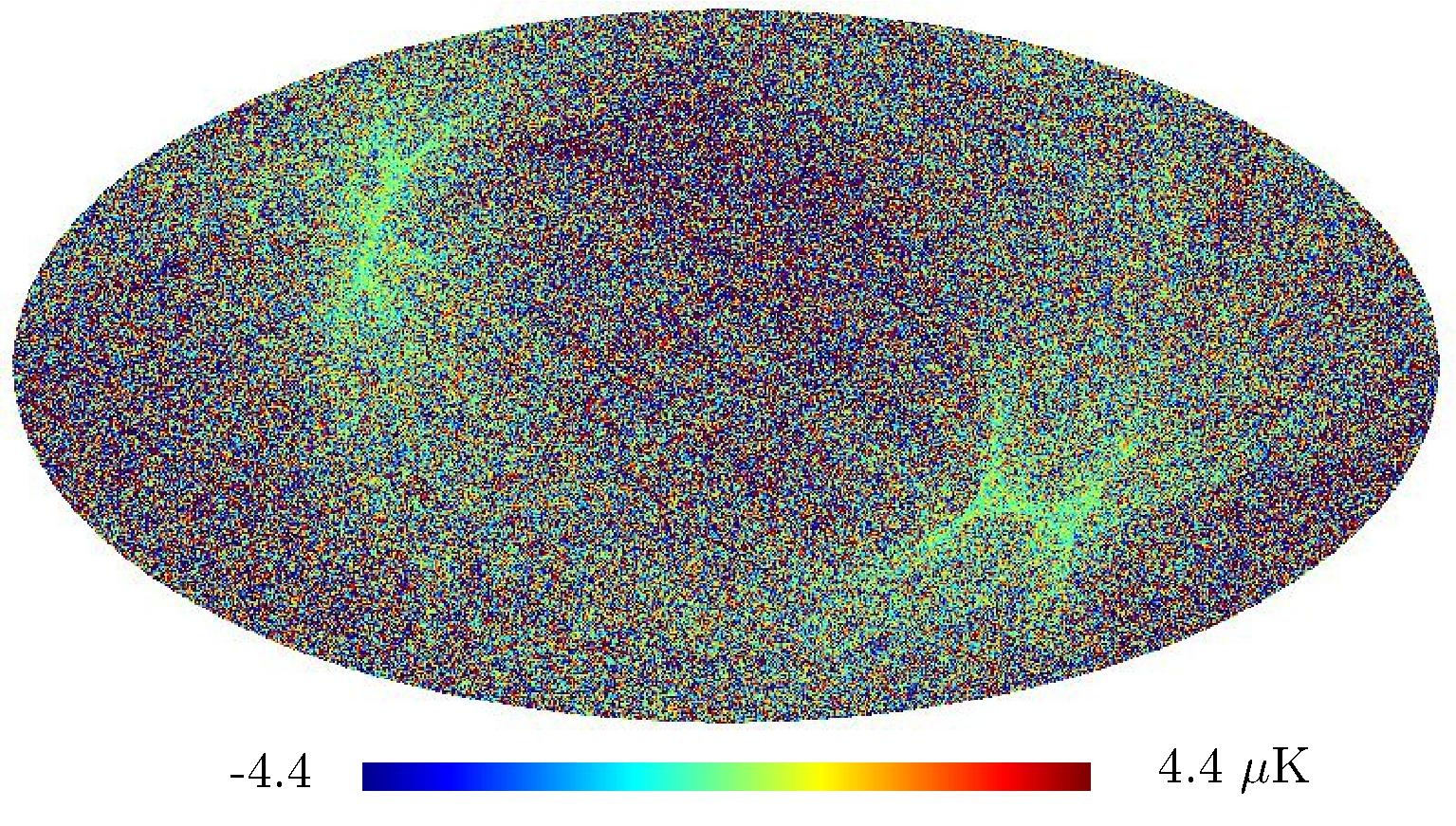
|
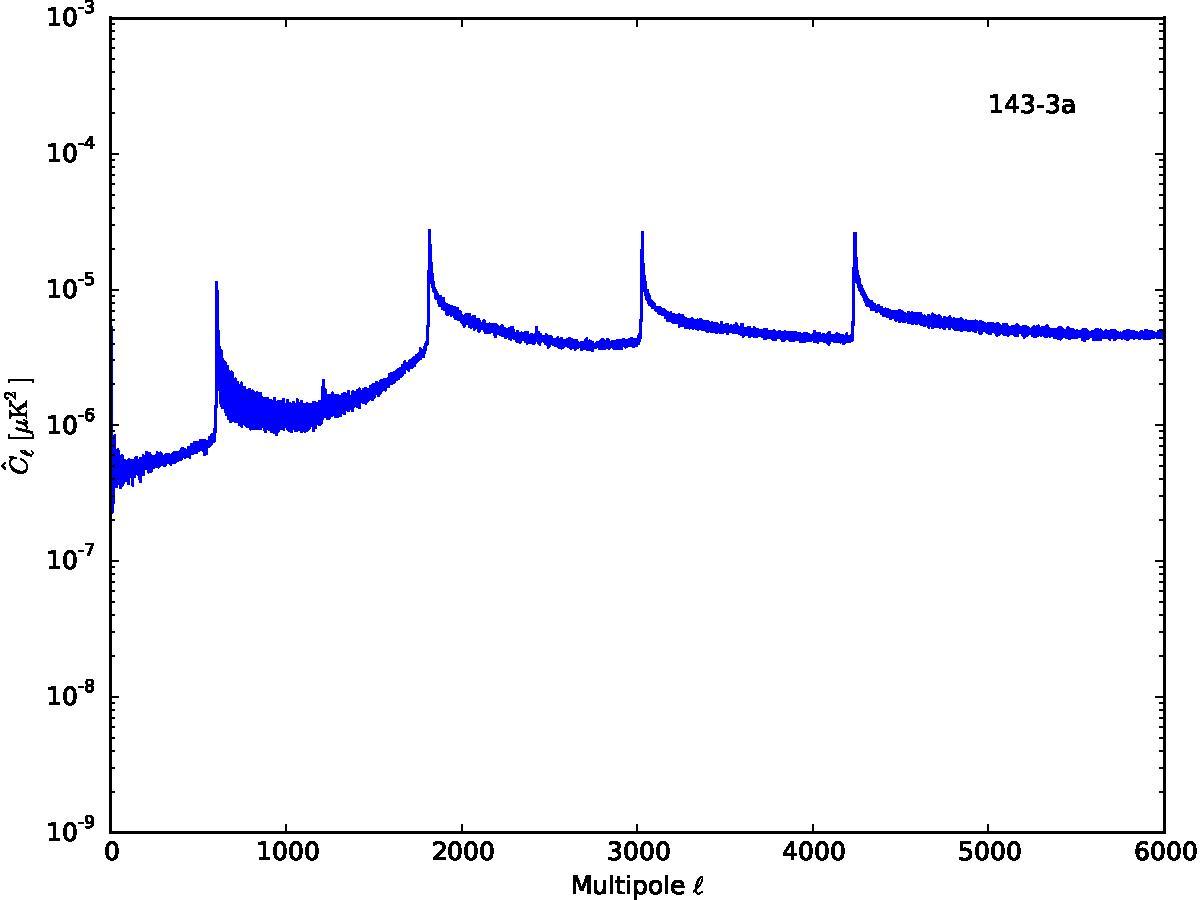
|
|
|
|
|
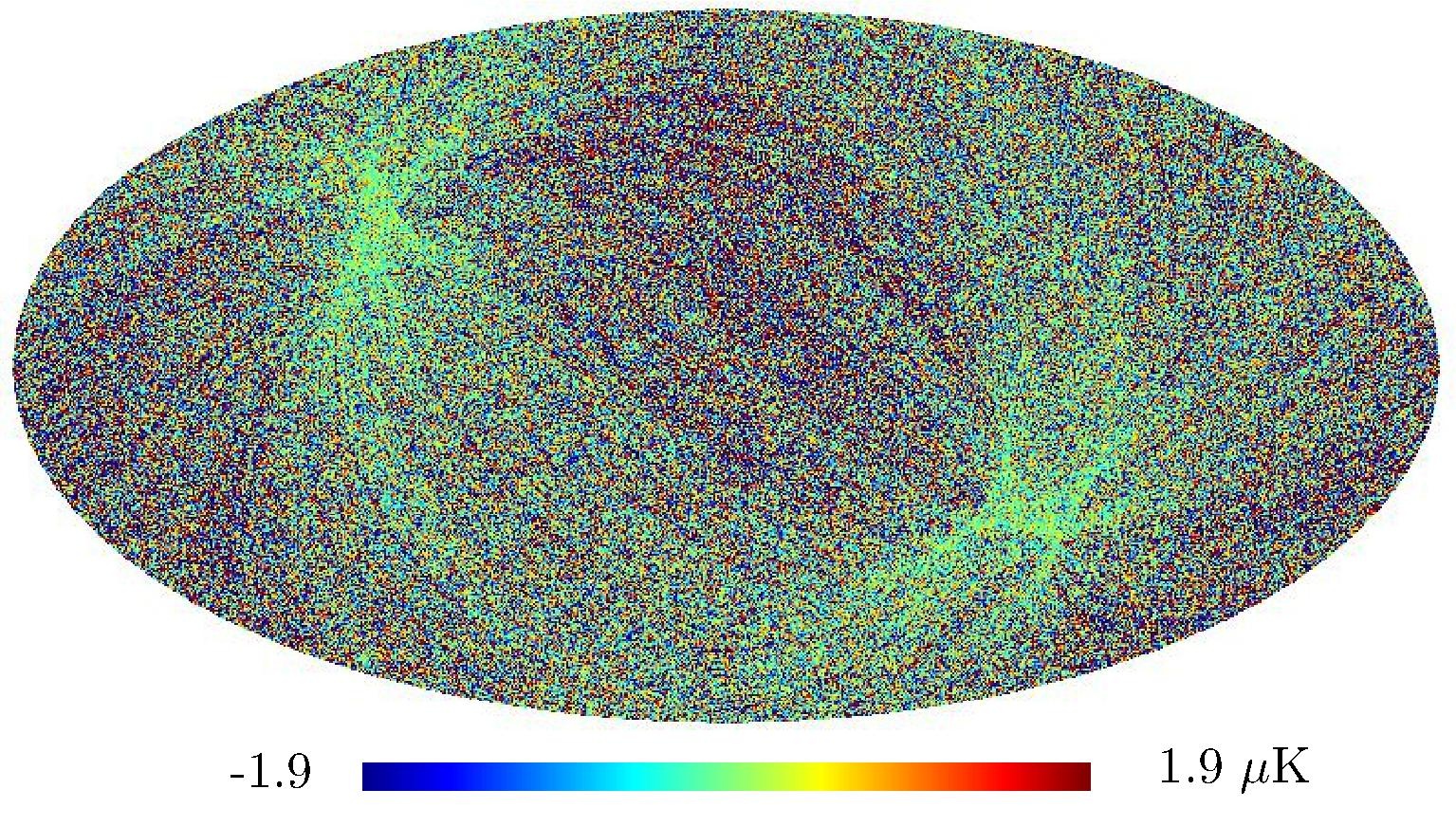
|
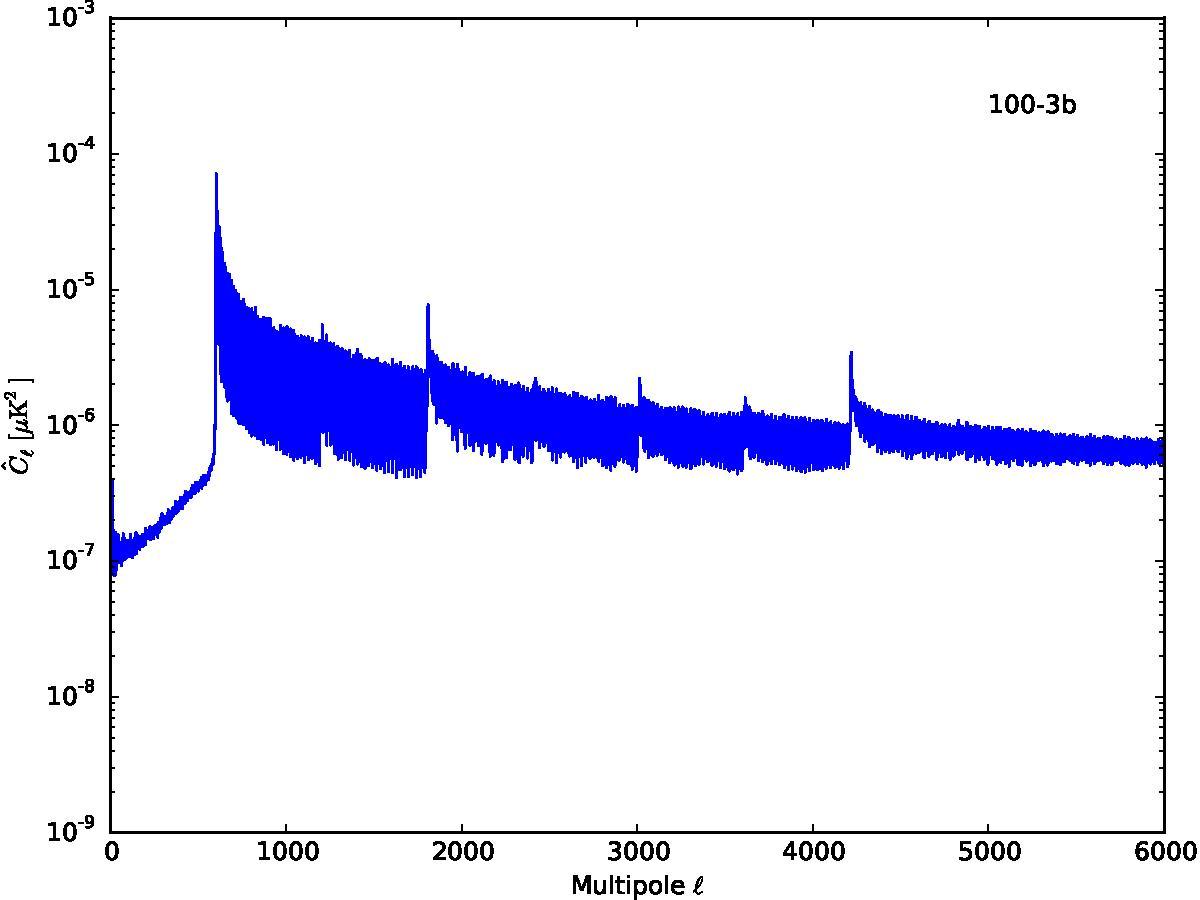
|
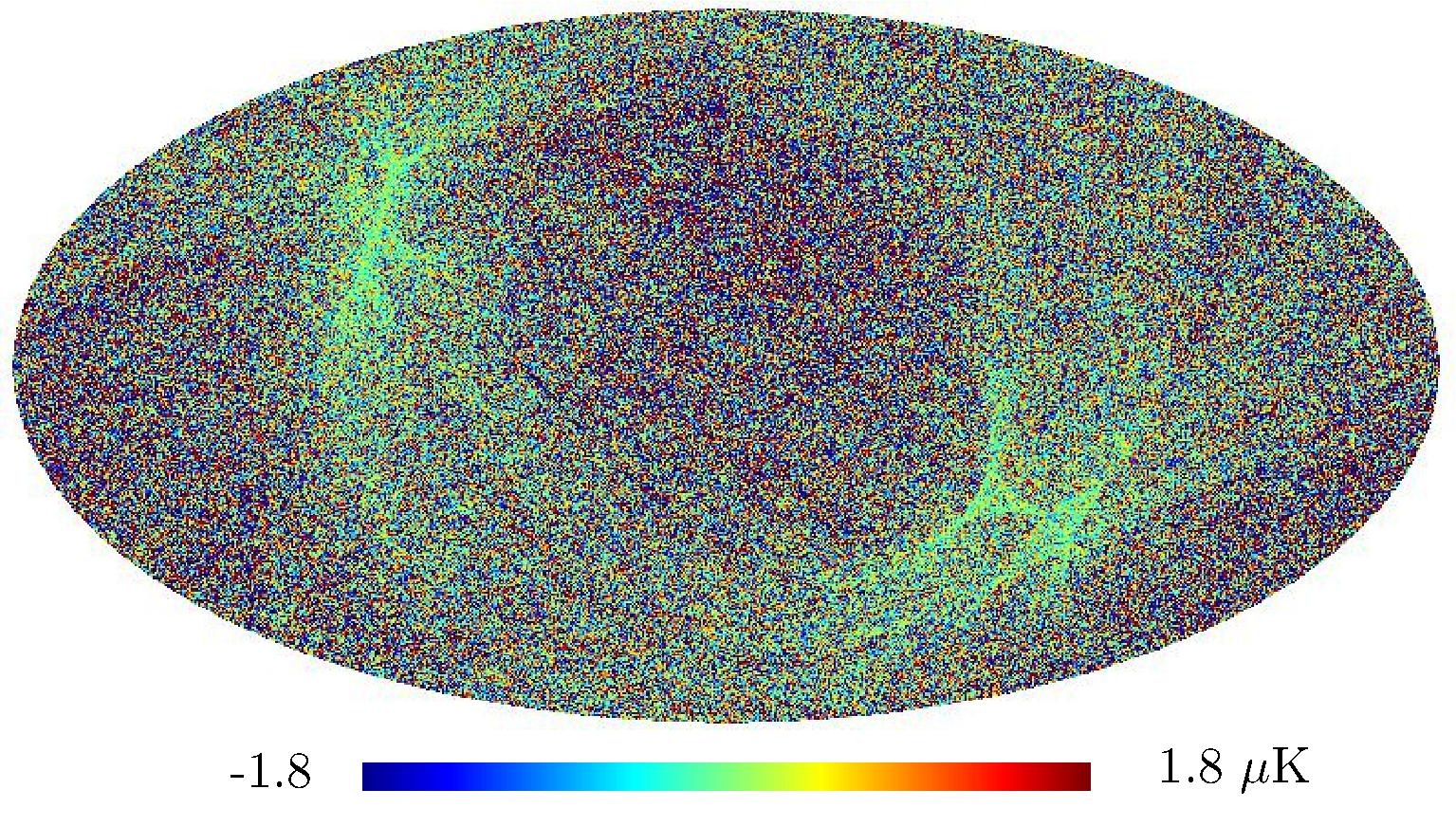
|
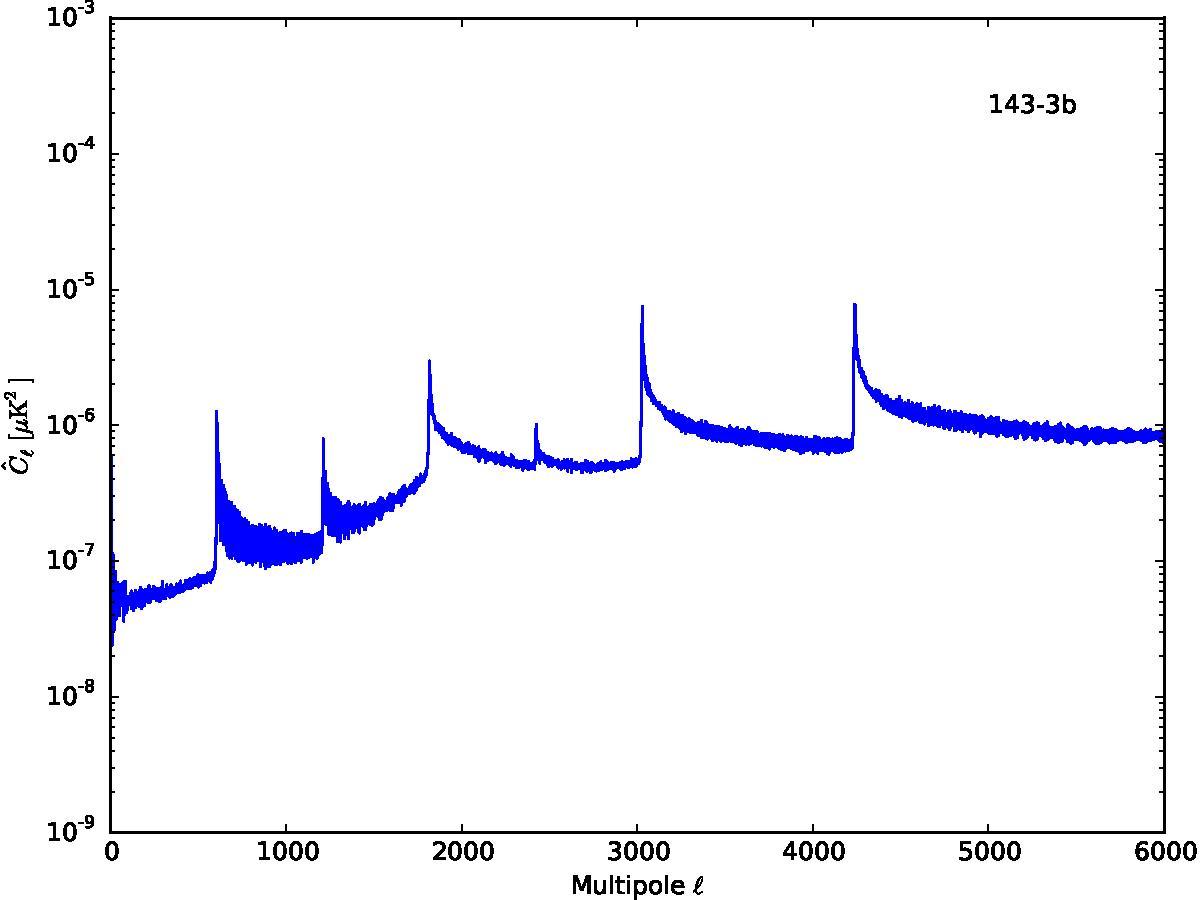
|
|
|
|
|
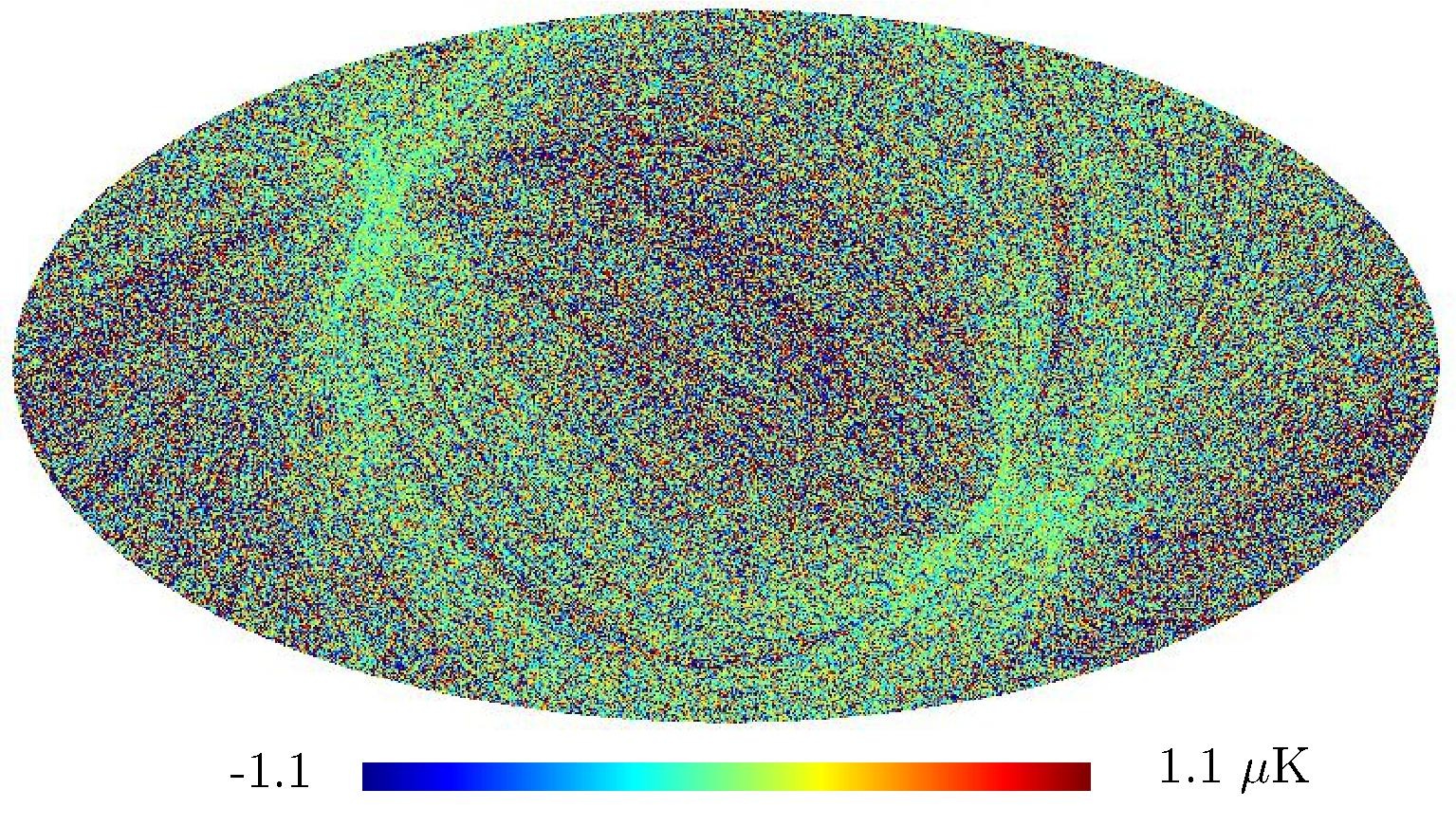
|
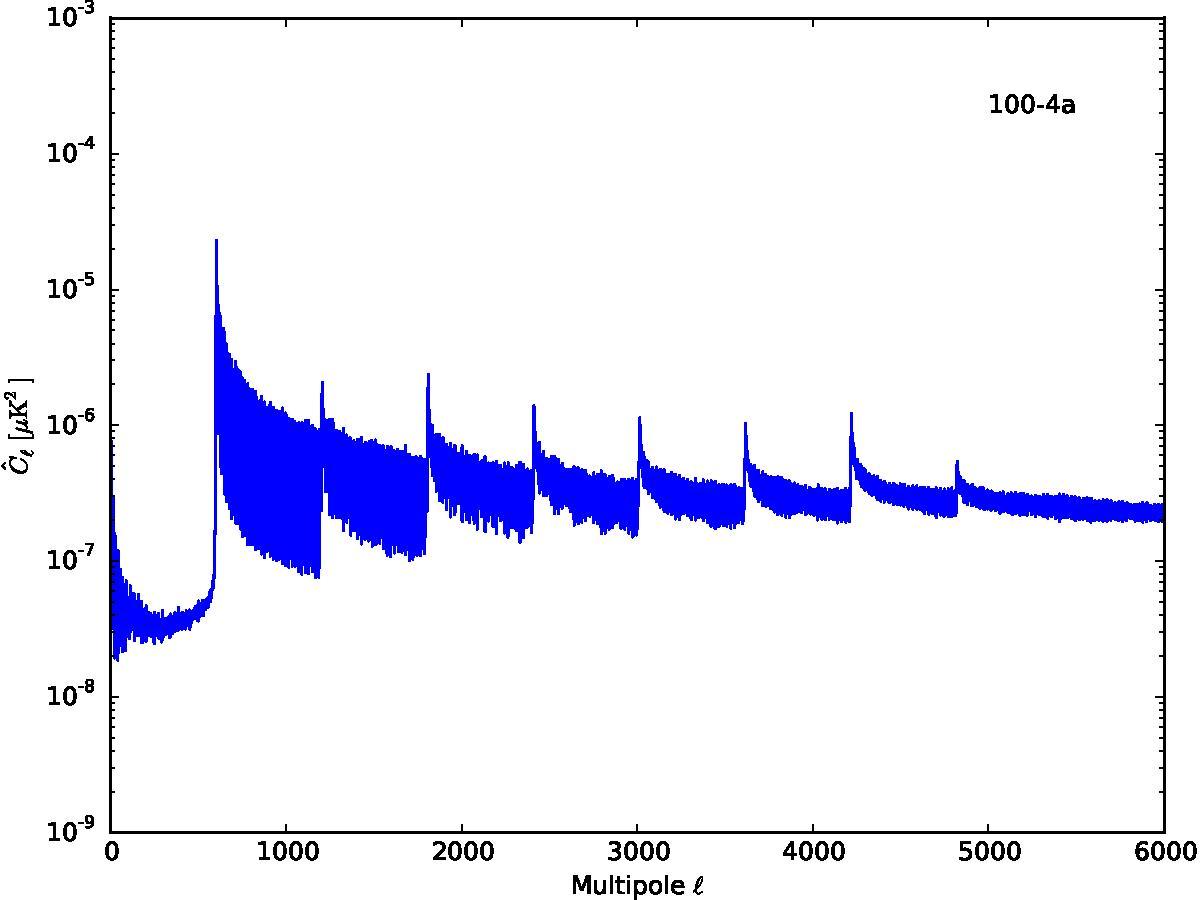
|
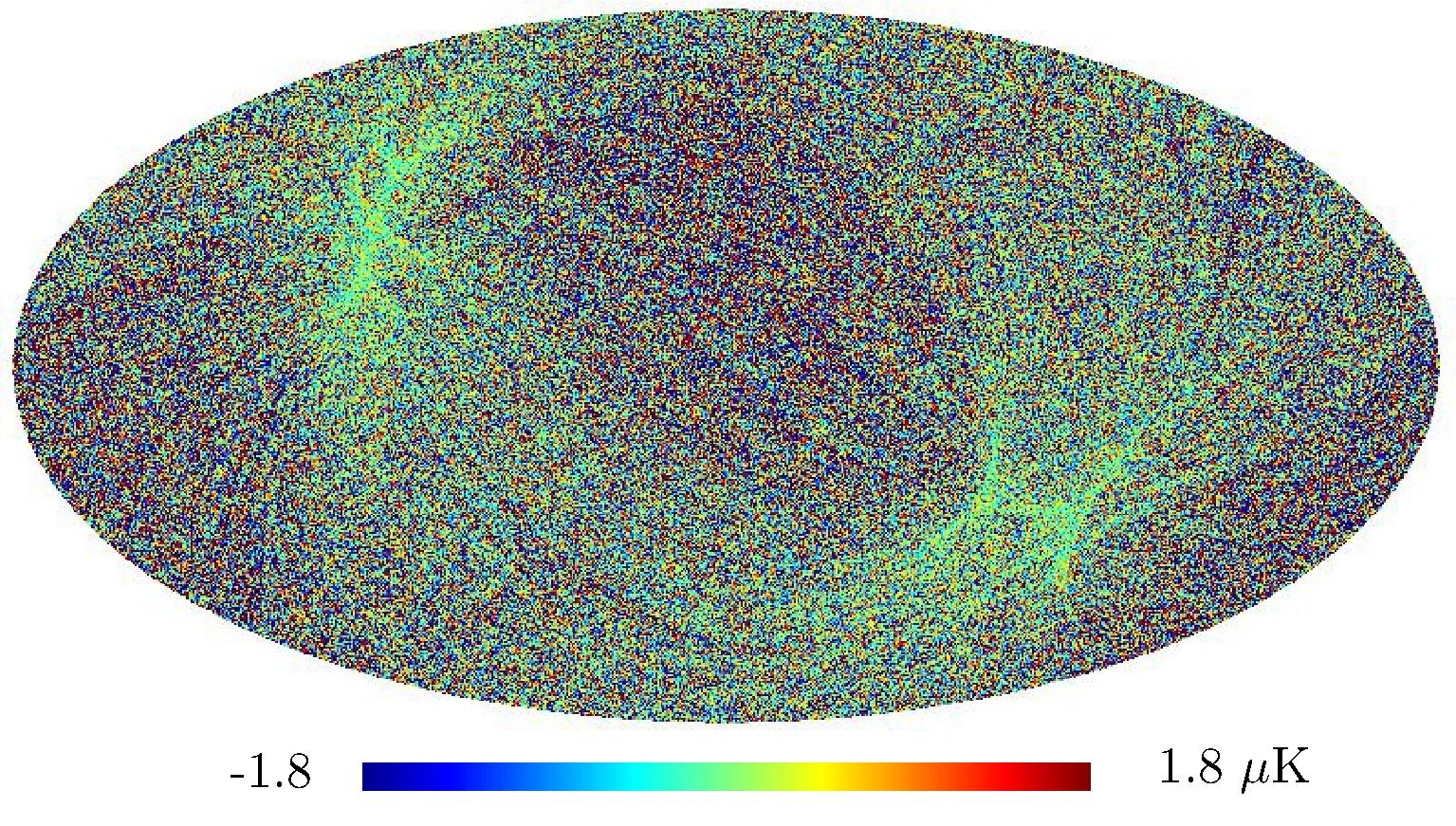
|
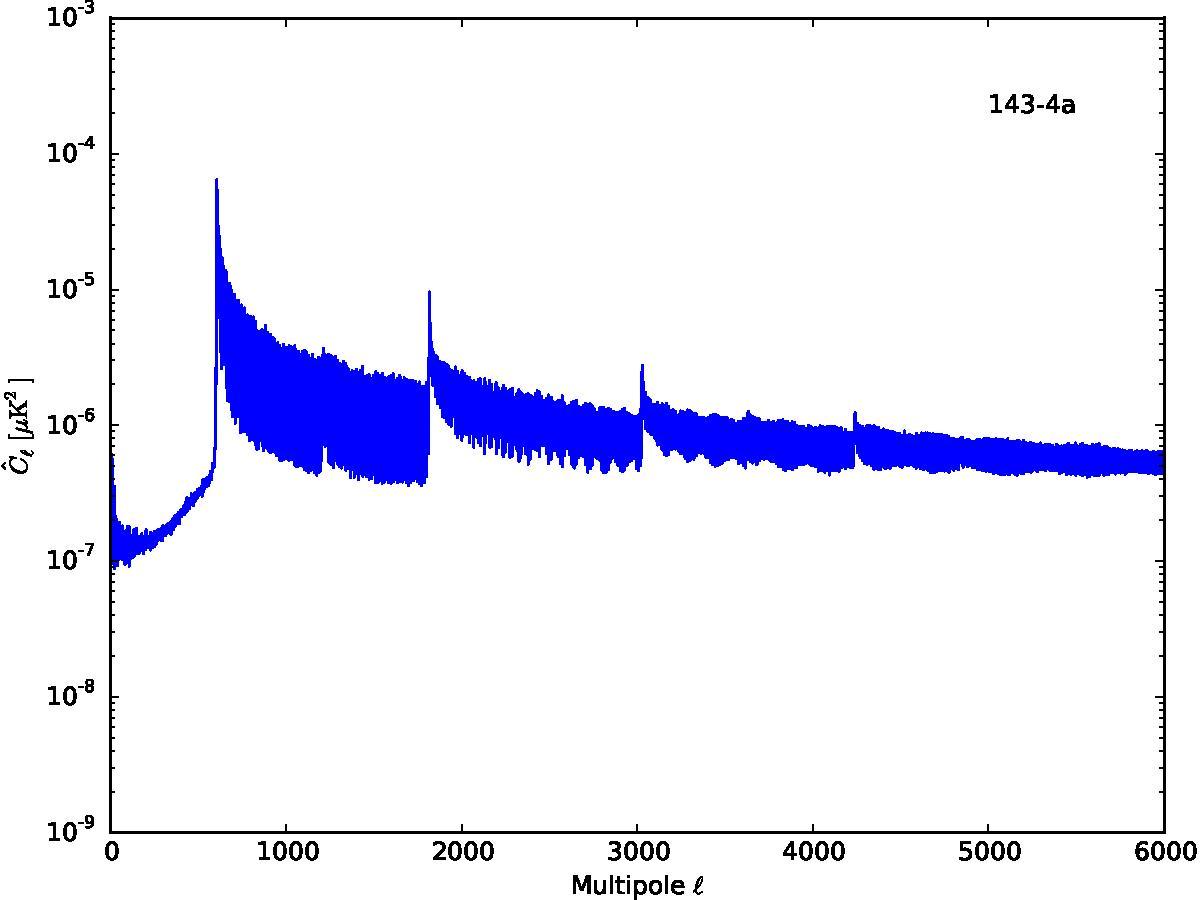
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
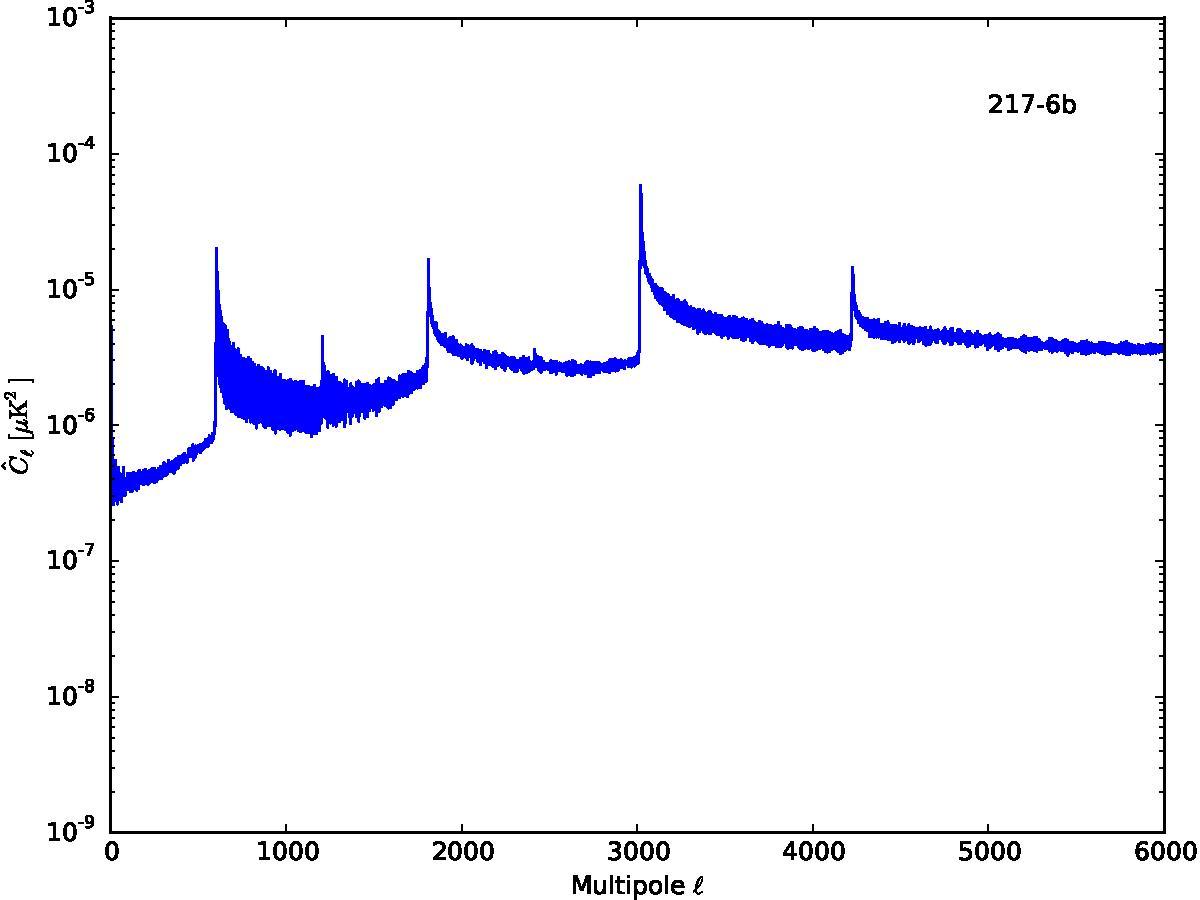
|
|
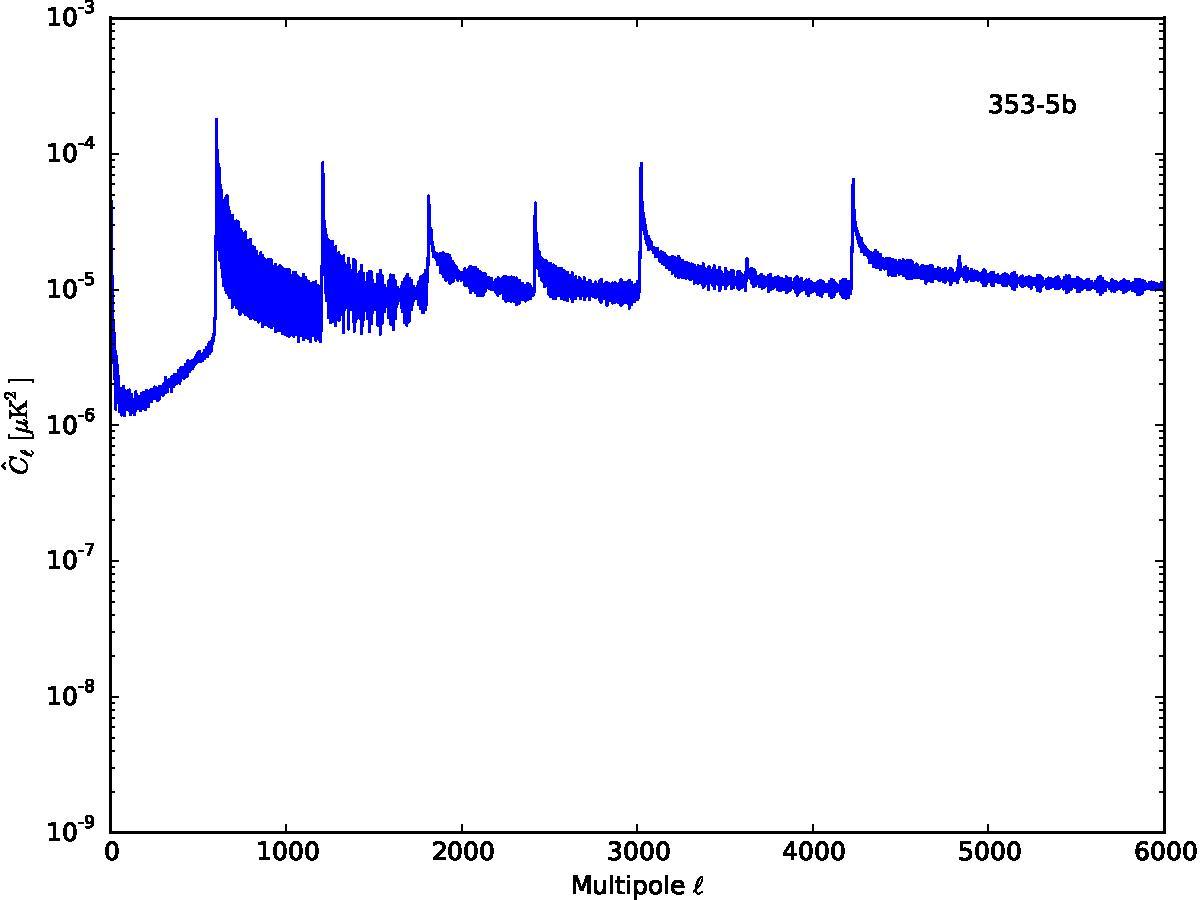
|
| . | . | 
|
|
|
|
|
|
| . | . | 
|
|
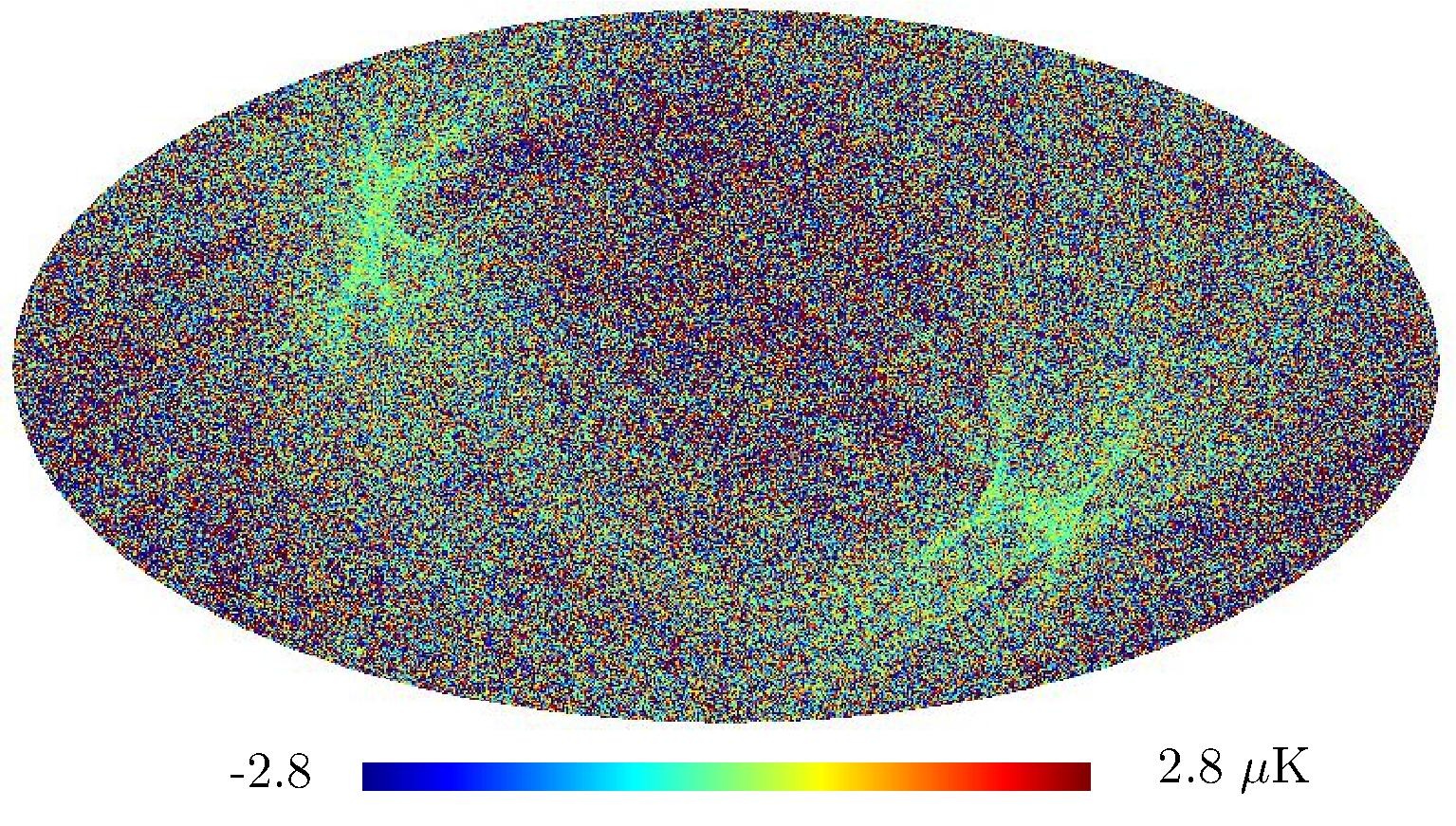
|
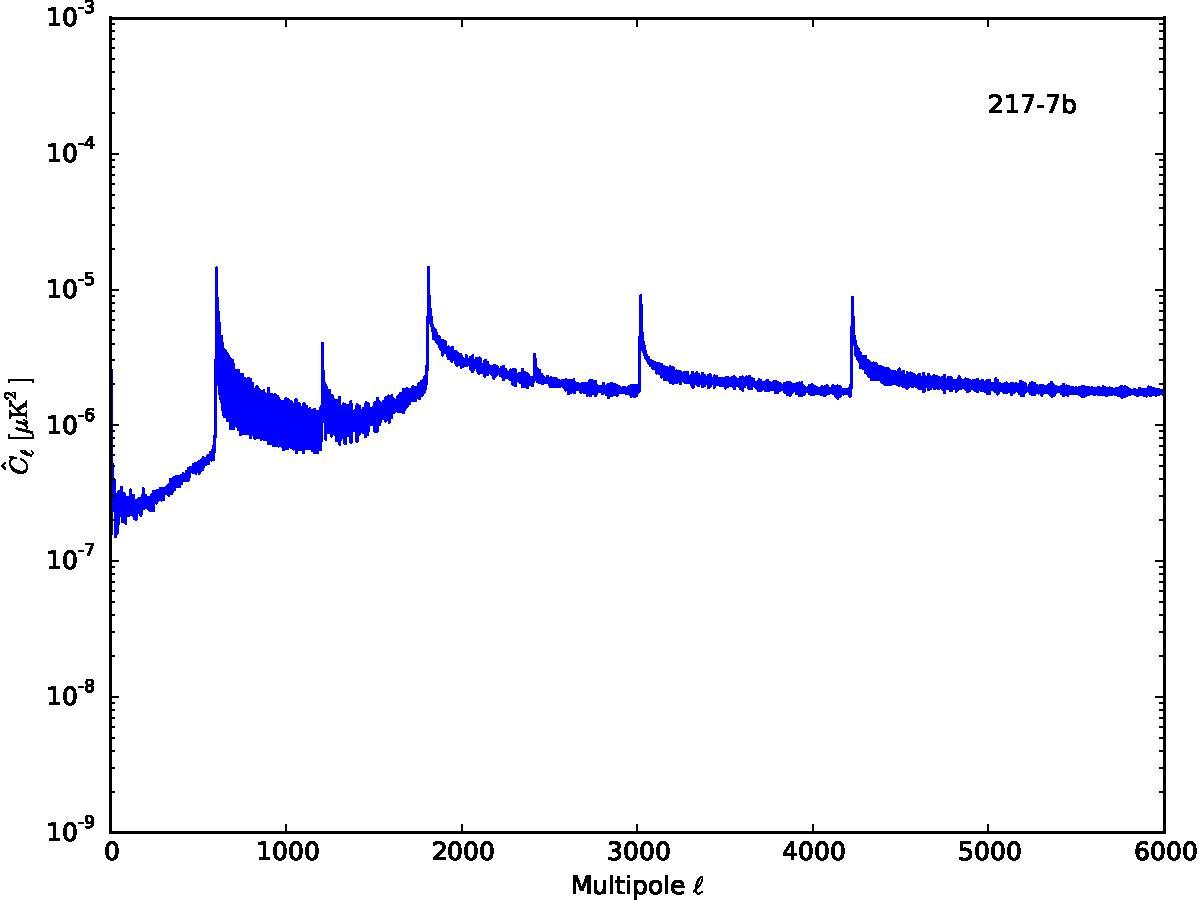
|
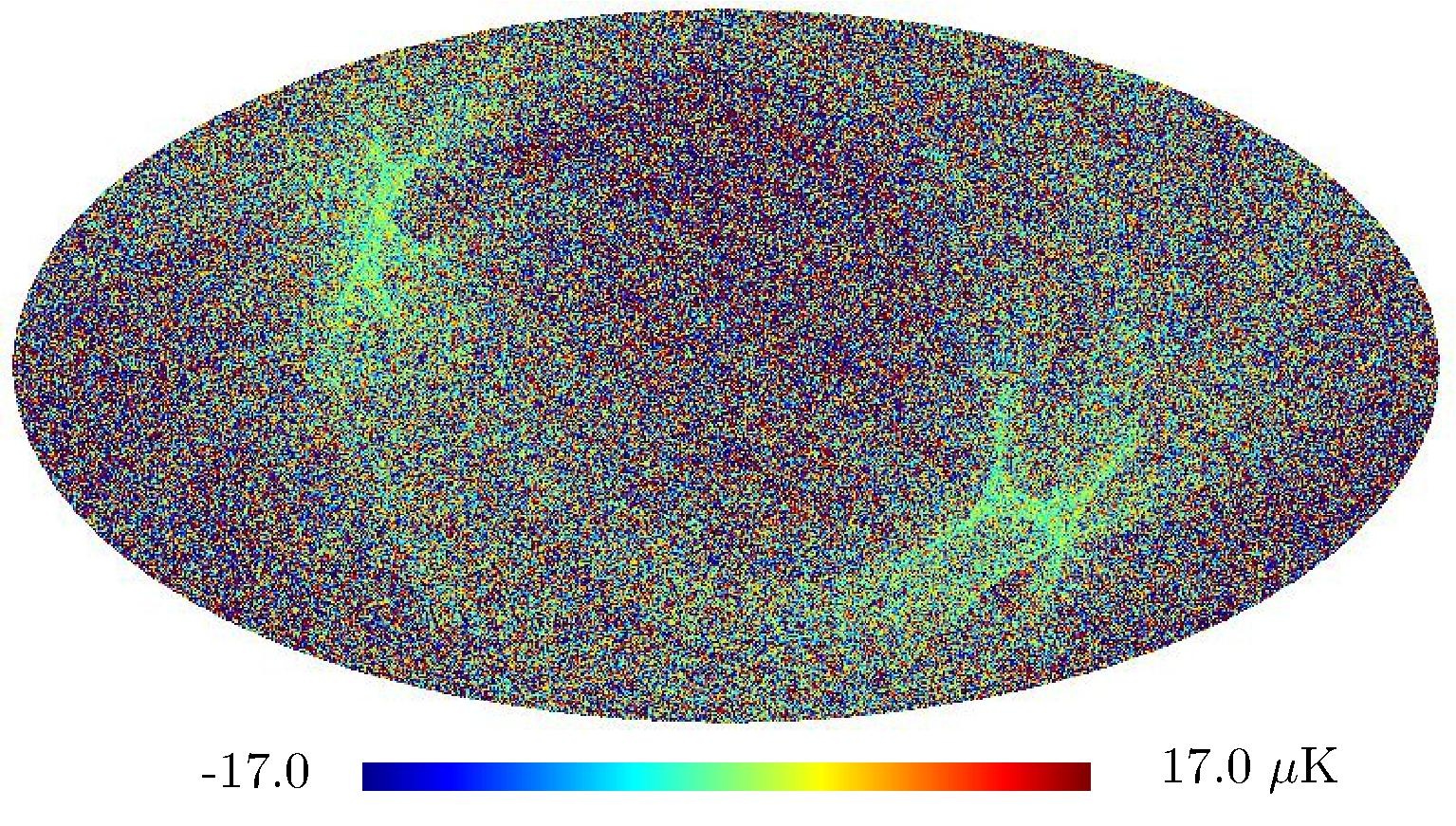
|
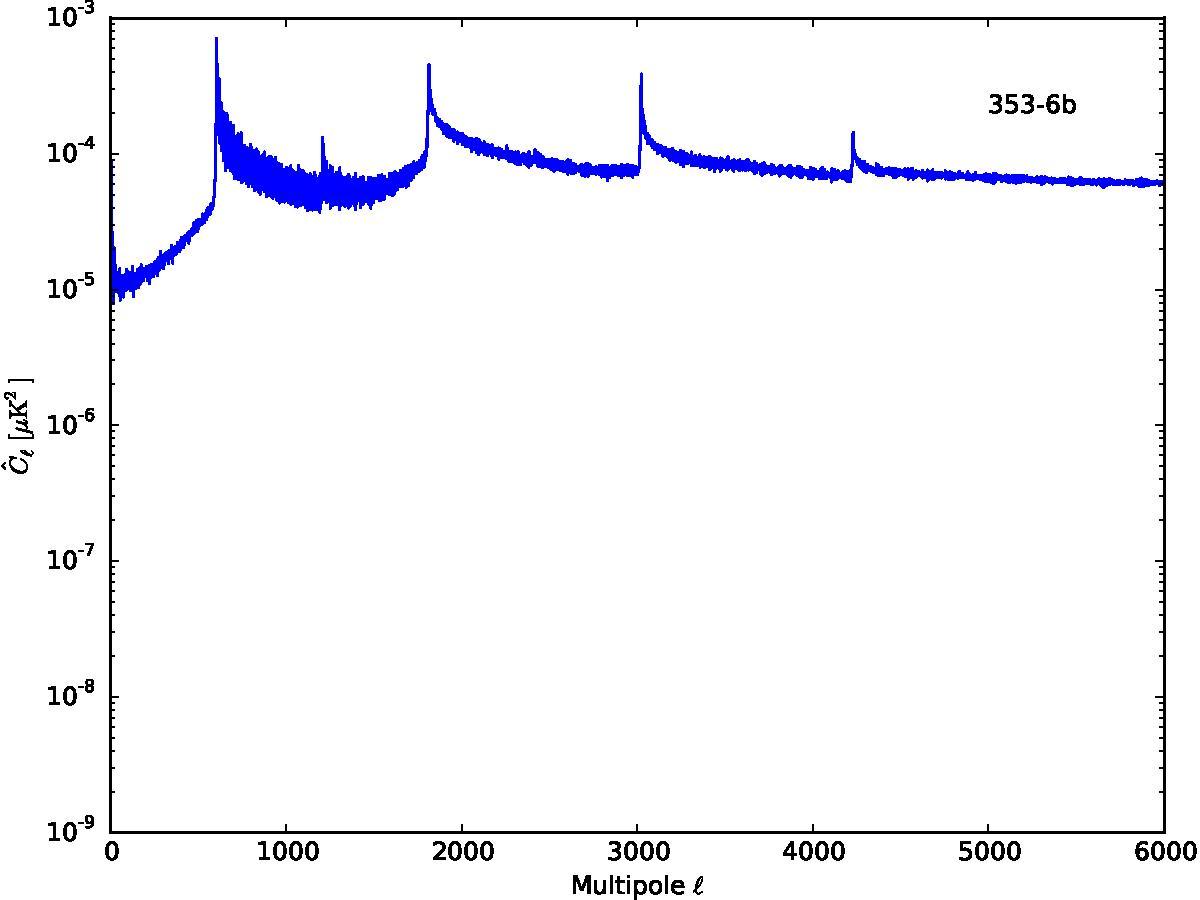
|
| . | . | 
|
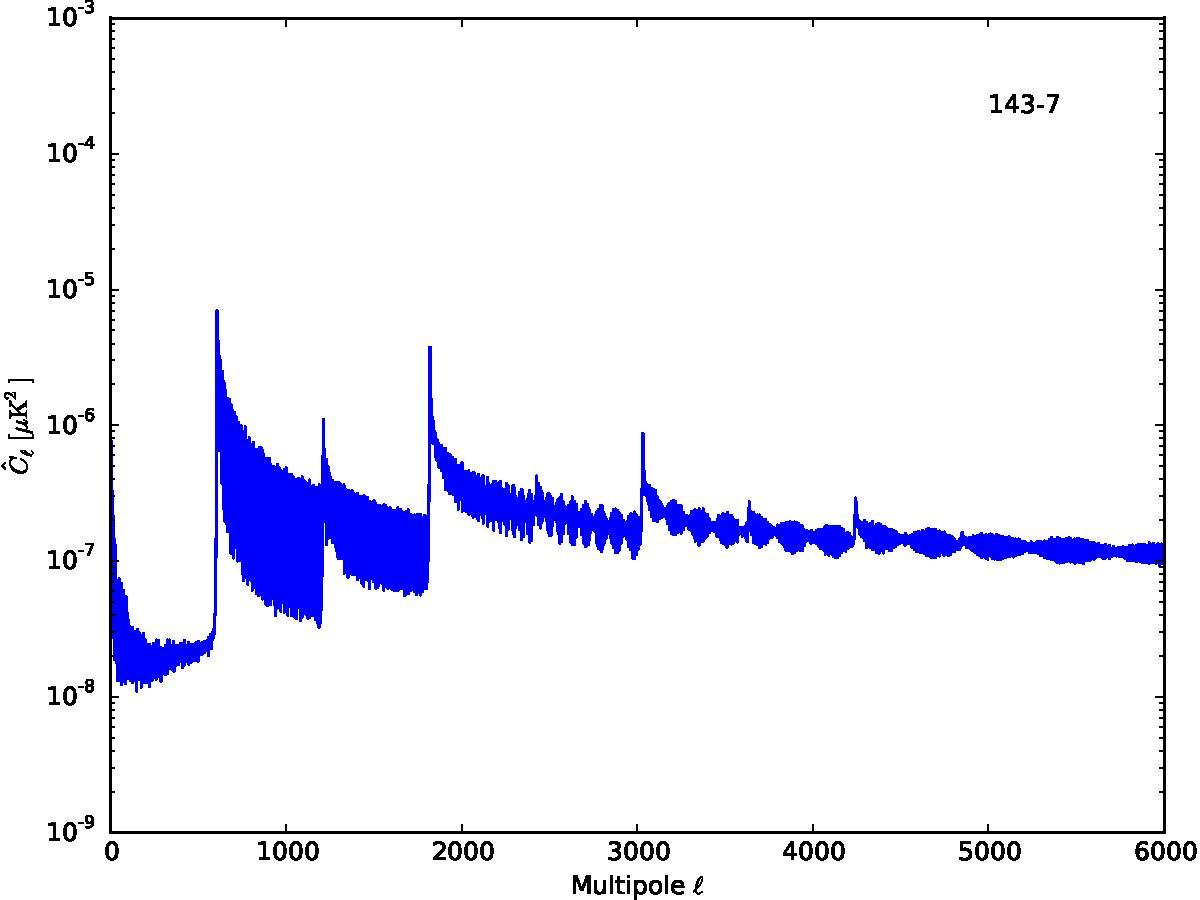
|
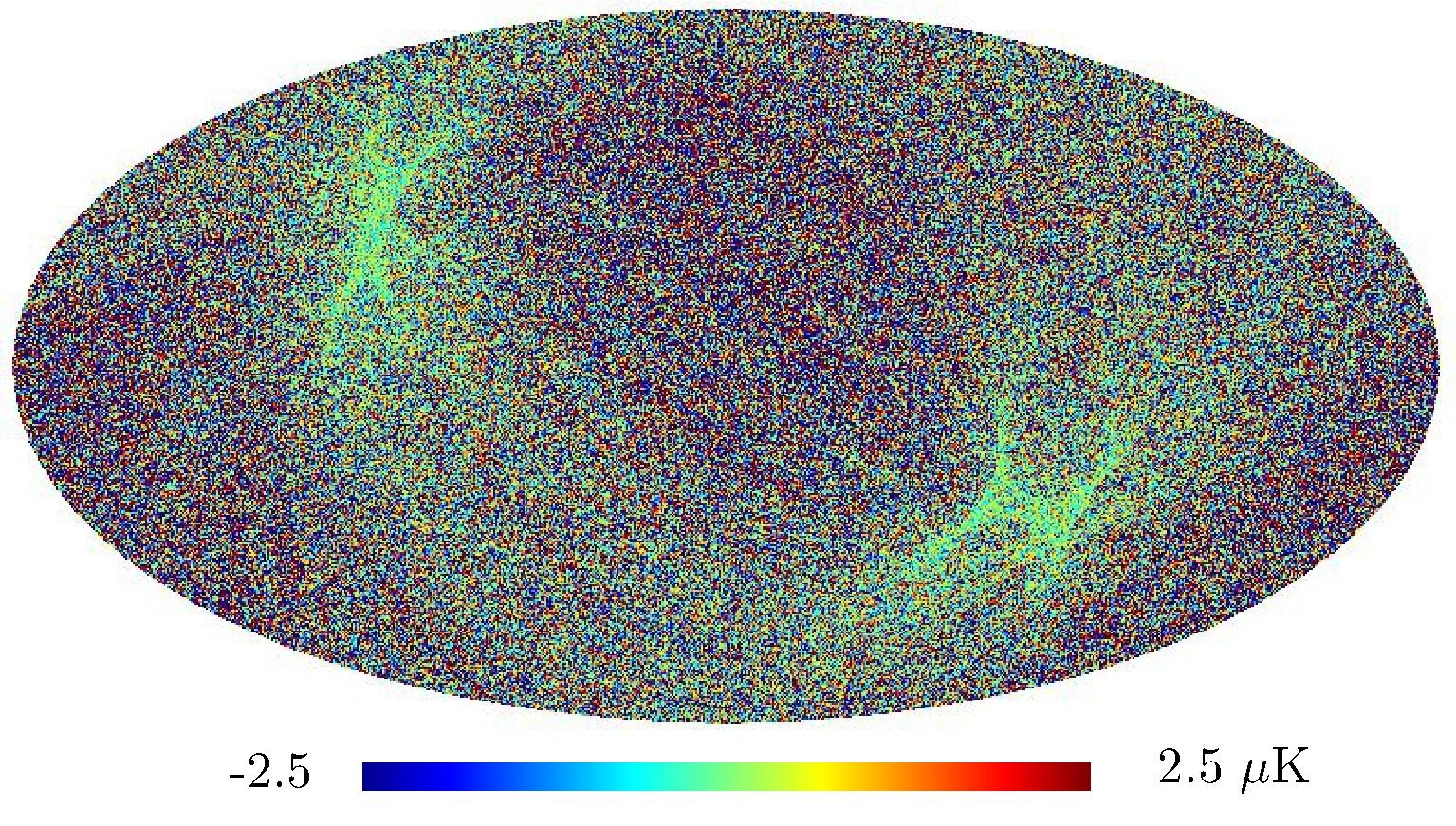
|
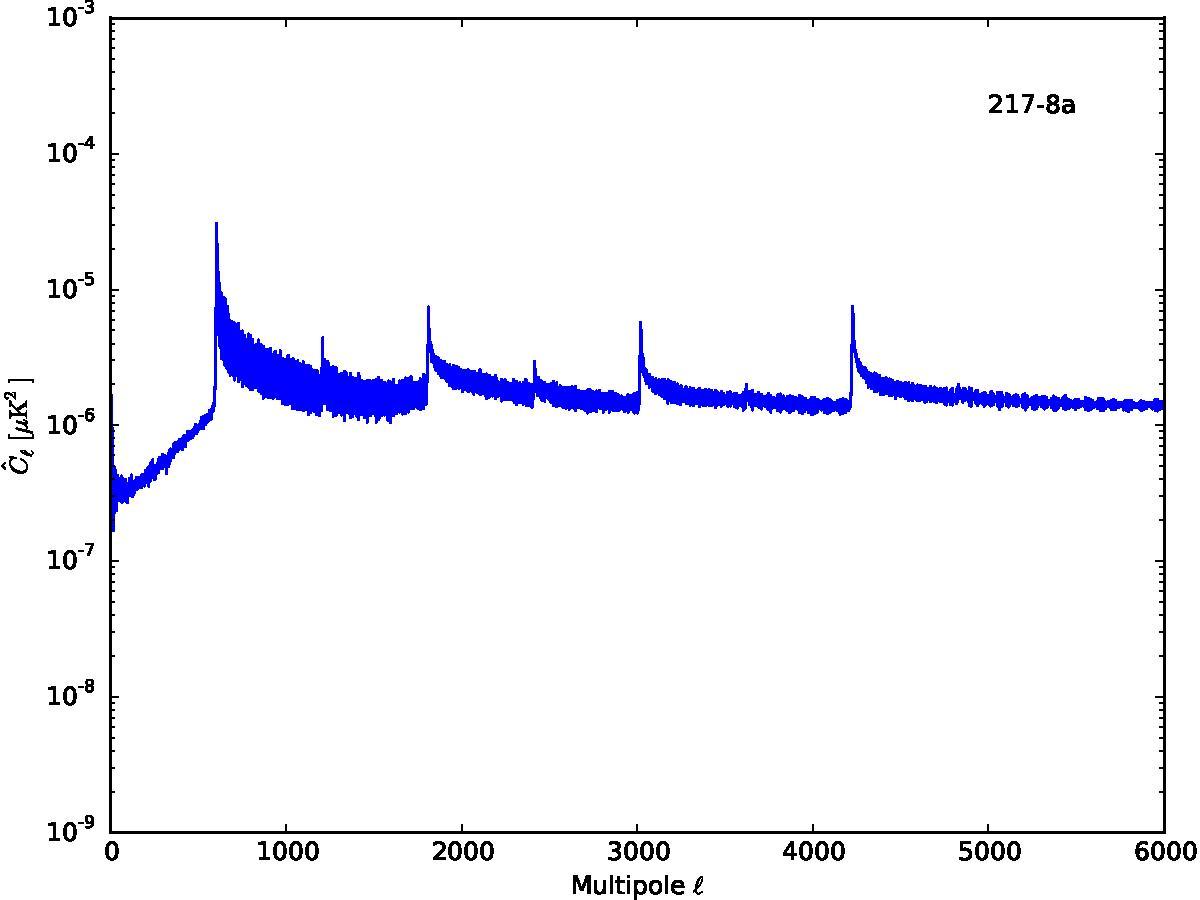
|
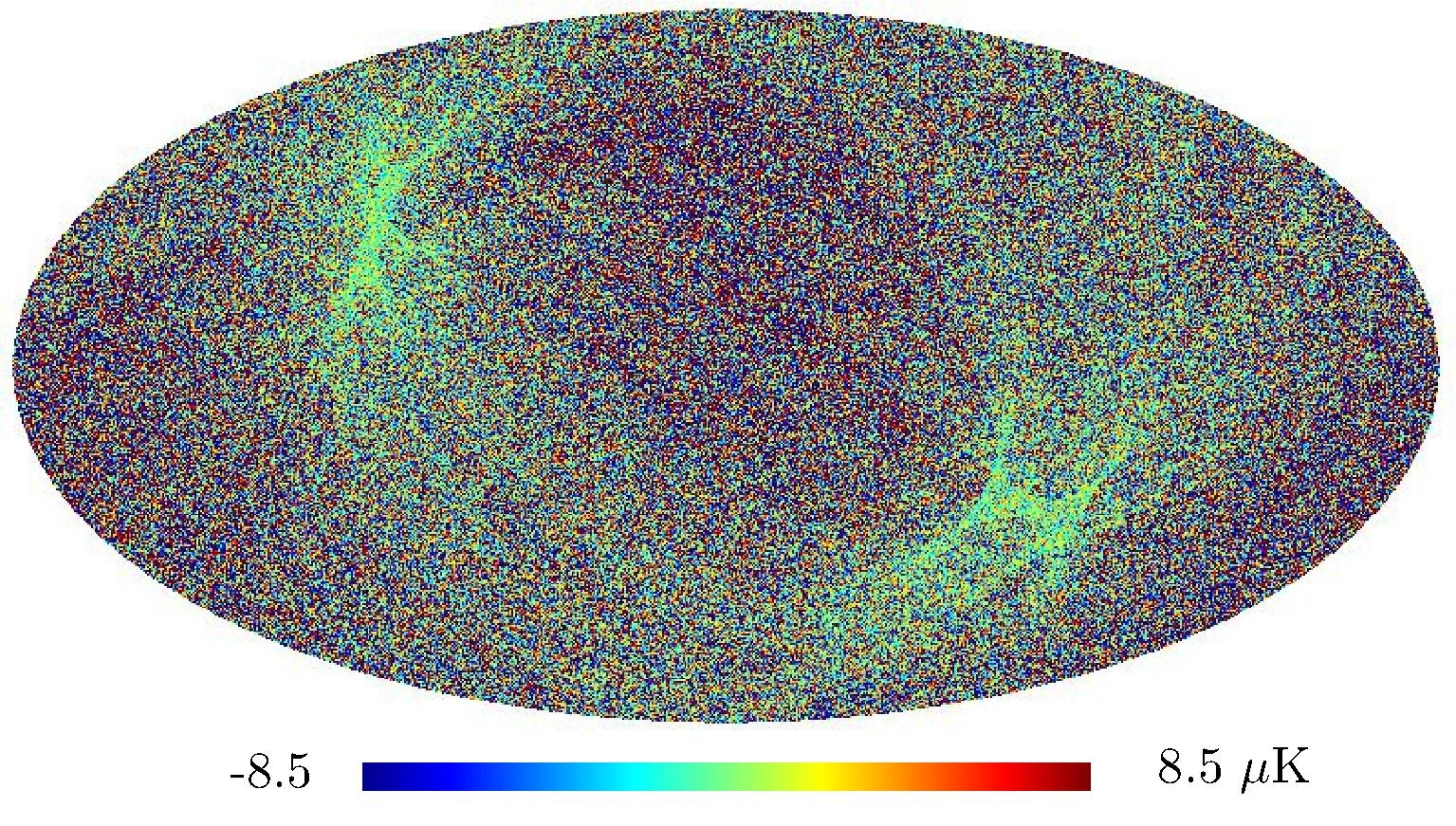
|
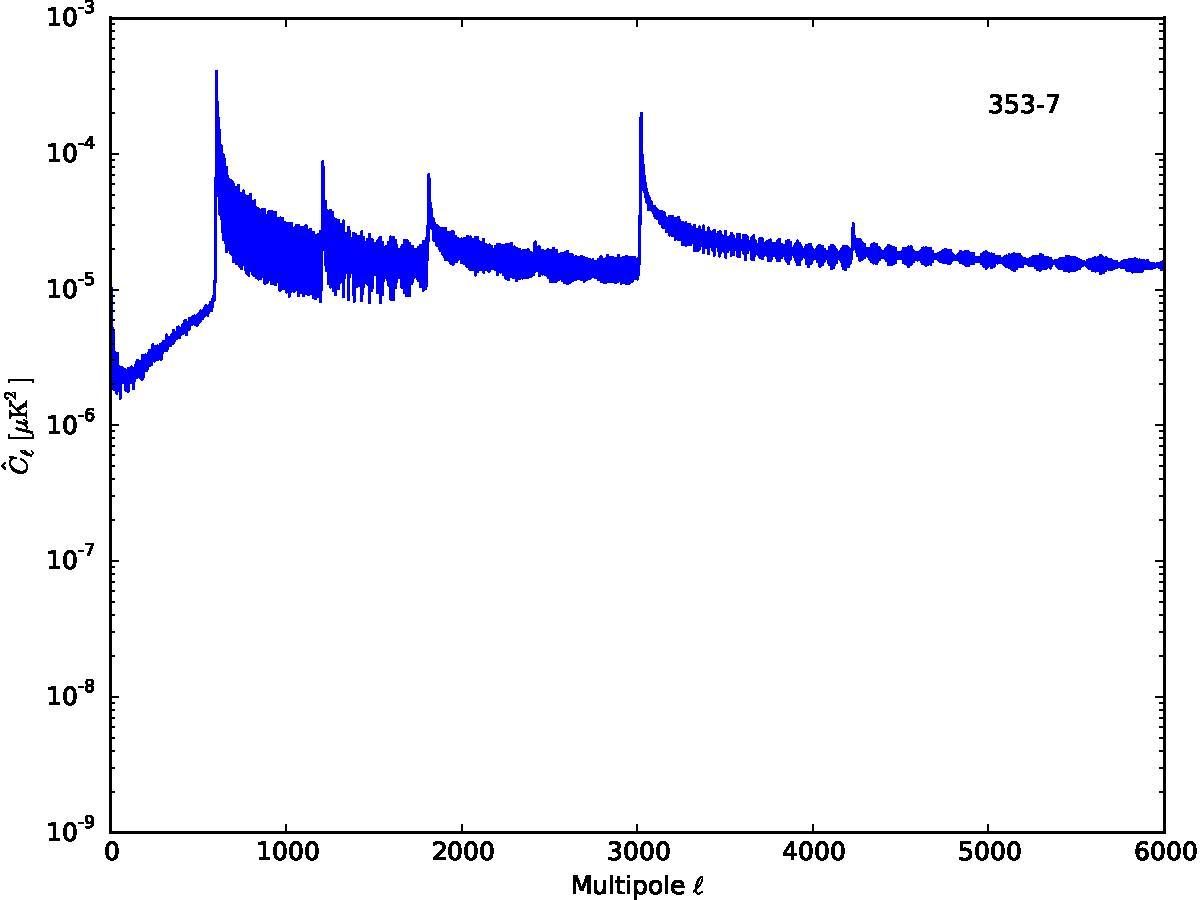
|
| . | . | . | . | 
|
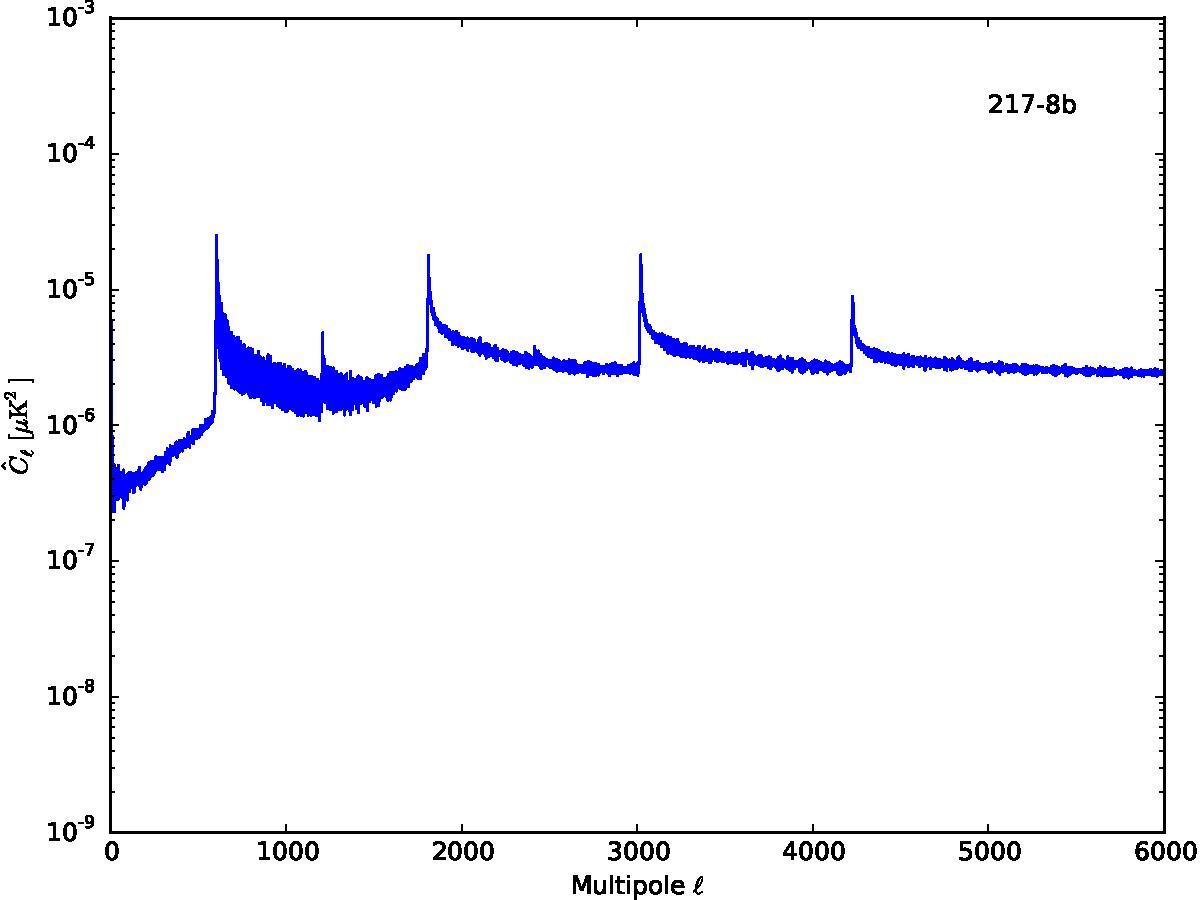
|
|
|
Section 5.13: complementary figures of Fig. 47
References[edit]
- Jump up ↑ Planck 2018 results. III. High Frequency Instrument data processing and frequency maps, Planck Collaboration, 2020, A&A, 641, A3.
- Jump up ↑
(Planck) High Frequency Instrument
Data Processing Center
Planck Legacy Archive
EMI/EMC influence of the 4K cooler mechanical motion on the bolometer readout electronics.
analog to digital converter