Difference between revisions of "Catalogues"
(→Selection function) |
(→Selection function) |
||
| Line 2,372: | Line 2,372: | ||
* http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-union-survey_R2.08.fits (union catalogue, survey mask) | * http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-union-survey_R2.08.fits (union catalogue, survey mask) | ||
| − | * http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-union- | + | * http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-union-cosmolog_R2.08.fits (union catalogue, cosmology mask) |
* http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-intersec-survey_R2.08.fits (intersection catalogue, survey mask) | * http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-intersec-survey_R2.08.fits (intersection catalogue, survey mask) | ||
* http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-intersec-cosmolog_R2.08.fits (intersection catalogue, cosmology mask) | * http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-intersec-cosmolog_R2.08.fits (intersection catalogue, cosmology mask) | ||
Latest revision as of 12:58, 26 January 2021
The 2015 compact source catalogues will not be regenerated using data from the 2018 release and remain the most up-to-date products.
Contents
[hide]- 1 (2015) Second Catalogue of Compact Sources (PCCS2 and PCCS2E)
- 2 (2015) Bayesian Extraction and Estimation Package (BeeP) reprocessing of PCCS2+PCCS2E at 857 GHz
- 3 (2015) Planck Catalogue of Galactic Cold Clumps
- 4 (2015) Planck list of high-redshift source candidates
- 5 (2015) Second SZ Catalogue
- 6 References
(2015) Second Catalogue of Compact Sources (PCCS2 and PCCS2E)[edit]
The second Planck Catalogue of Compact Sources (PCCS2) is a set of single-frequency source catalogues extracted from the Planck full-mission maps in intensity and polarization (LFI_SkyMap_0??_1024_R2.01_full.fits and HFI_SkyMap_???_2048_R2.00_full.fits). The catalogues have been constructed as described in PCCS and in section 2 of Planck-2015-A26[1]. The validation of the catalogues is described in section 3 of Planck-2015-A26[1].
The catalogue at 100 GHz and above has been divided into two sub-catalogues: the PCCS2, in which the sources have been detected in regions of the sky where it is possible to estimate the reliability of the detections, either statistically or by using external catalogues; and PCCS2E, in which the detected sources are located in regions of the sky where it is not possible to make an estimate of their reliability.
By definition, the reliability of the whole PCCS2 is ≥ 80%, and a flag is available that allows the user to select a subsample of sources with a higher level of reliability (e.g., 90% or 95%).
The nine Planck full-mission frequency channel maps are used as input to the source detection pipelines. They contain 48 months of data for LFI channels and 29 months of data for HFI channels. Therefore the flux densities of sources obtained from the full-mission maps are the average of at least eight observations for LFI channels or at least four observations for HFI channels. The relevant properties of the frequency maps and main parameters used to generate the catalogues are summarized in Tables 1 and 2.
Four different photometry methods have been used. For one of the methods (the native photometry from the Mexican-hat wavelet detection algorithm), the analysis is performed on patches containing tangent-plane projections of the map. For the other methods (aperture photometry, point spread function fitting, and Gaussian fitting), the analysis is performed directly on the full-sky maps.
The analysis in polarization has been performed in a non-blind fashion, looking at the position of the sources previously detected in intensity. As a result, polarization flux densities and polarization angles have been measured for hundreds of sources with a significance >99.99%. This high threshold in significance has been chosen to minimize the possibility of misinterpreting a peak of the polarized background as a source. This implies that, in general, most of the polarized sources are very bright, introducing an additional selection effect.
| Channel | 30 | 44 | 70 | 100 | 143 | 217 | 353 | 545 | 857 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency [GHz] | 28.4 | 44.1 | 70.4 | 100.0 | 143.0 | 217.0 | 353.0 | 545.0 | 857.0 |
| Wavelength [μm] | 10561 | 6807 | 4260 | 3000 | 2098 | 1382 | 850 | 550 | 350 |
| Number of sources | |||||||||
| PCCS2 | 1560 | 934 | 1296 | 1742 | 2160 | 2135 | 1344 | 1694 | 4891 |
| PCCS2E | — | — | — | 2487 | 4139 | 16842 | 22665 | 31068 | 43290 |
| Union PCCS2+PCCS2E | — | — | — | 4229 | 6299 | 18977 | 24009 | 32762 | 48181 |
| Number of sources in the extragalactic zonea | |||||||||
| PCCS2 | 745 | 367 | 504 | 1742 | 2160 | 2135 | 1344 | 1694 | 4891 |
| PCCS2E | — | — | — | 0 | 0 | 26 | 289 | 839 | 2097 |
| Union PCCS2+PCSS2E | — | — | — | 1742 | 2160 | 2161 | 1633 | 2533 | 6988 |
| Flux densities [mJy] in the extragalactic zonea | |||||||||
| PCCS2 | |||||||||
| Minimumb | 376 | 603 | 444 | 232 | 147 | 127 | 242 | 535 | 720 |
| 90% completeness | 426 | 676 | 489 | 269 | 177 | 152 | 304 | 555 | 791 |
| Uncertainty | 87 | 134 | 101 | 55 | 35 | 29 | 55 | 105 | 168 |
| PCCS2E | |||||||||
| Minimumb | — | — | — | — | — | 189 | 350 | 597 | 939 |
| 90% completeness | — | — | — | — | — | 144 | 311 | 557 | 927 |
| Uncertainty | — | — | — | — | — | 35 | 73 | 144 | 278 |
Table 1 Notes
a 30-70 GHz: the extragalactic zone is defined by |b| > 30°. For 100-857 GHz the numbers outside of the Galactic region where the reliability cannot be accurately assessed. Note that for the PCCS2E the only sources that occur in this region lie in the filament mask.
b Minimum flux density of the catalogue in the extragalactic zone after excluding the faintest 10% of sources.
| Channel | 30 | 44 | 70 | 100 | 143 | 217 | 353 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of significantly polarized sources in PCCS2 | 122 | 30 | 34 | 20 | 25 | 11 | 1 |
| Minimum polarized flux densitya [mJy] | 117 | 181 | 284 | 138 | 148 | 166 | 453 |
| Polarized flux density uncertainty [mJy] | 46 | 88 | 91 | 30 | 26 | 30 | 81 |
| Minimum polarized flux density for 90% completeness [mJy] | 199 | 412 | 397 | 135 | 100 | 136 | 347 |
| Minimum polarized flux density for 95% completeness [mJy] | 251 | 468 | 454 | 160 | 111 | 153 | 399 |
| Minimum polarized flux density for 100% completeness [mJy] | 600 | 700 | 700 | 250 | 147 | 257 | 426 |
| Number of significantly polarized sources in PCCS2E | — | — | — | 43 | 111 | 325 | 666 |
| Minimum polarized flux densitya [mJy] | — | — | — | 121 | 87 | 114 | 348 |
| Polarized flux density uncertainty [mJy] | — | — | — | 52 | 44 | 55 | 178 |
| Minimum polarized flux density for 90% completeness [mJy] | — | — | — | 410 | 613 | 270 | 567 |
| Minimum polarized flux density for 95% completeness [mJy] | — | — | — | 599 | 893 | 464 | 590 |
| Minimum polarized flux density for 100% completeness [mJy] | — | — | — | 835 | 893 | 786 | 958 |
Table 2 Notes
a Minimum polarized flux density of the catalogue of significantly polarized sources after excluding the faintest 10% of sources.
Catalogues[edit]
The PCCS2 catalogues (at each frequency) are contained in the FITS files
- COM_PCCS_030_R2.04.fits
- COM_PCCS_044_R2.04.fits
- COM_PCCS_070_R2.04.fits
- COM_PCCS_100_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_143_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_217_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_353_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_545_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_857_R2.01.fits .
The PCCS2E catalogues are contained in the FITS files
- COM_PCCS_100-excluded_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_143-excluded_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_217-excluded_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_353-excluded_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_545-excluded_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_857-excluded_R2.01.fits
The structure of these files is as follows.
| Extension 0: Primary header, no data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FITS keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| INSTRUME | String | Instrument (LFI / HFI) | |
| VERSION | String | Version of PCCS (PCCS2 / PCCS2_E) | |
| DATE | String | Date file created: yyyy-mm-dd | |
| ORIGIN | String | Name of organization responsible for the data (LFI-DPC / HFI-DPC) | |
| TELESCOP | String | Telescope (PLANCK) | |
| CREATOR | String | Pipeline version | |
| DATE-OBS | String | days | Beginning of the survey: yyyy-mm-dd |
| DATE-END | String | days | End of the survey: yyyy-mm-dd |
| FWHM | Real*4 | arcmin | FWHM from an elliptical Gaussian fit to the effective beam |
| OMEGA_B | Real*4 | arcmin2 | Area of the effective beam |
| FWHM_EFF | Real*4 | arcmin | FWHM computed from OMEGA_B assuming beam is Gaussian |
| OMEGA_B1 | Real*4 | arcmin2 | Beam area within a radius of 1 × FWHM_EFF |
| OMEGA_B2 | Real*4 | arcmin2 | Beam area within a radius of 2 × FWHM_EFF |
| Extension 1: BINTABLE, EXTNAME = PCCS2_fff (where fff is the frequency channel) | |||
| Column Name | Data type | Units | Description |
| Identification | |||
| NAME | String | Source name (see note 1) | |
| Source position | |||
| GLON | Real*8 | deg | Galactic longitude based on extraction algorithm |
| GLAT | Real*8 | deg | Galactic latitude based on extraction algorithm |
| RA | Real*8 | deg | Right ascension (J2000) transformed from (GLON,GLAT) |
| DEC | Real*8 | deg | Declination (J2000) transformed from (GLON,GLAT) |
| Photometry | |||
| DETFLUX | Real*4 | mJy | Flux density of source as determined by detection method |
| DETFLUX_ERR | Real*4 | mJy | Uncertainty (1 σ) in derived flux density from detection method |
| APERFLUX | Real*4 | mJy | Flux density of source as determined from aperture photometry |
| APERFLUX_ERR | Real*4 | mJy | Uncertainty (1 σ) in derived flux density from aperture photometry |
| PSFFLUX | Real*4 | mJy | Flux density of source as determined from PSF fitting |
| PSFFLUX_ERR | Real*4 | mJy | Uncertainty (1 σ) in derived flux density from PSF fitting |
| GAUFLUX | Real*4 | mJy | Flux density of source as determined from 2-D Gaussian fitting |
| GAUFLUX_ERR | Real*4 | mJy | Uncertainty (1 σ) in derived flux density from 2-D Gaussian fitting |
| GAU_SEMI1 | Real*4 | arcmin | Gaussian fit along axis 1 (FWHM; see note 2 for axis definition) |
| GAU_SEMI1_ERR | Real*4 | arcmin | Uncertainty (1 σ) in derived Gaussian fit along axis 1 |
| GAU_SEMI2 | Real*4 | arcmin | Gaussian fit along axis 2 (FWHM) |
| GAU_SEMI2_ERR | Real*4 | arcmin | Uncertainty (1 σ) in derived Gaussian fit along axis 2 |
| GAU_THETA | Real*4 | deg | Gaussian fit orientation angle (see note 2) |
| GAU_THETA_ERR | Real*4 | deg | Uncertainty (1 σ) in derived Gaussian fit orientation angle |
| GAU_FWHM_EFF | Real*4 | arcmin | Gaussian fit effective FWHM |
| Polarization measurements (30-353 GHz only) | |||
| P | Real*4 | mJy | Polarization flux density of the sources as determined by a matched filter (see note 3) |
| P_ERR | Real*4 | mJy | Uncertainty (1 σ) in derived polarization flux density (see note 3) |
| ANGLE_P | Real*4 | degrees | Orientation of polarization with respect to NGP (see notes 2 and 3) |
| ANGLE_P_ERR | Real*4 | degrees | Uncertainty (1 σ) in orientation of polarization (see note 3) |
| APER_P | Real*4 | mJy | Polarization flux density of the sources as determined by aperture photometry (see note 3) |
| APER_P_ERR | Real*4 | mJy | Uncertainty (1 σ) in derived polarization flux density (see note 3) |
| APER_ANGLE_P | Real*4 | degrees | Orientation of polarization with respect to NGP (see notes 2 and 3) |
| APER_ANGLE_P_ERR | Real*4 | degrees | Uncertainty (1 σ) in orientation of polarization (see note 3) |
| P_UPPER_LIMIT | Real*4 | mJy | Polarization flux density 99.99% upper limit. This is provided only when the P column is set to NULL; otherwise this column itself contains NULL. |
| APER_P_UPPER_LIMIT | Real*4 | mJy | Polarization flux density 99.99% upper limit. This is provided only when the APER_P column is set to NULL; otherwise this column itself contains NULL. |
| Marginal polarization measurements (100-353 GHz only) – see note 4 | |||
| P_STAT | Integer*2 | Polarization detection status | |
| PX | Real*4 | mJy | Polarization flux density of the sources as determined by a matched filter using a Bayesian polarization estimator |
| PX_ERR_LOWER | Real*4 | mJy | PX uncertainty; lower 95% error bar |
| PX_ERR_UPPER | Real*4 | mJy | PX uncertainty; upper 95% error bar |
| ANGLE_PX | Real*4 | deg | Orientation of polarization with respect to NGP using Bayesian polarization estimator (see note 2) |
| ANGLE_PX_ERR_LOWER | Real*4 | deg | ANGLE_PX uncertainty; lower 95% error bar |
| ANGLE_PX_ERR_UPPER | Real*4 | deg | ANGLE_PX uncertainty; upper 95% error bar |
| Flags and validation | |||
| EXTENDED | Integer*2 | Extended source flag (see note 5) | |
| EXT_VAL | Integer*2 | External validation flag (see note 6) | |
| ERCSC | String | Name of the ERCSC counterpart, if any | |
| PCCS | String | Name of the PCCS counterpart, if any | |
| Flags and validation (PCCS2 only) | |||
| HIGHEST_RELIABILITY_CAT | Integer*4 | See note 7 | |
| Flags and validation (PCCS2E, 100-857 GHz only) | |||
| WHICH_ZONE | Integer*2 | See note 8 | |
| Flags and validation (217-857 GHz only) | |||
| CIRRUS_N | Integer*2 | Number of sources (S/N > 5) detected at 857 GHz within a 1° radius. | |
| SKY_BRIGHTNESS | Real*4 | MJy sr-1 | The mean 857 GHz brightness within a 2° radius. This may be used as another indicator of cirrus contamination. |
| Flux densities at other frequencies (857 GHz only) | |||
| APERFLUX_217 | Real*4 | mJy | Estimated flux density at 217 GHz |
| APERFLUX_ERR_217 | Real*4 | mJy | Uncertainty in flux density at 217 GHz |
| APERFLUX_353 | Real*4 | mJy | Estimated flux density at 353 GHz |
| APERFLUX_ERR_353 | Real*4 | mJy | Uncertainty in flux density at 353 GHz |
| APERFLUX_545 | Real*4 | mJy | Estimated flux density at 545 GHz |
| APERFLUX_ERR_545 | Real*4 | mJy | Uncertainty in flux density at 545 GHz |
Notes
- Format is PCCS2 fff Glll.ll±bb.bb for sources in the PCCS2 and PCCS2E fff Glll.ll±bb.bb for sources in the PCCS2E, where "fff" is the frequency channel and l and b the position of the source in Galactic coordinates truncated to two decimal places.
- We follow the IAU/IEEE convention (Hamaker & Bregman 1996) for defining the angle of polarization of a source in this catalogue, and this convention is also used for the other angles in the catalogue. The angle is measured from the North Galactic Pole in a clockwise direction from -90° to 90°. Note that this is different than the convention used for the CMB maps.
- Provided when the significance of the polarization measurement is > 99.99% and set to NULL otherwise.
- The P_STAT flag gives the status of the marginal polarization detection. Possible values are:
- 3 – bright, the P field filled in and all PX fields set to NULL;
- 2 – significant, the P field is set to NULL, 0 is outside the PX 95% HPD, and all PX fields are filled;
- 1 – marginal, the P field is set to NULL, 0 is inside the PX 95% HPD (but the mode of the PX posterior distribution is not 0) and all PX fields are filled;
- 0 – no detection, the P field is set to NULL, the mode of the PX posterior distribution is 0, PX_ERRL, ANGLE_PX, ANGLE_PX_ERR_LOWER, and ANGLE_PX_ERR_UPPER are set to NULL.
- The EXTENDED flag has the value of "0" if the source is compact and the value of "1" if it is extended. The source size is determined by the geometric mean of the Gaussian fit FWHMs, with the criterion for extension being √(GAU_FWHMMAJ * GAU_FWHMIN) > 1.5 times the beam FWHM.
- The EXT_VAL flag gives the status of the external validation. Possible values are:
- 3 – the source has a clear counterpart in one of the catalogues used as ancillary data;
- 2 – the source does not have a clear counterpart in one of the catalogues used as ancillary data, but it has been detected by the internal multi-frequency method;
- 1 – the source does not have a clear counterpart in one of the catalogues used as ancillary data and it has not been detected by the internal multi-frequency method, but it has been detected in a previous Planck source catalogue;
- 0 – the source does not have a clear counterpart in one of the catalogues used as ancillary data and has not been detected by the internal multi-frequency method.
- The HIGHEST_RELIABILTY_CAT column contains the highest reliability catalogue to which the source belongs. As the full catalogue reliability is ≥ 80%, this is the lowest possible value in this column. Where possible this is provided in steps of 1%, otherwise it is in steps of 5%.
- The WHICH_ZONE column encodes the zone in which the source lies:
- 1 – source lies inside the filament mask;
- 2 – source lies inside the Galactic zone;
- 3 – sources lies in both the filament mask and Galactic zone.
Zone map[edit]
For each HFI frequency channel there is an associated map that defines where the quantified-reliability (PCCS2) and unquantified-reliability (PCCS2E) zones are on the sky.
The files are called
- COM_PCCS_100-zoneMask_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_143-zoneMask_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_217-zoneMask_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_353-zoneMask_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_545-zoneMask_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_857-zoneMask_R2.01.fits .
The structure of the files is shown in the following table.
| Extension 0: Primary header, no data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FITS keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| DATE | String | Date of creation of file | |
| Extension 1: BINTABLE, HEALPix map (see note 1) | |||
| FITS keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| PIXTYPE | String | HEALPIX | HEALPix pixelation |
| ORDERING | String | RING | Pixel ordering |
| NSIDE | Int*4 | 2048 | HEALPix resolution parameter |
| NPIX | Int*4 | 50331648 | Number of pixels |
| COORDSYS | String | G | Coordinate system |
| FREQ_CHL | String | Frequency channel | |
Notes
- This FITS extension contains an integer HEALPix map, which encodes the information on which of four possible regions on the sky each pixel belongs to:
- 0 – quantified-reliability zone (PCCS2);
- 1 – filament mask;
- 2 – Galactic zone;
- 3 – filament mask and Galactic zone.
S/N threshold map[edit]
For each HFI frequency channel there are a number of maps that contains the S/N threshold used to accept sources into the PCCS2 and PCCS2E catalogues.
For the full catalogue (80% reliability in the quantified reliability zone) they are
- COM_PCCS_100-SN-threshold_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_143-SN-threshold_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_217-SN-threshold_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_353-SN-threshold_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_545-SN-threshold_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_857-SN-threshold_R2.01.fits .
For 85% reliability they are
- COM_PCCS_100-SN-threshold-85pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_143-SN-threshold-85pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_217-SN-threshold-85pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_353-SN-threshold-85pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_545-SN-threshold-85pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_857-SN-threshold-85pc-reliability_R2.01.fits .
For 90% reliability they are
- COM_PCCS_100-SN-threshold-90pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_143-SN-threshold-90pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_217-SN-threshold-90pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_353-SN-threshold-90pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_545-SN-threshold-90pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_857-SN-threshold-90pc-reliability_R2.01.fits .
For 95% reliability they are
- COM_PCCS_100-SN-threshold-95pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_143-SN-threshold-95pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_217-SN-threshold-95pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_353-SN-threshold-95pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_545-SN-threshold-95pc-reliability_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_857-SN-threshold-95pc-reliability_R2.01.fits .
The structure of the files is shown in the following table.
| Extension 0: Primary header, no data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FITS keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| DATE | String | Date of creation of file | |
| Extension 1: BINTABLE, HEALPix map (see note 1) | |||
| FITS keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| PIXTYPE | String | HEALPIX | HEALPix pixelation |
| ORDERING | String | RING | Pixel ordering |
| NSIDE | Int*4 | 2048 | HEALPix resolution parameter |
| NPIX | Int*4 | 50331648 | Number of pixels |
| COORDSYS | String | G | Coordinate system |
| FREQ_CHL | String | Frequency channel | |
Notes
- This FITS extension contains a single precision HEALPix map of the S/N threshold applied in the generation of the catalogue at that position on the sky.
Noise map[edit]
For each HFI frequency channel there is an associated map that contains the detection noise as a function of position on the sky.
The files are called
- COM_PCCS_100-noise-level_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_143-noise-level_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_217-noise-level_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_353-noise-level_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_545-noise-level_R2.01.fits
- COM_PCCS_857-noise-level_R2.01.fits .
The structure of the files shown in the following table.
| Extension 0: Primary header, no data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FITS keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| DATE | String | Date of creation of file | |
| Extension 1: BINTABLE, HEALPix map (see note 1) | |||
| FITS keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| PIXTYPE | String | HEALPIX | HEALPix pixelation |
| ORDERING | String | RING | Pixel ordering |
| NSIDE | Int*4 | 2048 | HEALPix resolution parameter |
| NPIX | Int*4 | 50331648 | Number of pixels |
| COORDSYS | String | G | Coordinate system |
| FREQ_CHL | String | Frequency channel | |
Notes
- This FITS extension contains a single precision HEALPix map of the detection noise at each location on the sky, in units of Jy.
Previous releases: (2013) PCCS and (2011) ERCSC[edit]
Second Planck Release (2013): Description of the PCCS
First Planck Release (2011): Description of the 2011 ERCSC (Early Compact Source, Cold Core and SZ Catalogues )
(2015) Bayesian Extraction and Estimation Package (BeeP) reprocessing of PCCS2+PCCS2E at 857 GHz[edit]
BeeP’s catalogue was developed using the data and the methodology described in the companion paper Planck-2020-LV[14].
Traits:
- It is a catalogue of compact objects.
- It is the result of a ‘non-blind’ exercise where Planck’s PCCS2+2E catalogue positions at 857 GHz were used. It contains exactly the same number of rows as the original catalogue and no attempt of detecting new sources was made.
- It is a parametric Bayesian multi-channel algorithm. The source parameter estimates are derived from the posterior distributions of a data model likelihood.
- It employs Planck all-sky temperature maps at GHz channels from the Planck 2015 release and the GHz IRIS map, a reprocessed IRAS map.
The catalogue product is made of three components:
- A table with source parameter estimates and uncertainty summary statistics: COM_PCCS_BEEP_R2.00.fits.
- A collection of Spectral Energy Density (SED) figures. Not yet available
- A collection of figures with the parameter posterior distributions. Not yet available
Table of source parameter estimates.[edit]
The table with the source parameters contains 48181 rows, as many as in Planck 857 GHz channel PCCS2 and PCCSE catalogues combined. Each row has 108 fields (columns). If a field value is ill defined or not available, then its value is set to largest negative value of the double type in the IEEE standard: . The table of source parameter estimates (columns) is divided into 5 sections:
General
Contains fields that are independent of the physical model used to described the source, or background, emission. It holds the reliability assessment fields (see section A.1.2 and 6.2.3 of the companion paper).
- BeeP position columns were obtained using the MBB SED model.
- If a likelihood maximum was not found, then MAXFOUND is set to , otherwise is .
- NPSNR is BeeP’s proxy for the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) in a statistical sense (detection significance) like ‘how many sigmas this detection is’. It cannot be read as the flux density divided by the flux density error bar. A Gaussian homogeneous background is assumed.
- SRCSIG is BeeP’s detection significance. It is derived from NPSNR with a non-Gaussianity correction based on RELTH applied.
- EST_QUALITY indicates the expected quality of the source parameter estimates. The highest quality is 5. Then, if a source does not meet the conditions in table, the correspondent penalty is subtracted.
- The field "NAME" has the exact same source name as in Planck’s 857 GHz channel PCCS2+2E and should be used to reference any source in this catalogue.
Thermal sub-catalogue (see section 6.2.1 of the companion paper)
- The sources Spectral Energy Density (SED) was modeled after a Modified Black-Body (MBB) with parameters: Temperature (), Spectral index () and Flux density at a reference channel ().
- The MBB parameters, together with the source radius and position, make the likelihood parameter set.
- Colour correction coefficients were included in the likelihood.
‘Free’ amplitude at each channel sub-catalogue
Contains a sub-catalogue of independent flux density measurements (not dependent on a SED physical model) at each of the utilized channels (see section A.1.2 of the companion paper).
- Main goal was to allow a direct comparison with catalogues obtained at each channel independently. No source SED model was used
- The likelihood parameter set was the flux density at each channel plus source position and radius. The best fit flux densities at each channel and error bars were computed from the flux density posterior distributions. With the pairs {}, a MBB curve was fitted using a Gaussian likelihood.
- During the estimation of the initial flux densities at each channel, colour-correction was not used. However when later fitting the MBB parameters colour-correction coefficients were included.
Background thermal properties catalogue (see section 6.3 of the companion paper)
- Main goal was to provide a measurement of the contrast between the thermal properties of the background and the source.
- The average brightness around each PCCS2+2E position ( pixels; ) and its standard deviation were computed for each individual channel. The map offset levels had previously been corrected.
- With the pairs {}, a MBB curve with colour correction, was fitted using a Gaussian likelihood.
- The Signal-to-Noise Ratio Raw (SNRr) was computed by dividing the source average brightness at each channel by the background brightness standard deviation. The source average brightness was estimated by dividing the MBB flux density estimate at that frequency by the total solid angle resulting from the convolution of the beam, at that channel, and the intrinsic source extension.
Source ID and association fields
Adds a BeeP source index. Contains the separation between BeeP’s catalogue positions and those in Planck’s 857 PCCS2+2E and flags potential multiple detections of the same physical object. The field BEEPSRCASS contains either the same index as that of the source or the index of a close neighbour if it is inside a radius of and its NPSNR is higher.
| Set | location | c (mJy) |
|---|---|---|
| PCCS2 | Planck’s PCCS2 region | 57 |
| PCCS2E | Planck’s PCCS2E region and | 168 |
| 820 |
Description of the catalogue columns.[edit]
| Field name | Type | Size | Units | Description | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | char | 20 | PCCS2+2E Source name | ||
| PCCS2RA | double | 8 | Degrees | J2000 RA in PCCS2+2E | |
| PCCS2DEC | double | 8 | Degrees | J2000 DEC in PCCS2+2E | |
| BEEPGLON | double | 8 | Degrees | Galactic longitude estimated by BeeP | Average of 95% highest likelihood samples |
| BEEPGLAT | double | 8 | Degrees | Galactic latitude estimated by BeeP | Average of 95% highest likelihood samples |
| BEEPRA | double | 8 | Degrees | J2000 RA estimated by BeeP | Computed from BEEPGLON and BEEPGLAT |
| BEEPDEC | double | 8 | Degrees | J2000 DEC estimated by BeeP | Computed from BEEPGLON and BEEPGLAT |
| PCCS2GLON | double | 8 | Degrees | Galactic longitude in PCCS2+2E | |
| PCCS2GLAT | double | 8 | Degrees | Galactic latitude in PCCS2+2E | |
| NPSNR | double | 8 | Unitless | Source detection significance uncorrected | Background assumed Gaussian (see section A.1.2 of PIP LV) |
| RELTH | double | 8 | Unitless | 95% percentile of the likelihood background statistic | Used to correct for the background non-gaussinaty (see section A.1.2 of PIP LV) |
| ACCEPT | double | 8 | Unitless | Sample acceptance ratio of the MCMC chain | If low () might be indicative of unreliable estimates |
| INPIX | double | 8 | Unitless | Percentage of pixels in-painted in the field | Very high numbers might indicate unreliable estimates |
| MAXFOUND | double | 8 | 0 / 1 | If a likelihood maximum was found within a radius of 3 pixels from the original location | If a maximum is not found this is an indication that BeeP’s position might not be a compact source |
| SRCSIG | double | 8 | Unitless | Source detection significance | Corrected for background non-gaussianity (see section A.1.2 of PIP LV) |
| EST_QUALITY | double | 8 | Unitless | Source parameter estimates quality flag [5 - 0]. | Quality starts at 5 and the penalties in table [table:QualityPenalties] are applied. Higher values mean higher quality. |
| POSERR | double | 8 | Arcmin | Source position uncertainty. Radius of uncertainty around source best fit position | is the Rayleigh distribution scale factor (see section 6.2.3 of PIP LV) |
| BETA | double | 8 | Unitless | Source spectral index (MBB); Modified Black Body | Posterior median value |
| BETAL2SB | double | 8 | Unitless | Source spectral index uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| BETAH2SB | double | 8 | Unitless | Source spectral index uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| TEMP | double | 8 | Kelvin | Source temperature (MBB); Modified Black Body | Posterior median value |
| TL2SB | double | 8 | Kelvin | Source temperature uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| TH2SB | double | 8 | Kelvin | Source temperature uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| EXT | double | 8 | Arcmin | Source extension before beam convolution | This radius is constant across all channels. The extension parameter was obtained with likelihood beam widths (see section A.2.3 of PIP LV); Posterior median value |
| EXTL2SB | double | 8 | Arcmin | Source extension uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| EXTH2SB | double | 8 | Arcmin | Source extension uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| R | double | 8 | Arcmin | Source radius before beam convolution | This radius is constant across all channels. The parameter was computed from EXT and gives an indication of whether the source is extended (see section 6.2.2 of PIP LV) |
| SREF | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at the reference frequency | Reference frequency is GHz; Posterior median value |
| SREFL2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at the reference frequency uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| SREFH2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at the reference frequency uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| S3000 | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz; MBB predicted at GHz | Posterior median value |
| S3000L2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| S3000H2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| S857 | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz; MBB predicted at GHz | Posterior median value |
| S857L2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| S857H2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| S545 | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz; MBB predicted at GHz | Posterior median value |
| S545L2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| S545H2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| S353 | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz; MBB predicted at GHz | Posterior median value |
| S353L2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| S353H2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| BETAMLIKE | double | 8 | Unitless | Source spectral index (MBB); Modified Black Body | Maximum likelihood estimate |
| TEMPMLIKE | double | 8 | Kelvin | Source temperature (MBB); Modified Black Body | Maximum likelihood estimate |
| SREFMLIKE | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at reference frequency; Modified Black Body | Maximum likelihood estimate |
| FREEGLON | double | 8 | Degrees | Galactic longitude (FREE channel amplitudes) | Average of 95% highest likelihood samples |
| FREEGLAT | double | 8 | Degrees | Galactic latitude (FREE channel amplitudes) | Average of 95% highest likelihood samples |
| FREES3000 | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz; Estimated directly at the IRIS map | Posterior median value |
| FREES3000L2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREES3000H2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREES857 | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz; Estimated directly at Planck’s GHz map | Posterior median value |
| FREES857L2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREES857H2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREES545 | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz; Estimated directly at Planck’s GHz map | Posterior median value |
| FREES545L2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREES545H2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREES353 | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz; Estimated directly at Planck’s GHz map | Posterior median value |
| FREES353L2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREES353H2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at GHz uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREEEXT | double | 8 | Arcmin | Source extension before beam convolution | This radius is constant across all channels. The extension parameter was obtained with likelihood beam widths (see section A.2.3 of PIP LV); Posterior median value |
| FREEEXTL2SB | double | 8 | Arcmin | Source extension uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREEEXTH2SB | double | 8 | Arcmin | Source extension uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREER | double | 8 | Arcmin | Source radius before beam convolution | This radius is constant across all channels. The parameter was computed from FREEEXT and gives an indication of whether the source is extended (see section 6.2.2 of PIP LV) |
| FREEBETA | double | 8 | Unitless | Source spectral index; Computed from the flux densities estimated at each channel[15] | Posterior median value |
| FREEBETAL2SB | double | 8 | Unitless | Source spectral index uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREEBETAH2SB | double | 8 | Unitless | Source spectral index uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREETEMP | double | 8 | Kelvin | Source temperature; Computed from the flux densities estimated at each channel | Posterior median value |
| FREETL2SB | double | 8 | Kelvin | Source temperature uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREETH2SB | double | 8 | Kelvin | Source temperature uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREESREF | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at the reference frequency; Estimated from the likelihood | Reference frequency is GHz; Posterior median value |
| FREESREFL2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at the reference frequency uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREESREFH2SB | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at the reference frequency uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| FREEBETAMLIKE | double | 8 | Unitless | Source spectral index; Computed from the flux densities estimated at each channel | Maximum likelihood estimate |
| FREETEMPMLIKE | double | 8 | Kelvin | Source temperature; Computed from the flux densities estimated at each channel | Maximum likelihood estimate |
| FREESREFMLIKE | double | 8 | Jy | Flux density at the reference frequency; Computed from the flux densities estimated at each channel | Maximum likelihood estimate |
| FREESCHI2 | double | 8 | Unitless | of the maximum likelihood estimates | Reduced |
| BKGB3000 | double | 8 | Jy/pixel[16] | Background brightness at GHz | Average over the patch ( pixels) |
| BKGB30001S | double | 8 | Jy/pixel | Background brightness standard deviation at GHz | Standard deviation over the patch ( pixels) |
| BKGB857 | double | 8 | Jy/pixel | Background brightness at GHz | Average over the patch ( pixels) |
| BKGB8571S | double | 8 | Jy/pixel | Background brightness standard deviation at GHz | Standard deviation over the patch ( pixels) |
| BKGB545 | double | 8 | Jy/pixel | Background brightness at GHz | Average over the patch ( pixels) |
| BKGB5451S | double | 8 | Jy/pixel | Background brightness standard deviation at GHz | Standard deviation over the patch ( pixels) |
| BKGB353 | double | 8 | Jy/pixel | Background brightness at GHz | Average over the patch ( pixels) |
| BKGB3531S | double | 8 | Jy/pixel | Background brightness standard deviation at GHz | Standard deviation over the patch ( pixels) |
| BKGBETA | double | 8 | Unitless | Background spectral index (MBB); Computed from the background brightness estimated at each channel[17] | Posterior median value |
| BKGBETAL2SB | double | 8 | Unitless | Background spectral index uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| BKGBETAH2SB | double | 8 | Unitless | Background spectral index uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| BKGTEMP | double | 8 | Kelvin | Background temperature (MBB) | Posterior median value |
| BKGTL2SB | double | 8 | Kelvin | Background temperature uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| BKGTH2SB | double | 8 | Kelvin | Background temperature uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| BKGBREF | double | 8 | Jy/pixel | Background brightness at the reference frequency; Estimated from the likelihood | Reference frequency is GHz; Posterior median value |
| BKGBREFL2SB | double | 8 | Jy/pixel | Background brightness at the reference frequency uncertainty lower boundary | Lower boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| BKGBREFH2SB | double | 8 | Jy/pixel | Background brightness at the reference frequency uncertainty upper boundary | Upper boundary is the marginal posterior percentile () |
| BKGBETAMLIKE | double | 8 | Unitless | Background spectral index (MBB) | Maximum likelihood estimate |
| BKGTEMPMLIKE | double | 8 | Kelvin | Background temperature (MBB) | Maximum likelihood estimate |
| BKGBREFMLIKE | double | 8 | Jy | Background brightness at the reference frequency | Maximum likelihood estimate |
| BKGCHI2 | double | 8 | Unitless | of the maximum likelihood estimates | Reduced |
| SNRR3000 | double | 8 | Unitless | Signal to Noise Ratio Raw (SNRr) at GHz | Source average brightness divided the background standard deviation brightness |
| SNRR30001S | double | 8 | Unitless | 1 error bar of the SNRr at GHz | Source brightness error bar divided the background standard deviation brightness |
| SNRR857 | double | 8 | Unitless | Signal to Noise Ratio Raw at GHz | Source average brightness divided the background standard deviation brightness |
| SNRR8571S | double | 8 | Unitless | 1 error bar of the SNRr at GHz | Source brightness error bar divided the background standard deviation brightness |
| SNRR545 | double | 8 | Unitless | Signal to Noise Ratio Raw at GHz | Source average brightness divided the background standard deviation brightness |
| SNRR5451S | double | 8 | Unitless | 1 error bar of the SNRr at GHz | Source brightness error bar divided the background standard deviation brightness |
| SNRR353 | double | 8 | Unitless | Signal to Noise Ratio Raw at GHz | Source average brightness divided the background standard deviation brightness |
| SNRR3531S | double | 8 | Unitless | 1 error bar of the SNRr at GHz | Source brightness error bar divided the background standard deviation brightness |
| SRCINDEX | double | 8 | Unitless | Source index | |
| SRCSEP | double | 8 | Arcmin | Separation between BeeP’s catalogue positions and PCCS2+2E’s | BEEPGLON and BEEPGLAT used |
| BEEPSRCASS | double | 8 | Unitless | Index of associated source | A source can be associated with another one if there is a source within a radius with higher NPSNR |
Position and flux density correction[edit]
In sections B.2, B.3 and B.4 of the companion paper, it is suggested that the catalogue error bars of the source position (POSERR) and flux density (SREFH2SB, SREFL2SB) estimates may be over-optimistic for objects with high NPSNR. If a more accurate estimate of the uncertainty is desirable, then a correction must be added to the catalogue values.
Position correction[edit]
On the grounds of the suggestion in the companion paper formulas B.3 and B.7, we recommend the following correction to be added: where POSERR must be expressed in arcmin. In the paper’s figure B.6 we show, in red and green, the effect of applying the suggested correction.
Flux density correction[edit]
where is one of the constants in table 1 and can be given either by
for a symmetric error bar, or
and
if the non-symmetrical character of the uncertainty needs to be preserved.
Example of a symmetrical correction: Source PCCS2 857 G002.95+57.96 (NPSNR). where we have used the correction constant for the ‘PCCS2 region’, mJy.
In figures 11 and B.7, we show, in red and blue, the effect of applying the symmetrical correction.
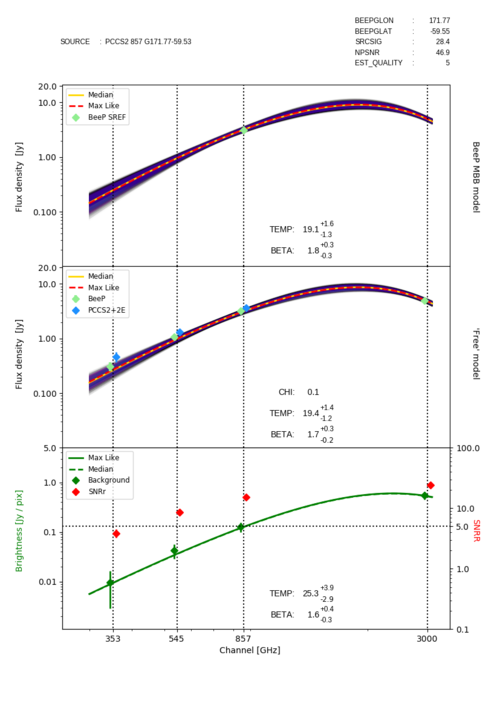
Spectral Energy Density (SED) plots[edit]
BeeP’s estimate of the flux density at 857 GHz, and in the middle panel BeeP’s Free estimates of the flux density at each frequency. In the lower panel, dark green diamonds are the background brightness estimates at each frequency, and the green curves are the maximum likelihood (dashed) and the median (solid) models. Red diamonds are the average source brightness divided by the background rms brightness in that patch, i.e., raw S/N. The data points are slightly displaced from their nominal frequencies to avoid overlaps. | Source ‘SED plot’, showing the SED curves for the MBB (upper panel) and Free (middle panel) models for one source (NGC 895). The background is given in the bottom panel. The yellow and red dashed curves are the median and maximum-likelihood fits, respectively. The purple and black bands are the and regions, respectively, of the full posterior density. Blue diamonds are the PCCS2+2E flux-density estimates (APERFLUX). The green diamonds are: in the upper panel BeeP’s estimate of the flux density at 857 GHz, and in the middle panel BeeP’s Free estimates of the flux density at each frequency. In the lower panel, dark green diamonds are the background brightness estimates at each frequency, and the green curves are the maximum likelihood (dashed) and the median (solid) models. Red diamonds are the average source brightness divided by the background rms brightness in that patch, i.e., raw S/N. The data points are slightly displaced from their nominal frequencies to avoid overlaps.Another component of the catalogue is a collection of figures, one for each row, that displays the SED curves for each of the models. There are three different panels in each figure,
- SOURCE: Is the PCCS2+2E name of the source.
- BEEPGLON and BEEPGLAT: Are the Galactic longitude and latitude computed by BeeP using the MBB SED model.
- SRCSIG, NPSNR and EST_QUALITY are the fields defining the reliability of the source and the estimation quality (see companion paper section 5.4).
- Upper panel - MBB SED curves.
This figure shows the SED curves drawn from the MBB parameter samples when marginalising over all others. There is a curve for each sample drawn from BeeP’s posterior. In purple, if the sample was inside the HPD[18] of the full posterior, otherwise in black. The golden line is drawn from the Median of the marginalised distributions and the dashed red line from the maximum likelihood solution. The green diamond is BeeP’s estimate of the reference flux density (at 857 GHz).
- Middle panel - ‘Free’ channel amplitudes.
The green diamonds are BeeP’s posterior medians of the flux densities at each channel[19]. The purple and black lines have the same meaning as in the upper panel but the posterior samples were drawn from fitting a MBB SED model, using a Gaussian likelihood, to the green diamonds and respective error bars. Blue diamonds are the PCCS2+2E flux-density estimates (APERFLUX).
- Lower panel - Background/Foreground contrast parameters.
The dark green diamonds are the background brightness estimates at each frequency. The green curves were fitted to the individual brightness estimates using a MBB model and a Gaussian likelihood just like in the case of the middle panel. The green dashed line is the maximum likelihood solution and the solid the Median. The red diamonds are BeeP’s SNRr: Source average brightness divided by the background brightness standard deviation in that patch.
- The TEMP and BETA numerical parameter values, shown in all panels, are the marginalised posterior medians.
- The values are the reduced of the maximum likelihood solution.
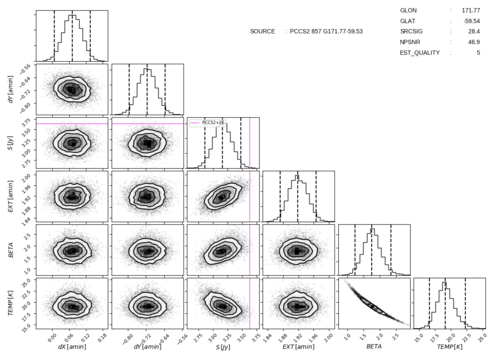
Parameter posterior distributions (‘corner plots’)[edit]
This component of the catalogue is another collection of figures showing the MBB parameter posterior distributions of BeeP’s likelihood in the form of a ‘corner’ plot (see figure 5).
- SOURCE: Is the PCCS2+2E name of the source.
- GLON and GLAT: Are the Galactic longitude and latitude in the PCCS2+2E catalogue. These are the coordinates of the parameters and .
- SRCSIG, NPSNR and EST_QUALITY are the fields defining the reliability of the source and the estimation quality (see companion paper section 5.4).
- The figures in the diagonal are the marginal distributions (histogram) of each MBB parameter and the non-diagonal show the joint distribution (bi-dimensional histogram) of the row-column parameters.
- Darker patterns mean higher probability density.
- The vertical lines in the marginals ate the {} percentiles.
- The violet line is the PCCS2+2E catalogue flux density at the GHz channel (APERFLUX).
(2015) Planck Catalogue of Galactic Cold Clumps[edit]
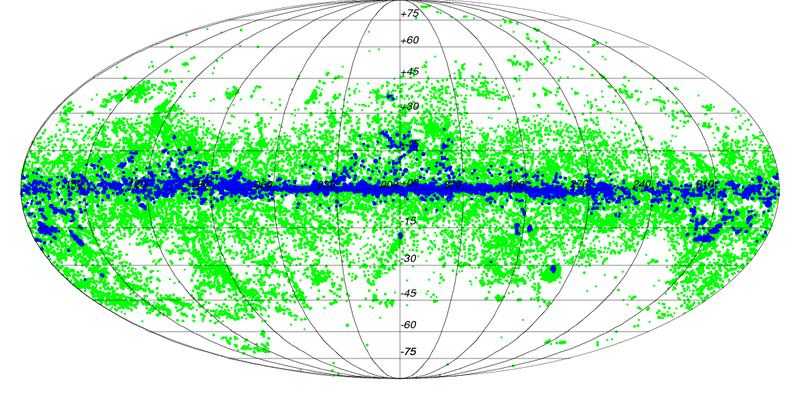
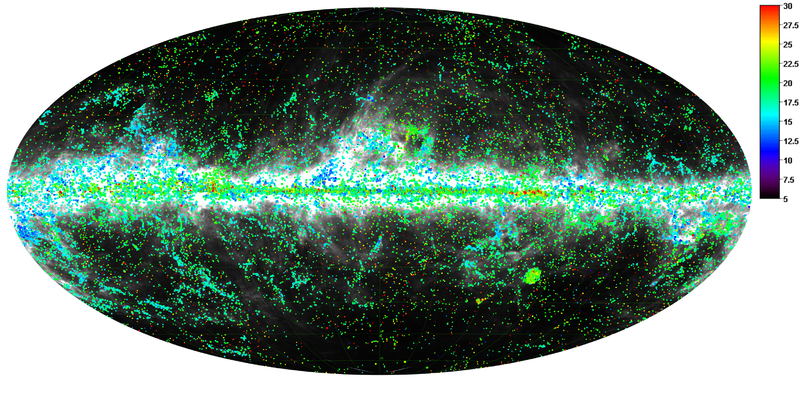
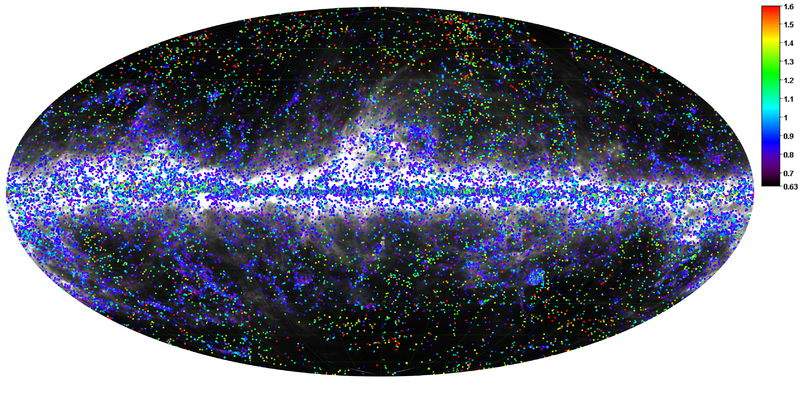
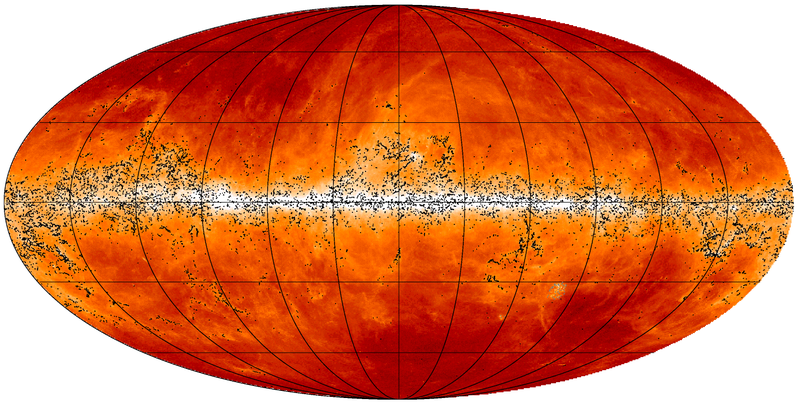
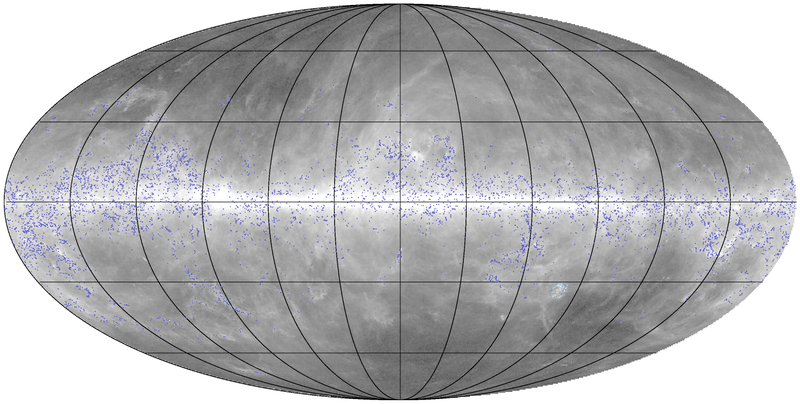
The Planck Catalogue of Galactic Cold Clumps (PGCC) is a list of 13188 Galactic sources and 54 sources located in the Small and Large Magellanic Clouds. The sources have been identified in Planck data as sources colder than their environment. The PGCC has been built using 48 months of Planck data at 857, 545, and 353 GHz, combined with the 3-THz IRAS data, as described in Planck-2015-A28[20].
The all-sky distribution of the PGCC sources is plotted below on the 857-GHz emission shown in logarithmic scale between 10-2 to 102 MJy sr-1.
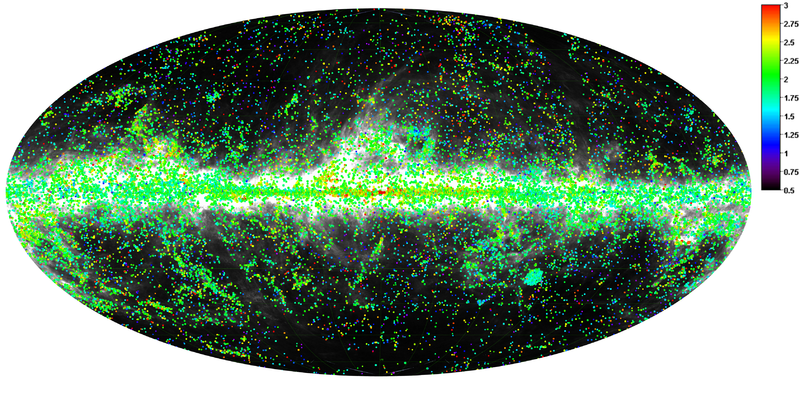
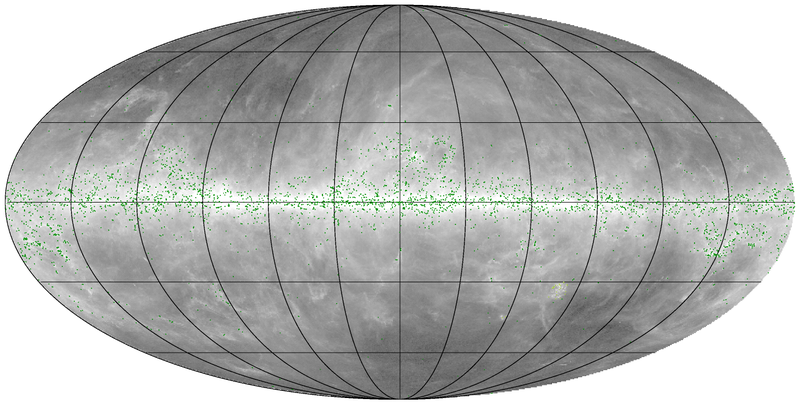
Sources are divided into three categories based on the reliability of the flux density estimates in the IRAS 3-THz and Planck 857, 545, and 353 GHz bands:
- FLUX_QUALITY=1, sources with flux density estimates S/N > 1 in all bands;
- FLUX_QUALITY=2, sources with flux density estimates S/N > 1 only in the 857-, 545-, and 353-GHz Planck bands, considered as very cold source candidates;
- FLUX_QUALITY=3, sources without any reliable flux density estimates, listed as poor candidates.
The all-sky distributions of the PGCC sources per FLUX_QUALITY category are plotted below of the 857-GHz map in grey scale, varying in logarithmically between 10-2 and 102 MJy sr-1.
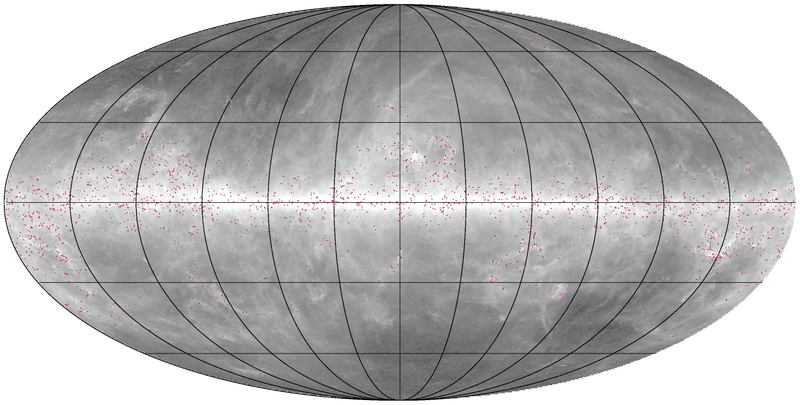
Distance estimates have been obtained for 5574 PGCC sources using seven different methods, as described in Planck-2015-A28[20]. A flag is set to quantify the quality of the distance estimates, defined as follows:
- DIST_QUALITY=0, no distance estimate;
- DIST_QUALITY=1, single distance estimate;
- DIST_QUALITY=2, multiple distance estimates which are consistent within 1σ;
- DIST_QUALITY=3, multiple distance estimates which are not consistent within 1σ;
- DIST_QUALITY=4, single upper limits.
The all-sky distribution of sources with robust distance estimates is shown below.
The catalogue is contained in the FITS file HFI_PCCS_GCC_R2.02.fits. Its structure is shown in the following table.
| Identification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| NAME | String | Source Name | |
| SNR | real*8 | Maximum S/N over the 857, 545, and 353 GHz Planck cold residual maps | |
| SNR_857 | real*8 | S/N of the cold residual detection at 857 GHz | |
| SNR_545 | real*8 | S/N of the cold residual detection at 545 GHz | |
| SNR_353 | real*8 | S/N of the cold residual detection at 353 GHz | |
| Source position | |||
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| GLON | real*8 | deg | Galactic longitude based on morphology fitting |
| GLAT | real*8 | deg | Galactic latitude based on morphology fitting |
| RA | real*8 | deg | Right ascension (J2000) in degrees transformed from (GLON, GLAT) |
| DEC | real*8 | deg | Declination (J2000) in degrees transformed from (GLON, GLAT) |
| Morphology | |||
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| GAU_MAJOR_AXIS | real*8 | arcmin | FWHM along the major axis of the elliptical Gaussian |
| GAU_MAJOR_AXIS_SIG | real*8 | arcmin | 1σ uncertainty on the FWHM along the major axis |
| GAU_MINOR_AXIS | real*8 | arcmin | FWHM along the minor axis of the elliptical Gaussian |
| GAU_MINOR_AXIS_SIG | real*8 | arcmin | 1σ uncertainty on the FWHM along the minor axis |
| GAU_POSITION_ANGLE | real*8 | rad | Position angle of the elliptical Gaussian (see note 1) |
| GAU_POSITION_ANGLE_SIG | real*8 | rad | 1σ uncertainty on the position angle |
| Photometry | |||
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| FLUX_3000_CLUMP | real*8 | Jy | Flux density of the clump at 3 THz |
| FLUX_3000_CLUMP_SIG | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty on the flux density of the clump at 3 THz |
| FLUX_857_CLUMP | real*8 | Jy | Flux density of the clump at 857 GHz |
| FLUX_857_CLUMP_SIG | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty on the flux density of the clump at 857 GHz |
| FLUX_545_CLUMP | real*8 | Jy | Flux density of the clump at 545 GHz |
| FLUX_545_CLUMP_SIG | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty on the flux density of the clump at 545 GHz |
| FLUX_353_CLUMP | real*8 | Jy | Flux density of the clump at 353 GHz |
| FLUX_353_CLUMP_SIG | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty on the flux density of the clump at 353 GHz |
| FLUX_3000_WBKG | real*8 | Jy | Flux density of the warm background at 3 THz (see note 2) |
| FLUX_3000_WBKG_SIG | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty on the flux density of warm background at 3 THz |
| FLUX_857_WBKG | real*8 | Jy | Flux density of the warm background at 857 GHz |
| FLUX_857_WBKG_SIG | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty on the flux density of the warm background at 857 GHz |
| FLUX_545_WBKG | real*8 | Jy | Flux density of the warm background at 545 GHz |
| FLUX_545_WBKG_SIG | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty on the flux density of the warm background at 545 GHz |
| FLUX_353_WBKG | real*8 | Jy | Flux density of the warm background at 353 GHz |
| FLUX_353_WBKG_SIG | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty on the flux density of the warm background at 353 GHz |
| FLUX_QUALITY | int*4 | 1-3 | Category of flux density reliability (see note 3) |
| FLUX_BLENDING | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if blending issue with flux density estimate (see note 4) |
| FLUX_BLENDING_IDX | int*8 | Catalogue index of the closest source responsible for blending | |
| FLUX_BLENDING_ANG_DIST | real*8 | arcmin | Angular distance to the closest source responsible for blending |
| FLUX_BLENDING_BIAS_3000 | real*8 | % | Relative bias of the flux density at 3 THz due to blending |
| FLUX_BLENDING_BIAS_857 | real*8 | % | Relative bias of the flux density at 857 GHz due to blending |
| FLUX_BLENDING_BIAS_545 | real*8 | % | Relative bias of the flux density at 545 GHz due to blending |
| FLUX_BLENDING_BIAS_353 | real*8 | % | Relative bias of the flux density at 353 GHz due to blending |
| Distance | |||
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| DIST_KINEMATIC | real*8 | kpc | Distance estimate [1] using kinematics |
| DIST_KINEMATIC_SIG | real*8 | kpc | 1σ uncertainty on the distance estimate [1] using kinematics |
| DIST_OPT_EXT_DR7 | real*8 | kpc | Distance estimate [2] using optical extinction on SDSS DR7 |
| DIST_OPT_EXT_DR7_SIG | real*8 | kpc | 1σ uncertainty on the distance estimate [2] using optical extinction on SDSS DR7 |
| DIST_OPT_EXT_DR9 | real*8 | kpc | Distance estimate [3] using optical extinction on SDSS DR9 |
| DIST_OPT_EXT_DR9_SIG | real*8 | kpc | 1σ uncertainty on the distance estimate [3] using optical extinction on SDSS DR9 |
| DIST_NIR_EXT_IRDC | real*8 | kpc | Distance estimate [4] using near-IR extinction towards IRDCs |
| DIST_NIR_EXT_IRDC_SIG | real*8 | kpc | 1σ uncertainty on the distance estimate [4] using near-IR extinction towards IRDCs |
| DIST_NIR_EXT | real*8 | kpc | Distance estimate [5] using near-IR extinction |
| DIST_NIR_EXT_SIG | real*8 | kpc | 1σ uncertainty on the distance estimate [5] using near-IR extinction |
| DIST_MOLECULAR_COMPLEX | real*8 | kpc | Distance estimate [6] using molecular complex association |
| DIST_MOLECULAR_COMPLEX_SIG | real*8 | kpc | 1σ uncertainty on the distance estimate [6] using molecular complex association |
| DIST_HKP_GCC | real*8 | kpc | Distance estimate [7] from the Herschel Key-Programme Galactic Cold Cores |
| DIST_HKP_GCC_SIG | real*8 | kpc | 1σ uncertainty on the distance estimate [7] from the Herschel Key-Programme Galactic Cold Cores |
| DIST_OPTION | int*4 | 0-7 | Option of the best distance estimate used in other physical properties |
| DIST_QUALITY | int*4 | 0-4 | Quality flag of the consistency between distance estimates (see note 5) |
| DIST | real*8 | kpc | Best distance estimate used for further physical properties |
| DIST_SIG | real*8 | kpc | 1σ uncertainty on the best distance estimate |
| Temperature | |||
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| TEMP_CLUMP | real*8 | K | Temperature of the clump with β as a free parameter |
| TEMP_CLUMP_SIG | real*8 | K | 1σ uncertainty on the clump temperature with β free |
| TEMP_CLUMP_LOW1 | real*8 | K | Lower 68% confidence limit of the clump temperature with β free |
| TEMP_CLUMP_UP1 | real*8 | K | Upper 68% confidence limit of the clump temperature with β free |
| BETA_CLUMP | real*8 | Spectral index β of the clump | |
| BETA_CLUMP_SIG | real*8 | 1σ uncertainty (from MCMC) on the emissivity spectral index β of the clump | |
| BETA_CLUMP_LOW1 | real*8 | Lower 68% confidence limit of the emissivity spectral index β of the clump | |
| BETA_CLUMP_UP1 | real*8 | Upper 68% confidence limit of the emissivity spectral index β of the clump | |
| TEMP_BETA2_CLUMP | real*8 | K | Temperature of the clump with β = 2 |
| TEMP_BETA2_CLUMP_SIG | real*8 | K | 1σ uncertainty on the temperature of the clump with β = 2 |
| TEMP_BETA2_CLUMP_LOW1 | real*8 | K | Lower 68% confidence limit of the clump temperature with β = 2 |
| TEMP_BETA2_CLUMP_UP1 | real*8 | K | Upper 68% confidence limit of the clump temperature with β = 2 |
| TEMP_WBKG | real*8 | K | Temperature of the warm background with β as a free parameter (see note 6) |
| TEMP_WBKG_SIG | real*8 | K | 1σ dispersion of the warm background temperature with β free |
| TEMP_WBKG_LOW1 | real*8 | K | Lower 68% confidence limit of the warm background temperature with β free |
| TEMP_WBKG_UP1 | real*8 | K | Upper 68% confidence limit of the warm background temperature with β free |
| BETA_WBKG | real*8 | Spectral index β of the warm background (see note 6) | |
| BETA_WBKG_SIG | real*8 | 1σ uncertainty (from MCMC) of the emissivity spectral index β of the warm background | |
| BETA_WBKG_LOW1 | real*8 | Lower 68% confidence limit of the emissivity spectral index β of the warm background | |
| BETA_WBKG_UP1 | real*8 | Upper 68% confidence limit of the emissivity spectral index β of the warm background | |
| TEMP_BETA2_WBKG | real*8 | K | Temperature of the warm background with β = 2 |
| TEMP_BETA2_WBKG_SIG | real*8 | K | 1σ uncertainty on the temperature of the warm background with β = 2 |
| TEMP_BETA2_WBKG_LOW1 | real*8 | K | Lower 68% confidence limit of the warm background temperature with β = 2 |
| TEMP_BETA2_WBKG_UP1 | real*8 | K | Upper 68% confidence limit of the warm background temperature with β = 2 |
| Physical properties | |||
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| NH2 | real*8 | cm-2 | Column density NH2 of the clump |
| NH2_SIG | real*8 | cm-2 | 1σ uncertainty on the column density |
| NH2_LOW[1,2,3] | real*8 | cm-2 | Lower 68%, 95%, and 99% confidence limit of the column density |
| NH2_UP[1,2,3] | real*8 | cm-2 | Upper 68%, 95%, and 99% confidence limit of the column density |
| MASS | real*8 | M☉ | Mass estimate of the clump |
| MASS_SIG | real*8 | M☉ | 1σ uncertainty on the mass estimate of the clump |
| MASS_LOW[1,2,3] | real*8 | M☉ | Lower 68%, 95%, and 99% confidence limit of the mass estimate |
| MASS_UP[1,2,3] | real*8 | M☉ | Upper 68%, 95%, and 99% confidence limit of the mass estimate |
| DENSITY | real*8 | cm-3 | Mean density of the clump |
| DENSITY_SIG | real*8 | cm-3 | 1σ uncertainty on the mean density estimate of the clump |
| DENSITY_LOW[1,2,3] | real*8 | cm-3 | Lower 68%, 95%, and 99% confidence limit of the mean density estimate |
| DENSITY_UP[1,2,3] | real*8 | cm-3 | Upper 68%, 95%, and 99% confidence limit of the mean density estimate |
| SIZE | real*8 | pc | Physical size of the clump |
| SIZE_SIG | real*8 | pc | 1σ uncertainty on the physical size estimate of the clump |
| SIZE_LOW[1,2,3] | real*8 | pc | Lower 68%, 95%, and 99% confidence limit of the physical size estimate |
| SIZE_UP[1,2,3] | real*8 | pc | Upper 68%, 95%, and 99% confidence limit of the physical size estimate |
| LUMINOSITY | real*8 | L☉ | Luminosity of the clump |
| LUMINOSITY_SIG | real*8 | L☉ | 1σ uncertainty on the luminosity estimate of the clump |
| LUMINOSITY_LOW[1,2,3] | real*8 | L☉ | Lower 68%, 95%, and 99% confidence limit of the luminosity estimate |
| LUMINOSITY_UP[1,2,3] | real*8 | L☉ | Upper 68%, 95%, and 99% confidence limit of the luminosity estimate |
| Flags | |||
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| XFLAG_LMC | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if part of the LMC |
| XFLAG_SMC | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if part of the SMC |
| XFLAG_ECC | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the ECC |
| XFLAG_PCCS_857 | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the PCCS 857 GHz band |
| XFLAG_PCCS_545 | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the PCCS 545 GHz band |
| XFLAG_PCCS_353 | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the PCCS 353 GHz band |
| XFLAG_PCCS_217 | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the PCCS 217 GHz band |
| XFLAG_PCCS_143 | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the PCCS 143 GHz band |
| XFLAG_PCCS_100 | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the PCCS 100 GHz band |
| XFLAG_PCCS_70 | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the PCCS 70 GHz band |
| XFLAG_PCCS_44 | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the PCCS 44 GHz band |
| XFLAG_PCCS_30 | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the PCCS 30 GHz band |
| XFLAG_PSZ | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the PCCS PSZ |
| XFLAG_PHZ | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the PCCS HZ |
| XFLAG_HKP_GCC | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the Herschel HKP-GCC |
Notes
- 1: The position angle of the 2D ellipse is defined as the angle between the axis parallele to the Galactic plane and the major axis, measured clockwise.
- 2: The warm background flux densities are computed using the same solid angle as for the clump flux densities, but on the warm conponent map.
- 3: See text above for a full description of the FLUX_QUALITY flag, for which "1" is best.
- 4: This relative bias due to blending provides a rough estimate of the factor that should be applied to the clump flux densities to obtain a corrected estimate. It has been completed using on a very simple modelling of clump morphologies and the local environment. It therefore should be used with caution.
- 5: See text above for a full description of the DIST_QUALITY flag.
- 6: Temperature and spectral index of the warm background are based on the warm background flux density estimates obtained on the same solid angle used for the clumps
(2015) Planck list of high-redshift source candidates[edit]
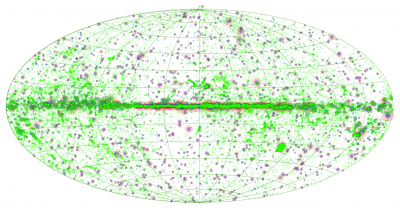
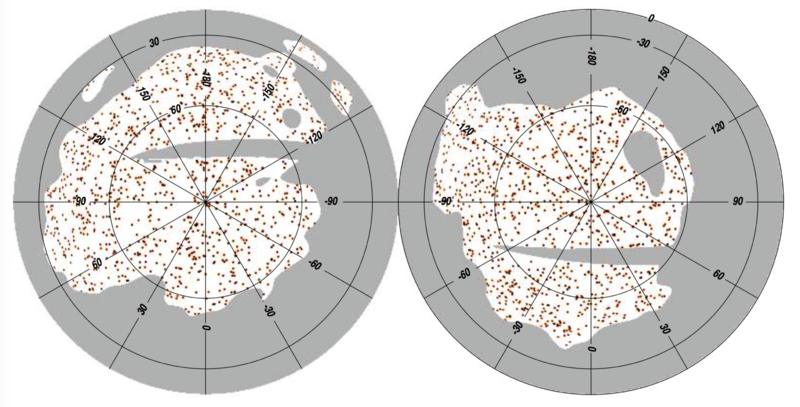
The Planck list of high-redshift source candidates (PHZ) is a list of 2151 sources located in the cleanest 26% of the sky and identified as point sources exhibiting an excess in the submillimetre compared to their environment. It has been built using the 48 months ofPlanck data at 857, 545, 353, and 217 GHz, combined with the 3-THz IRAS data, as described in Planck-2015-XXXIX[21]. These sources are considered as high-z source candidates (z>1.5-2), given the very low contamination by Galactic cirrus, and their typical colour-colour ratios. A subsample of the PHZ list has already been followed-up with Herschel, and chararcterized as overdensities of red galaxies for more than 93% of the population, and as strongly lensed galaxies in 3% of the cases, as detailed in Planck-2014-XXVIII[22].
The all-sky distribution of the PHZ sources is shown below on an orthographic projection.
The PHz source list is contained in the FITS file HFI_PCCS_HZ_R2.00.fits.
Its structure is as follows.
| Identification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| NAME | String | Source name | |
| SNR_X545 | real*8 | S/N in the 545 GHz excess map | |
| SNR_D857 | real*8 | S/N in the 857 GHz cleaned map | |
| SNR_D545 | real*8 | S/N in the 545 GHz cleaned map | |
| SNR_D353 | real*8 | S/N in the 353 GHz cleaned map | |
| Source position | |||
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| GLON | real*8 | deg | Galactic longitude based on morphology fitting |
| GLAT | real*8 | deg | Galactic latitude based on morphology fitting |
| RA | real*8 | deg | Right ascension (J2000) in degrees transformed from (GLON, GLAT) |
| DEC | real*8 | deg | Declination (J2000) in degrees transformed from (GLON, GLAT) |
| Morphology | |||
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| GAU_MAJOR_AXIS | real*8 | arcmin | FWHM along the major axis of the elliptical Gaussian |
| GAU_MAJOR_AXIS_SIG | real*8 | arcmin | 1σ uncertainty on the FWHM along the major axis |
| GAU_MINOR_AXIS | real*8 | arcmin | FWHM along the minor axis of the elliptical Gaussian |
| GAU_MINOR_AXIS_SIG | real*8 | arcmin | 1σ uncertainty on the FWHM along the minor axis |
| GAU_POSITION_ANGLE | real*8 | rad | Position angle of the elliptical Gaussian (see note 1) |
| GAU_POSITION_ANGLE_SIG | real*8 | rad | 1σ uncertainty on the position angle |
| Photometry | |||
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| FLUX_CLEAN_857 | real*8 | Jy | Flux density of the clump at 857 GHz |
| FLUX_CLEAN_857_SIG_SKY | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty at 857 GHz due to sky confusion |
| FLUX_CLEAN_857_SIG_DATA | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty at 857 GHz due to measurement error |
| FLUX_CLEAN_857_SIG_GEOM | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty at 857 GHz due to elliptical Gaussian fit accuracy |
| FLUX_CLEAN_545 | real*8 | Jy | Flux density of the clump at 545 GHz |
| FLUX_CLEAN_545_SIG_SKY | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty at 545 GHz due to sky confusion |
| FLUX_CLEAN_545_SIG_DATA | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty at 545 GHz due to measurement error |
| FLUX_CLEAN_545_SIG_GEOM | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty at 545 GHz due to elliptical Gaussian fit accuracy |
| FLUX_CLEAN_353 | real*8 | Jy | Flux density of the clump at 353 GHz |
| FLUX_CLEAN_353_SIG_SKY | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty at 353 GHz due to sky confusion |
| FLUX_CLEAN_353_SIG_DATA | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty at 353 GHz due to measurement error |
| FLUX_CLEAN_353_SIG_GEOM | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty at 353 GHz due to elliptical Gaussian fit accuracy |
| FLUX_CLEAN_217 | real*8 | Jy | Flux density of the clump at 217 GHz |
| FLUX_CLEAN_217_SIG_SKY | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty at 217 GHz due to sky confusion |
| FLUX_CLEAN_217_SIG_DATA | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty at 217 GHz due to measurement error |
| FLUX_CLEAN_217_SIG_GEOM | real*8 | Jy | 1σ uncertainty at 217 GHz due to elliptical Gaussian fit accuracy |
| Physical Properties | |||
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| PROB_COLCOL | real*8 | Colour-colour selection probability | |
| EBV_MEAN | real*8 | Mean extinction E(B − V)xgal within the source PSF | |
| EBV_APER | real*8 | Aperture estimate of the extinction E(B − V)xgal within the source PSF | |
| EBV_APER_SIG | real*8 | 1σ uncertainty of the aperture extinction E(B − V)xgal within the source PSF | |
| ZPHOT_[25,30,35,40,45,50]K | real*8 | Submm photometric redshift estimate with Txgal = 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, and 50 K | |
| ZPHOT_[25,30,35,40,45,50]K_LOW | real*8 | Lower limit of the 68 % confidence level | |
| ZPHOT_[25,30,35,40,45,50]K_UP | real*8 | Upper limit of the 68 % confidence level | |
| ZPHOT_[25,30,35,40,45,50]K_CHI2 | real*8 | Reduced χ2 of the best fit | |
| LFIR_[25,30,35,40,45,50]K | real*8 | L☉ | FIR luminosity estimate with = 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, and 50 K |
| LFIR_[25,30,35,40,45,50]K_LOW | real*8 | L☉ | Lower limit of the 68 % confidence level |
| LFIR_[25,30,35,40,45,50]K_UP | real*8 | L☉ | Upper limit of the 68 % confidence level |
| SFR_[25,30,35,40,45,50]K | real*8 | M☉yr-1 | Star Formation Rate estimate with Txgal = 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, and 50 K |
| SFR_[25,30,35,40,45,50]K_LOW | real*8 | M☉yr-1 | Lower limit of the 68 % confidence level |
| SFR_[25,30,35,40,45,50]K_UP | real*8 | M☉yr-1 | Upper limit of the 68 % confidence level |
| Flags | |||
| FITS Keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| XFLAG_PLANCK | string | Contains the list of Planck catalogues matching the source: PCCS 857-, 545-, 353-, 217-, 143-, 100-, 70-, 44-, 33-GHz, PSZ, and PGCC | |
| XFLAG_HERSCHEL | int*4 | 0/1 | 1 if present in the Herschel follow-up programme |
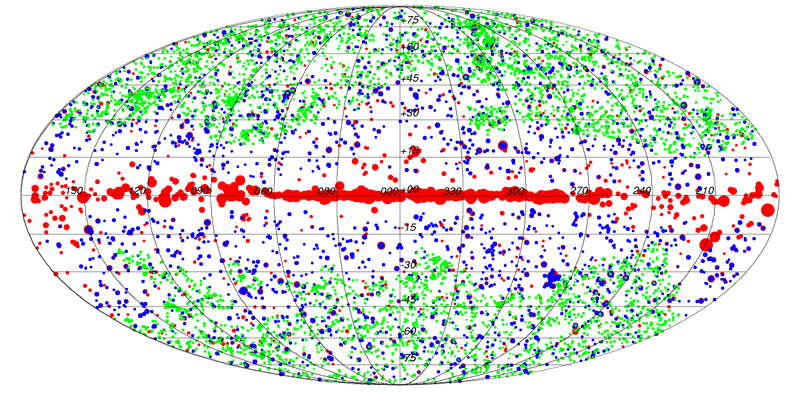
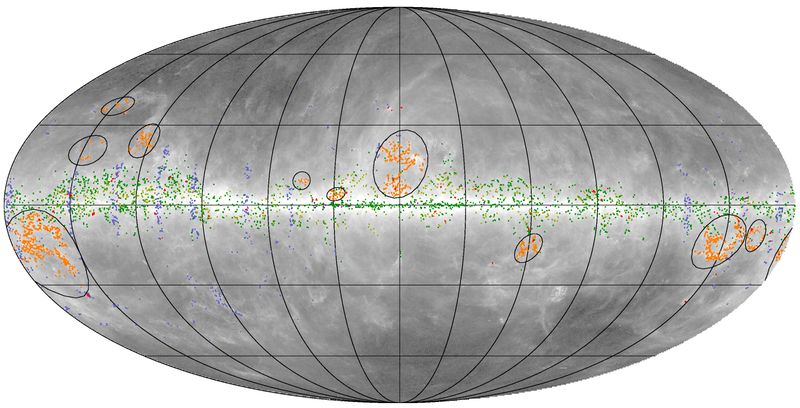
(2015) Second SZ Catalogue[edit]
The Planck SZ catalogue is constructed as described in SZ catalogue and in sections 2 and 3 of Planck-2015-A27[23]. Three pipelines are used to detect SZ clusters: two independent implementations of the Matched Multi-Filter (MMF1 and MMF3), and PowellSnakes (PwS). The main catalogue is constructed as the union of the catalogues from the three detection methods. The completeness and reliability of the catalogues have been assessed through internal and external validation, as described in section 4 of Planck-2015-A27[23].
The size of a detected object is given in terms of the scale size, θs, and the flux is given in terms of the total integrated Comptonization parameter, Y = Y5R500. The parameters of the generalized NFW profile assumed by the detection pipelines are written in the headers of the catalogues. For the sake of convenience, the conversion factor from Y to Y500 is also provided in the header.
The union catalogue contains the coordinates of a detection, its signal-to-noise ratio, an estimate of Y and its uncertainty, together with a summary of the validation information, including external identification of a cluster and its redshift, if they are available. The pipeline from which the information is taken is called the reference pipeline. If more than one pipeline makes the same detection, the information is taken from the the pipeline that makes the most significant detection. Where the redshift is known, we provide the SZ mass for the reference pipeline.
The individual catalogues contain the coordinates and the signal-to-noise ratios of the detections, and information on the sizes and flux densities of the detections. The entries are cross-referenced to the detections in the union catalogue. The full information on the degeneracy between θs and Y is included in the individual catalogues in the form of the two-dimensional probability distribution for each detection. It is computed on a well-sampled grid to produce a two-dimensional image for each detection. This is provided in this form so it can be combined with a model or external data to produce tighter constraints on the source parameters. The individual catalogues also contain Planck measurements of the SZ mass observable, MSZ, as calculated using a Y-M scaling relation and an assumed redshift, in order to break the Y-θs degeneracy. These are provided for each detection as functions of assumed redshift, in the range 0.01 < z < 1, along with the upper and lower 68% confidence limits.
The selection function of the union catalogue, the intersection catalogue, and the individual catalogues are provided in additional files. The selection function files contain the probability of detection for clusters of given intrinsic parameters θ500 and Y500. The file includes the definition of the survey area in the form of a HEALPix mask, and is evaluated for a range of signal-to-noise thresholds between 4.5 and 10.
Union catalogue[edit]
The union catalogue is contained in HFI_PCCS_SZ-union_R2.08.fits.
| Extension 0: primary header, no data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FITS keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| INSTRUME | String | Instrument (HFI) | |
| VERSION | String | Version of catalogue | |
| DATE | String | Date file created: yyyy-mm-dd | |
| ORIGIN | String | Name of organization responsible for the data (HFI-DPC) | |
| TELESCOP | String | Telescope (PLANCK) | |
| CREATOR | String | Pipeline version | |
| DATE-OBS | String | Start date of the survey: yyyy-mm-dd | |
| DATE-END | String | End date of the survey: yyyy-mm-dd | |
| PROCVER | String | Data version | |
| PP_ALPHA | Real*4 | GNFW pressure profile α parameter | |
| PP_BETA | Real*4 | GNFW pressure profile β parameter | |
| PP_GAMMA | Real*4 | GNFW pressure profile γ parameter | |
| PP_C500 | Real*4 | GNFW pressure profile c500 parameter | |
| PP_Y2YFH | Real*4 | Conversion factor from Y to Y500 | |
| Extension 1: BINTABLE, EXTNAME = PSZ2_UNION | |||
| Column Name | Data type | Units | Description |
| INDEX | Int*4 | Index used to cross-reference with individual catalogues | |
| NAME | String | Source name (see note 1) | |
| GLON | Real*8 | deg | Galactic longitude |
| GLAT | Real*8 | deg | Galactic latitude |
| RA | Real*8 | deg | Right ascension (J2000) transformed from (GLON,GLAT) |
| DEC | Real*8 | deg | Declination (J2000) transformed from (GLON,GLAT) |
| POS_ERR | Real*4 | arcmin | Position uncertainty (95% confidence interval) |
| SNR | Real*4 | Signal-to-noise ratio of the detection | |
| PIPELINE | Int*4 | Pipeline from which information is taken (reference pipeline): 1= MMF1; 2 = MMF3; 3 = PwS | |
| PIPE_DET | Int*4 | Pipelines that detect this object (see note 2) | |
| PCCS2 | Bool | Indicates whether detection matches with any in PCCS2 catalogues | |
| PSZ | Int*4 | Index of matching detection in PSZ1, or -1 if new detection | |
| IR_FLAG | Int*1 | Flag denoting heavy IR contamination | |
| Q_NEURAL | Real*4 | Neural network quality flag (see note 3) | |
| Y5R500 | Real*4 | 10-3 arcmin2 | Mean marginal Y5R500 as determined by reference pipeline |
| Y5R500_ERR | Real*4 | 10-3 arcmin2 | Uncertainty on Y5R500 as determined by reference pipeline |
| VALIDATION | Int*4 | External validation status (see note 4) | |
| REDSHIFT_ID | String | External identifier of cluster associated with redshift measurement (see note 5) | |
| REDSHIFT | Real*4 | Redshift of cluster (see note 5) | |
| MSZ | Real*4 | 1014 M☉ | SZ mass proxy (see note 6) |
| MSZ_ERR_UP | Real*4 | 1014 M☉ | Upper bound of 68% SZ mass proxy confidence interval (see note 6) |
| MSZ_ERR_LOW | Real*4 | 1014 M☉ | Lower bound of 68% SZ mass proxy confidence interval (see note 6) |
| MCXC | String | Identifier of X-ray counterpart in the MCXC, if one is present | |
| REDMAPPER | String | Identifier of optical counterpart in the RedMAPPer catalogue, if one is present | |
| ACT | String | Identifier of SZ counterpart in the ACT catalogues, if one is present | |
| SPT | String | Identifier of SZ counterpart in the SPT catalogues, if one is present | |
| WISE_FLAG | Int*4 | Confirmation flag of WISE overdensity (see note 7) | |
| AMI_EVIDENCE | Real*4 | Bayesian evidence for AMI counterpart detection (see note 8) | |
| COSMO | Bool | Indicates whether detection is in the cosmology sample | |
| COMMENT | String | Comments on this detection | |
Notes
- Format is PSZ2 Glll.ll±bb.b where l and b are the Galactic coordinates, truncated to two decimal places.
- The three least significant decimal digits are used to represent detection or non-detection by the pipelines. The order of the digits is: hundreds = MMF1; tens = MMF3; units = PwS. If it is detected then the corresponding digit is set to 1, otherwise it is set to 0.
- Neural network quality flag is 1-Qbad, following the definitions in Aghanim et al. 2014.
- Summary of the external validation, encoding the most robust external identification: 10 = ENO follow-up; 11 = RTT follow-up; 12 = PanSTARRs; 13 = RedMAPPer non-blind; 14 = SDSS high-z; 15 = AMI; 16 = WISE; 20 = legacy identification from the PSZ1; 21 = MCXC; 22 = SPT; 23 = ACT; 24 = RedMAPPer; 25 = legacy identification from PSZ1 with externally updated redshift; 30 = NED; and -1 = no known external counterpart.
- The redshift source is the most robust external identification listed in the VALIDATION field.
- MSZ is the hydrostatic mass assuming the best-fit Y-M scaling relation of Arnaud (2010) as a prior. The uncertainties are statistical and based on the Planck measurement uncertainties only. Not included in the uncertainties are the statistical errors on the scaling relation, the intrinsic scatter in the relation, or systematic errors in data selection for the scaling relation fit.
- Assigned by visual inspection: 0 = no significant galaxy overdensity; 1 = possible galaxy overdensity; 2 = probable galaxy overdensity; 3 = significant galaxy overdensity detected; -1 = possible galaxy overdensity (affected by bright star artefacts); -2 = no significant galaxy overdensity (affected by bright star artefacts); -3 = no assessment possible (affected by bright star artefacts); and -10 = not analysed.
- Defined in the paper.
Individual catalogues[edit]
The individual pipeline catalogues are contained in the FITS files
- HFI_PCCS_SZ-MMF1_R2.08.fits (MMF1 pipeline)
- HFI_PCCS_SZ-MMF3_R2.08.fits (MMF3 pipeline)
- HFI_PCCS_SZ-PwS_R2.08.fits (PowellSnakes pipeline).
Their structure is shown in the following table.
| Extension 0: Primary header, no data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FITS keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| INSTRUME | String | Instrument (HFI) | |
| VERSION | String | Version of catalogue | |
| DATE | String | Date file created: yyyy-mm-dd | |
| ORIGIN | String | Name of organization responsible for the data (HFI-DPC) | |
| TELESCOP | String | Telescope (PLANCK) | |
| CREATOR | String | Pipeline version | |
| DATE-OBS | String | Start time of the survey: yyyy-mm-dd | |
| DATE-END | String | End time of the survey: yyyy-mm-dd | |
| PROCVER | String | Data version | |
| PP_ALPHA | Real*4 | GNFW pressure profile α parameter | |
| PP_BETA | Real*4 | GNFW pressure profile β parameter | |
| PP_GAMMA | Real*4 | GNFW pressure profile γ parameter | |
| PP_C500 | Real*4 | GNFW pressure profile c500 parameter | |
| PP_Y2YFH | Real*4 | Conversion factor from Y to Y500 | |
| Extension 1: BINTABLE, EXTNAME = PSZ2_INDIVIDUAL | |||
| Column name | Data type | Units | Description |
| INDEX | Int*4 | Index from union catalogue | |
| NAME | String | Source name (see note 1) | |
| GLON | Real*8 | deg | Galactic longitude |
| GLAT | Real*8 | deg | Galactic latitude |
| RA | Real*8 | deg | Right ascension (J2000) transformed from (GLON, GLAT) |
| DEC | Real*8 | deg | Declination (J2000) transformed from (GLON, GLAT) |
| POS_ERR | Real*4 | arcmin | Position uncertainty (95% confidence interval) |
| SNR | Real*4 | Signal-to-noise ratio of detection | |
| TS_MIN | Real*4 | Minimum value of θs in grid in second extension HDU (see note 2) | |
| TS_MAX | Real*4 | Maximum value of θs in grid in second extension HDU (see note 2) | |
| Y_MIN | Real*4 | Minimum value of Y in grid in second extension HDU (see note 2) | |
| Y_MAX | Real*4 | Maximum value of Y in grid in second extension HDU (see note 2) | |
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| PIPELINE | String | Name of detection pipeline | |
| Extension 2: IMAGE, EXTNAME = PSZ2_PROBABILITY (see note 2) | |||
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| NAXIS1 | Integer | 256 | Dimension 1 |
| NAXIS2 | Integer | 256 | Dimension 2 |
| NAXIS3 | Integer | Ndet | Dimension 3 = Number of detections |
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| PIPELINE | String | Name of detection pipeline | |
| Extension 3: IMAGE, EXTNAME = PSZ2_MSZ_ARRAY (see note 3) | |||
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| NAXIS1 | Integer | 100 | Dimension 1 |
| NAXIS2 | Integer | 4 | Dimension 2 |
| NAXIS3 | Integer | Ndet | Dimension 3 = Number of detections |
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| PIPELINE | String | Name of detection pipeline | |
Notes
- Format PSZ2 Glll.ll±bb.bb where l and b are the Galactic coordinates truncated to two decimal places.
- Extension 2 contains a three-dimensional image with the two-dimensional probability distribution in θs and Y for each detection. The probability distributions are evaluated on a 256 × 256 linear grid between the limits specified in extension 1. The limits are determined independently for each detection. The dimension of the 3D image is 256 × 256 × Ndet, where Ndet is the number of detections. The first dimension is θs and the second dimension is Y.
- Extension 3 contains a three-dimensional image with the information on the MSZ observable per cluster as a function of assumed redshift. The image dimensions are 100 × 4 × Ndet, where Ndet is the number of detections. The first dimension is the assumed redshift. The second dimension has size 4: the first element is the assumed redshift value corresponding to the MSZ values; the second element is the MSZ lower 68% confidence bound; the third element is the MSZ estimate; and the fourth element is the MSZ upper 68% confidence bound, all in units of 1014 M☉. These uncertainties are based on the Planck measurement uncertainties only. Not included in the error estimates are the statistical errors on the scaling relation, the intrinsic scatter in the relation, or systematic errors in data selection for the scaling relation fit.
Selection function[edit]
The selection function for the union, intersection, and individual pipeline catalogues are contained in the FITS files
- http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-union-survey_R2.08.fits (union catalogue, survey mask)
- http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-union-cosmolog_R2.08.fits (union catalogue, cosmology mask)
- http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-intersec-survey_R2.08.fits (intersection catalogue, survey mask)
- http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-intersec-cosmolog_R2.08.fits (intersection catalogue, cosmology mask)
- http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-MMF1-survey_R2.08.fits (MMF1 catalogue, survey mask)
- http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-MMF1-cosmolog_R2.08.fits (MMF1 catalogue, cosmology mask)
- http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-MMF3-survey_R2.08.fits (MMF3 catalogue, survey mask)
- http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-MMF3-cosmolog_R2.08.fits (MMF3 catalogue, cosmology mask)
- http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-PwS-survey_R2.08.fits (PowellSnakes catalogue, survey mask)
- http://pla.esac.esa.int/pla/aio/product-action?SOURCE_LIST_ASSOCIATED_PRODUCT.FILE_ID=HFI_PCCS_SZ-selfunc-PwS-cosmolog_R2.08.fits (PowellSnakes catalogue, cosmology mask).
Their structure is shown in the following table.
| Extension 0: Primary header, no data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FITS keyword | Data type | Units | Description |
| INSTRUME | String | Instrument (HFI) | |
| VERSION | String | Version of catalogue | |
| DATE | String | Date file created: yyyy-mm-dd | |
| ORIGIN | String | Name of organization responsible for the data (HFI-DPC) | |
| TELESCOP | String | Telescope (PLANCK) | |
| CREATOR | String | Pipeline version | |
| DATE-OBS | String | Start time of the survey: yyyy-mm-dd | |
| DATE-END | String | End time of the survey: yyyy-mm-dd | |
| PROCVER | String | Data version | |
| JOIN | String | Join type (UNION, INTERSEC, MMF1, MMF3, PwS) | |
| MASK | String | Mask name (SURVEY, COSMOLOG) | |
| Extension 1: BINTABLE, HEALPix map (see note 1) | |||
| FITS keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| PIXTYPE | String | HEALPIX | HEALPix pixelation |
| ORDERING | String | RING | Pixel ordering |
| NSIDE | Int*4 | 2048 | HEALPix resolution parameter |
| NPIX | Int*4 | 50331648 | Number of pixels |
| COORDSYS | String | G | Coordinate system |
| Extension 2: IMAGE, EXTNAME = SELFUNC (see note 2) | |||
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| NAXIS1 | Integer | 30 | Dimension 1 |
| NAXIS2 | Integer | 32 | Dimension 2 |
| NAXIS3 | Integer | 12 | Dimension 3 |
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| AXIS1 | String | CY500 | Name of axis 1 |
| AXIS2 | String | T500 | Name of axis 2 |
| AXIS3 | String | SNRCUT | Name of axis 3 |
| UNITS | String | PERCENT | Units of selection function |
| COMPTYPE | String | DIFF | Type of selection function (differential) |
| Extension 3: IMAGE, EXTNAME = YGRID (see note 3) | |||
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| NAXIS1 | Integer | 30 | Dimension 1 |
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| COL1 | String | CY500 | Grid values of Y500 |
| Extension 4: IMAGE, EXTNAME = TGRID (see note 4) | |||
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| NAXIS1 | Integer | 32 | Dimension 1 |
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| COL1 | String | T500 | Grid values of θ500 |
| Extension 5: IMAGE, EXTNAME = SNR_THRESH (see note 5) | |||
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| NAXIS1 | Integer | 12 | Dimension 1 |
| Keyword | Data type | Value | Description |
| COL1 | String | S/N | Grid values of S/N threshold |
Notes
- Extension 1 contains a mask defining the survey region, given by an Nside = 2048 ring-ordered HEALPix map in GALACTIC coordinates. Pixels in the survey region have the value 1.0, while pixels outside the survey region have value 0.0.
- Extension 2 contains a three-dimensional image, giving the survey completeness probability distribution for various S/N thresholds. The information is stored in an image of size 30 × 32 × 12. The first dimension is Y500, the second dimension is θ500 and the third dimension is the signal-to-noise threshold. The units are percentages and lie in the range 0-100, denoting the detection probability of a cluster in the given (Y500, θ500) bin.
- Extension 3 contains the Y500 grid values for the completeness data cube in the second extension. It has length 30 and spans the range from 1.12480 × 10-4 arcmin2 to 7.20325 × 10-2 arcmin2 in logarithmic steps.
- Extension 4 contains the θ500 grid values for the completeness data cube in the second extension. It has length 32 and spans the range from 0.9416 arcmin to 35.31 arcmin in logarithmic steps.
- Extension 5 contains the signal-to-noise threshold grid values for the completeness data cube in the second extension. It has length 12 and contains thresholds from 4.5 to 10.0 in steps of 0.5.
Previous releases: (2013) PSZ1[edit]
Second Planck Release (2013): Description of the Planck SZ Catalogue
(Planck) Low Frequency Instrument
(Planck) High Frequency Instrument
Flexible Image Transfer Specification
Data Processing Center
Full-Width-at-Half-Maximum
Early Release Compact Source Catalog
Cosmic Microwave background
(Hierarchical Equal Area isoLatitude Pixelation of a sphere, <ref name="Template:Gorski2005">HEALPix: A Framework for High-Resolution Discretization and Fast Analysis of Data Distributed on the Sphere, K. M. Górski, E. Hivon, A. J. Banday, B. D. Wandelt, F. K. Hansen, M. Reinecke, M. Bartelmann, ApJ, 622, 759-771, (2005).
Sunyaev-Zel'dovich