|
|
| Line 175: |
Line 175: |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | <!--
| |
| | | | |
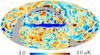
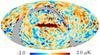
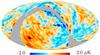
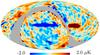
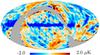
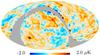
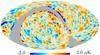
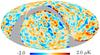
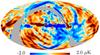
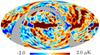
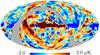
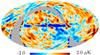
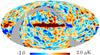
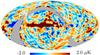
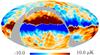
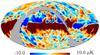
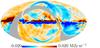
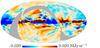
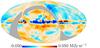
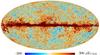
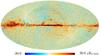
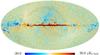
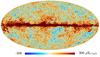
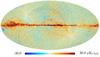
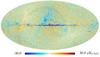
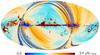
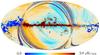
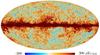
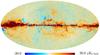
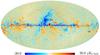
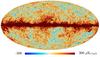
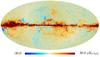
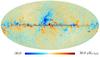
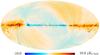
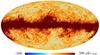
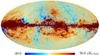
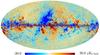
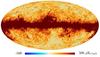
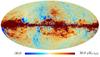
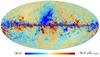
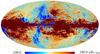
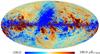
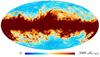
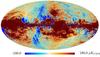
| − | HFI validation is mostly modular. In other words, each part of the pipeline, e.g., timeline processing or mapmaking, has the results of its work validated at each step of the processing, looking specifically for known issues. In addition, we perform additional validation with an eye towards overall system integrity, by looking at generic differences between sets of maps, in which most problems will become apparent (whether known or not). Both these approaches are described below.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==Expected systematics and tests (bottom-up approach)==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Like all experiments, Planck-HFI had a number of specific issues that it needed to be tracked to verify that they were not compromising the data. While these are discussed in appropriate sections, here we gather them together to give brief summaries of the issues and refer the reader to the appropriate section for more details.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | * Cosmic rays – unprotected by the atmosphere and more sensitive than previous bolometric experiments, HFI saw many more cosmic ray hits than its predecessors. These were detected, the worst parts of the data flagged as unusable, and "tails" were modelled and removed. This is described in [[TOI_processing#Glitch_statistics|the section on glitch statistics]]<!-- and in [[#Cosmic_rays|the section on cosmic rays]],--> as well as in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03e|1|the 2013 HFI glitch removal paper}}.
| |
| − | * "Elephants" – cosmic rays also hit the HFI 100-mK stage and cause the temperature to vary, inducing small temperature and thus noise variations in the detectors. These elephants are removed with the rest of the thermal fluctuations, described directly below.
| |
| − | * Thermal fluctuations – HFI is an extremely stable instrument, but there are small thermal fluctuations. These are discussed in [[TOI_processing#Thermal_template_for_decorrelation|the timeline processing section on thermal decorrelation]]<!-- and in [[#1.6K_and_4K_stage_fluctuations|the section on 1.6-K and 4-K thermal fluctuations]]-->.
| |
| − | * Random telegraphic signal (RTS) or "popcorn noise" – some channels were occasionally affected by what seems to be a baseline that abruptly changes between two levels, which has been variously called popcorn noise or random telegraphic signal. These data are usually flagged. This is described in [[TOI_processing#Noise_stationarity|the section on noise stationarity]]<!-- and [[#RTS_noise|the section on Random Telegraphic Signal Noise]]-->.
| |
| − | * Jumps – similar to (but distinct from) popcorn noise, small jumps were occasionally found in the data streams. These jumps are usually corrected, as described in [[TOI_processing#jump_correction|the section on jump corrections]].
| |
| − | * 4-K cooler-induced EM noise – the 4-K cooler induced noise in the detectors with very specific frequency signatures, which can be filtered. This is described in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03|1|the 2013 HFI DPC Paper}}<!--, [[#4K_lines_Residuals|the section below on 4-K line residuals]]-->; their stability is discussed in [[TOI_processing#4K_cooler_lines_variability|the section on 4-K cooler line stability]].
| |
| − | * Compression – on-board compression is used to overcome our telemetry bandwidth limitations. This is explained in {{PlanckPapers|planck2011-1-5}}.
| |
| − | * Noise correlations – correlations in noise between detectors seems to be negligible, except for two polarization-sensitive detectors in the same horn. This is discussed in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03e|1|the 2013 HFI Glitch removal paper}}.
| |
| − | * Pointing – the final pointing reconstruction for Planck is near the arcsecond level. This is discussed in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03|1|the 2013 HFI DPC Paper}}.
| |
| − | * Focal plane geometry – the relative positions of different horns in the focal plane are reconstructed using planets. This is also discussed in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03|1|the 2013 HFI DPC paper}}.
| |
| − | * Main beam – the main beams for HFI are discussed in the {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03d|1|2013 Beams and Transfer function paper}}.
| |
| − | * Ruze envelope – random imperfections, or dust on the mirrors, can mildly increase the size of the beam. This is discussed in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03d|1|the 2013 Beams and Transfer function paper}}.
| |
| − | * Dimpling – the mirror support structure causes a pattern of small imperfections in the beams, which generate small sidelobe responses outside the main beam. This is discussed in the {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03d|1|the 2013 Beams and Transfer function paper}}.
| |
| − | * Far sidelobes – small amounts of light can sometimes hit the detectors from just above the primary or secondary mirrors, or even from reflections off the baffles. While small, when the Galactic centre is in the right position, this can be detected in the highest frequency channels, and so is removed from the data. This is discussed in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03d|1|the 2013 Beams and Transfer function paper}} and also in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-pip88|1|the 2013 Zodiacal emission paper}}.
| |
| − | * Planet fluxes – comparing the known flux densities of planets with the calibration on the CMB dipole is a useful check of calibration for the CMB channels, and is the primary calibration source for the submillimetre channels. This is done in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03b|1|the 2013 Mapmaking and Calibration paper}}.
| |
| − | * Point source fluxes – as with planet fluxes, we also compare fluxes of known, bright point sources with the CMB dipole calibration. This is done in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03b|1|the 2013 Mapmaking and Calibration paper}}.
| |
| − | * Time constants – the HFI bolometers do not react instantaneously to light; there are small time constants, discussed in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03d|1|the 2013 Beams and Transfer function paper}}.
| |
| − | * ADC correction – the HFI analogue-to-digital converters are not perfect, and are not used perfectly. Their effects on the calibration are discussed in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03c|1|the 2013 Mapmaking and Calibration paper}}.
| |
| − | <!--* Gain changes with temperature changes-->
| |
| − | <!--* Optical cross-talk – this is negligible, as noted in [[#Optical_Cross-Talk|the optical cross-talk note]]. -->
| |
| − | * Bandpass – the transmission curves, or "bandpasses" have shown up in a number of places. This is discussed in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03d|1|the 2013 spectral response paper}}.
| |
| − | <!--* Saturation – while this is mostly an issue only for Jupiter observations, it should be remembered that the HFI detectors cannot observe arbitrarily bright objects. This is discussed in [[#Saturation|the section below on saturation]].-->
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <!---==Generic approach to systematics==
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <font style="color:red;font-size:300%">This section is Under (Re-)Construction</font>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Some (null) tests done at the map level are described in {{PlanckPapers|planck2013-p03b}} and {{PlanckPapers|planck2014-a09}}.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Some further tests will be described in the "CMB Power spectra and liklihood paper".
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Finally detailed end-to-end simulations (from lowest level instrument behaviour to maps) are still ongoing for a detailed characterization, which will accompany the 100-217GHz polarisation maps when they are made available, probably by the summer of 2015.--->
| |
| − |
| |
| − | -->
| |
| | | | |
| | ==References== | | ==References== |