Difference between revisions of "Appendix of HFI DPC paper"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Those masks are provided in the PLA.<!-- LVLV --> | Those masks are provided in the PLA.<!-- LVLV --> | ||
| − | The difference between the downgraded of the CO simulated map at N<sub>side</sub>=128 and at N<sub>side</sub>=2048 provides the level of the bias introduced by the downgraded CO template at each bolometer. Residual frequency maps have been computed using this information projected for each bolometer multiplied by the CO bandpass coefficient computed by SRoll. The table displays the mamps of the ratio of the variance inside each pixel at nside=128 in logarithmic scale between the CO frequency residual map and the noise level estimated from the End-to-end simulations. This bias is well determined and specific masks adapted to each scientific analysis can be computed from these ratio maps. It can also be noted that very few pixels have been | + | The difference between the downgraded of the CO simulated map at N<sub>side</sub>=128 and at N<sub>side</sub>=2048 provides the level of the bias introduced by the downgraded CO template at each bolometer. Residual frequency maps have been computed using this information projected for each bolometer multiplied by the CO bandpass coefficient computed by SRoll. The table displays the mamps of the ratio of the variance inside each pixel at nside=128 in logarithmic scale between the CO frequency residual map and the noise level estimated from the End-to-end simulations. This bias is well determined and specific masks adapted to each scientific analysis can be computed from these ratio maps. It can also be noted that very few pixels have been biased at the level of the noise nearby the galactic center. |
The table also gives the sky fraction masked by thresholding (100, 10, 1 %) the rms of the CO bandpass correction at N<sub>side</sub>=2048 inside the pixel at N<sub>side</sub>=128 referred to the rms of the noise at N<sub>side</sub>=2048 inside the pixel at N<sub>side</sub>=128. | The table also gives the sky fraction masked by thresholding (100, 10, 1 %) the rms of the CO bandpass correction at N<sub>side</sub>=2048 inside the pixel at N<sub>side</sub>=128 referred to the rms of the noise at N<sub>side</sub>=2048 inside the pixel at N<sub>side</sub>=128. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
|U | |U | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |100% |
|0.01 | |0.01 | ||
|0.01 | |0.01 | ||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
|0.01 | |0.01 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |10% |
|0.55 | |0.55 | ||
|0.97 | |0.97 | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
|0.29 | |0.29 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |1% |
|7.39 | |7.39 | ||
|8.63 | |8.63 | ||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
|3.38 | |3.38 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |template maps |
|[[File:100-I_CO_Subpix.png|100px]] | |[[File:100-I_CO_Subpix.png|100px]] | ||
|[[File:100-Q_CO_Subpix.png|100px]] | |[[File:100-Q_CO_Subpix.png|100px]] | ||
Revision as of 14:52, 7 November 2017
This page is intented to provide complementary figures to those of the 2017 HFI DPC paper (Planck-2020-A3[1]).
Section 3.1.2: masks of the very bright regions where the sub-pixel effect in the CO foreground templates prevent them to be used for cosmology or astrophysics analysis
Those masks are provided in the PLA.
The difference between the downgraded of the CO simulated map at Nside=128 and at Nside=2048 provides the level of the bias introduced by the downgraded CO template at each bolometer. Residual frequency maps have been computed using this information projected for each bolometer multiplied by the CO bandpass coefficient computed by SRoll. The table displays the mamps of the ratio of the variance inside each pixel at nside=128 in logarithmic scale between the CO frequency residual map and the noise level estimated from the End-to-end simulations. This bias is well determined and specific masks adapted to each scientific analysis can be computed from these ratio maps. It can also be noted that very few pixels have been biased at the level of the noise nearby the galactic center.
The table also gives the sky fraction masked by thresholding (100, 10, 1 %) the rms of the CO bandpass correction at Nside=2048 inside the pixel at Nside=128 referred to the rms of the noise at Nside=2048 inside the pixel at Nside=128.
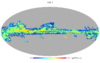
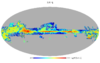
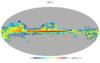
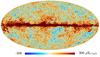
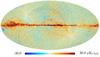
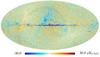
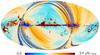
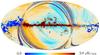
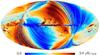
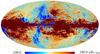
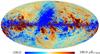
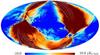
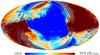
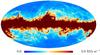
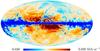
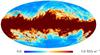
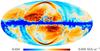
Section 3.2: complementary figures of Fig. 11
| 2015 maps | 2017 maps | difference | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Q | U | I | Q | U | I | Q | U | |
| 100 GHz | 
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
| 143 GHz | 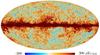
|
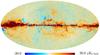
|
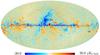
|
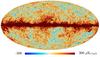
|
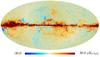
|
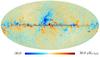
|
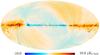
|

|

|
| 217 GHz | 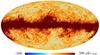
|
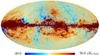
|
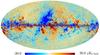
|
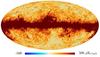
|
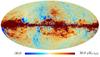
|
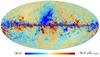
|
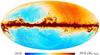
|
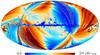
|
|
| 353 GHz | 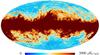
|
|
|
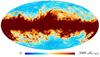
|
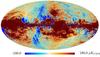
|
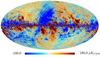
|
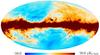
|
|
|
| 545 GHz | 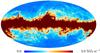
|
. | . | 
|
. | . | 
|
. | . |
| 857 GHz | 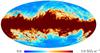
|
. | . | 
|
. | . | 
|
. | . |
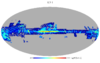
Section 5.3.10: for convenience, we reproduce here Figures 6, 7 and 8 of Rosset et al.
This paper is published as Rosset et al. Planck pre-launch status: High Frequency Instrument polarization calibration. 2010b, A&A, 520, A13. ([2]) The figures 6, 7 et 8 reproduced hereunder are given in the version on ArXiv 1004.2595
| gain errors (1) | polarization efficiency errors (2) | orientation errors (3) |
|---|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: convert: unable to extend cache `/tmp/magick-1182cWVL635sjpzL': File too large @ error/cache.c/OpenPixelCache/4091.
|
Error creating thumbnail: convert: unable to extend cache `/tmp/magick-1191Malf9SwGz5Hd': File too large @ error/cache.c/OpenPixelCache/4091.
|
Error creating thumbnail: convert: unable to extend cache `/tmp/magick-1198tkenQky506uy': File too large @ error/cache.c/OpenPixelCache/4091.
|
(1) in rms due to gain errors from 0.01% to 1% for E-mode (top) and B-mode (bottom) compared to initial spectrum (solid black lines). Cosmic variance for E-mode is plotted in dashed black line.
(2) in rms due to polarization efficiency errors from 0.1% to 4% for E-mode (top) and B-mode (bottom) compared to initial spectrum (solid black lines). Cosmic variance for E-mode is plotted in dashed black line.
(3) in rms due to various orientation errors from 0.25 to 2 degrees for E-mode (top) and B-mode (bottom) compared to initial spectrum (solid black lines). Cosmic variance for E-mode is plotted in dashed black line.
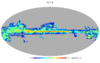
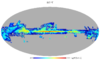
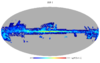
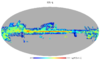
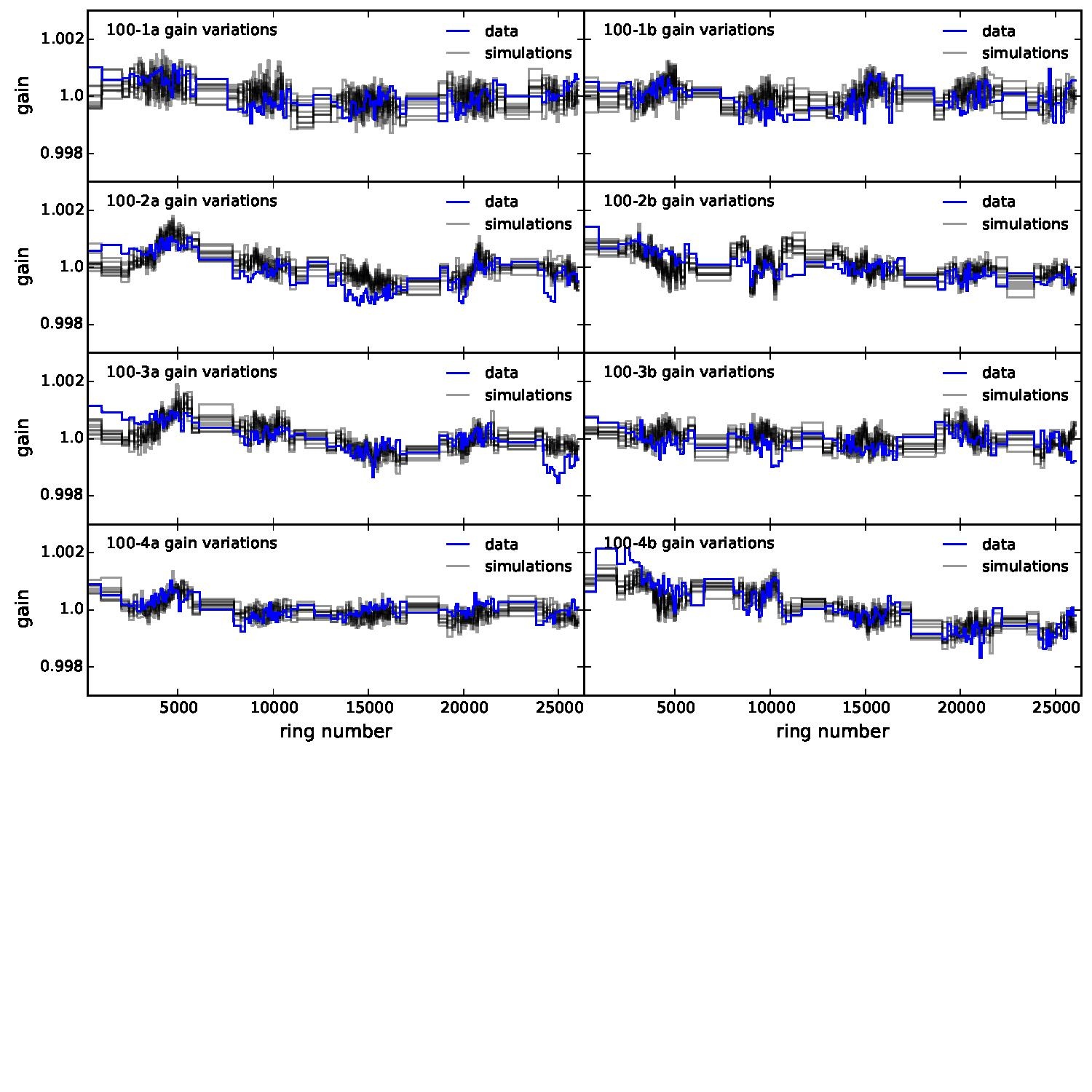
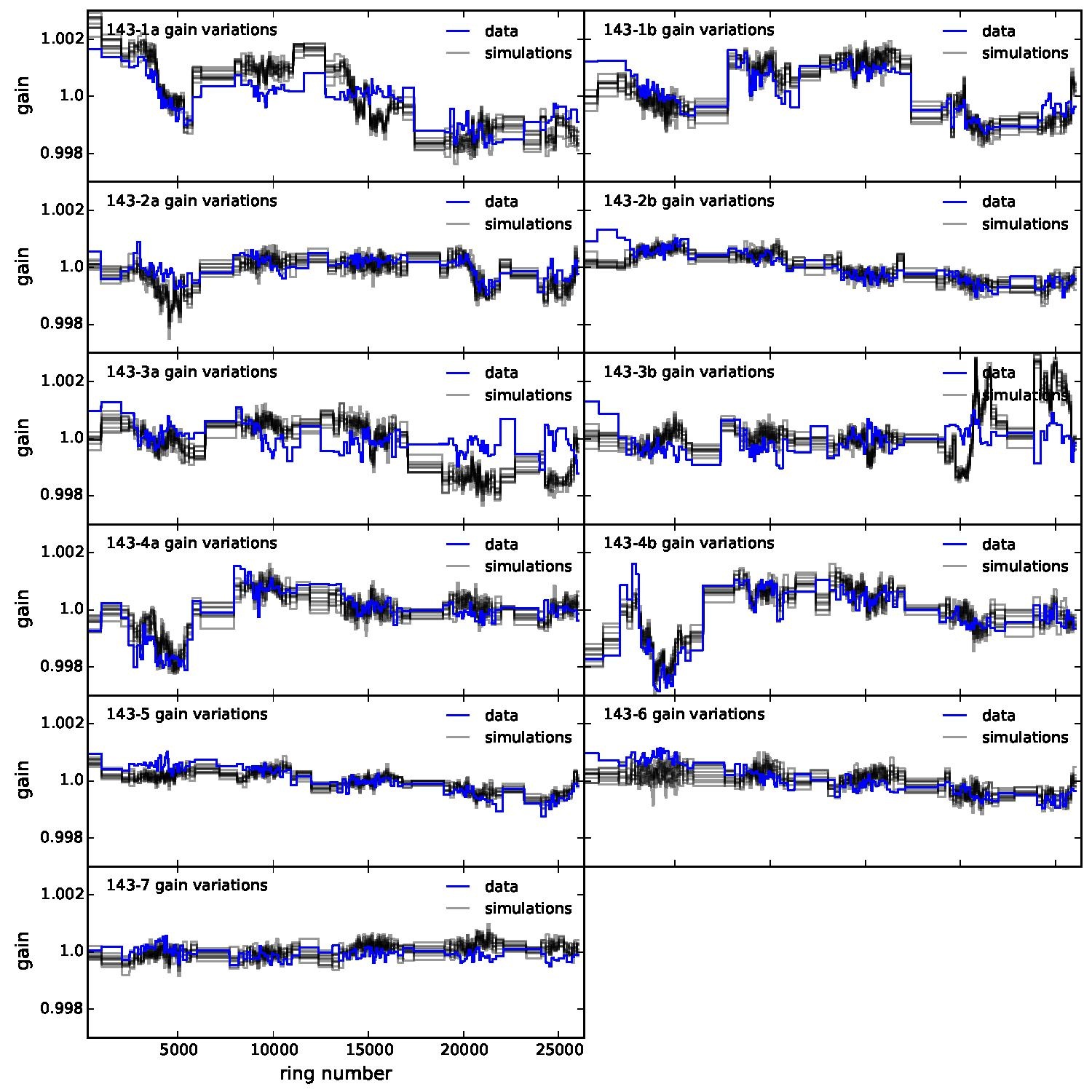
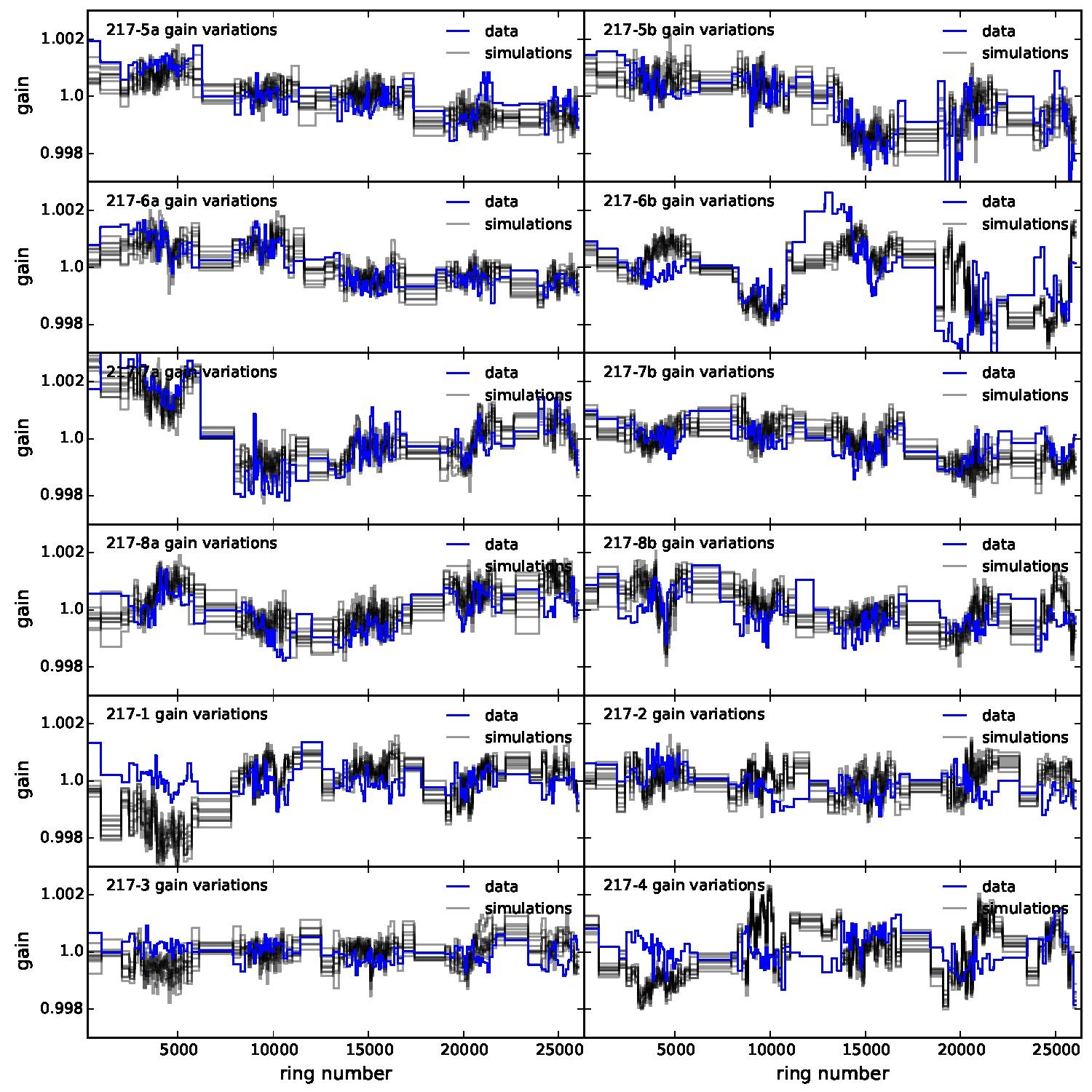
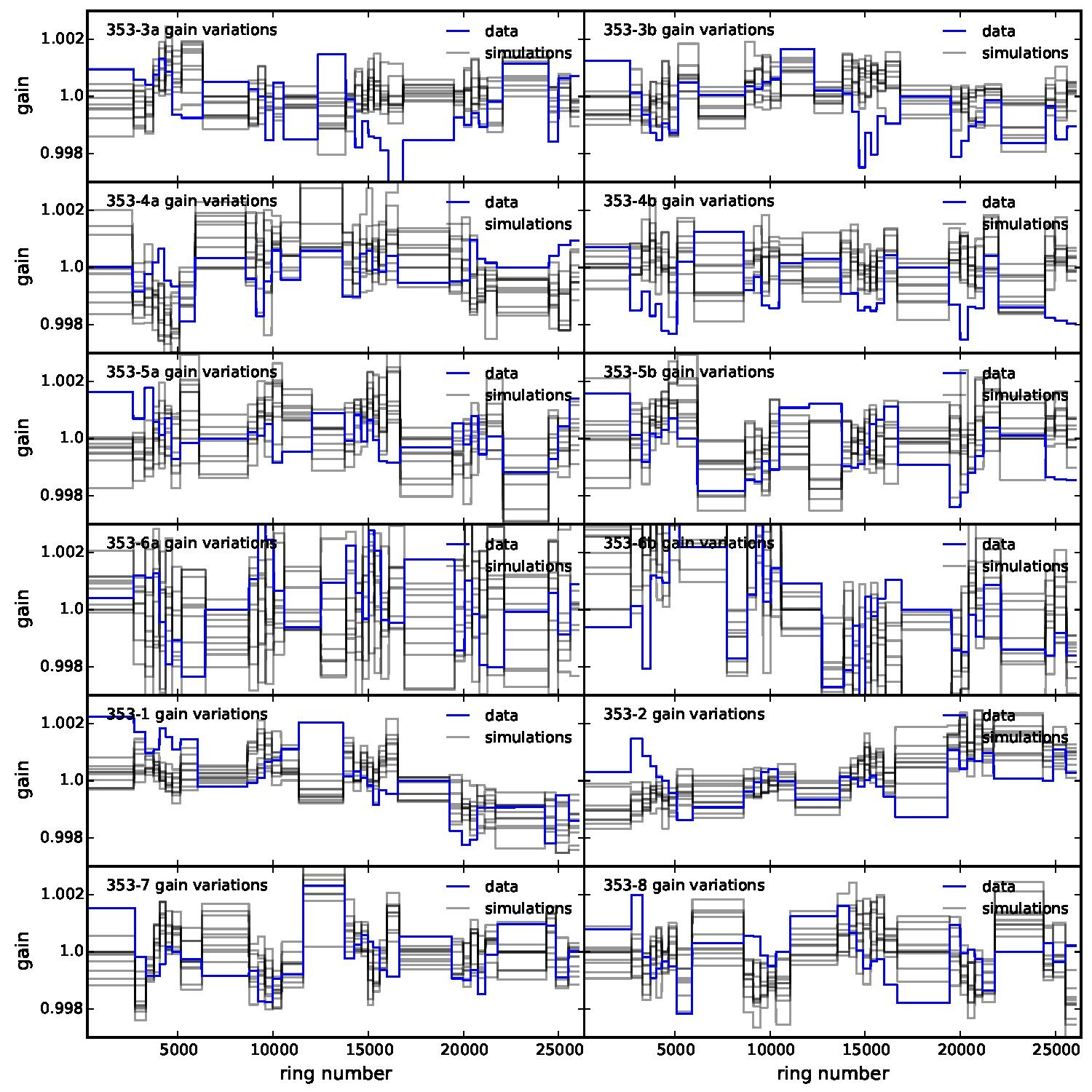
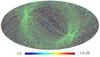
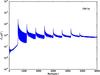
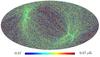
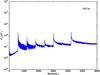
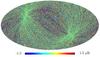
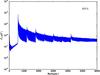
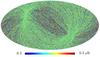
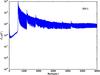
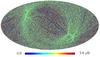
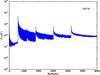
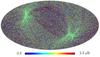
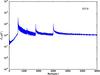
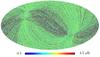
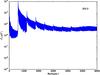
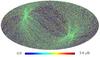
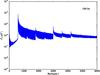
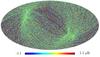
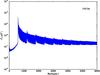
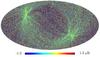
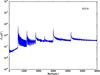
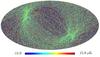
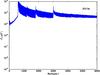
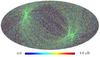
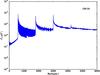
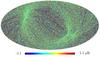
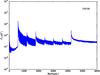
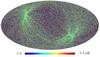
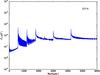
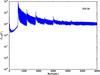
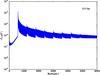
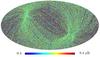
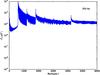
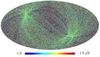
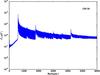
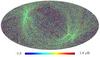
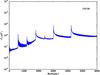
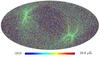
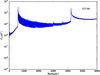
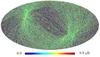
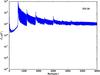
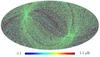
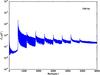
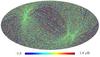
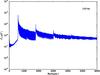
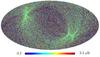
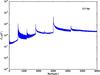
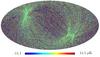
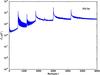
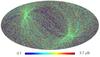
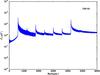
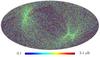
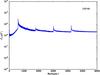
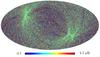
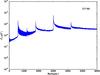
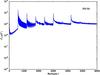
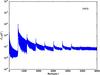
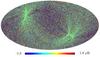
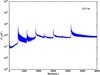
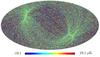
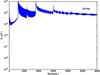
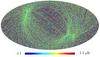
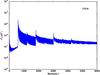
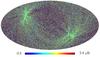
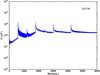
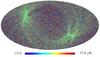
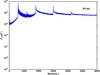
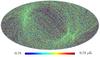
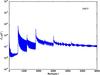
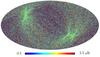
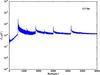
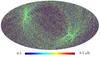
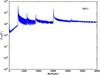
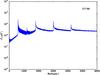
Section 5.5: complementary figures of Fig. 29
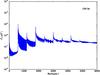
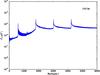
| 100 GHz bolometers | 143 GHz bolometers | 217 GHz bolometers | 353 GHz bolometers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 100px | 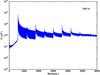
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| . | . | 
|
|
|
|
|
|
| . | . | 
|
|
|
|
|
|
| . | . | 
|
|
|
|
|
|
| . | . | . | . | 
|
|
|
|
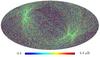
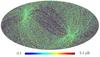
Section 5.13: complementary figures of Fig. 47
References[edit]
- ↑ Planck 2018 results. III. High Frequency Instrument data processing and frequency maps, Planck Collaboration, 2020, A&A, 641, A3.
- ↑
(Planck) High Frequency Instrument
Data Processing Center
Planck Legacy Archive
EMI/EMC influence of the 4K cooler mechanical motion on the bolometer readout electronics.
analog to digital converter