Difference between revisions of "HFI time response model"
m |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == LFER4 model == | + | == LFER4 model (PR1 /2013 release) == |
| + | Here we describe the "Low frequency excess response" 4 model. | ||
If we write the input signal (power) on a bolometer as | If we write the input signal (power) on a bolometer as | ||
<math>\label{bol_in} | <math>\label{bol_in} | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
After integration, the <i>n</i>-sample of a bolometer can be written as <math>\label{eqn:output} | After integration, the <i>n</i>-sample of a bolometer can be written as <math>\label{eqn:output} | ||
Y(t_n) = (-1)^n F(\omega) H'(\omega) e^{i t_n \omega} | Y(t_n) = (-1)^n F(\omega) H'(\omega) e^{i t_n \omega} | ||
| − | </math> where <math>\label{tfele} | + | </math>, where <math>\label{tfele} |
H'(\omega) = \frac 12 \sum_{k=0}^\infty | H'(\omega) = \frac 12 \sum_{k=0}^\infty | ||
e^{-i(\frac{\pi\omega}{2\omega_r}+\omega\Delta t)} \Bigg[ | e^{-i(\frac{\pi\omega}{2\omega_r}+\omega\Delta t)} \Bigg[ | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
The output signal in equation eqn:output can be demodulated (thus removing the (-1)<sup><i>n</i></sup>) and compared to the input signal in equation bol_in. The overall transfer function is composed of the bolometer transfer function and the effective electronics transfer function, <math>H'(\omega)</math>: <math>TF(\omega) = F(\omega) H'(\omega)</math>. | The output signal in equation eqn:output can be demodulated (thus removing the (-1)<sup><i>n</i></sup>) and compared to the input signal in equation bol_in. The overall transfer function is composed of the bolometer transfer function and the effective electronics transfer function, <math>H'(\omega)</math>: <math>TF(\omega) = F(\omega) H'(\omega)</math>. | ||
| − | The shape of <math>H(\omega)</math> is obtained combining low- and high-pass filters with Sallen Key topologies (with their respective time constants) and accounting also for the stray capacitance low-pass filter given by the bolometer impedance combined with the stray capacitance of the cables. The sequence of filters that define the electronic band-pass function <math>H(\omega) = h_0*h_1*h_2*h_3*h_4*h_{5}</math> are listed in the following table. | + | The shape of <math>H(\omega)</math> is obtained combining low- and high-pass filters with Sallen-Key topologies (with their respective time constants) and accounting also for the stray capacitance low-pass filter given by the bolometer impedance combined with the stray capacitance of the cables. The sequence of filters that define the electronic band-pass function <math>H(\omega) = h_0*h_1*h_2*h_3*h_4*h_{5}</math> are listed in the following table. |
<center> | <center> | ||
{| class="wikitable" align="center" style="text-align:left" border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" | {| class="wikitable" align="center" style="text-align:left" border="1" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" | ||
| − | |+ '''HFI electronics filter sequence.''' | + | |+ '''HFI electronics filter sequence.''' Here we define <math>s = i \omega</math>. |
|- bgcolor="ffdead" | |- bgcolor="ffdead" | ||
! Filter || Parameters || Function | ! Filter || Parameters || Function | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |0. Stray capacitance low-pass filter || <math>\tau_{stray}= R_{bolo} C_{stray}</math> || <math>h_0 = \frac{1}{1.0+\tau_{stray}*s}</math> | + | |0. Stray capacitance low-pass filter || <math>\tau_{\rm stray}= R_{\rm bolo} C_{\rm stray}</math> || <math>h_0 = \frac{1}{1.0+\tau_{\rm stray}*s}</math> |
|- | |- | ||
|1. Low-pass filter || <math>R_1=1</math>k<math>\Omega</math> <br /> <math>C_1=100</math>nF || <math>h_1 = \frac{2.0+R_1*C_1*s}{2.0*(1.0+R_1*C_1*s)}</math> | |1. Low-pass filter || <math>R_1=1</math>k<math>\Omega</math> <br /> <math>C_1=100</math>nF || <math>h_1 = \frac{2.0+R_1*C_1*s}{2.0*(1.0+R_1*C_1*s)}</math> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |2. Sallen Key high-pass filter || <math>R_2=51</math>k<math>\Omega</math><br /> <math>C_2=1\mu</math> || <math>h_2= \frac{(R_2*C_2*s)^2}{(1.0+R_2*C_2*s)^2}</math>3 | + | |2. Sallen-Key high-pass filter || <math>R_2=51</math>k<math>\Omega</math><br /> <math>C_2=1\mu</math>F || <math>h_2= \frac{(R_2*C_2*s)^2}{(1.0+R_2*C_2*s)^2}</math>3 |
|- | |- | ||
|3. Sign reverse with gain || || <math>h_3=-5.1</math> | |3. Sign reverse with gain || || <math>h_3=-5.1</math> | ||
| Line 45: | Line 46: | ||
|4. Single pole low-pass filter with gain || <math>R_4=10</math>k<math>\Omega</math><br /> <math>C_4=10</math>nF || <math>h_4= \frac{1.5}{1.0+R_4*C_4*s}</math> | |4. Single pole low-pass filter with gain || <math>R_4=10</math>k<math>\Omega</math><br /> <math>C_4=10</math>nF || <math>h_4= \frac{1.5}{1.0+R_4*C_4*s}</math> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |5. Single pole high-pass filter coupled to a Sallen Key low-pass filter || <math>R_9=18.7</math>k<math>\Omega</math><br /><math>R_{12}=37.4</math>k<math>\Omega</math><br /> <math>C=10.0</math>nF<br /><math>R_{78}=510</math>k<math>\Omega</math><br /> <math>C_{18}=1.0\mu</math>F<br /><math>K_3 = R_9^2*R_{78}*R_{12}^2*C^2*C_{18}</math><br /> <math>K_2 = R_9*R_{12}^2*R_{78}*C^2+R_{9}^2*R_{12}^2*C^2+R_9*R_{12}^2*R_{78}*C_{18}*C</math><br /> <math>K_1 =R_9*R_{12}^2*C+R_{12}*R_{78}*R_9*C_{18}</math> || <math>h_{5} = \frac{2.0*R_{12}*R_9*R_{78}*C_{18}*s}{s^3*K_3 + | + | |5. Single pole high-pass filter coupled to a Sallen-Key low-pass filter || <math>R_9=18.7</math>k<math>\Omega</math><br /><math>R_{12}=37.4</math>k<math>\Omega</math><br /> <math>C=10.0</math>nF<br /><math>R_{78}=510</math>k<math>\Omega</math><br /> <math>C_{18}=1.0\mu</math>F<br /><math>K_3 = R_9^2*R_{78}*R_{12}^2*C^2*C_{18}</math><br /> <math>K_2 = R_9*R_{12}^2*R_{78}*C^2+R_{9}^2*R_{12}^2*C^2+R_9*R_{12}^2*R_{78}*C_{18}*C</math><br /> <math>K_1 =R_9*R_{12}^2*C+R_{12}*R_{78}*R_9*C_{18}</math> || <math>h_{5} = \frac{2.0*R_{12}*R_9*R_{78}*C_{18}*s}{s^3*K_3 + |
s^2*K_2+ | s^2*K_2+ | ||
s*K_1 + R_{12}*R_9 } </math> | s*K_1 + R_{12}*R_9 } </math> | ||
| Line 52: | Line 53: | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| − | == Parameters of LFER4 model == | + | === Parameters of LFER4 model === |
| − | The LFER4 model has are a total of 10 parameters(<math>A_1</math>,<math>A_2</math>,<math>A_3</math>,<math>A_4</math>,<math>\tau_1</math>,<math>\tau_2</math>,<math>\tau_3</math>,<math>\tau_4</math>,<math>S_{phase}</math>,<math>\tau_{stray}</math>) | + | The LFER4 model has are a total of 10 parameters for each bolometer (<math>A_1</math>,<math>A_2</math>,<math>A_3</math>,<math>A_4</math>,<math>\tau_1</math>,<math>\tau_2</math>,<math>\tau_3</math>,<math>\tau_4</math>,<math>S_{\rm phase}</math>,<math>\tau_{\rm stray}</math>) nine of which are independent. The free parameters of the LFER4 model are determined using in-flight data in the following ways: |
| − | * <math>S_{phase}</math> is fixed at the value of the REU setting | + | * <math>S_{\rm phase}</math> is fixed at the value of the REU setting; |
| − | * <math>\tau_{stray}</math> is measured during the QEC test | + | * <math>\tau_{\rm stray}</math> is measured during the QEC test of the CPV phase; |
| − | * <math>A_1</math>, <math>\tau_1</math>, <math>A_2</math>, <math>\tau_2</math> are fit forcing the compactness of the scanning beam | + | * <math>A_1</math>, <math>\tau_1</math>, <math>A_2</math>, <math>\tau_2</math> are fit by forcing the compactness of the scanning beam; |
| − | * <math>A_3</math>, <math>\tau_3</math>, <math>A_{4}</math> <math>\tau_4</math> are fit by forcing agreement of | + | * <math>A_3</math>, <math>\tau_3</math>, <math>A_{4}</math> <math>\tau_4</math> are fit by forcing agreement of Survey 2 and Survey 1 maps; |
| − | * | + | * the overall normalization of the LFER4 model is forced to be 1.0 at the signal frequency of the dipole. |
| − | The details of determining the model parameters are given in (reference P03c paper) and the best-fit parameters listed below. | + | The details of determining the model parameters are given in (reference P03c paper) and the best-fit parameters are listed below. |
<center> | <center> | ||
| Line 68: | Line 69: | ||
|+ '''LFER4 model parameters''' | |+ '''LFER4 model parameters''' | ||
|- bgcolor="ffdead" | |- bgcolor="ffdead" | ||
| − | ! Bolometer || <math>A_1</math> || <math>\tau_1</math> (s) || <math>A_2</math> || <math>\tau_2</math> (s) || <math>A_3</math> || <math>\tau_3</math> (s) || <math>A_4</math> || <math>\tau_4</math> (s) || <math>\tau_{stray}</math> (s) || <math>S_{phase}</math> (s) | + | ! Bolometer || <math>A_1</math> || <math>\tau_1</math> (s) || <math>A_2</math> || <math>\tau_2</math> (s) || <math>A_3</math> || <math>\tau_3</math> (s) || <math>A_4</math> || <math>\tau_4</math> (s) || <math>\tau_{\rm stray}</math> (s) || <math>S_{\rm phase}</math> (s) |
|- | |- | ||
| 100-1a|| 0.392|| 0.01|| 0.534|| 0.0209|| 0.0656|| 0.0513|| 0.00833|| 0.572|| 0.00159|| 0.00139 | | 100-1a|| 0.392|| 0.01|| 0.534|| 0.0209|| 0.0656|| 0.0513|| 0.00833|| 0.572|| 0.00159|| 0.00139 | ||
| Line 171: | Line 172: | ||
|} | |} | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == PR2 (2015) and PR3 (2018) Model == | ||
| + | |||
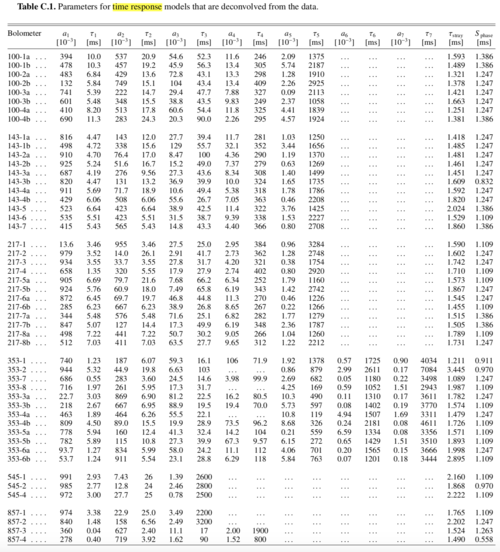
| + | For the data associated to the PR2 (2015) and PR3 (2018) releases, the bolometer time transfer function is described by the sum of five single-pole low-pass functions, each with a time constant τi and an associated amplitude ai. The parameters for the model are in the table below (from {{PlanckPapers|planck2014-a08}}). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:2015_time_response_params.png|frameless|500px|center|Parameters of the time response model used for PR2 and PR3]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <References /> | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:HFI design, qualification and performance|012]] | [[Category:HFI design, qualification and performance|012]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:15, 22 June 2018
Contents
LFER4 model (PR1 /2013 release)[edit]
Here we describe the "Low frequency excess response" 4 model. If we write the input signal (power) on a bolometer as , the bolometer physical impedance can be written as , where is the angular frequency of the signal and is the complex intrinsic bolometer transfer function. For HFI the bolometer transfer function is modelled as the sum of four single pole low-pass filters: . The modulation of the signal is performed with a square wave, written here as a composition of sine waves of decreasing amplitude: , where we have used the Euler relation and is the angular frequency of the square wave. The modulation frequency is and was set to Hz in flight. This signal is then filtered by the complex electronic transfer function . Setting we have . This signal is then sampled at high frequency, (). Here is one of the parameters of the HFI electronics and corresponds to the number of high frequency samples in each modulation semi-period. In order to obtain an output signal sampled every seconds, we must integrate on a semiperiod, as done in the HFI readout. To also include a time shift , the integral is calculated between and (with period of the modulation). The time shift is encoded in the HFI electronics by the parameter , with the relation .
After integration, the n-sample of a bolometer can be written as , where
The output signal in equation eqn:output can be demodulated (thus removing the (-1)n) and compared to the input signal in equation bol_in. The overall transfer function is composed of the bolometer transfer function and the effective electronics transfer function, : .
The shape of is obtained combining low- and high-pass filters with Sallen-Key topologies (with their respective time constants) and accounting also for the stray capacitance low-pass filter given by the bolometer impedance combined with the stray capacitance of the cables. The sequence of filters that define the electronic band-pass function are listed in the following table.
| Filter | Parameters | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 0. Stray capacitance low-pass filter | ||
| 1. Low-pass filter | k nF |
|
| 2. Sallen-Key high-pass filter | k F |
3 |
| 3. Sign reverse with gain | ||
| 4. Single pole low-pass filter with gain | k nF |
|
| 5. Single pole high-pass filter coupled to a Sallen-Key low-pass filter | k k nF k F |
Parameters of LFER4 model[edit]
The LFER4 model has are a total of 10 parameters for each bolometer (,,,,,,,,,) nine of which are independent. The free parameters of the LFER4 model are determined using in-flight data in the following ways:
- is fixed at the value of the REU setting;
- is measured during the QEC test of the CPV phase;
- , , , are fit by forcing the compactness of the scanning beam;
- , , are fit by forcing agreement of Survey 2 and Survey 1 maps;
- the overall normalization of the LFER4 model is forced to be 1.0 at the signal frequency of the dipole.
The details of determining the model parameters are given in (reference P03c paper) and the best-fit parameters are listed below.
| Bolometer | (s) | (s) | (s) | (s) | (s) | (s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100-1a | 0.392 | 0.01 | 0.534 | 0.0209 | 0.0656 | 0.0513 | 0.00833 | 0.572 | 0.00159 | 0.00139 |
| 100-1b | 0.484 | 0.0103 | 0.463 | 0.0192 | 0.0451 | 0.0714 | 0.00808 | 0.594 | 0.00149 | 0.00139 |
| 100-2a | 0.474 | 0.00684 | 0.421 | 0.0136 | 0.0942 | 0.0376 | 0.0106 | 0.346 | 0.00132 | 0.00125 |
| 100-2b | 0.126 | 0.00584 | 0.717 | 0.0151 | 0.142 | 0.0351 | 0.0145 | 0.293 | 0.00138 | 0.00125 |
| 100-3a | 0.744 | 0.00539 | 0.223 | 0.0147 | 0.0262 | 0.0586 | 0.00636 | 0.907 | 0.00142 | 0.00125 |
| 100-3b | 0.608 | 0.00548 | 0.352 | 0.0155 | 0.0321 | 0.0636 | 0.00821 | 0.504 | 0.00166 | 0.00125 |
| 100-4a | 0.411 | 0.0082 | 0.514 | 0.0178 | 0.0581 | 0.0579 | 0.0168 | 0.37 | 0.00125 | 0.00125 |
| 100-4b | 0.687 | 0.0113 | 0.282 | 0.0243 | 0.0218 | 0.062 | 0.00875 | 0.431 | 0.00138 | 0.00139 |
| 143-1a | 0.817 | 0.00447 | 0.144 | 0.0121 | 0.0293 | 0.0387 | 0.0101 | 0.472 | 0.00142 | 0.00125 |
| 143-1b | 0.49 | 0.00472 | 0.333 | 0.0156 | 0.134 | 0.0481 | 0.0435 | 0.27 | 0.00149 | 0.00125 |
| 143-2a | 0.909 | 0.0047 | 0.0763 | 0.017 | 0.00634 | 0.1 | 0.00871 | 0.363 | 0.00148 | 0.00125 |
| 143-2b | 0.912 | 0.00524 | 0.0509 | 0.0167 | 0.0244 | 0.0265 | 0.0123 | 0.295 | 0.00146 | 0.00125 |
| 143-3a | 0.681 | 0.00419 | 0.273 | 0.00956 | 0.0345 | 0.0348 | 0.0115 | 0.317 | 0.00145 | 0.00125 |
| 143-3b | 0.82 | 0.00448 | 0.131 | 0.0132 | 0.0354 | 0.0351 | 0.0133 | 0.283 | 0.00161 | 0.000832 |
| 143-4a | 0.914 | 0.00569 | 0.072 | 0.0189 | 0.00602 | 0.0482 | 0.00756 | 0.225 | 0.00159 | 0.00125 |
| 143-4b | 0.428 | 0.00606 | 0.508 | 0.00606 | 0.0554 | 0.0227 | 0.00882 | 0.084 | 0.00182 | 0.00125 |
| 143-5 | 0.491 | 0.00664 | 0.397 | 0.00664 | 0.0962 | 0.0264 | 0.0156 | 0.336 | 0.00202 | 0.00139 |
| 143-6 | 0.518 | 0.00551 | 0.409 | 0.00551 | 0.0614 | 0.0266 | 0.0116 | 0.314 | 0.00153 | 0.00111 |
| 143-7 | 0.414 | 0.00543 | 0.562 | 0.00543 | 0.0185 | 0.0449 | 0.00545 | 0.314 | 0.00186 | 0.00139 |
| 217-5a | 0.905 | 0.00669 | 0.0797 | 0.0216 | 0.00585 | 0.0658 | 0.00986 | 0.342 | 0.00157 | 0.00111 |
| 217-5b | 0.925 | 0.00576 | 0.061 | 0.018 | 0.00513 | 0.0656 | 0.0094 | 0.287 | 0.00187 | 0.00125 |
| 217-6a | 0.844 | 0.00645 | 0.0675 | 0.0197 | 0.0737 | 0.0316 | 0.0147 | 0.297 | 0.00154 | 0.00125 |
| 217-6b | 0.284 | 0.00623 | 0.666 | 0.00623 | 0.0384 | 0.024 | 0.0117 | 0.15 | 0.00146 | 0.00111 |
| 217-7a | 0.343 | 0.00548 | 0.574 | 0.00548 | 0.0717 | 0.023 | 0.0107 | 0.32 | 0.00152 | 0.00139 |
| 217-7b | 0.846 | 0.00507 | 0.127 | 0.0144 | 0.0131 | 0.0479 | 0.0133 | 0.311 | 0.00151 | 0.00139 |
| 217-8a | 0.496 | 0.00722 | 0.439 | 0.00722 | 0.0521 | 0.0325 | 0.0128 | 0.382 | 0.00179 | 0.00111 |
| 217-8b | 0.512 | 0.00703 | 0.41 | 0.00703 | 0.0639 | 0.0272 | 0.0139 | 0.232 | 0.00173 | 0.00125 |
| 217-1 | 0.0136 | 0.00346 | 0.956 | 0.00346 | 0.0271 | 0.0233 | 0.00359 | 1.98 | 0.00159 | 0.00111 |
| 217-2 | 0.978 | 0.00352 | 0.014 | 0.0261 | 0.00614 | 0.042 | 0.00194 | 0.686 | 0.0016 | 0.00125 |
| 217-3 | 0.932 | 0.00355 | 0.0336 | 0.00355 | 0.0292 | 0.0324 | 0.00491 | 0.279 | 0.00174 | 0.00125 |
| 217-4 | 0.658 | 0.00135 | 0.32 | 0.00555 | 0.0174 | 0.0268 | 0.00424 | 0.473 | 0.00171 | 0.00111 |
| 353-3a | 0.554 | 0.00704 | 0.36 | 0.00704 | 0.0699 | 0.0305 | 0.0163 | 0.344 | 0.0017 | 0.00125 |
| 353-3b | 0.219 | 0.00268 | 0.671 | 0.00695 | 0.0977 | 0.0238 | 0.0119 | 0.289 | 0.00157 | 0.00111 |
| 353-4a | 0.768 | 0.00473 | 0.198 | 0.00993 | 0.0283 | 0.0505 | 0.00628 | 0.536 | 0.00181 | 0.00125 |
| 353-4b | 0.684 | 0.00454 | 0.224 | 0.0108 | 0.0774 | 0.08 | 0.0149 | 0.267 | 0.00166 | 0.00111 |
| 353-5a | 0.767 | 0.00596 | 0.159 | 0.0124 | 0.0628 | 0.0303 | 0.0109 | 0.357 | 0.00156 | 0.00111 |
| 353-5b | 0.832 | 0.00619 | 0.126 | 0.0111 | 0.0324 | 0.035 | 0.0096 | 0.397 | 0.00166 | 0.00111 |
| 353-6a | 0.0487 | 0.00176 | 0.855 | 0.006 | 0.0856 | 0.0216 | 0.0105 | 0.222 | 0.00199 | 0.00125 |
| 353-6b | 0.829 | 0.00561 | 0.127 | 0.00561 | 0.0373 | 0.0252 | 0.00696 | 0.36 | 0.00228 | 0.00111 |
| 353-1 | 0.41 | 0.000743 | 0.502 | 0.00422 | 0.0811 | 0.0177 | 0.0063 | 0.329 | 0.00132 | 0.00097 |
| 353-2 | 0.747 | 0.00309 | 0.225 | 0.00726 | 0.0252 | 0.0447 | 0.00267 | 0.513 | 0.00154 | 0.00097 |
| 353-7 | 0.448 | 0.0009 | 0.537 | 0.0041 | 0.0122 | 0.0273 | 0.00346 | 0.433 | 0.00178 | 0.00125 |
| 353-8 | 0.718 | 0.00223 | 0.261 | 0.00608 | 0.0165 | 0.038 | 0.00408 | 0.268 | 0.00177 | 0.00111 |
| 545-1 | 0.991 | 0.00293 | 0.00743 | 0.026 | 0.00139 | 2.6 | 0 | 0 | 0.00216 | 0.00111 |
| 545-2 | 0.985 | 0.00277 | 0.0128 | 0.024 | 0.00246 | 2.8 | 0 | 0 | 0.00187 | 0.00097 |
| 545-4 | 0.972 | 0.003 | 0.0277 | 0.025 | 0.000777 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 | 0.00222 | 0.00111 |
| 857-1 | 0.974 | 0.00338 | 0.0229 | 0.025 | 0.00349 | 2.2 | 0 | 0 | 0.00176 | 0.00111 |
| 857-2 | 0.84 | 0.00148 | 0.158 | 0.00656 | 0.00249 | 3.2 | 0 | 0 | 0.0022 | 0.00125 |
| 857-3 | 0.36 | 4.22e-05 | 0.627 | 0.0024 | 0.0111 | 0.017 | 0.002 | 1.9 | 0.00152 | 0.00126 |
| 857-4 | 0.278 | 0.0004 | 0.719 | 0.00392 | 0.00162 | 0.09 | 0.00152 | 0.8 | 0.00149 | 0.000558 |
PR2 (2015) and PR3 (2018) Model[edit]
For the data associated to the PR2 (2015) and PR3 (2018) releases, the bolometer time transfer function is described by the sum of five single-pole low-pass functions, each with a time constant τi and an associated amplitude ai. The parameters for the model are in the table below (from Planck-2015-A07[1]).
References[edit]
- ↑ Planck 2015 results. VII. High Frequency Instrument data processing: Time-ordered information and beam processing, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A7.
(Planck) High Frequency Instrument
Readout Electronic Unit
Calibration and Performance Verification