Difference between revisions of "LFI design, qualification, and performance"
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
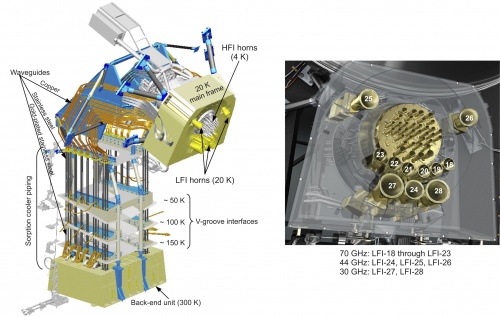
| − | [[File:lfi_instrument.jpg| | + | [[File:lfi_instrument.jpg|500px|Left panel: the LFI instrument with main thermal stages, focal plane, waveguides and sorption cooler piping highlighted. Right panel: labelling of feed horns on the LFI focal plane.]] |
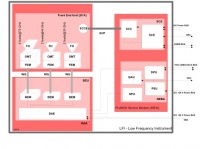
| − | [[File:LFIblockdiagram.jpg| | + | [[File:LFIblockdiagram.jpg|200px|Block Diagram of LFI]] |
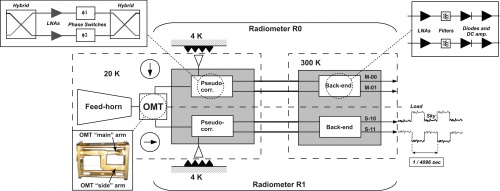
| − | [[File:rca_schematic.jpg| | + | [[File:rca_schematic.jpg|500px|A complete RCA from feed-horn to analog voltage output. The insets show the OMT, the details of the 20 K pseudo-correlator and of the back-end radio-frequency amplification, low-pass filtering, detection and DC amplification]] |
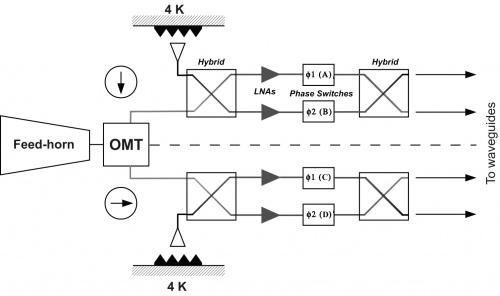
| − | [[File:phase_switch_operation.jpg| | + | [[File:phase_switch_operation.jpg|500px|Close-up of the two front-end modules of an RCA. There are four phase switches, labelled A, B, C and D. Each switch can be fixed in one of its two positions (labelled as 0, 1) or switch at 4 kHz between 0 and 1. Phase switches are clocked and biased by the DAE in pairs: A/C and B/D (see text for further explanation).]] |
Revision as of 14:26, 18 October 2012
Contents
Overview[edit]
The first :
- uno
- due
- tre
- quattro
Only a.
The LFI description[edit]
Each LFI radiometer g , signals at the frequency of the phase switch. By changing the phase switches configuration, the output can be a sequence of either or signals.
a tunable offset, , then it amplifies the signal with a tunable gain, ,
- Radiometer Chain Overall Design
- Radiometer Array Assembly
- REBA
- Radiometer Chain Overall Design
- Instrument On-board Software
- Instrument Operations
- Instrument Budgets
LFI Ground Tests[edit]
LFI In-flight Calibration[edit]
LFI Performance[edit]
- Instrument Scientific Performance
- Instrument Technical Performance
(Planck) Low Frequency Instrument
LFI Data Acquisition Electronics
LFI Radiometer Electronics Box Assembly