Difference between revisions of "Scanning Beams"
m (→HFI Beams) |
(→HFI Beams) |
||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
== HFI Beams == | == HFI Beams == | ||
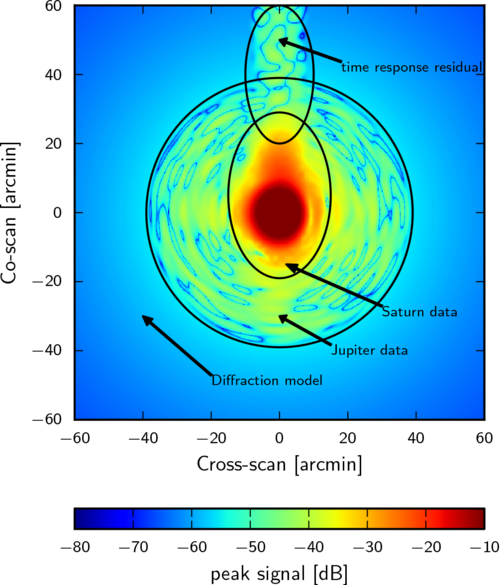
| − | The HFI scanning beams are a combination of observations of Saturn, for the central parts, and Jupiter for the wings, as described in the [[Beams | Beams]] section of this document, and in section 4.1 of {{PlanckPapers | planck2014-a08}} on "Hybrid beams". Saturn data are used where they are signal-dominated; when the S/N of Saturn drops to < 9, Jupiter data are used, after binning them azimuthally. Beyond that, i.e., below the noise floor of the Jupiter data, and out to 100 arcmin, a power law (& | + | The HFI scanning beams are a combination of observations of Saturn, for the central parts, and Jupiter for the wings, as described in the [[Beams | Beams]] section of this document, and in section 4.1 of {{PlanckPapers | planck2014-a08}} on "Hybrid beams". Saturn data are used where they are signal-dominated; when the S/N of Saturn drops to < 9, Jupiter data are used, after binning them azimuthally. Beyond that, i.e., below the noise floor of the Jupiter data, and out to 100 arcmin, a power law (∝θ<sup>-3</sup>) is used, where the exponent is derived from GRASP physical optics models. The figure below, taken from the [[Beams#Key_Changes | Beams]] section of this document, shows graphically the different portions of the beam model. |
Revision as of 00:01, 22 March 2018
LFI beams[edit]
Maps are released of the Stokes parameters of the band-averaged scanning beams. The averages are performed using the RIMO bandpass, assuming a flat spectrum of the incoming radiation. The Stokes parameter maps contain the complete information about the field intensity and polarization properties. The Main Beam, Intermediate Beam, and Sidelobes are released separately.
More information on LFI beams can be found in Planck-2015-A04[1] and on HFI beams in Planck-2015-A07[2]
File Names[edit]
The file names are of the form
LFI_ScanBeam-{mb,ib,sl}_{fff}-{rrr}_R2.{nn}.stokes,
where:
- fff denotes the frequency;
- mb denotes the Main Beams;
- ib denotes the Intermediate Beam;
- sl denotes the Sidelobes;
- rrr denotes the radiometer;
- R2.nn is the version.
At the present time, HFI is not releasing the Scanning Beams.
FITS file structure[edit]
The FITS files contain a primary extension with no data and a minimal header, as well as one BINTABLE extension with data and with a description of the data in the header keywords. The BINTABLE extension consist of four columns, each containing the array of one Stokes parameter. The columns are:
- "Beamdata", containing I;
- "BeamdataQ", containing Q;
- "BeamdataU", containing U;
- "BeamdataV", containing V.
The Main Beam, Intermediate Beams, and Sidelobes are saved with a different data format, as described below.
- Main Beams are projected onto the tangent plane to the sphere, and sampled on a grid. The grid includes an angular region expressed by the keyword "angularCut", and its dimensions are given by the keywords "Nx" and "Ny", representing the number of columns and rows. Each column of the BINDATA extension contains a sequence of the Nx×Ny samples of the map in row major order. The keywords "Xcentre" and "Ycentre" express the coordinates of the beam maximum (i.e., where the sphere intersects the tangent plane).
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BEAMDATA | Real*4 | None | Stokes parameter I | |
| BEAMDATAQ | Real*4 | None | Stokes parameter Q | |
| BEAMDATAU | Real*4 | None | Stokes parameter U | |
| BEAMDATAV | Real*4 | None | Stokes parameter V | |
| Keyword | Data Type | Value | Description | Comment |
| Nx | Int | 601 | Number of x-axis samples | x axis aligned with the direction of the "S" arm |
| Ny | Int | 601 | Number of y-axis samples | y axis aligned with the direction of the "M" arm |
| Xcentre | Int | 301 | x coordinate of the beam centre | |
| Ycentre | Int | 301 | y coordinate of the beam centre | |
| Xdelta | Float | x step in radians | ||
| Ydelta | Float | y step in radians |
- Intermediate Beams and Sidelobes are sampled on the sphere. The resolution in θ and φ are given by the keywords "Ntheta" and "Nphi". The columns of the BINDATA extension contain the sequence of Nphi Stokes parameters for each θ.
| Column Name | Data Type | Units | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BEAMDATA | Real*4 | None | Stokes parameter I | |
| BEAMDATAQ | Real*4 | None | Stokes parameter Q | |
| BEAMDATAU | Real*4 | None | Stokes parameter U | |
| BEAMDATAV | Real*4 | None | Stokes parameter V | |
| Keyword | Data Type | Value | Description | Comment |
| Ntheta | Int | Number of θ samples | Colatitude | |
| Nphi | Int | Number of φ samples | Longitude | |
| Mintheta | Float | Minimum value of θ | ||
| Maxtheta | Float | Maximum value of θ | ||
| angularCut | Float | Angular cut [deg] |
HFI Beams[edit]
The HFI scanning beams are a combination of observations of Saturn, for the central parts, and Jupiter for the wings, as described in the Beams section of this document, and in section 4.1 of Planck-2015-A07[2] on "Hybrid beams". Saturn data are used where they are signal-dominated; when the S/N of Saturn drops to < 9, Jupiter data are used, after binning them azimuthally. Beyond that, i.e., below the noise floor of the Jupiter data, and out to 100 arcmin, a power law (∝θ-3) is used, where the exponent is derived from GRASP physical optics models. The figure below, taken from the Beams section of this document, shows graphically the different portions of the beam model.
The beams are provided in FITS files named
- HFI_ScanBeam_{det-name}_R2.nn.fits,
where det-name is of the form 100-1a, and nn is the version number. Each file contains a single "IMAGE" extension. The image is 6001×6001 pixels of size 2arcsec×2arcsec (given in the "DELTAX" and "DELTAY" keywords), centred on pixel 3001,3001, and normalized to 1 at the maximum, where "X" and "Y" and are in the Dxx reference system.
References[edit]
- ↑ Planck 2015 results. IV. LFI beams and window functions, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A4.
- ↑ 2.02.1 Planck 2015 results. VII. High Frequency Instrument data processing: Time-ordered information and beam processing, Planck Collaboration, 2016, A&A, 594, A7.
(Planck) Low Frequency Instrument
(Planck) High Frequency Instrument
Flexible Image Transfer Specification