Difference between revisions of "LFIAppendix"
| Line 334: | Line 334: | ||
[[File:4kload.jpg|thumb|center|400px|'''Figure 1. 4-K reference load targets mounted on the HFI 4-K shield.''']] | [[File:4kload.jpg|thumb|center|400px|'''Figure 1. 4-K reference load targets mounted on the HFI 4-K shield.''']] | ||
| − | Targets are formed from a back section and a front section. The back sections are made of ECCOSORB CR117, which shows higher RF absorption but also high reflectivity. To reduce the target global reflectivity, a front section, connected with an ECCOSORB-specific cement to the back one, faces the radiometer Reference Horn. This last element is cast from ECCOSORB CR110, whose RF reflectivity is lower than that of CR117. The target design is optimized to further reduce both reflectivity and leakage. Each target is metal-backed and | + | Targets are formed from a back section and a front section. The back sections are made of ECCOSORB CR117, which shows higher RF absorption but also high reflectivity. To reduce the target global reflectivity, a front section, connected with an ECCOSORB-specific cement to the back one, faces the radiometer Reference Horn. This last element is cast from ECCOSORB CR110, whose RF reflectivity is lower than that of CR117. The target design is optimized to further reduce both reflectivity and leakage. Each target is metal-backed and is mounted in a metal enclosure. |
Thermal tests were performed in the IASF-Bologna 4-K cryo facility, equipped with a GM cooler, with a heat lift up to 1.5 W at 4 K. The setup simulated the real environment in the payload, where targets are mounted on the HFI 4-K shield in front of the quasi-cylindrical LFI main frame at about 20 K. The same setup was also used to test the susceptibility to fluctuations of the LFI. | Thermal tests were performed in the IASF-Bologna 4-K cryo facility, equipped with a GM cooler, with a heat lift up to 1.5 W at 4 K. The setup simulated the real environment in the payload, where targets are mounted on the HFI 4-K shield in front of the quasi-cylindrical LFI main frame at about 20 K. The same setup was also used to test the susceptibility to fluctuations of the LFI. | ||
| Line 359: | Line 359: | ||
* The Data Acquisition Unit (DAU) performs the analogue-to-digital conversion of the analogue housekeeping data of the REBA itself (temperatures and voltages). The REBA ASW collects the HK data from the DAU. | * The Data Acquisition Unit (DAU) performs the analogue-to-digital conversion of the analogue housekeeping data of the REBA itself (temperatures and voltages). The REBA ASW collects the HK data from the DAU. | ||
* The Signal Processing Unit (SPU) is a computing subunit in charge of the reduction and compression of the science data and implements part of the REBA ASW, the SPU ASW (stored in the EEPROM located in the DPU board and transferred to the SPU by the DPU ASW). It receives the science data from the DAE through an IEEE 1355 link implemented in an SMCS chip. A second IEEE 1355 link is used to control the remote DAE SMCS chip. The third IEEE 1355 link communicates with the DPU. A "Data Ready" electrical signal is connected between the DAE and the SPU; this signal produces an interruption in the SPU when the DAE is ready to transfer data. | * The Signal Processing Unit (SPU) is a computing subunit in charge of the reduction and compression of the science data and implements part of the REBA ASW, the SPU ASW (stored in the EEPROM located in the DPU board and transferred to the SPU by the DPU ASW). It receives the science data from the DAE through an IEEE 1355 link implemented in an SMCS chip. A second IEEE 1355 link is used to control the remote DAE SMCS chip. The third IEEE 1355 link communicates with the DPU. A "Data Ready" electrical signal is connected between the DAE and the SPU; this signal produces an interruption in the SPU when the DAE is ready to transfer data. | ||
| − | * The Digital Processing Unit (DPU) is a computing subunit and implements part of the REBA ASW, the DPU ASW. The DPU is in charge of the control and monitoring of the instrument as well as | + | * The Digital Processing Unit (DPU) is a computing subunit and implements part of the REBA ASW, namely the DPU ASW. The DPU is in charge of the control and monitoring of the instrument as well as communication with the spacecraft (CDMS). It contains another SMCS chip with three IEEE 1355 links that communicate with the SPU and the DAE. An MIL-STD 1553B link is used to communicate with the CDMS. One IEEE 1355 link is used by the DPU ASW to communicate with the DAE to control the SMCS chip of DAE. The second one is used to communicate with the DAE to transfer commands and HK. The third one is used by the DPU ASW to communicate with the SPU (commands and TM). Two Reset electrical lines are provided by the DPU to reset each of the two SMCS chips of the DAE. The DPU ASW is stored in the EEPROM. |
| − | A detailed description of the Planck LFI REBA can be found in {{BibCite|herreros2009}}. | + | A detailed description of the Planck LFI REBA can be found in Ref. {{BibCite|herreros2009}}. |
==== ''Instrument on-board software'' ==== | ==== ''Instrument on-board software'' ==== | ||
| − | The REBA software is the on board software of LFI. It is installed in the two computing subunits of REBA: the DPU, responsible | + | The REBA software is the on-board software of LFI. It is installed in the two computing subunits of the REBA: the DPU, responsible for the control and monitoring of the instrument and the interface with the spacecraft; and the SPU, responsible for the data reduction and compression. |
The REBA software can be classified (see Fig. 2) into: | The REBA software can be classified (see Fig. 2) into: | ||
: 1. the REBA Start-up Software (SUSW), installed in the PROM memories, which is the bootstrap code to switch on both the subunits; | : 1. the REBA Start-up Software (SUSW), installed in the PROM memories, which is the bootstrap code to switch on both the subunits; | ||
Revision as of 06:19, 2 January 2015
Contents
[hide]Annexes: LFI Instrument[edit]
Here we report a more detailed definition of each component of the LFI instrument, which were already briefly described in the main LFI instrument page.
Radiometer Array Assembly (RAA) components[edit]
Feed Horns (FHs)[edit]
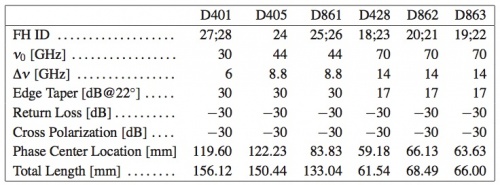
Dual-profiled corrugated horns were selected at all LFI frequencies as the best design in terms of the shape of the main lobe, level of the side lobes, control of the phase centre, and compactness. Dual-profiled LFI horns are composed of a sine-squared profiled section, and an exponential profile near the aperture plane. In order to optimize the optical matching of the feeds phase centres to the telescope focal surface, while preventing obscuration between horns, LFI has six different feedhorn designs. For each frequency, the number of feeds and the number of different designs are reported in Table 1 below.
| Frequency (GHz) | Number of horns | Number of designs |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 2 | 1 |
| 44 | 3 | 2 |
| 70 | 6 | 3 |
LFI feedhorn design specifications are reported in the Table 2 below.
The design process led to a corrugation profile composed of a mixture of a sine-squared section, starting from the throat, and an exponential section near the aperture plane. The length of this last part has a direct impact on the location of the phase centre. The analytical expression of the corrugation profile, R(z), is
in the sine section, and
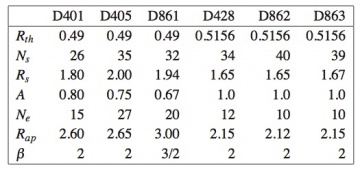
in the exponential region. Here, Rth is the throat radius, Rs is the sine-squared region end radius (or exponential region initial radius), Rap is the aperture radius, Ls is the sine-squared region length, and Le is the exponential region length. The parameter A (0 ≤ A ≤ 1) modulates the first region profile between linear and pure sine-squared type. The parameters Le/(Le + Ls), A, and Rs can be used to control, as far as possible, the position and frequency stability of the phase centre and the compactness of the structure. The feedhorn parameters are reported in Table 3 below.
The qualification campaign, mainly focused on RF return loss and pattern (amplitude and phase) measurements, was successfully concluded. The agreement between the pattern measurements and the expected performance (simulated using the nominal corrugation profile) was excellent, both in amplitude and in phase. Moreover, reflection measurements showed a good impedance match for all the horns, the return loss being better than -30 dB over the whole 20% of operational bandwidth.
Details of the design, flight model and tests of Planck-LFI feedhorns can be found in Ref. [1].
OrthoMode Transducers (OMTs)[edit]
The Ortho–Mode Transducers (OMTs) separate the radiation collected by the feedhorn into two orthogonal polarization components. They each consist of a circular to square waveguide transition (directly connected to the FH), a square waveguide section, and two separate rectangular waveguides (the main and side arms, which separate and pick up the orthogonal polarization, connected with the FEU). On the side arms there is always a 90° bend, while a twist is also necessary on the main (30 and 44 GHz) and side (70 GHz) arms, in order to match the FEU polarization.
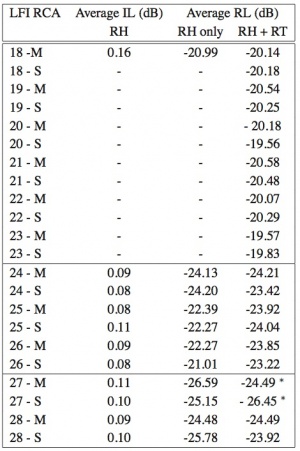
The required and measured performance for the LFI OMTs at all frequencies is reported in the following Tables 4 and 5:
| OMT ID | Bandwidth [GHz] | X–Pol [dB] (Main) | X–Pol [dB] (Side) | Return loss [dB] (Main) | Return loss [dB] (Side) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 14 | <29 | <30 | -15.0 | -20.0 |
| 19 | 14 | <26 | <28 | -15.0 | -20.0 |
| 20 | 14 | <32 | <35 | -15.0 | -20.0 |
| 21 | 14 | <32 | <37 | -15.0 | -18.0 |
| 22 | 14 | <26 | <28 | -15.0 | -18.0 |
| 23 | 14 | <26 | <28 | -15.0 | -20.0 |
| 24 | 8.8 | <38 | <40 | -13.0 | -18.0 |
| 25 | 8.8 | <31 | <32 | -13.0 | -18.0 |
| 26 | 8.8 | <27 | <25 | -13.0 | -17.0 |
| 27 | 6 | <38 | <44 | -16.0 | -23.0 |
| 28 | 6 | <36 | <38 | -16.0 | -22.0 |
The details of the flight models and measurements of the Planck LFI ortho-mode transducers can be found in Ref. [2].
Front End Modules (FEMs)[edit]
The Front End Modules are located in the FPU, just downstream of the Feed Horn and the Ortho-Mode Transducers. 70 GHz FEMs are mounted onto the inner wall of the mainframe (the wall facing the HFI instrument) from the HFI side. 44 and 30 GHz FEMs are inserted into the main frame from the WG side and fixed to the bottom plate. Screws to bthe ottom plate are inserted from the WG side. The LFI FEMs are the first active stage of amplification of the radiometer chain. Each FEM contains four amplification paths. Each path is composed of several cascaded LNAs, followed by a phase switch. Two passive hybrids, at the input and output of the FEM, are used to mix pairs of signals of the same radiometer (see Fig. 2 in the RAA section). This determines the instabilities of each chain to be applied to both the sky and load signals.
The passive hybrid coupler ("magic-tee") combines the signals from the sky and cold load with a fixed phase offset of either 90° or 180° between them. It has a 20% bandwidth, low loss, and amplitude balance required at the output to ensure adequate signal isolation.
The FEM LNAs (InP MMICs) are biased, providing one drain line per channel (that is four per FEM) and two gate lines per channel (that is eight per FEM). The FEM phase switches are biased, providing two lines per channel (that is eight per FEM) each capable of providing a direct bias current or a reverse bias voltage.
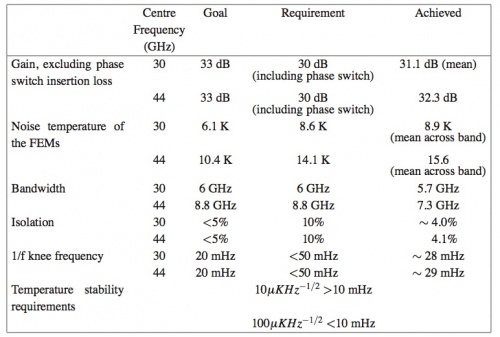
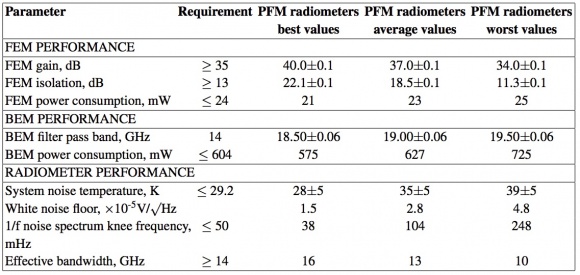
The LFI FEM parameters necessary to meet the science objectives at 30 and 44 GHz were given as requirements and goals and are summarized in Table 6 below, where they are compared with the values actually achieved. The FEM units met the requirements, within the measurement errors, for most parameters and in particular the noise temperature. The units came close to the more stringent goals in several parameters. Of particular note are the noise temperatures achieved; these along with the wide bandwidths are critical for the high sensitivity required for the Planck mission. Some LNAs within the FEMs met the goals at 30 GHz and 44 GHz within the measurements errors and reached 3 and 5 times the theoretical quantum limit, respectively, at the band centres. Furthermore, a range of tests showed that LNAs and FEMs achieved the stability levels required to meet the observing strategy of Planck. In particular, the 1/f noise knee frequency ≤29 mHz, close to the goal, met the conditions imposed by the 60 second rotation period of the spacecraft. The linear polarization performance of the FEMs exceeded the requirements of the mission. The isolation between the E- and H- polarizations was measured to be between 51 and 58 dBs for the various FEMs. The LFI radiometers have very well determined position angle precision, being set by the accuracy of the waveguide engineering. The 30 and 44 GHz geometry is accurate to about 0.1° ; the corresponding precision is approximately 1° in the HFI polarimeters. The temperature stability requirement values are also given in Table 6 below.
The details of the design, development and verification of the 30 and 44 GHz front-end modules for the Planck Low Frequency Instrument can be found in Ref. [3].
Regarding the 70 GHz channels, for the LNA selection of the FEMs, nine different wafers from various processing runs were evaluated, and only the LNAs with the best performance were assembled as the first stage amplifiers in the FEM ACAs. For the phase-switch selection, four different wafers were evaluated. When the signal is passed to an output, the gain is 35 dB or higher for almost the entire required range, and on average, the Planck requirement was fulfilled. In all FEMs, the average channel gains ranged from 34.0 to 40.0 dB (uncertainty ± 0.1 dB). When the signal is isolated from an output, the gain is 20 dB lower or more at all frequencies. This difference in gain is used as the measure for isolation. In all the six FEMs, the channel isolation values ranged from 11.3-22.1 dB (uncertainty ± 0.1 dB).
Table 7 below summarizes the best, the worst, and the average values of the key performance parameters. The uncertainties shown are based on worst case estimates.
The details of the design, development, and verification of the 70 GHz front-end modules for the Planck Low Frequency Instrument can be found in Ref. [4].
Waveguides (WGs)[edit]
The LFI Front End Unit (FEU) is connected to the Back End Unit (BEU) by 44 rectangular waveguides, approximately 1.5-2.0 m long. Each waveguide exhibits low VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio), low thermal conductivity, low insertion loss, and low mass. In addition, the waveguide path shall permit the LFI/HFI integration and the electrical bonding between FPU and BEU. Because of the Focal Plane Unit arrangement, the waveguides are in general twisted and bent in different planes and with different angles, depending on the particular waveguide. From the thermal point of view the waveguides have to connect two systems (BEM and FEM) that are at very different temperatures. At BEM level the waveguides are at a temperature of 300 K, while at FEM level the temperature is 20 K. The waveguides have to reduce the thermal flow from 300 K to 20 K. This can be seen in the conceptual sketch of the LFI configuration shown in Fig. 1 (left panel) of the LFI overview section.
All the required characteristics cannot be realised with a single material waveguide configuration; a composite waveguide configuration is therefore needed. The WGs can be considered divided into three sections: (1) 400 mm of Stainless Steel (gold plated) straight waveguide section, attached to the BEU, ending after the 3rd V–groove; (2) 300 mm of non–plated Stainless Steel (SS), with identical SS-sections for all the channels except for internal dimensions, depending on frequency, and with the guides connected to all the V-grooves in order to dissipate the heat produced at BEU level; and (3) bent and twisted 400 μm-thin electroformed copper waveguide, starting at the end of the SS–section and attached to the FEU, whose length varyies from around 800 mm to 1300 mm, with 2 to 4 Cu-joints. The copper waveguides section is connected to a mechanical support structure at five points in order to increase the stiffness of the waveguide.
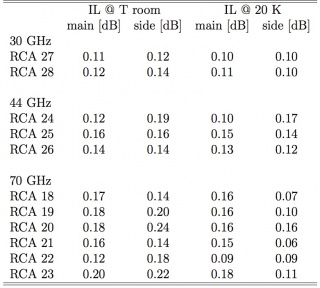
The performance for the LFI waveguides at all frequencies are reported in Table 8 (following):
| Frequency | ν band [GHz] | Number | IL [dB] @20 K | RL [dB] | Isolation [dB] | R [mΩ] @20 K | R [mΩ] @300 K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 27-33 | 8 | <2.5 (1.0) | <-25 | <-30 | 11.8 | 27.3 |
| 44 | 39.6-48.4 | 12 | <3.0 (1.5) | <-25 | <-30 | 14.7 | 34.1 |
| 70 | 63-77 | 24 | <5.0 (3.5) | <-25 | <-30 | 26.2 | 60.5 |
From the thermal point of view the waveguides have to connect two systems (BEM and FEM) that are at different temperatures. At the BEM level the waveguides are at a temperature of 300 K, while at the FEM level the temperature is 20 K. Along the Stainless Steel section the waveguides have to reduce the thermal flow from 300 K to 20 K. The Stainless Steel waveguide is connected to all the V-grooves in order to dissipate the heat produced at BEU level.
Details of the Planck-LFI flight model of the composite waveguides can be found in Ref. [5].
Back End Modules (BEMs)[edit]
The BEMs are composed of four identical channels each made of Low Noise Amplifiers (LNAs), an RF Band Pass Filter, an RF to DC diode detector, and DC amplifiers. The FEM output signals are connected by waveguides from the Focal Plane Unit (FPU) assembly to the Back End Modules (BEMs) housed adjacent to the Data Acquisition Electronics (DAE) assembly. To maintain compatibility with the FEMs, each BEM accommodates four receiver channels from the four waveguide outputs of each FEM. The BEM internal signal routes are not cross-coupled and can be regarded as four identical parallel circuits. Each BEM is constructed as two mirror halves. The two amplifier/detector assemblies each contain two amplifier/detector circuits. Each is supplied from one of a pair of printed circuit boards, which also house two DC output amplifiers.
In the 30 GHz BEM, each LNA consists of two cascaded MMIC amplifiers. The bandpass filter is based on microstrip coupled-line structure. Its design is a three order Chebyshev response bandpass filter. The detector is composed of a hybrid reactive/passive matching network, and a Schottky diode. A commercial Agilent beam-lead and zero-bias diode was selected. The detector diode is followed by a low noise operational amplifier that provides most of the DC amplification. A second stage is implemented using an operational amplifier to provide a balanced bipolar output.
In the 44 GHz BEM, each LNA consists of self-designed MMIC amplifiers manufactured with the process ED02AH from OMMIC, which employs a 0.2 μm gate length Pseudomorphic-High Mobility Transistor (P-HEMT) on GaAs. The topology chosen for the band-pass filter is a third order Chebyshev bandpass filter made on a PTFE substrate, based on microstrip coupled-line structure. The detector is composed of a hybrid reactive/passive matching network and a Schottky diode. A commercial Agilent beam-lead and zero-bias diode was selected. The detector diode is followed by a low noise operational amplifier that provides most of the DC amplification. A second stage is implemented using an operational amplifier to provide a balanced bipolar output.
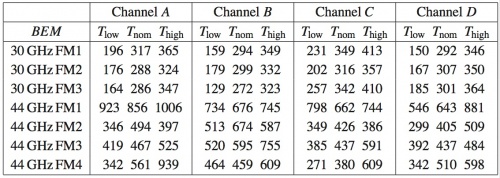
Table 9 below shows the values of the equivalent noise temperature for each flight model BEM at three different temperatures in the range of possible operating temperature. The large variability of the equivalent noise temperature of 44 GHz BEM units was due to their strong dependence on the input matching network result, which was observed to be a very critical parameter, not easy to control during the assembly process of the MMIC.
The raw measurements of the output spectrum are used for the determination of the 1/f knee frequency. The results for the four channels of a 30 GHz BEM unit are given in the table below.
The details of the design, development and verification of the 30 and 44 GHz back-end modules for the Planck Low Frequency Instrument can be found in Ref. [6].
The 70 GHz BEM is constructed of machined aluminium with separate filter, amplifier/detector assemblies and an overall housing for other circuits and components. The BEM filter characteristics hold very accurately for every channel in the six BEMs. The -3 dB passband, 62-81 GHz, was the same in every filter within 0.5 GHz. The BEM frequency response was measured as a function of input microwave power. Also, the pass bands roll at almost exactly 63 GHz and 77 GHz. The linearity of the channel is very good as well, especially from -57 dBm upwards. The dynamic range was at least 15 dB from -57 dBm to -42 dBm. In three cases, the BEMs fulfilled the power consumption requirement, while the limit was exceeded for the other three. For the total set of six BEMs, the limit, 3.6 W, was exceeded by approximately 140 mW. Table 7 above summarizes the best, the worst, and the average values of the key performance parameters. The uncertainties shown are based on worst case estimates.
The details of the design, development and verification of the 70 GHz back-end modules for the Planck Low Frequency Instrument can be found in Ref.[4].
4-K Load[edit]
The purpose of the 4-K reference load (4KRL) is to provide the radiometer with a stable reference signal. Reducing the input offset (the radiometric temperature difference between the sky and the reference load) reduces the minimum achievable radiometer 1/f noise knee frequency for a given amplifier fluctuation spectrum. A reference load temperature that matches the sky temperature (approximately 2.7 K) would be ideal. In the 4KRL design, the reference temperature is provided by the HFI outer radiation shield, at a temperature around 4 K. The 4KRL performance is reported in Table 11 below.
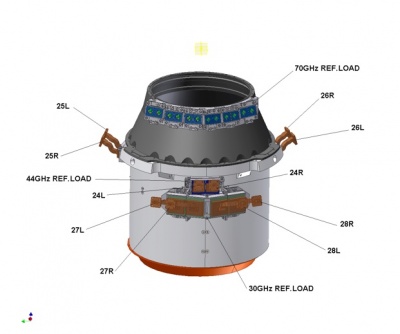
The 4-K reference load unit is formed by single targets, one for each radiometer (two for each FEM). The horns used to couple to the 4-K reference load targets need to be relatively small because the targets themselves are small. An optimization process produced a different horn design for each LFI band; their dimensions increase with reducing frequency. Due to the LFI Focal Plane design, where higher frequency radiometers (70 GHz) are placed around the HFI cryostat and the lower frequency radiometers (30 and 44 GHz) in a second row, the target mounting structure is separated into two parts )see Fig. 1 below), the upper one being located around the conical part of the HFI outer shield. Reference targets are mounted on a supporting structure, thermally and mechanically connected to the HFI outer shield. Each target faces a reference horn, two for each FEM. This ensemble is fixed to a support structure on the HFI 4-K shield. The thermal link between the mounting structure and the HFI is obtained via fixation point only. Thermal washers are interposed to damp temperature fluctuations on targets induced by the HFI outer shield temperature oscillations. The lower part is fixed in the cylindrical part, and is made with the same target geometry as the upper part, being fixed onto the HFI shield. The reference horns face the loads and are connected to the FEMs through WGs. Reference WGs and RHs are either included in the FEM (70 GHz) or are external to FEM (30 and 44 GHz).
Targets are formed from a back section and a front section. The back sections are made of ECCOSORB CR117, which shows higher RF absorption but also high reflectivity. To reduce the target global reflectivity, a front section, connected with an ECCOSORB-specific cement to the back one, faces the radiometer Reference Horn. This last element is cast from ECCOSORB CR110, whose RF reflectivity is lower than that of CR117. The target design is optimized to further reduce both reflectivity and leakage. Each target is metal-backed and is mounted in a metal enclosure.
Thermal tests were performed in the IASF-Bologna 4-K cryo facility, equipped with a GM cooler, with a heat lift up to 1.5 W at 4 K. The setup simulated the real environment in the payload, where targets are mounted on the HFI 4-K shield in front of the quasi-cylindrical LFI main frame at about 20 K. The same setup was also used to test the susceptibility to fluctuations of the LFI.
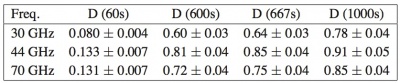
The thermo-mechanical damping was evaluated from the transient test, inducing sinusoidal temperature fluctuation with periods of 60, 600, 667 (typical Sorption Cooler period), and 1000 seconds at the level of the attachment point of the loads on the support structures. The fluctuation at the level of the targets was then acquired and the transfer function (amplitude and phase) estimated from the ratio of the amplitudes. The final results are summarized in Table 12.
Details of the design and performance of the LFI 4-K reference load units are given in Ref. [7].
REBA[edit]
The Radiometer Electronics Box Assembly (REBA) is the electronic box in charge of processing the digitized scientific data and for managing the overall instrument. It is also in charge of communication with the spacecraft. There are two REBA boxes, one nominal and one redundant. The redundancy concept is cold, which means that both boxes are never ON at the same time; the operation of each unit shall be managed by the spacecraft switching on the corresponding unit. The REBA ASW (Application SoftWare) is the same in each REBA box.
Each REBA consists of the following subunits.
- The Power Supply Unit (PSU) that feeds the REBA unit. It consists of a DC/DC converter that converts the primary power received from the spacecraft PDU to the secondary regulated voltages required only by the REBA and provides galvanic isolation towards the spacecraft side of the interface. The PSU DC/DC converter also receives the On-Board Clock (OBC) from the CDMS that is used to increment the internal On-Board Time register. There is no software interface with the REBA ASW.
- The Data Acquisition Unit (DAU) performs the analogue-to-digital conversion of the analogue housekeeping data of the REBA itself (temperatures and voltages). The REBA ASW collects the HK data from the DAU.
- The Signal Processing Unit (SPU) is a computing subunit in charge of the reduction and compression of the science data and implements part of the REBA ASW, the SPU ASW (stored in the EEPROM located in the DPU board and transferred to the SPU by the DPU ASW). It receives the science data from the DAE through an IEEE 1355 link implemented in an SMCS chip. A second IEEE 1355 link is used to control the remote DAE SMCS chip. The third IEEE 1355 link communicates with the DPU. A "Data Ready" electrical signal is connected between the DAE and the SPU; this signal produces an interruption in the SPU when the DAE is ready to transfer data.
- The Digital Processing Unit (DPU) is a computing subunit and implements part of the REBA ASW, namely the DPU ASW. The DPU is in charge of the control and monitoring of the instrument as well as communication with the spacecraft (CDMS). It contains another SMCS chip with three IEEE 1355 links that communicate with the SPU and the DAE. An MIL-STD 1553B link is used to communicate with the CDMS. One IEEE 1355 link is used by the DPU ASW to communicate with the DAE to control the SMCS chip of DAE. The second one is used to communicate with the DAE to transfer commands and HK. The third one is used by the DPU ASW to communicate with the SPU (commands and TM). Two Reset electrical lines are provided by the DPU to reset each of the two SMCS chips of the DAE. The DPU ASW is stored in the EEPROM.
A detailed description of the Planck LFI REBA can be found in Ref. [8].
Instrument on-board software[edit]
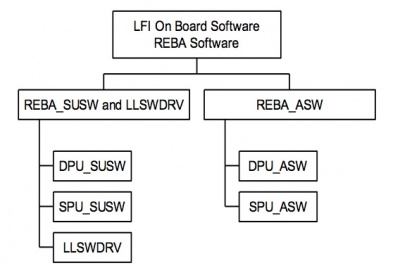
The REBA software is the on-board software of LFI. It is installed in the two computing subunits of the REBA: the DPU, responsible for the control and monitoring of the instrument and the interface with the spacecraft; and the SPU, responsible for the data reduction and compression. The REBA software can be classified (see Fig. 2) into:
- 1. the REBA Start-up Software (SUSW), installed in the PROM memories, which is the bootstrap code to switch on both the subunits;
- 2. the Application Software (ASW), which performs the nominal operations of the REBA;
- 3. the REBA Low Level Software Drivers (LLSWDRV) which are functions provided to the ASW to access the hardware capabilities.
The SPU SUSW and DPU SUSW, located in the PROM memories of SPU and DPU, respectively, are in charge of the booting of the subunits.
The REBA ASW performs the following main functions:
- SPU ASW reduction and compression of the scientific data;
- DPU ASW: control and monitoring of the instrument, interface with the spacecraft to transfer data and receive commands to/from ground, communication with the SPU SUSW during the start-up procedure to load the SPU ASW.
The REBA ASW checks periodically the following parameters:
- − Science TM rate produced on board in order to control the filling of the spacecraft mass memory;
- − CPU load of the SPU;
- − Focal Plane temperature sensors;
- − The communication links between REBA and DAE.
In case of deviations from nominal values, the REBA ASW activates autonomy functions that put the instrument in a safe state or recover from non-nominal situations. Autonomy functions allows to:
- - Re-enable, in some cases, previously disabled science processing;
- - Switch-off the Front End Unit by sending Disable RCA DC/DC commands to the DAE;
- - Try to resume the communication between REBA and DAE or ask the CDMS to switch off the RAA.
The DPU ASW reports the activation of any autonomous function by sending to the CDMS an event report. The REBA monitors some LFI HK parameters in order to manage to some extent the safety of the instrument.
Reduction and compression of science data[edit]
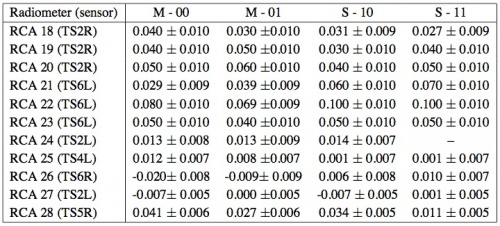
To asses stability against 1/f noise, the Low Frequency Instrument (LFI) on-board the Planck mission will acquire data at a rate much higher than the data rate allowed by the science telemetry bandwidth of 35.5 kbps. The data are processed by an on-board pipeline, followed on-ground by a decoding and reconstruction step, to reduce the volume of data to a level compatible with the bandwidth while minimizing the loss of information. The on-board processing of the scientific data used by Planck/LFI to fit the allowed data-rate is an intrinsically lossy process which distorts the signal in a manner which depends on a set of five free parameters () for each of the 44 LFI detectors. Here we briefly describe the characteristics of this algorithm and the level of distortion introduced by the on-board processing as a function of these parameters. A full description of the Planck LFI on-board data handling system and the tuning and optimization method of the on-board processing chain can be found in [9].
The strategy adopted to fit into the bandwidth relies on three on-board processing steps: downsampling, pre-processing the data to ensure loss-less compression, and loss-less compression itself. To demonstrate these steps, a model of the input signal shall be used. It has to be noted that while the compression is loss-less, the pre-processing is not, due to the need to rescale the data and convert them in integers, (a process named data re-quantization). However, the whole strategy is designed to asses a strict control of the way in which lossy operations are done, of the amount of information loss in order to asses optimal compression rate with minimal information loss.
A schematic representation of the sequence in which these steps are applied on-board and whenever possible reversed on-ground is given in Fig. 3 below.
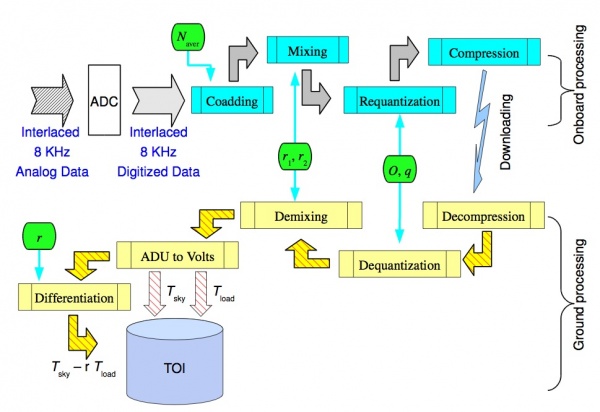
The figure refers to a single radiometer chain and is ideally splitted into two parts: the upper part depicts the on-board processing with cyan boxes denoting the main steps. The corresponding on-ground processing is depicted in the lower part with the main steps colored in yellow. Green pads represents the processing parameters. The first four of them are referred to as REBA parameters, and they are applied both on-board and on-ground. The parameters are: the number of ADC raw samples to be coadded to form an instrumental sample, , the two mixing parameters , the offset to be added to data after mixing and prior to re-quantization, and the re-quantization step . It is important to note that the on-board parameters are set by telecommands and are stamped in each scientific packet. The gain modulation factor, (see Eq. (2) in RCA section above), is a parameter of the ground processing and is computed from the total power data received on ground. The final products in the form of Time Ordered Data (TOI) either in total power or differentiated are stored in an archive represented by the light-blue cylinder.
All the needed optimization steps are performed by an automated software tool, the Onboard Computing Analysis (OCA), which simulates the on-board processing, explores the space of possible combinations of parameters, and produces a set of statistical indicators, among them: the compression rate and the processing noise . For Planck/LFI it is required that while, as for other systematics, would have to be less than 10% of rms of the instrumental white noise. An analytical model is developed that is able to extract most of the relevant information on the processing errors and the compression rate as a function of the signal statistics and the processing parameters to be tuned. This model is of interest for the instrument data analysis to asses the level of signal distortion introduced in the data by the on-board processing.
Once the instrument is completed tuned and stable, a tuning process is applied in order to optimize the REBA parameters. The procedure foresees to acquire chunks of about 15 minutes of averaged data to be analyzed by OCA. After setting the (optimized) REBA parameters, another session of 15 minutes of acquisition is applied, this time with the nominal processing.
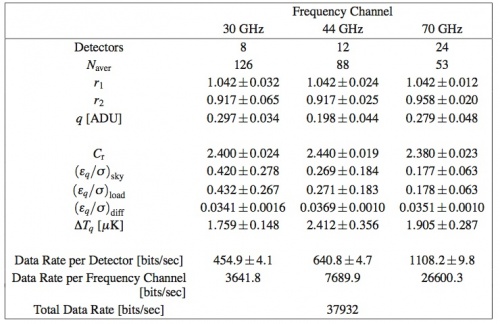
The values for the optimal REBA parameters are mainly determined by the frequency of the radiometric channel with some dispersion from detector to detector. Table 13 below gives representative median values for from on ground System Level tests (CSL) as well as for the quantities in Fig. 4 below and the resulting data rate. is omitted since it is the most variable parameter and it has no significant impact on and . Table 13 below reports also the number of detectors for each frequency channel, the values which are kept constant, the compressed data rate per detector, per frequency channel and for the instrument as a whole. Quantities are reported in the form where represents the standard deviation taken as a measure of the internal dispersion of within the given subset of detectors, this number must not be interpreted as an error and it must not be propagated.
The performance has been verified against the requirements with the result that the required data rate of 35.5 kbps has been achieved while keeping the processing error at a level of 3.8% of the instrumental white noise and well below the target 10% level.
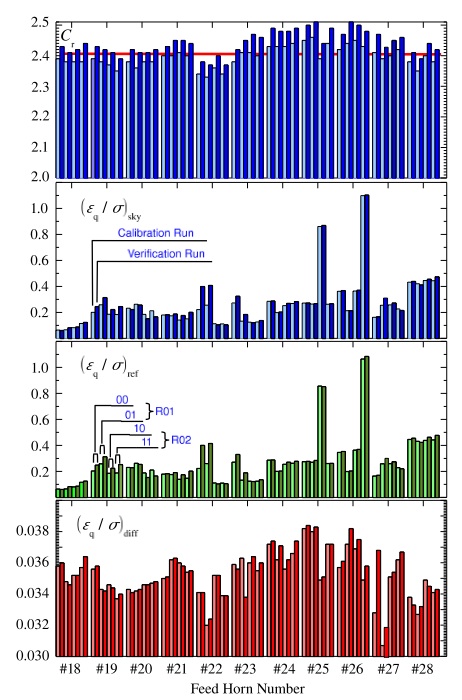
In flight the procedure is to acquire continuously data by using the nominal processing. Short chunks of unprocessed data is daily acquired in turn from each detector. The comparison of unprocessed with processed data allows to monitor of the processing error. In addition the REBA tuning might be repeated daily on the chunk of unprocessed data in order to test whether some REBA parameters on-board the satellite should be changed or not.
Instrument operations[edit]
LFI operational modes[edit]
The operations of the LFI are designed to be automatic and require little if any intervention from the ground. A small amount of commands is required for operating the instrument and eventually for diagnostic and reconfiguration purposes. Each sky survey is conducted by the LFI with the instrument in the Normal Operations Mode mode. No deployable elements, or mechanically moving parts are included in the instrument. The scanning of the sky is achieved by progressive repointing of the satellite spin axis, with the Sun direction always within a cone 10 degrees from the spin axis. Within the Normal Science Mode the instrument can be configured in order to fit with different science or diagnostic needs without changing the power consumption and thus the temperature in the FPU. Changes in power consumption in the FPU are minimized and should occur only in the case that failures in the radiometers that could create interference problems require an RCA to be switched off. Power adjustments on the first stage of the HEMT amplifiers which are contemplated, require extremely small power level variations.
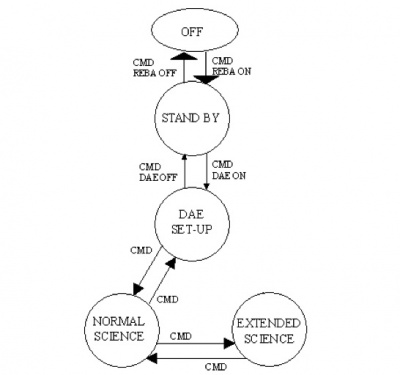
A scheme of the nominal transitions between the LFI Operation Modes are shown in Fig. 5, a brief summary is given below.
- 1. OFF MODE: During this operating mode the instrument is completely off for example during the launch.
- 2. STAND-BY: During this mode only the REBA can be operated. It is the first interface to the instrument whenever the LFI is switched on. When the instrument is in this mode the RAA must be OFF because no data can be received and no control is possible on the radiometer chains.
- 3. DAE SET-UP: During this mode the REBA and the DAE are ON, but no radiometer chains are active. Nevertheless science data can be generated and contain only the background noise of the instrument.
- 4. NORMAL SCIENCE: During this mode the RAA is seen by the REBA as a set of 44 independent instruments. This means that each instrument can be operated, by the same SW, in different modes without affecting the LFI modes. Science data from the DAE are continuously acquired by the REBA that decides, on the basis of the activation table, which packets (either science or diagnostic) have to be produced. The whole set of HK is continuously acquired and sent to ground. This mode is the nominal for the LFI observation operations.
- 5. EXTENDED SCIENCE: This mode is similar to the previous except that for the total amount of telemetry sent to the ground. In fact this mode shall be used when, in particular cases, (e.g. calibration…) a larger telemetry rate is needed and made available by an agreement with HFI and the CDMS.
During launch, for contingency situations and/or to allow diagnostics of other spacecraft subsystems (e.g. HFI or others) LFI is in the OFF mode. When, upon a command from ground the REBA is powered on, the instrument is in its STAND-BY mode. A step-by-step bootstrap procedure commanded from ground documented by HK is initialized to turn the DAE on. This sets-up the internal communications, and allows the LFI subsystems to collect and deliver a full set of HK. The instrument is in DAE SET-UP mode. The following step is to upload from ground the DAE settings and processing parameters; then, to switch on the RCA on ground command. At this stage, on ground command, the acquisition of science data can start. A further step is needed to move to NORMAL SCIENCE, namely start processing and compressing the science raw data. When this is accomplished, science packets can be sent to ground.
Instrument technical performance[edit]
Spectral response[edit]
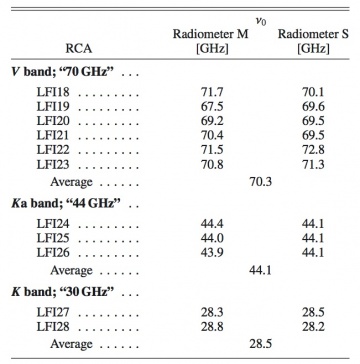
The in-band receiver response has been thoroughly modelled and measured for all the LFI detectors during ground tests. The complete set of bandpass curves has been published in [10] where all the details of the LFI radiometer's spectral response are given. From each curve we have derived the effective centre frequency according to:
where is the receiver bandwidth and is the bandpass response. Table 14 below gives the centre frequencies of the 22 LFI radiometers. For each radiometer, is calculated by weight-averaging the bandpass response of the two individual diodes with the same weights used to average detector timestreams. For simplicity and for historical reasons, we will continue to refer to the three channels as the 30, 44, and 70 GHz channels.
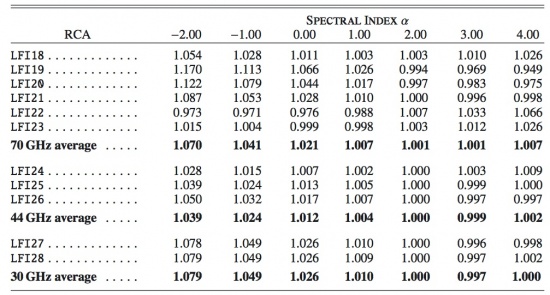
Colour corrections, , needed to derive the brightness temperature of a source with a power-law spectral index , are given in the table 15 below. The values are averaged for the 11 RCAs and for the three frequency channels. Details about the definition of colour corrections are provided in Planck-Early-V[11].
Bandpass estimation[edit]
As detailed in [10], our most accurate method to measure the LFI bandpasses is based on measurements of individual components integrated into the LFI Advanced RF Model (LARFM) to yield a synthesised radiometer bandpass. The LARFM is a software tool based on the open-source Quasi Universal Circuit Simulator (QUCS). The measured frequency responses of the various subsystems (feed-OMT, FEM, BEM) are considered as lumped S-parameter components. Measurements of single components are obtained with standard methods and provide highly reliable results, with precision of order 0.1-0.2 dB over the entire band. Waveguides are simulated with an analytical model, in order to reproduce the effect of their temperature gradient and the effect of standing waves caused by impedance mismatch at the interfaces between the FEM and BEM. This is because the 1.8-meter long waveguides were not measured at unit level in cryogenic conditions. The model provides accurate agreement with the measured waveguide response in the conditions of the test measurements (300 K). The composite bandpasses are estimated to have a precision of about 1.5 to 2 dB.
We also attempted an end-to-end measurement of the RCA spectral response in the cryo-facility as an independent check. Unfortunately, these measurements suffered some subtle systematic effects in the test setup (standing waves at 70 GHz; polarisation mismatch and narrow frequency coverage at 30 and 44 GHz), preventing an accurate cross-check. However, the comparison shows a general agreement within limits of the test reliability and repeatability.
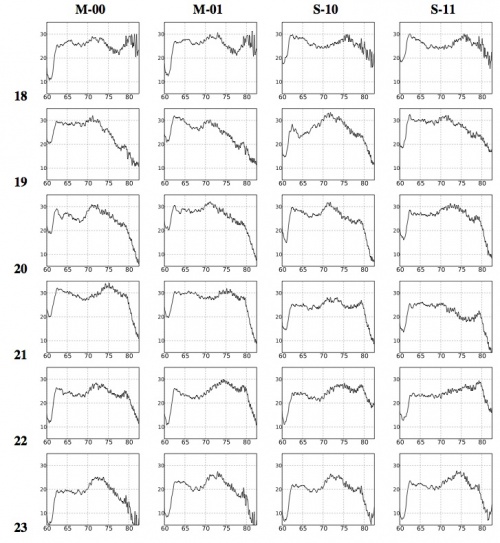
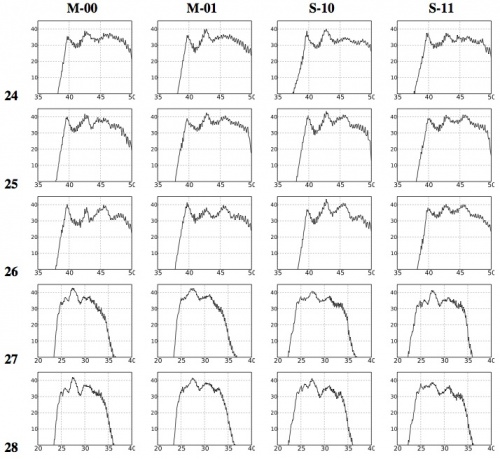
Figg. 6 and 7 below show all the LFI bandpasses obtained by the frequency response data of each radiometer unit assembled by the LARFM. The 70 GHz channels show a low bandpass ripple, of about 10 dB, which is within scientific requirements. The spike between 60 and 61 GHz, below the low frequency cut-off, is due to a systematic effect present in all the BEM gain measurements and caused by the test setup. We removed this range from the bandpasses made available at the Data Processing Centre in order to avoid possible spurious effects and therefore the frequency coverage is 61-80 GHz. The high frequency cut-off is not well defined in most of the channels. The 30 and 44 GHz bandpasses show a more complex shape, driven by the BEM spectral response, but still within dB. The low frequency cut-off is always well defined, while the high frequency cut-off is not well defined in RCA 24 and 26. However, comparing with the high frequency cut-off of RCA 25, it is expected that the additional bandwidth is very low. Frequency coverage is 25-50 GHz for the 44 GHz channels and 21.3-40 GHz for the 30 GHz channels.
Stability[edit]
Thanks to its differential scheme, the LFI is insensitive to many effects caused by 1/f noise, thermal fluctuations, or electrical instabilities. As detailed in [12] [Planck early paper III ], one effect detected during the first survey was the daily temperature fluctuation in the back-end unit induced by the downlink transponder, which was powered on each day for downlinks during the first 258 days of the mission. As expected, the effect is highly correlated between the sky and reference load signals. In the difference, the variation is reduced by a factor of about (1 − r), where r is the gain modulation factor defined in Eq. (2) in the RCA section.
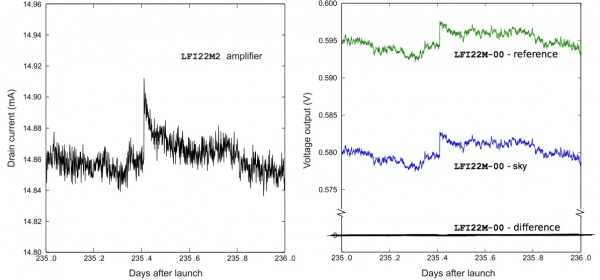
A particular class of signal fluctuations occasionally observed during operations is due to electrical instabilities that appear as abrupt increases in the measured drain current of the front-end amplifiers, with a relaxation time variable from few seconds to some hundreds of seconds. Typically, these events cause a simultaneous change in the sky and reference load signals. Because they are essentially common-mode, their residual on the differenced data is negligible (Fig. 8), and the data are suitable for science production. In a few cases the residual fluctuation in the differential output was large enough (a few millikelvin in calibrated antenna temperature units) to be flagged, and the data were not used. The total amount of discarded data for all LFI channels until Operational Day 389 was about 2000 s per detector, or 0.008%.
A further peculiar effect appeared in the 44 GHz detectors, where single isolated samples, either on the sky or the reference voltage output, were far from the rest. Over a reference period of four months, 15 occurrences of single-sample spikes (out of 24 total anomaly events) were discarded, an insignificant loss of data.
Thermal susceptibility[edit]
As already mentioned in In-flight Calibration section and detailed in [13], during the CPV campaign, susceptibility tests were performed in order to characterize the LFI instrument susceptibility to thermal and electrical variations.
The effect of temperature fluctuations on the LFI radiometers is originated in the Planck cold end interface of the hydrogen sorption cooler to the instrument focal plane. The temperature is actively controlled through a dedicated stage, the Thermal Stabilization Assembly (TSA), providing a first reduction of the effect. The thermal mass of the focal plane strongly contribute to reduce residual fluctuations. The physical temperature fluctuations propagated at the front end modules cause a correlated fluctuation in the radiometer signal degrading the quality of scientific data. The accurate characterization of this effect is crucial for possibly removing it from raw data by exploiting the housekeeping information of thermal sensors.
The propagation of the temperature oscillations through the focal plane and the instrument response to thermal changes were characterized through two main tests:
- the thermal dynamic response aimed at measuring the dynamic thermal behaviour of the LFI Focal Plane;
- the radiometers thermal susceptibility.
Thermal Dynamic Response[edit]
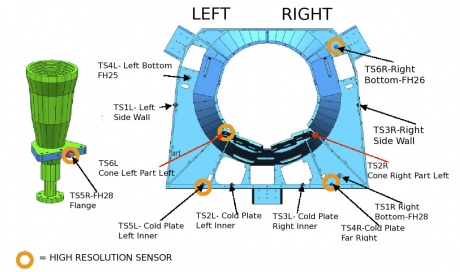
In order to amplify the effect and to get a more accurate measurement, the active control from the TSA was switched off. The resulting increased fluctuations, propagating at the cooler frequencies, were used to evaluate transfer functions between the TSA stage and the FPU sensors (see Fig. 9 below). The analysis produced damping factors of 2–5 at about 1 mHz. The source of fluctuations was characterized by two typical periods of the sorption cooler during the final CPV phase: (i) the single bed cycle time, 940 s, (ii) the complete cooler period, six times larger, 5640 s.
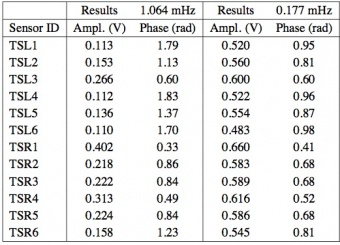
Results are shown in Table 16. Sorting the sensors by the transfer function amplitudes in descending order (second column of the table), the route of the propagation of temperature fluctuations through the focal plane sensors (shown in Fig. 9) was reproduced as expected: the largest amplitudes are in the sensor closest to the right bottom corner interface with the working cooler and they decrease in the direction left upwards. The measured values in flight showing a good agreement with what measured during the CSL ground test.
Radiometer Thermal Susceptibility[edit]
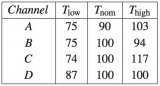
Fluctuations of the focal plane temperature would cause variations of important parameters (mainly the low noise amplifier gains and noise temperatures), impacting the radiometer output signal. The response of the LFI radiometers to thermal fluctuations was estimated by inducing discrete temperature steps on the focal plane through TSA set-point changes. The set-point was changed over four values (Fig. 47, left) and after a stabilization of at least two hours, the measured receivers output was characterized as a function of each temperature variation of about 0.3 K.
The slope of the resulting vs plot is the measured response of the receivers to a change in the temperature. Results, reported in the Table 17, confirmed that physical temperature fluctuations in the main frame are furtherly reduced when convolved with the radiometer thermal susceptibility coefficients: the derived output fluctuations, measured in antenna temperature, were actually reduced by an extra factor of 10 to 200 (according to the channel considered), of the same order of ground test results. This corresponds to reduce the mean peak-to-peak amplitudes of fluctuations measured by high resolution sensors, of the order of 4 mK in steady condition, of at least one order of magnitude in the output timestream.
Instrument Budgets[edit]
Power Budget[edit]
| Subsystem | Unit | Assembly | Sub-Assembly | Budget [W] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAA | 45.599 | |||
| FEU | 0.329 | |||
| FE structure | N/A | |||
| Feed Horns | N/A | |||
| OMTs | N/A | |||
| FEMs | 0.329 | |||
| 30 GHz | 0.056 | |||
| 44 GHz | 0.121 | |||
| 70 GHz | 0.152 | |||
| BEU | 45.270 | |||
| DAE | 31.986 | |||
| BEMs | 13.284 | |||
| 30 GHz | 4.914 | |||
| 44 GHz | 4.633 | |||
| 70 GHz | 3.737 | |||
| Waveguides | N/A | |||
| RAA harness | N/A | |||
| 4-K Load | N/A | |||
| REBA | 22.700 | |||
| System Harness | N/A | |||
| Total | 68.299 |
Mass Budget[edit]
The maximum allocated mass for the Planck Instruments is 445 kg, 89 kg are allocated for the LFI instrument. The distribution of the instrument and cooler mass to the different interfaces in the system is as given in table 19 below.
| Subsystem | Unit | Assembly | Sub-Assembly | Budget [kg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAA | 77.900 | |||
| FEU | 22.935 | |||
| FE structure | 17.680 | |||
| Feed Horns+OMTs | 2.825 | |||
| 30 GHz | 0.680 | |||
| 44 GHz | 0.732 | |||
| 70 GHz | 1.413 | |||
| FEMs | 2.430 | |||
| 30 GHz | 0.810 | |||
| 44 GHz | 1.110 | |||
| 70 GHz | 0.510 | |||
| BEU | 25.542 | |||
| DAE | 23.130 | |||
| BEMs | 2.412 | |||
| 30 GHz | 0.624 | |||
| 44 GHz | 0.864 | |||
| 70 GHz | 0.924 | |||
| Waveguides | 23.005 | |||
| WG structure | 15.940 | |||
| WGs | 7.065 | |||
| RAA harness | 5.491 | |||
| BEU internal harness | 4.489 | |||
| DAE-FEU cryo-harness | 1.002 | |||
| 4-K Load | 0.927 | |||
| REBA (2 units) | 8.480 | |||
| System Harness | 3.495 | |||
| Total | 89.875 |
Telemetry Budget[edit]
All the science data flow coming from the foreseen on-board data processing can be summarized in the following table 20.
| 30 GHz | 44 GHz | 70 GHz | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total samples | 65 | 94 | 154 | |
| Compression factor | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 | |
| Compressed samples | 27 | 39 | 64 | |
| Science data available (word) | 490 | 490 | 490 | |
| Time per packet (s) | 18.035 | 12.570 | 7.651 | |
| Corresponding sky arc () | 108 | 75 | 46 | |
| Packet frequency (Hz) | 0.444 | 0.955 | 3.317 | |
| Net Data Volume (word/s) | 217.352 | 467.778 | 1536.986 | 2222.116 |
| Net Data Volume (kbps) | 3.478 | 7.484 | 24.592 | 35.554 |
This result refers to the net science telemetry rate that LFI sends to ground. If we add the overhead due to the packet header (protocol) and the tertiary header we obtain a gross science telemetry rate of 37.150 kbps. This number should be added to the data coming from the calibration channel (uncompressed data used to verify the correct functionalities of the on-board compression algorithm, see Reduction and Compression of Science Data section) sent to ground in parallel. This channel has a worst case gross data production of 5.140 kbps for a total science data of 42.290 kbps.
The gross housekeeping telemetry budget is 2.425 kbps for a total budget of 44.715 kbps. The total data budget allocated to the LFI is 53.5 kbps well above the LFI total telemetry budget.
References[edit]
- Jump up ↑ Planck-LFI flight model feed horns, F. Villa, O. D'Arcangelo, M. Pecora, L. Figini, R. Nesti, A. Simonetto, C. Sozzi, M. Sandri, P. Battaglia, P. Guzzi, M. Bersanelli, R. C. Butler, N. Mandolesi, Journal of Instrumentation, 4, 2004-+, (2009).
- Jump up ↑ The Planck-LFI flight model ortho-mode transducers, O. D'Arcangelo, A. Simonetto, L. Figini, E. Pagana, F. Villa, M. Pecora, P. Battaglia, M. Bersanelli, R. C. Butler, S. Garavaglia, P. Guzzi, N. Mandolesi, C. Sozzi, Journal of Instrumentation, 4, 2005-+, (2009).
- Jump up ↑ Design, development and verification of the 30 and 44 GHz front-end modules for the Planck Low Frequency Instrument, R. J. Davis, A. Wilkinson, R. D. Davies, W. F. Winder, N. Roddis, E. J. Blackhurst, D. Lawson, S. R. Lowe, C. Baines, M. Butlin, A. Galtress, D. Shepherd, B. Aja, E. Artal, M. Bersanelli, R. C. Butler, C. Castelli, F. Cuttaia, O. D'Arcangelo, T. Gaier, R. Hoyland, D. Kettle, R. Leonardi, N. Mandolesi, A. Mennella, P. Meinhold, M. Pospieszalski, L. Stringhetti, M. Tomasi, L. Valenziano, A. Zonca, Journal of Instrumentation, 4, 2002-+, (2009).
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.04.1 Design, development, and verification of the Planck Low Frequency Instrument 70 GHz Front-End and Back-End Modules, J. Varis, N. J. Hughes, M. Laaninen, V.-H. Kilpiä, P. Jukkala, J. Tuovinen, S. Ovaska, P. Sjöman, P. Kangaslahti, T. Gaier, R. Hoyland, P. Meinhold, A. Mennella, M. Bersanelli, R. C. Butler, F. Cuttaia, E. Franceschi, R. Leonardi, P. Leutenegger, M. Malaspina, N. Mandolesi, M. Miccolis, T. Poutanen, H. Kurki-Suonio, M. Sandri, L. Stringhetti, L. Terenzi, M. Tomasi, L. Valenziano, Journal of Instrumentation, 4, 2001-+, (2009).
- Jump up ↑ The Planck-LFI flight model composite waveguides, O. D'Arcangelo, L. Figini, A. Simonetto, F. Villa, M. Pecora, P. Battaglia, M. Bersanelli, R. C. Butler, F. Cuttaia, S. Garavaglia, P. Guzzi, N. Mandolesi, A. Mennella, G. Morgante, L. Pagan, L. Valenziano, Journal of Instrumentation, 4, 2007-+, (2009).
- Jump up ↑ LFI 30 and 44 GHz receivers Back-End Modules, E. Artal, B. Aja, M. L. de la Fuente, J. P. Pascual, A. Mediavilla, E. Martinez-Gonzalez, L. Pradell, P. de Paco, M. Bara, E. Blanco, E. García, R. Davis, D. Kettle, N. Roddis, A. Wilkinson, M. Bersanelli, A. Mennella, M. Tomasi, R. C. Butler, F. Cuttaia, N. Mandolesi, L. Stringhetti, Journal of Instrumentation, 4, 2003-+, (2009).
- Jump up ↑ Planck-LFI: design and performance of the 4 Kelvin Reference Load Unit, L. Valenziano, F. Cuttaia, A. De Rosa, L. Terenzi, A. Brighenti, G. P. Cazzola, A. Garbesi, S. Mariotti, G. Orsi, L. Pagan, F. Cavaliere, M. Biggi, R. Lapini, E. Panagin, P. Battaglia, R. C. Butler, M. Bersanelli, O. D'Arcangelo, S. Levin, N. Mandolesi, A. Mennella, G. Morgante, G. Morigi, M. Sandri, A. Simonetto, M. Tomasi, F. Villa, M. Frailis, S. Galeotta, A. Gregorio, R. Leonardi, S. R. Lowe, M. Maris, P. Meinhold, L. Mendes, L. Stringhetti, A. Zonca, A. Zacchei, Journal of Instrumentation, 4, 2006-+, (2009).
- Jump up ↑ The Planck-LFI Radiometer Electronics Box Assembly, J. M. Herreros, M. F. Gómez, R. Rebolo, H. Chulani, J. A. Rubiño-Martin, S. R. Hildebrandt, M. Bersanelli, R. C. Butler, M. Miccolis, A. Peña, M. Pereira, F. Torrero, C. Franceschet, M. López, C. Alcalá, Journal of Instrumentation, 4, 2008-+, (2009).
- Jump up ↑ Optimization of Planck-LFI on-board data handling, M. Maris, M. Tomasi, S. Galeotta, M. Miccolis, S. Hildebrandt, M. Frailis, R. Rohlfs, N. Morisset, A. Zacchei, M. Bersanelli, P. Binko, C. Burigana, R. C. Butler, F. Cuttaia, H. Chulani, O. D'Arcangelo, S. Fogliani, E. Franceschi, F. Gasparo, F. Gomez, A. Gregorio, J. M. Herreros, R. Leonardi, P. Leutenegger, G. Maggio, D. Maino, M. Malaspina, N. Mandolesi, P. Manzato, M. Meharga, P. Meinhold, A. Mennella, F. Pasian, F. Perrotta, R. Rebolo, M. Türler, A. Zonca, Journal of Instrumentation, 4, 2018-+, (2009).
- ↑ Jump up to: 10.010.1 Planck-LFI radiometers' spectral response, A. Zonca, C. Franceschet, P. Battaglia, F. Villa, A. Mennella, O. D'Arcangelo, R. Silvestri, M. Bersanelli, E. Artal, R. C. Butler, F. Cuttaia, R. J. Davis, S. Galeotta, N. Hughes, P. Jukkala, V.-H. Kilpiä, M. Laaninen, N. Mandolesi, M. Maris, L. Mendes, M. Sandri, L. Terenzi, J. Tuovinen, J. Varis, A. Wilkinson, Journal of Instrumentation, 4, 2010-+, (2009).
- Jump up ↑ Planck early results. V. The Low Frequency Instrument data processing, A. Zacchei, D. Maino, C. Baccigalupi, M. Bersanelli, A. Bonaldi, L. Bonavera, C. Burigana, R. C. Butler, F. Cuttaia, G. de Zotti, J. Dick, M. Frailis, S. Galeotta, J. González-Nuevo, K. M. Górski, A. Gregorio, E. Keihänen, R. Keskitalo, J. Knoche, H. Kurki-Suonio, C. R. Lawrence, S. Leach, J. P. Leahy, M. López-Caniego, N. Mandolesi, M. Maris, F. Matthai, P. R. Meinhold, A. Mennella, G. Morgante, N. Morisset, P. Natoli, F. Pasian, F. Perrotta, G. Polenta, T. Poutanen, M. Reinecke, S. Ricciardi, R. Rohlfs, M. Sandri, A.-S. Suur-Uski, J. A. Tauber, D. Tavagnacco, L. Terenzi, M. Tomasi, J. Valiviita, F. Villa, A. Zonca, A. J. Banday, R. B. Barreiro, J. G. Bartlett, N. Bartolo, L. Bedini, K. Bennett, P. Binko, J. Borrill, F. R. Bouchet, M. Bremer, P. Cabella, B. Cappellini, X. Chen, L. Colombo, M. Cruz, A. Curto, L. Danese, R. D. Davies, R. J. Davis, G. de Gasperis, A. de Rosa, G. de Troia, C. Dickinson, J. M. Diego, S. Donzelli, U. Dörl, G. Efstathiou, T. A. Enßlin, H. K. Eriksen, M. C. Falvella, F. Finelli, E. Franceschi, T. C. Gaier, F. Gasparo, R. T. Génova-Santos, G. Giardino, F. Gómez, A. Gruppuso, F. K. Hansen, R. Hell, D. Herranz, W. Hovest, M. Huynh, J. Jewell, M. Juvela, T. S. Kisner, L. Knox, A. Lähteenmäki, J.-M. Lamarre, R. Leonardi, J. León-Tavares, P. B. Lilje, P. M. Lubin, G. Maggio, D. Marinucci, E. Martínez-González, M. Massardi, S. Matarrese, M. T. Meharga, A. Melchiorri, M. Migliaccio, S. Mitra, A. Moss, H. U. Nørgaard-Nielsen, L. Pagano, R. Paladini, D. Paoletti, B. Partridge, D. Pearson, V. Pettorino, D. Pietrobon, G. Prézeau, P. Procopio, J.-L. Puget, C. Quercellini, J. P. Rachen, R. Rebolo, G. Robbers, G. Rocha, J. A. Rubiño-Martín, E. Salerno, M. Savelainen, D. Scott, M. D. Seiffert, J. I. Silk, G. F. Smoot, J. Sternberg, F. Stivoli, R. Stompor, G. Tofani, L. Toffolatti, J. Tuovinen, M. Türler, G. Umana, P. Vielva, N. Vittorio, C. Vuerli, L. A. Wade, R. Watson, S. D. M. White, A. Wilkinson, A&A, 536, A5, (2011).
- Jump up ↑ Planck early results. III. First assessment of the Low Frequency Instrument in-flight performance, A. Mennella, R. C. Butler, A. Curto, F. Cuttaia, R. J. Davis, J. Dick, M. Frailis, S. Galeotta, A. Gregorio, H. Kurki-Suonio, C. R. Lawrence, S. Leach, J. P. Leahy, S. Lowe, D. Maino, N. Mandolesi, M. Maris, E. Martínez-González, P. R. Meinhold, G. Morgante, D. Pearson, F. Perrotta, G. Polenta, T. Poutanen, M. Sandri, M. D. Seiffert, A.-S. Suur-Uski, D. Tavagnacco, L. Terenzi, M. Tomasi, J. Valiviita, F. Villa, R. Watson, A. Wilkinson, A. Zacchei, A. Zonca, B. Aja, E. Artal, C. Baccigalupi, A. J. Banday, R. B. Barreiro, J. G. Bartlett, N. Bartolo, P. Battaglia, K. Bennett, A. Bonaldi, L. Bonavera, J. Borrill, F. R. Bouchet, C. Burigana, P. Cabella, B. Cappellini, X. Chen, L. Colombo, M. Cruz, L. Danese, O. D'Arcangelo, R. D. Davies, G. de Gasperis, A. de Rosa, G. de Zotti, C. Dickinson, J. M. Diego, S. Donzelli, G. Efstathiou, T. A. Enßlin, H. K. Eriksen, M. C. Falvella, F. Finelli, S. Foley, C. Franceschet, E. Franceschi, T. C. Gaier, R. T. Génova-Santos, D. George, F. Gómez, J. González-Nuevo, K. M. Górski, A. Gruppuso, F. K. Hansen, D. Herranz, J. M. Herreros, R. J. Hoyland, N. Hughes, J. Jewell, P. Jukkala, M. Juvela, P. Kangaslahti, E. Keihänen, R. Keskitalo, V.-H. Kilpia, T. S. Kisner, J. Knoche, L. Knox, M. Laaninen, A. Lähteenmäki, J.-M. Lamarre, R. Leonardi, J. León-Tavares, P. Leutenegger, P. B. Lilje, M. López-Caniego, P. M. Lubin, M. Malaspina, D. Marinucci, M. Massardi, S. Matarrese, F. Matthai, A. Melchiorri, L. Mendes, M. Miccolis, M. Migliaccio, S. Mitra, A. Moss, P. Natoli, R. Nesti, H. U. Nørgaard-Nielsen, L. Pagano, R. Paladini, D. Paoletti, B. Partridge, F. Pasian, V. Pettorino, D. Pietrobon, M. Pospieszalski, G. Prézeau, M. Prina, P. Procopio, J.-L. Puget, C. Quercellini, J. P. Rachen, R. Rebolo, M. Reinecke, S. Ricciardi, G. Robbers, G. Rocha, N. Roddis, J. A. Rubiño-Martín, M. Savelainen, D. Scott, R. Silvestri, A. Simonetto, P. Sjoman, G. F. Smoot, C. Sozzi, L. Stringhetti, J. A. Tauber, G. Tofani, L. Toffolatti, J. Tuovinen, M. Türler, G. Umana, L. Valenziano, J. Varis, P. Vielva, N. Vittorio, L. A. Wade, C. Watson, S. D. M. White, F. Winder, A&A, 536, A3, (2011).
- Jump up ↑ In-flight calibration and verification of the Planck-LFI instrument, A. Gregorio, F. Cuttaia, A. Mennella, M. Bersanelli, S. Maris, P. Meinhold, Submitted to Journal of Instrumentation, (2013).
(Planck) Low Frequency Instrument
LFI Radiometer Array Assembly
Feed Horn
LFI cryogenic amplifying stage Front End Unit
LFI Ortho Module Transducer
Focal Plane Unit
(Planck) High Frequency Instrument
LFI Waveguide
LFI cryogenic amplifying stage Front End Module
LFI warm electronics Back End Unit
LFI warm electronics Back End Module
LFI Data Acquisition Electronics
High Electron Mobility Transistor
LFI Radiometer Electronics Box Assembly
Command and Data Management System
House Keeping
Signal Processing Unit
Data Processing Unit
LFI Radiometer Chain Assembly
analog to digital converter
Centre Spatial de Liège
[LFI meaning]: absolute calibration refers to the 0th order calibration for each channel, 1 single number, while the relative calibration refers to the component of the calibration that varies pointing period by pointing period.
Calibration and Performance Verification
hermal Stabilization Assembly