Difference between revisions of "Ground Segment and Operations"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Category:Ground Segment and Operations| | + | == Geographical distribution of the Planck Ground Segment== |
| + | |||
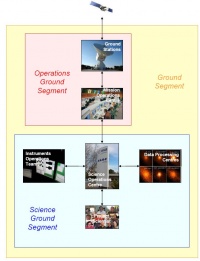
| + | The Planck Ground Segment is made of four geographically distributed centres: | ||
| + | |||
| + | === The Mission Operations Centre === | ||
| + | The mission operations centre (MOC), located at ESA’s operations | ||
| + | centre in Darmstadt (Germany), is responsible for | ||
| + | all aspects of flight control and of the health and safety of the | ||
| + | Planck satellite, including both instruments. It plans and executes | ||
| + | all necessary satellite activities, including instrument | ||
| + | commanding requests by the instrument operations centres. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[file:ESOC.jpg|thumb|200px|The European Space Operations Centre in Darmstadt, Germany, home of the Planck Mission Operations Centre.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | MOC communicates with the satellite using ESA’s 35-m antenna | ||
| + | located in New Norcia (Australia), or that in Cebreros (Spain), over a daily 3-h period, | ||
| + | during which it uplinks a scheduled activity timeline | ||
| + | which is autonomously executed by the satellite, and downlinks | ||
| + | the science and housekeeping (HK) data acquired by the satellite during the past 24 h. The downlinked data are | ||
| + | transferred from the antenna to the MOC over a period of | ||
| + | typically 8 h; at MOC they are put onto a data server from | ||
| + | where they are retrieved by the two Data Processing Centres. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === The Planck Science Office === | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[file:ESAC_6.JPG|thumb|200px|The European Space Astronomy Centre in Villanueva de la Cañada, Madrid, Spain, see of the Planck Science Office.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Planck Science Office (PSO)is located at ESA’s European Space Astronomy Centre in Villanueva de la Cañada surroundings (Madrid, Spain). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Its main responsibilities include: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * coordinating scientific operations of the Planck instruments | ||
| + | |||
| + | * designing, planning and executing the Planck observation strategy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It provides to MOC a detailed pointing plan with a periodicity of about one month. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * creating and updating the specifications of the Planck Legacy Archive developed by the Science Archives Team at ESAC | ||
| + | |||
| + | * testing and operating the PLA | ||
| + | |||
| + | === The LFI instrument operations and data-processing centre === | ||
| + | The LFI instrument operations and data processing centre, | ||
| + | located at the Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste (Italy), is notably | ||
| + | responsible for: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * the optimal operation of the LFI instrument | ||
| + | |||
| + | * the processing of the data acquired by LFI into the final scientific products of the mission. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === The HFI instrument operations and data-processing centre === | ||
| + | The HFI instrument operations and data processing centres, | ||
| + | located respectively at the Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale | ||
| + | in Orsay (France) and at the Institut d’Astrophysique de Paris | ||
| + | (France), are similarly responsible for the optimal operation | ||
| + | of the HFI instrument, and (with several other institutes in | ||
| + | France and the UK) for the processing of the data acquired | ||
| + | by HFI into the final scientific products of the mission. | ||
| + | |||
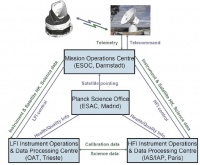
| + | == The data flow in the Planck Ground Segment == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Planck Science Office (PSO), located at ESAC, Spain, sends the pointing lists (Pre-Programmed Pointing Lists) to the Mission Operations Centre at ESOC in Darmstadt, Germany. | ||
| + | The Flight Dynamics team at ESOC adapts them into Augmented Pre-Programmed Pointing Lists (APPL) taking into account ground station scheduling, Operational Day (OD) boundaries and other issues. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[file:GS.jpg|thumb|200px|General schematics of European Space Agency Science Ground Segments. This picture exhibits the way ESA Ground Segments are generally organized.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[file:GSPlanck.JPG|thumb|200px|Specific schematics of the Planck Science Ground Segment. This picture exhibits the way the specific Planck Science Ground Segment works.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | MOC sends pointing and instrument commands to the spacecraft, and receives the house-keeping telemetry and science data through the ground stations (for Planck, mostly the New Norcia and Cebreros ones). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Science data is then transferred to both Data Processing Centres (DPC) which process the data and send quality reports to PSO. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Science products (timelines, maps, etc) are exchanged between DPCs in order to help calibration and other scientific issues. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | Tauber et al. 2010, A&A 520, A1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Ground Segment and Operations|004]] | ||
[[Category:PSOBook]] | [[Category:PSOBook]] | ||
Revision as of 19:05, 17 March 2013
Contents
Geographical distribution of the Planck Ground Segment[edit]
The Planck Ground Segment is made of four geographically distributed centres:
The Mission Operations Centre[edit]
The mission operations centre (MOC), located at ESA’s operations centre in Darmstadt (Germany), is responsible for all aspects of flight control and of the health and safety of the Planck satellite, including both instruments. It plans and executes all necessary satellite activities, including instrument commanding requests by the instrument operations centres.
MOC communicates with the satellite using ESA’s 35-m antenna located in New Norcia (Australia), or that in Cebreros (Spain), over a daily 3-h period, during which it uplinks a scheduled activity timeline which is autonomously executed by the satellite, and downlinks the science and housekeeping (HK) data acquired by the satellite during the past 24 h. The downlinked data are transferred from the antenna to the MOC over a period of typically 8 h; at MOC they are put onto a data server from where they are retrieved by the two Data Processing Centres.
The Planck Science Office[edit]
The Planck Science Office (PSO)is located at ESA’s European Space Astronomy Centre in Villanueva de la Cañada surroundings (Madrid, Spain).
Its main responsibilities include:
- coordinating scientific operations of the Planck instruments
- designing, planning and executing the Planck observation strategy.
It provides to MOC a detailed pointing plan with a periodicity of about one month.
- creating and updating the specifications of the Planck Legacy Archive developed by the Science Archives Team at ESAC
- testing and operating the PLA
The LFI instrument operations and data-processing centre[edit]
The LFI instrument operations and data processing centre, located at the Osservatorio Astronomico di Trieste (Italy), is notably responsible for:
- the optimal operation of the LFI instrument
- the processing of the data acquired by LFI into the final scientific products of the mission.
The HFI instrument operations and data-processing centre[edit]
The HFI instrument operations and data processing centres, located respectively at the Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale in Orsay (France) and at the Institut d’Astrophysique de Paris (France), are similarly responsible for the optimal operation of the HFI instrument, and (with several other institutes in France and the UK) for the processing of the data acquired by HFI into the final scientific products of the mission.
The data flow in the Planck Ground Segment[edit]
The Planck Science Office (PSO), located at ESAC, Spain, sends the pointing lists (Pre-Programmed Pointing Lists) to the Mission Operations Centre at ESOC in Darmstadt, Germany. The Flight Dynamics team at ESOC adapts them into Augmented Pre-Programmed Pointing Lists (APPL) taking into account ground station scheduling, Operational Day (OD) boundaries and other issues.
MOC sends pointing and instrument commands to the spacecraft, and receives the house-keeping telemetry and science data through the ground stations (for Planck, mostly the New Norcia and Cebreros ones).
Science data is then transferred to both Data Processing Centres (DPC) which process the data and send quality reports to PSO.
Science products (timelines, maps, etc) are exchanged between DPCs in order to help calibration and other scientific issues.
References[edit]
Tauber et al. 2010, A&A 520, A1
[ESA's] Mission Operation Center [Darmstadt, Germany]
European Space Agency
House Keeping
Planck Science Office
Planck Legacy Archive
(Planck) Low Frequency Instrument
(Planck) High Frequency Instrument
European Space Operations Centre (Darmstadt)
Augmented Preprogrammed Pointing List
Operation Day definition is geometric visibility driven as it runs from the start of a DTCP (satellite Acquisition Of Signal) to the start of the next DTCP. Given the different ground stations and spacecraft will takes which station for how long, the OD duration varies but it is basically once a day.
Data Processing Center